
Understanding the individual components of agricultural machinery is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in the field. In this guide, we will explore the intricate layout of essential mechanical elements that drive effective operations in farming equipment. Having a clear visual reference for these components can greatly assist in both troubleshooting and routine maintenance.
With a focus on durable machines used in agriculture, this detailed examination provides insights into the structural elements and mechanisms that ensure the reliability of heavy-duty farm equipment. Whether you are conducting repairs or simply enhancing your knowledge of agricultural machinery, a thorough comprehension of these interconnected systems is invaluable.
As we delve deeper, you’ll find clear explanations of various mechanical units, their functions, and how they work together to support agricultural productivity. This understanding forms the foundation for keeping your equipment in top shape for years of dependable service.
Overview of Key Components
Understanding the various elements that make up this agricultural machine is essential for maintaining its performance and reliability. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle, from its mechanical functions to its hydraulic systems.
- Engine: The powerhouse of the machine, ensuring optimal efficiency and durability during heavy-duty work.
- Transmission: Responsible for providing the necessary torque and speed adjustments, ensuring smooth transitions and operational control.
- Hydraulics: Vital for operating lifting mechanisms and other attachments, contributing to the overall versatility of the equipment.
- Cooling System: Keeps the engine running at a stable temperature, preventing overheating during prolonged use.
- Electrical System: Powers lights, controls, and other essential electronic functions for the machine’s operation.
Each of
Key Engine Components Breakdown
The engine consists of several critical elements that ensure smooth performance and longevity. Understanding these components helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining the system effectively. Below is a breakdown of the main parts and their roles within the engine structure.
- Cylinder Block: The foundation of the engine where the cylinders are housed and the combustion process takes place.
- Pistons: These move within the cylinders, converting the fuel’s energy into mechanical force.
- Crankshaft: Connected to the pistons, it converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves, ensuring proper air and fuel flow.
- Valves: Regulate the intake of air and fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers fuel into the combustion chamber at the correct pressure and timing.
- Pump: The core of the system, responsible for generating the necessary pressure to drive the hydraulic fluid through the circuit.
- Control valves: These regulate the flow and direction of the fluid, allowing the operator to control the movement of different mechanical parts.
- Hydraulic hoses: Flexible connectors that transport the fluid between different components, ensuring the flow is maintained even in challenging conditions.
- Cylinders: Convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force, driving various actions like lifting or tilting mechanisms.
- Filters: Protect the system by removing impurities from the fluid, helping maintain system longevity and preventing malfunctions.
- Reservoir: Stores the hydraulic fluid and helps dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring consistent performance.
- Main Gearbox: The central unit responsible for regulating the speed and torque through various gears, allowing efficient movement across different terrains.
- Clutch Assembly: This section disengages the engine from the transmission during gear shifts, ensuring smooth transitions and preventing damage to internal components.
- Hydraulic System: A vital part that assists in gear shifting, using pressurized fluid to engage or disengage specific gears as needed.
- Shift Levers:
Electrical System Diagram and Parts
The electrical system is a vital component in ensuring the smooth operation of any agricultural machinery. Understanding the various elements involved in this system, from wiring to key components, can significantly aid in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Electrical Components
This section covers the primary components found in the machine’s electrical layout, including switches, wiring harnesses, fuses, and connectors. Each plays an essential role in ensuring proper power distribution and operational control.
Component Function Fuel System Components and Details
The fuel system is designed to deliver fuel efficiently and reliably to the engine, ensuring optimal performance under various operating conditions. It is composed of several critical elements that work together to control the flow and pressure of fuel, enabling the combustion process.
Key components include the fuel tank, responsible for storing fuel, and the fuel pump, which transfers fuel to the engine. Filters are also essential, as they purify the fuel before it reaches the combustion chamber. Other important parts, like injectors, ensure precise fuel delivery to the engine, maximizing efficiency and power output.
The entire system must be maintained regularly to prevent issues such as clogging or leaks, which could impair engine performance. Proper upkeep of each component is vital for the smooth operation of the machine and the overall fuel efficiency.
Cooling System Parts Explained
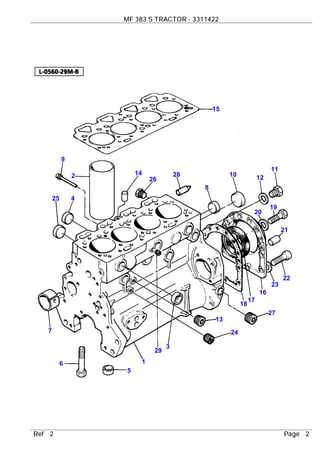
The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s temperature, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. In this section, we will break down the key components involved in this system and how they work together to regulate heat.
Key Components of the Cooling System
- Radiator: The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, helping to maintain a stable temperature.
- Water Pump: This pump circulates coolant through the engine and radiator, ensuring consistent flow and temperature regulation.
- Thermostat: A valve that controls the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, opening when the engine gets too hot.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and provides additional fluid when needed, helping the system stay balanced.
How the Cooling System Works
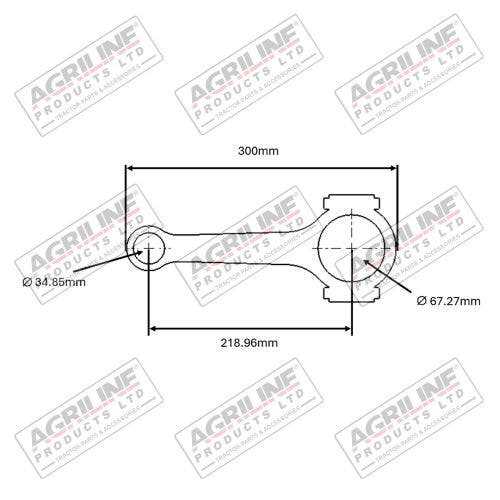
Clutch System Structure Overview
The clutch system plays a crucial role in the functioning of various machinery, enabling smooth engagement and disengagement of power transmission. Understanding its structure is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance during operation.
Key Components of the Clutch System
- Clutch Plate: This component engages and disengages the engine power, allowing for smooth transitions.
- Pressure Plate: It applies pressure on the clutch plate, ensuring firm contact and efficient power transfer.
- Release Bearing: This part facilitates the disengagement of the clutch when the pedal is pressed, allowing for smooth shifting.
- Flywheel: A critical component that stores rotational energy and helps maintain engine momentum.
Operational Mechanism
- The clutch pedal is pressed, which activates the release bearing.
- The release bearing disengages the pressure plate from the clutch plate.
- As a result, the engine’s power is temporarily disconnected from the drivetrain.
- When the pedal is released, the pressure plate re-engages the clutch plate, restoring power transmission.
Brake Components and Their Layout

The braking system is crucial for ensuring safety and control in vehicles. Understanding its components and their arrangement can enhance maintenance practices and overall performance. This section delves into the essential elements that comprise the braking mechanism, highlighting their functions and placement within the assembly.
Component Description Function Brake Pedal The lever used by the operator to engage the braking system. Transmits force to the master cylinder, initiating braking. Master Cylinder A hydraulic pump that converts mechanical force into hydraulic pressure. Supplies hydraulic fluid to the braking system. Brake Lines Hoses that transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brakes. Ensures fluid reaches the brake calipers or drums. Brake Calipers Devices that house the brake pads and clamp down on the rotor. Creates friction to slow down the vehicle. Brake Pads Friction materials mounted within the calipers. Contact the rotor to create the necessary friction for stopping. Brake Rotors Circular metal discs that the brake pads press against. Provide a surface for the pads to grip, facilitating deceleration. Steering System Parts Breakdown
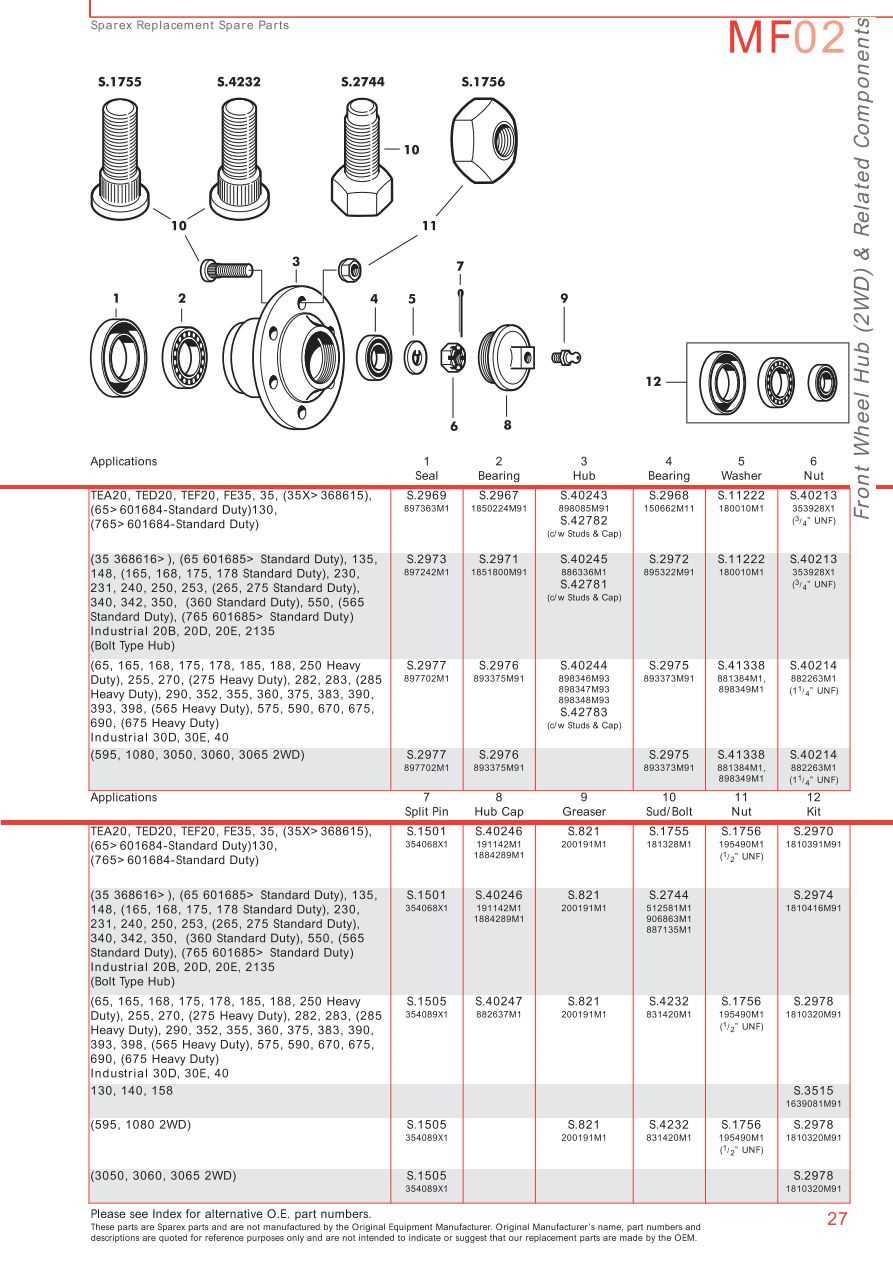
The steering mechanism is essential for the control and maneuverability of the vehicle. Understanding its components helps in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal performance.
Here is a breakdown of the key elements that constitute the steering system:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the operator to control direction.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the gearbox, allowing for the transmission of motion.
- Gearbox: Converts the rotational motion from the steering wheel into linear movement, affecting the wheels.
- Connecting Rods: Transfer the motion from the gearbox to the steering arms.
- Steering Arms: Attached to the wheels, they facilitate the turning action.
- Ball Joints: Allow for smooth movement and flexibility in the steering mechanism.
Maintaining these components ensures effective handling and stability of the vehicle. Regular checks and replacements of worn-out parts contribute to the overall reliability of the steering system.
Exhaust System Parts and Functions
The exhaust system is a crucial component of any engine, responsible for directing exhaust gases away from the engine while reducing harmful emissions. It consists of several elements that work together to ensure efficient operation and optimal performance. Understanding the various components and their functions can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining the system effectively.
Component Description Exhaust Manifold Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and channels them into the exhaust system. Catalytic Converter Reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances before they exit the exhaust. Resonator Helps in tuning the exhaust sound and can also assist in reducing noise. Muffler Reduces engine noise produced by the exhaust gases before they are expelled into the atmosphere. Exhaust Pipe Transports exhaust gases from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, releasing them safely into the air. Front and Rear Axle Components
The front and rear axle assemblies play a crucial role in the overall functionality and stability of agricultural machinery. These components are essential for maintaining traction, providing steering capabilities, and supporting the vehicle’s weight during various operations. Understanding their structure and function helps in the efficient maintenance and repair of the machinery.
Front Axle Components
- Spindle: The pivot point that allows the wheel to rotate and steer.
- Wheel Hub: The central part of the wheel assembly that connects to the spindle.
- Axle Housing: The casing that encases the axle and provides support.
- Kingpin: A pivotal component that connects the steering linkage to the axle.
- Suspension Arms: Parts that support the axle and help absorb shocks from the terrain.
Rear Axle Components
- Drive Shaft: Transfers power from the engine to the rear wheels.
- Differential: Allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, especially during turns.
- Axle Tubes: The long tubes that house the axle shafts and provide structural support.
- Axle Shafts: The rotating components that connect the differential to the wheels.
- Brake Assemblies: Essential for controlling the vehicle’s speed and ensuring safety.
Cabin and Control System
The cabin and control system of agricultural machinery play a crucial role in ensuring operator comfort and efficient machine management. A well-designed workspace enhances visibility, accessibility, and usability of controls, allowing the operator to focus on the tasks at hand while minimizing fatigue.
Modern cabins are equipped with various features that contribute to a better working environment. Ergonomic seating, climate control systems, and intuitive layouts of controls are some essential elements that improve the overall user experience. These components are designed to enhance productivity while providing a safe and comfortable space for the operator.
Component Description Operator Seat Ergonomically designed for comfort during long hours of operation. Control Panel Centralized interface for managing various functions of the machine. Visibility Enhancements Large windows and optimized layout for improved sightlines. Climate Control Heating and air conditioning systems to maintain a comfortable temperature. Sound Insulation Reduces external noise for a quieter working environment.
Hydraulic System Parts and Layout

The hydraulic system is essential for providing power to various functions and components of machinery. Its efficiency depends on the correct arrangement of components, ensuring smooth operation and reliable performance in demanding tasks.
Transmission Assembly and Key Sections
The transmission system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle by managing power distribution between the engine and the wheels. Understanding its key sections helps in identifying potential issues and maintaining the overall functionality of the machine. Below, we explore the major components of the transmission assembly and their respective functions.