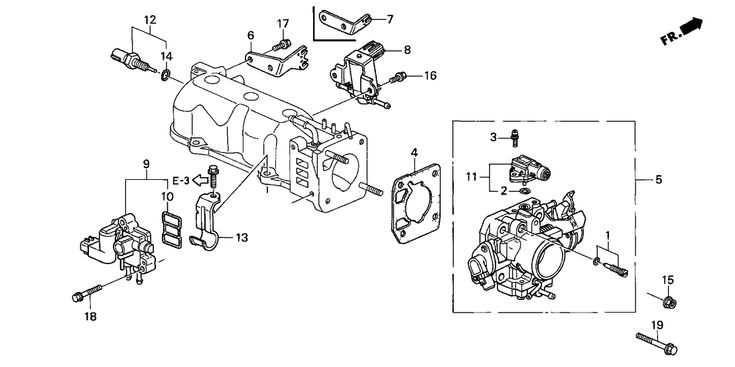
When it comes to maintaining and repairing an automobile, knowing the layout of its key mechanical components is essential. This knowledge allows for easier troubleshooting and helps ensure proper care. A detailed visual representation can significantly enhance understanding, allowing both experienced mechanics and DIY enthusiasts to identify specific areas that may need attention.
Exploring the structure of various systems within a vehicle, such as the engine or suspension, reveals how interconnected parts work together. Such insights can aid in recognizing potential issues before they become serious, and offer a clearer path to efficient repairs. With the right guide, keeping your car in top condition becomes much more achievable.
Using comprehensive diagrams and illustrations, users can better navigate complex mechanical systems, ensuring each task, from small fixes to major repairs, is done with precision and confidence. Understanding the placement and relationship of different elements allows for a smoother maintenance experience.
Engine Components Overview
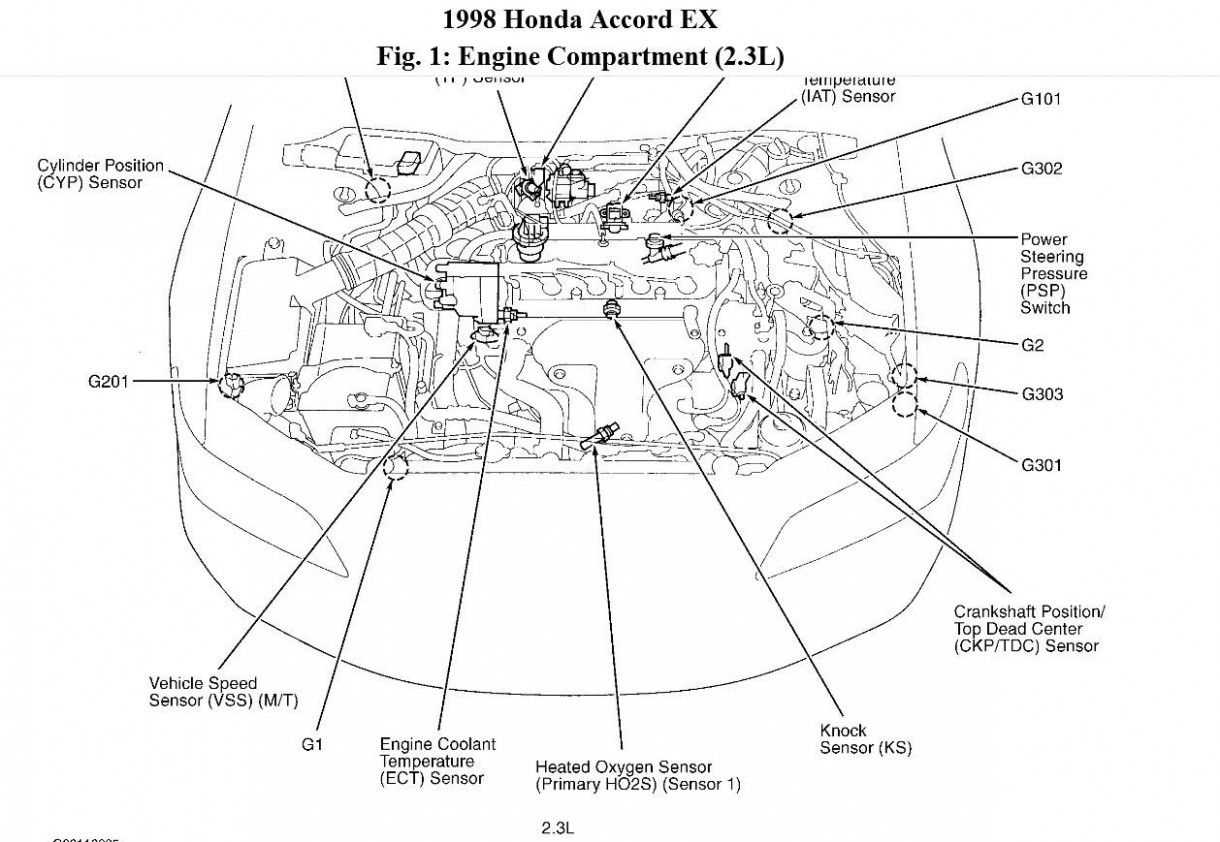
The internal combustion system in this vehicle is composed of various elements that work in unison to ensure optimal performance. These components are meticulously designed to provide power, efficiency, and durability over time. Understanding the key elements within this system is crucial for proper maintenance and long-term reliability.
Main Engine Structures
At the heart of the system lies the cylinder block, which houses the pistons and other critical moving parts. The cylinder head, placed above the block, ensures the proper combustion of fuel. These primary structures play a vital role in managing fuel consumption and power output.
Supporting Components
In addition to the primary structures, several supporting mechanisms help maintain engine efficiency. The alternator, for instance, powers the electrical systems, while the cooling system prevents overheating by regulating the temperature during operation. Together, these elements ensure smooth and consistent performance.
Suspension System Parts Breakdown
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable driving experience. It is responsible for absorbing impacts from the road, maintaining vehicle balance, and providing optimal control. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for identifying potential issues and performing maintenance.
Shock Absorbers: These components help dampen the impact from uneven surfaces, ensuring that the vehicle remains stable while driving. Without them, every bump would be much more pronounced, leading to an uncomfortable ride.
Control Arms: The control arms are key in connecting the wheels to the frame, allowing for controlled motion as the vehicle moves over rough terrain. They work with other components to maintain alignment and prevent excessive wear.
Springs: Springs bear the weight of the vehicle and compress or expand based on road conditions. They act in conjunction with the shock absorbers to balance comfort and performance.
Ball Joints: These flexible joints enable smooth movement of the control arms, contributing to the suspension’s ability to handle steering and motion adjustments while maintaining a firm connection to the wheels.
Each of these elements plays a pivotal role in keeping the vehicle responsive and comfortable, making them essential for the overall safety and performance of the
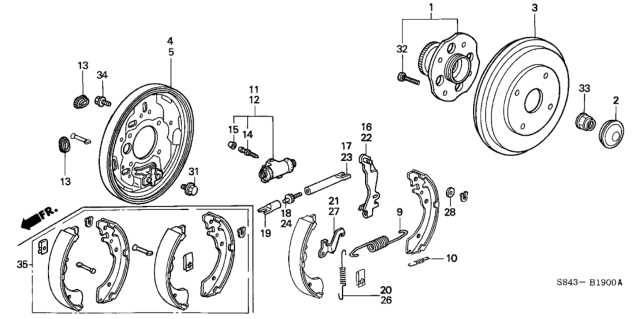
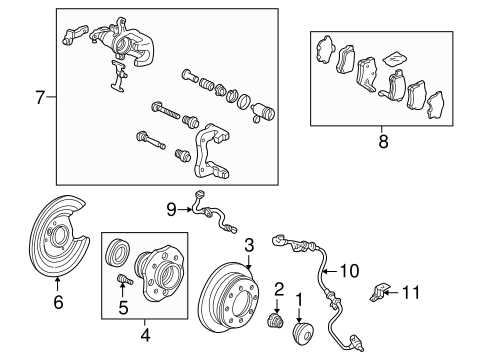
Brake System Components and Diagram
The braking mechanism is essential for vehicle safety, allowing controlled deceleration and stopping. This system consists of various elements that work together to ensure optimal performance during operation. Understanding these components can help in maintaining and diagnosing issues more effectively.
Main Components of the Brake System
Key elements include brake pads, rotors, calipers, and brake lines. The brake pads press against the rotors to create friction, while calipers house the pads and apply pressure. Brake lines deliver hydraulic fluid to engage the brakes when the pedal is pressed.
How the System Functions
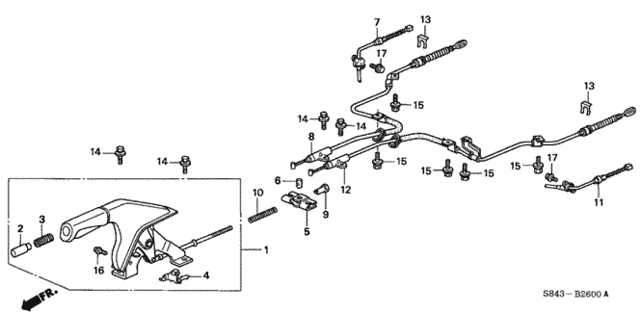
When the brake pedal is pushed, hydraulic pressure is transmitted through the brake lines, forcing the calipers to clamp the brake pads against the rotors. This friction slows down the wheels, allowing the vehicle to stop effectively. Regular inspection of these components ensures reliable operation and safety.
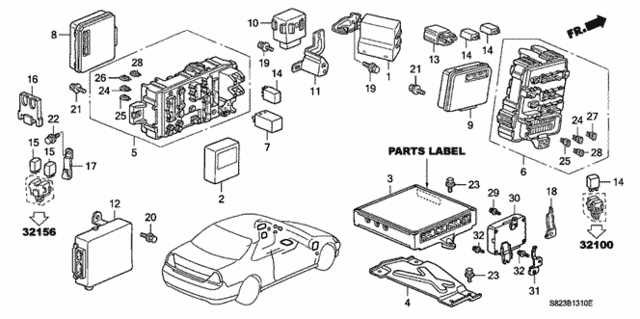
Electrical Wiring and Harness Layout
The organization of electrical wiring and harnesses is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality and safety of a vehicle’s electronic systems. The wiring system connects all the electrical components, allowing them to communicate and perform efficiently. A well-structured harness layout minimizes the risk of damage, shorts, or interference between circuits.
The following section outlines the main elements and structure of the electrical wiring and harness system:
- Main Wiring Network: Connects the primary power sources to major components like the engine control unit, lighting, and battery.
- Branch Connections: Smaller cables extending from the main network, linking sensors, switches, and auxiliary systems.
- Fusible Links and Relays: Protect circuits from overcurrent and manage the distribution of power to various parts.
- Grounding Points: Ensure electrical safety and prevent system malfunctions by providing stable grounding for all circuits.
In addition, proper routing and insulation of the wiring prevent wear and damage, which could lead to performance issues or even electrical failures. Regular inspection and maintenance of the harness
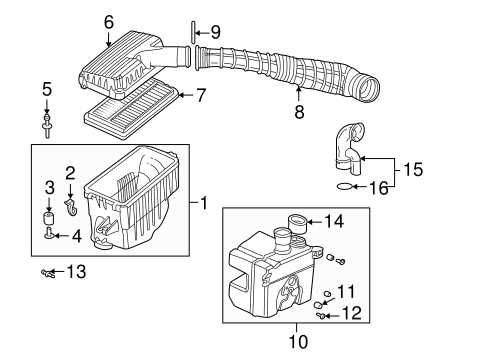
Fuel System Assembly Explanation
The fuel system is designed to efficiently deliver fuel from the tank to the engine. It is composed of several interconnected components that work together to ensure proper fuel flow and combustion. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these elements is crucial for maintaining engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Main Components of the Fuel System
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel and ensures it is available for the engine’s demands.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for moving fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure.
- Fuel Injectors: Deliver the fuel into the combustion chamber for ignition.
- Fuel Filter: Prevents contaminants from reaching the engine, ensuring clean fuel supply.
How the Fuel System Operates
The fuel system begins with the fuel pump drawing fuel from the tank. This fuel passes through the filter to remove impurities before it reaches the injectors. The injectors then atomize the fuel into fine droplets, which mix with air in the combustion chamber. This mixture is ignited to power the engine.
- Fuel is drawn from the tank by the pump.
- It passes through a filter
Exhaust System Components and Flow
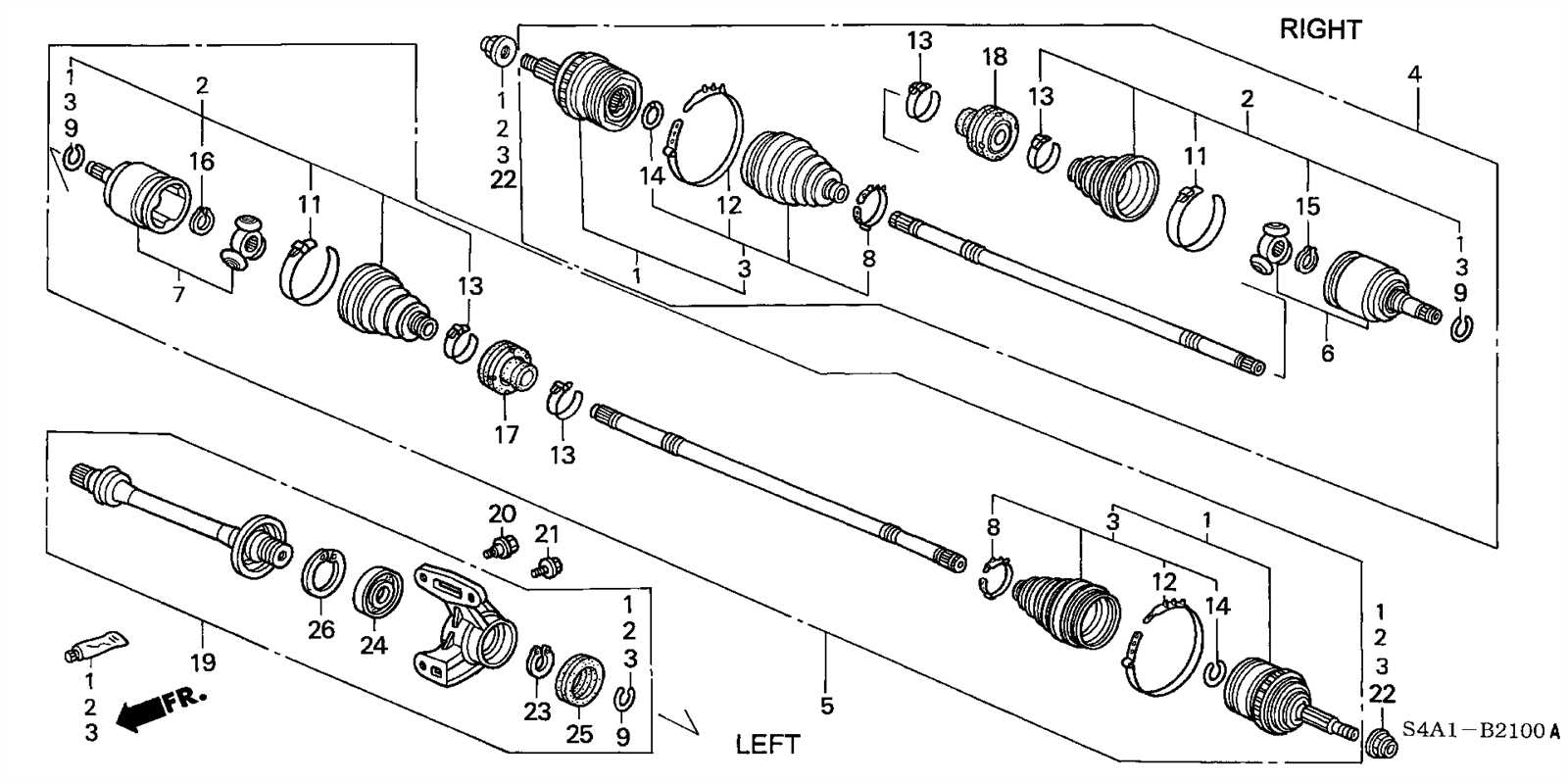
The exhaust system is a crucial element of a vehicle’s operation, responsible for directing exhaust gases away from the engine. This system not only ensures optimal engine performance but also reduces harmful emissions. Understanding the various components and their arrangement helps in appreciating how exhaust flow is managed effectively.
Component Description Exhaust Manifold Collects gases from the engine cylinders and channels them to the exhaust pipe. Oxygen Sensor Monitors the oxygen levels in the exhaust to optimize fuel efficiency. Catalytic Converter Transforms harmful gases into less harmful emissions before exiting the system. Muffler Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the system. Exhaust Pipe Transports exhaust gases from the manifold to the rear of the vehicle. Cooling System Parts and Connections
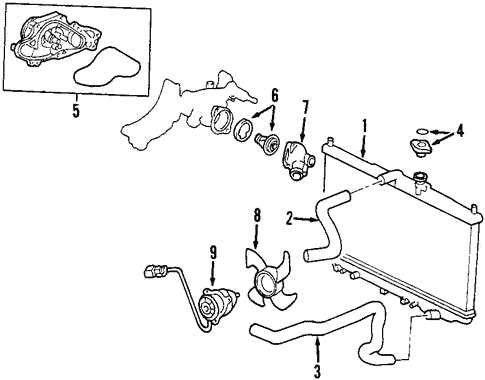
The cooling system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance. Understanding the various components and their interconnections is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section explores the key elements that make up the cooling system and how they interact with each other to regulate engine heat.
Key Components of the Cooling System
The primary components of the cooling system include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and hoses. The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, while the water pump circulates this coolant throughout the engine and the radiator. The thermostat regulates the coolant flow, ensuring that the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature. Hoses connect these components, allowing for seamless fluid movement.
Connections and Flow Paths
Proper connections between these components are vital for the cooling system’s efficiency. Coolant flows from the engine to the radiator through the upper hose, where it cools down before returning to the engine via the lower hose. Additionally, bypass hoses allow coolant to flow when the engine is cold, aiding in quick warm-up times. Understanding these flow paths is essential for diagnosing any issues that may arise within the cooling system.
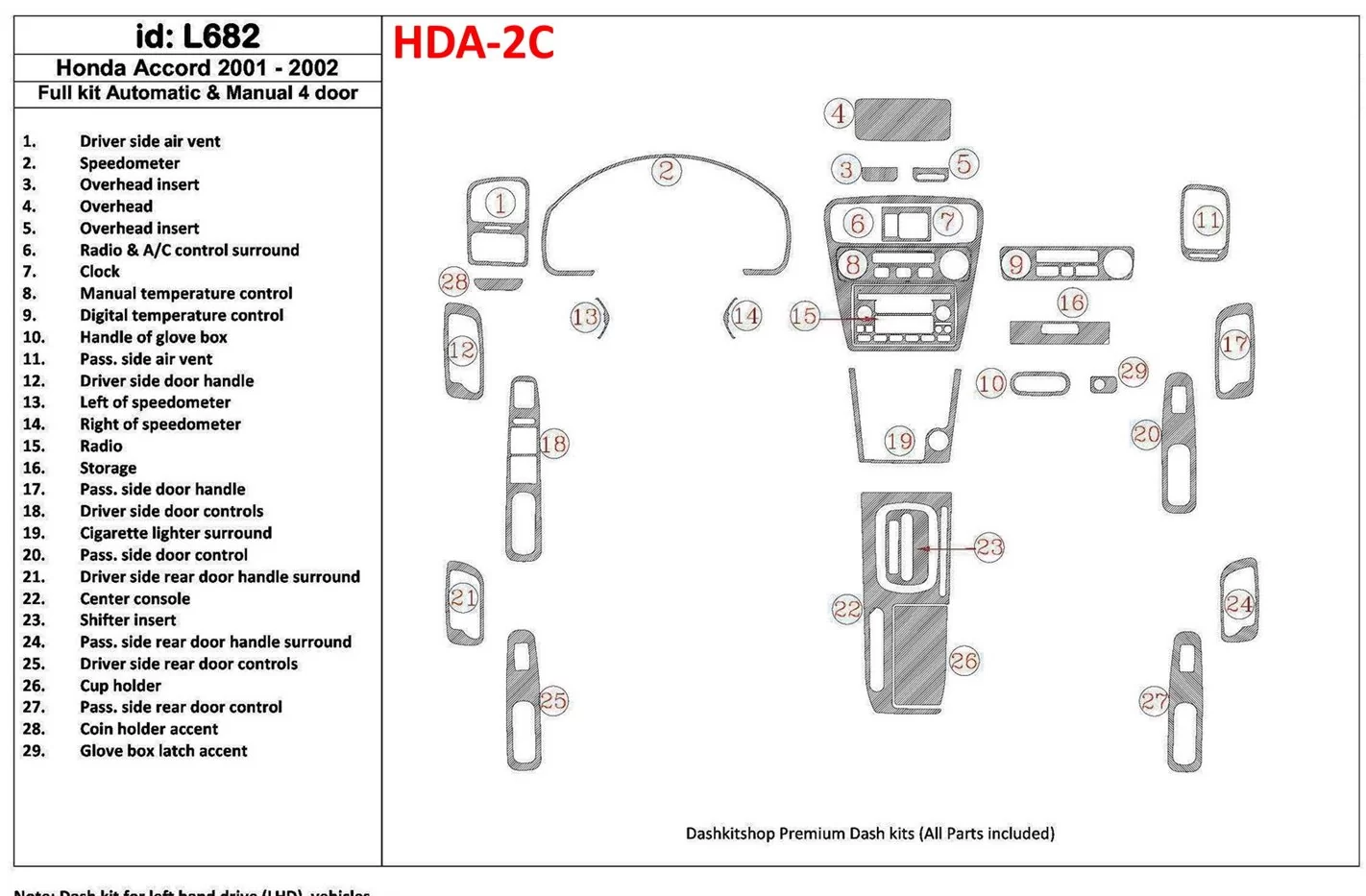
Interior Dashboard Components Overview
The dashboard of a vehicle serves as the central hub for both functionality and aesthetics within the cabin. This section provides an insight into the various elements that make up this critical area, highlighting their roles and interactions. Understanding these components enhances the appreciation of the vehicle’s design and functionality.
Key Elements of the Dashboard
Every dashboard comprises several essential parts that contribute to the driver’s experience. These include instruments for monitoring speed, fuel levels, and engine temperature, as well as controls for climate and entertainment systems. Each element is designed for intuitive use, ensuring that essential information is readily accessible while driving.
Functional Features
In addition to the primary instruments, the dashboard incorporates various functional features that enhance usability and comfort. These may include storage compartments, cup holders, and connectivity options for mobile devices, making the driving experience more enjoyable and efficient.
Component Function Speedometer Displays vehicle speed Fuel Gauge Indicates fuel level Tachometer Shows engine RPM Climate Controls Regulates cabin temperature Infotainment System Provides entertainment and navigation Transmission and Gearbox Parts Diagram
The transmission and gearbox assembly is essential for the effective operation of any vehicle, facilitating the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the various components within this system is crucial for maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Key Components Overview
This assembly comprises several vital elements, including gears, shafts, clutches, and synchronizers. Each part plays a significant role in enabling smooth shifting and efficient power delivery. Gears are responsible for adjusting the vehicle’s speed and torque, while shafts serve as the connection points that transmit motion throughout the system.
Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and maintenance of the transmission system can prevent costly repairs. It’s advisable to check fluid levels periodically and replace any worn components promptly. Additionally, understanding the functionality of clutches and synchronizers can aid in recognizing signs of wear and ensuring a seamless driving experience.
Steering System Components Breakdown
The steering mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth handling and precise control. Understanding the various elements that make up this system is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and safety.
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface through which the driver communicates their intended direction.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear, allowing for the transfer of motion.
- Steering Gearbox: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement, helping to steer the vehicle.
- Linkages: Components that connect the steering gearbox to the wheels, facilitating movement.
- Power Steering Pump: A hydraulic system that assists in steering, reducing the effort needed to turn the wheel.
- Ball Joints: Flexible connections that allow for the pivoting motion of the wheels while steering.
- Steering Rack: A part of the steering gear that translates the rotational motion into linear motion for the wheels.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure optimal functionality and safety on the road.
Lighting and Electrical Parts Layout

This section provides a comprehensive overview of the arrangement and functionality of lighting and electrical components in a vehicle. Understanding the configuration of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Proper illumination and electrical systems ensure safety and optimal performance on the road.
Key Components
- Headlights
- Taillights
- Turn signals
- Brake lights
- Interior lighting
- Battery
- Fuses
- Wiring harness
Functionality and Maintenance
- Headlights: Essential for visibility during nighttime driving and adverse weather conditions.
- Taillights: Important for signaling to other drivers when the vehicle is slowing down or stopping.
- Turn signals: Indicate the direction of turns, enhancing safety during lane changes.
- Brake lights: Notify following vehicles when brakes are applied.
- Interior lighting: Provides visibility within the cabin, especially at night.
- Battery: Supplies power to electrical systems and components.
- Fuses: Protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when necessary.
- Wiring harness: Connects various electrical components and facilitates the flow of current.