Understanding the intricate system of a farm vehicle requires a closer look at its structural makeup and functional elements. A well-organized overview of all essential sections is crucial for proper maintenance and repairs. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a tractor owner, knowing where each part fits into the overall machinery is key to ensuring smooth operations.
In this section, we will provide a detailed visual representation of the vehicle’s key assemblies, focusing on their connections and functions. From the engine block to the hydraulic system, each component plays a pivotal role in the performance of the equipment. A clear understanding of these sections will help you identify potential issues quickly and accurately.
Having access to a well-structured visual map of the vehicle’s layout not only simplifies troubleshooting but also aids in efficient repairs. Whether you are handling routine maintenance or dealing with specific malfunctions, this guide will serve as a valuable resource to support your work and improve the overall lifespan of your machinery.
Understanding the International 784 Parts Layout
The layout of components in a tractor is crucial for ensuring efficient operation and ease of maintenance. Every section and part plays a specific role in the overall functionality of the machine. Having a clear understanding of how these elements are organized allows operators to perform repairs, replacements, and adjustments with confidence and precision.
Component Classification
Tractors are designed with various systems that work together to deliver optimal performance. These systems include the engine, transmission, hydraulic mechanisms, and electrical circuits, each of which houses multiple individual elements. Proper categorization of these parts helps in troubleshooting and identifying areas requiring attention.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Recognizing the layout of these components also facilitates the process of upgrades. Whether replacing an old part or adding a new feature, knowing the exact placement and compatibility of each item is essential for ensuring long-term functionality. Regular inspections and timely replacements prevent costly damages and extend the lifespan of the machine.
Key Components of the Tractor System
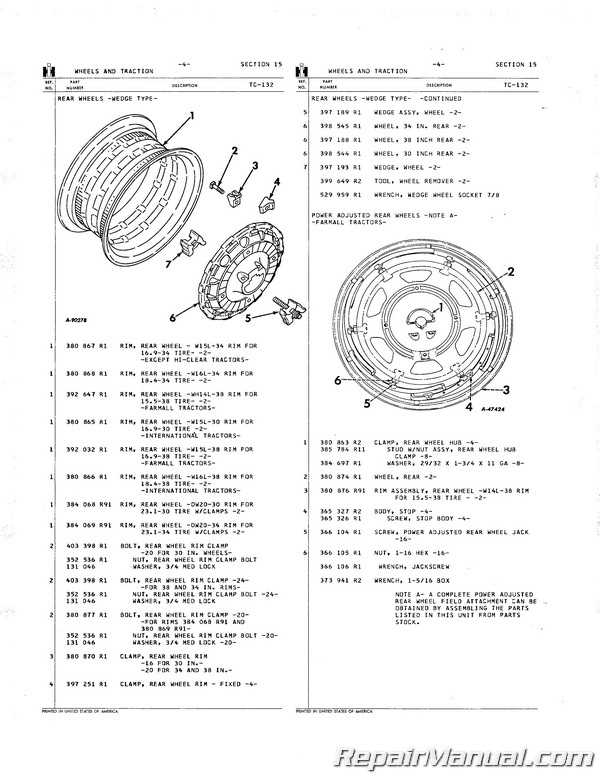
Understanding the core elements of a tractor’s mechanism is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. These fundamental units work in harmony to ensure optimal performance across various agricultural tasks, from tilling soil to hauling heavy loads. Each component plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality, affecting the power transmission, control systems, and operational stability of the vehicle.
Engine and Powertrain
The engine is the heart of the machine, converting fuel into power. It drives the mechanical systems that provide motion and energy to the other parts. Connected to the engine is the powertrain, which includes the transmission, differential, and final drives. These components work together to transfer the engine’s power to the wheels, allowing the tractor to move and perform various tasks. The efficiency of the powertrain determines how well the machine handles heavy-duty operations.
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system is crucial for operating attachments and tools. By using fluid pressure, it enables the tractor to lift, lower, and control implements such as plows and loaders. This system consists of pumps, cylinders, and valves that control the movement of implements with precision. Proper maintenance of the hydraulic system is essential for ensuring that attachments work seamlessly with the tractor’s other systems.
Engine Assembly and Related Parts
The engine assembly serves as the heart of the machine, ensuring optimal performance through its intricate components and systems. The proper functioning of each individual element within this setup is critical for the overall efficiency and durability of the equipment. From the internal combustion mechanism to the supporting accessories, each part must work in harmony to deliver consistent power output and reliability.
At the core of the engine are the main components such as the cylinder block, crankshaft, and pistons, which are responsible for converting fuel into energy. The surrounding systems, including the cooling and lubrication setups, play a vital role in maintaining temperature control and minimizing wear on the moving parts. Additionally, the electrical and fuel systems ensure smooth start-up and uninterrupted operation during use.
Each assembly part is meticulously designed to fit and function in a specific manner, ensuring compatibility with other systems in the machine. Regular maintenance and timely replacements of these elements are essential to avoid breakdowns and maintain peak performance. Understanding the composition of the engine assembly helps in identifying potential issues and optimizing the lifespan of the equipment.
Hydraulic System Overview
The hydraulic system is a critical component in agricultural machinery, enabling powerful and precise control over various operations. This system relies on fluid pressure to operate mechanisms such as lifting, steering, and braking. Proper maintenance and understanding of its layout are essential for ensuring smooth performance and longevity of the equipment.
Key Components
The system typically includes a pump, valves, cylinders, and hoses that work together to transmit fluid pressure. The pump generates the necessary pressure, while the valves regulate the flow of hydraulic fluid. Cylinders are responsible for converting this pressure into mechanical movement, allowing various attachments and tools to function effectively.
Fluid Flow and Efficiency
Efficient fluid flow is vital for the system’s operation, ensuring that all components receive adequate pressure and perform their tasks accurately. Leaks, air bubbles, or blockages can significantly reduce efficiency, leading to slower responses or even malfunctioning. Regular checks and proper fluid maintenance help prevent these issues, ensuring consistent performance during demanding tasks.
Transmission and Gear Mechanisms
The efficiency and power transmission of any machinery largely depend on its internal drive systems. These systems play a critical role in ensuring smooth operation by converting engine power into usable force that drives the wheels or other working components. The key components involved in this process include the transmission system and various gears, each playing a unique part in controlling speed and torque.
Transmission System Overview
The transmission system is responsible for transferring the engine’s power to the wheels through a series of interconnected components. It adjusts the power output, enabling the vehicle or machinery to move at different speeds depending on the work required. This system often includes a range of gears that allow for flexibility in operation, ensuring that the right balance between speed and torque is achieved for various tasks.
Gear Mechanism and Types
Gears are integral to the transmission, working together to modify the power flow. The type of gear arrangement used can significantly impact performance and efficiency. Below are common types of gear mechanisms found in many vehicles and machinery:
- Spur Gears: Simple, straight-toothed gears used to transfer motion in a straight line.
- Helical Gears: Similar to spur gears but with angled teeth, they offer smoother operation and reduced noise.
- Planetary Gears: A compact system of gears used for multiple speed variations in limited space.
- Bevel Gears: Used to change the direction of power flow, typically at a right angle.
Each of these gear types has its specific use, contributing to the overall functionality of the machine’s transmission system. Proper maintenance and understanding of how these components interact are essential for ensuring longevity and performance.
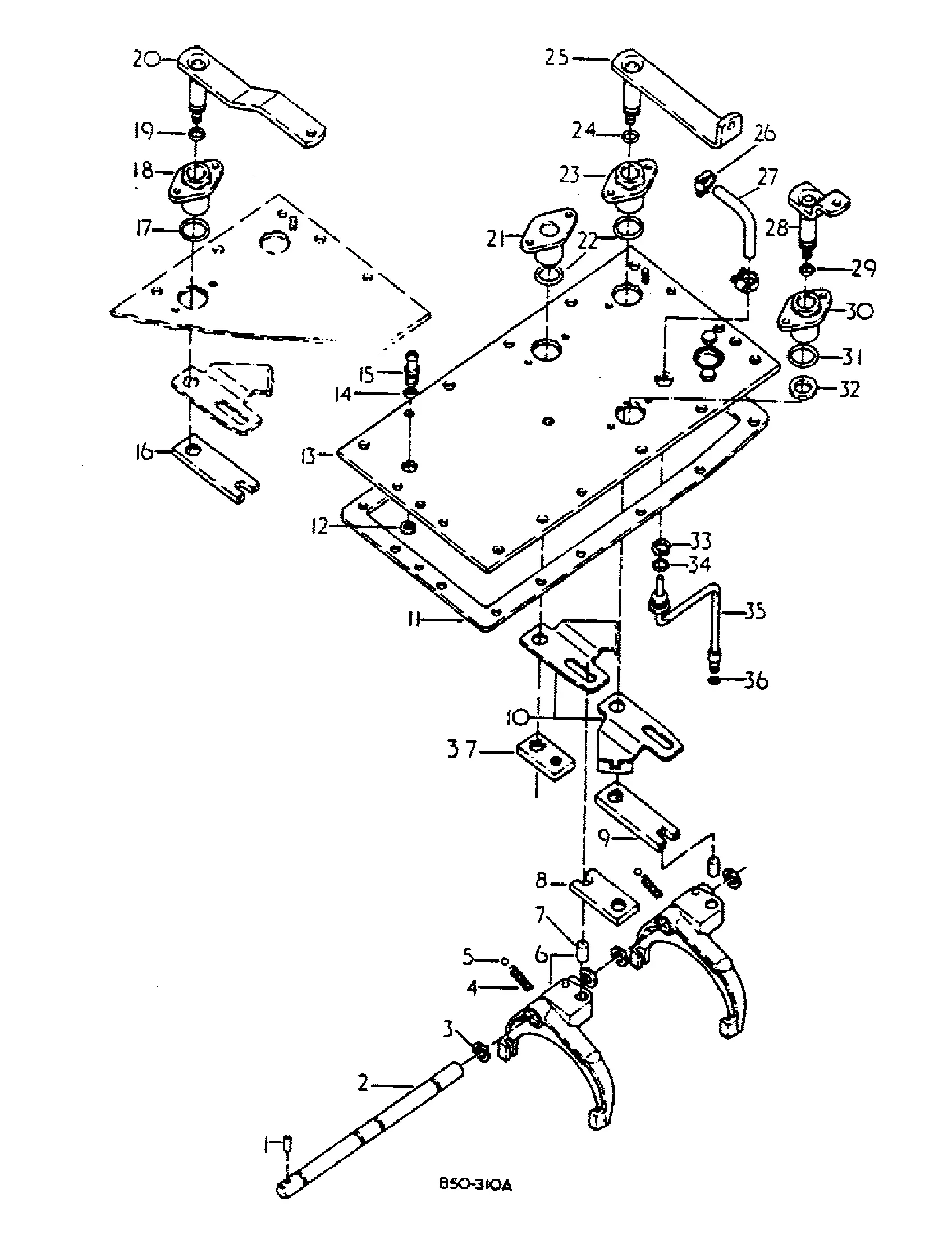
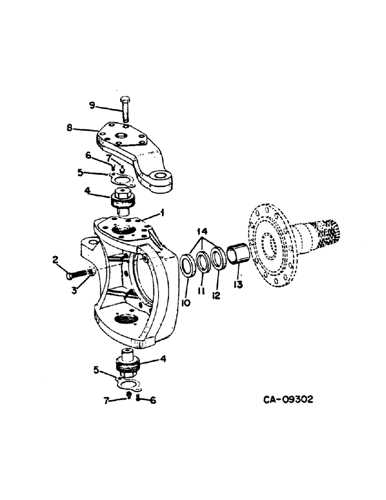
Front and Rear Axle Parts
The front and rear axle systems are critical for ensuring stability and efficient power transmission. Understanding the various components within these systems allows for better maintenance and overall performance. This section provides a detailed overview of key elements responsible for the functionality and durability of these mechanisms.
- Front Axle Assembly: The front axle is primarily responsible for steering and load-bearing. Its components are designed to handle lateral forces while providing smooth operation under various conditions.
- Steering Knuckles: These connect the wheels to the axle, allowing them to pivot while steering. Made from robust materials, they ensure precise movement and handling.
- Axle Shafts: These solid bars transmit power from the differential to the wheels. The durability of these shafts ensures consistent pe
Electrical Wiring and Connection Schematics
The electrical system plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of the machinery. Clear and well-structured wiring layouts are essential for seamless operation, allowing for efficient power distribution, communication between components, and safeguarding from potential failures.
Understanding the various electrical connections, fuses, relays, and switches is key to maintaining and troubleshooting the system. This section provides a structured overview of the fundamental elements involved in the wiring system.
- Power Sources: Outlines the primary connections between batteries, alternators, and distribution points.
- Fuses and Relays: Protection components that prevent electrical overloads, ensuring safety.
- Control Switches: Main points of interaction for operators to control functions, such as
Fuel System Diagrams Explained
The fuel system is a crucial component responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding its layout and functions is essential for maintaining engine performance and identifying issues when they arise. This section provides a detailed look into the key elements of the system, helping to clarify how fuel moves through various parts and what role each part plays in the overall operation of a machine’s engine.
Key Components and Flow

The system consists of several interconnected elements that work together to ensure proper fuel delivery. Each component plays a specific role in managing the flow, filtration, and injection of fuel. Here’s a breakdown of the main sections:
Component Function Fuel Tank Braking System and Components
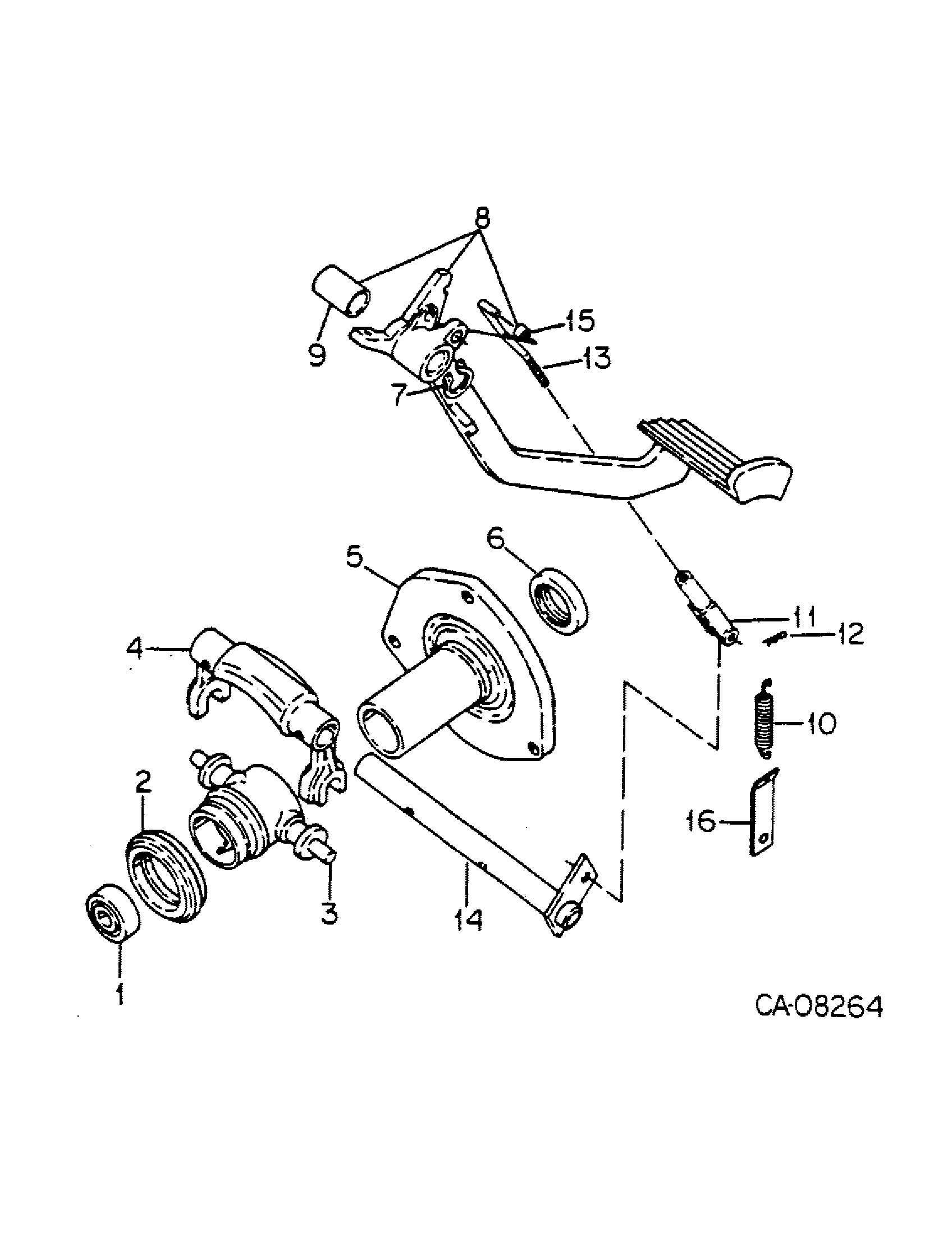
The braking mechanism is essential for ensuring safe operation, providing the necessary force to decelerate or halt the movement of machinery. Understanding how each element works in unison is crucial for maintaining the system’s efficiency and reliability. In this section, we will explore the key components involved in the braking process and how they contribute to optimal performance.
Main Components
- Brake Pedal: The initial point of contact, where the operator applies force to activate the system.
- Master Cylinder: Converts mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic force, distributing it throughout the system.
- Brake Lines: Pathways that transfer hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brakes themselves.
- Brake Shoes or Pads: Components that press against the wheel, creating the friction needed to slow
Cooling and Airflow Mechanisms
The cooling and airflow system plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal temperature of machinery, ensuring efficient operation and preventing overheating. Proper ventilation and temperature regulation are key to extending the lifespan of equipment and improving overall performance. In this section, we will explore the primary components and principles behind efficient cooling and airflow management.
Core Components
- Radiators: Radiators are essential for dissipating heat. They transfer excess heat from the engine or other parts of the system to the surrounding air, maintaining ideal working temperatures.
- Fans: Fans assist in forcing air through the cooling system, increasing airflow to remove heat more effectively. They ensure continuous circulation, especially during high-demand operations.
- Common Wearable Parts and Maintenance
Over time, machinery components that experience frequent use and friction are prone to wear and tear. Regular upkeep of these critical elements ensures smooth operation and prevents unexpected breakdowns. Identifying and maintaining these high-usage areas is key to prolonging the lifespan of equipment.
Belts are among the most commonly replaced items due to their constant motion and load-bearing function. Regular inspections for cracks or fraying help prevent failures. Proper tension adjustments also enhance durability.
Bearings are essential for reducing friction between moving parts. Worn bearings can lead to increased vibration, overheating, and potential damage. Regular lubrication and timely replacements are necessary to avoid extensive mechanical issues.
Seals and gaskets are vital for preventing leaks and
Comparing the 784 Parts to Other Models
When evaluating components across different models of agricultural equipment, it becomes essential to understand both the similarities and variations in design and functionality. By examining how key elements are structured and used in various machines, operators can make informed decisions regarding compatibility, performance, and maintenance. This section will delve into the significant comparisons between various models, highlighting areas where design philosophies diverge or converge.
One of the primary differences observed is in the configuration of essential systems, such as hydraulic assemblies and engine mounts. While some models prioritize efficiency with more modern materials, others maintain a more robust, traditional design. These distinctions often influence the overall reliability and longevity of the machinery in different field conditions.
Additionally, the arrangement of the transmission and drive mechanisms can vary significantly between models, affecting ease of repair and part availability. Some machines are known for their universal design approach, allowing a broader range of interchangeable pieces, while others may require more specialized solutions tailored to specific operational needs.
Ultimately, understanding how these various elements compare across models is crucial for those
How to Use the Parts Diagram Effectively
Understanding how to navigate visual schematics is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or repair equipment. These detailed illustrations provide a clear breakdown of mechanical components, allowing users to identify specific elements and their relationships within the overall system. Mastering the reading of these drawings can save time and ensure that you are making accurate replacements or repairs.
Step-by-step navigation through such illustrations begins with identifying key symbols and numbers associated with each element. Most layouts include a legend or reference guide, making it easier to match components with their descriptions. Pay attention to the organization of sections, which often follow a logical sequence from larger assemblies to smaller sub-units.
When working with these visual aids, it’s essential to stay organized and methodical. Start by isolating the area you need to focus on, then carefully cross-reference each component with its corresponding number in the list. This approach helps avoid confusion and ensures that you are addressing the correct part of the system.