Exploring the structure and arrangement of various elements within a vehicle can be crucial for both maintenance and repairs. A well-organized illustration of mechanical and electronic systems helps users identify the right pieces quickly and efficiently, ensuring that any necessary adjustments or replacements are done smoothly. Familiarity with this type of overview enhances the understanding of how everything works together.
Identifying essential elements in such a layout can significantly simplify the task of locating specific components. Whether it’s for routine maintenance or more complex repair tasks, having a clear overview of the internal arrangement provides a clearer pathway for action.
The ability to visualize connections between various sections helps users avoid confusion and saves time when working with multiple layers of technology. Proper guidance on where each part fits ensures an efficient and accurate approach to vehicle upkeep.
2013 VW Jetta Parts Overview
Understanding the key elements of this vehicle model’s components is essential for efficient maintenance and repair. Each component works in harmony to ensure optimal performance and reliability, contributing to both safety and driving comfort. From the engine’s complex mechanisms to the smaller fixtures, every element has its role in keeping the vehicle functional.
Below is a breakdown of the essential sections and components commonly found in this model:
| Section | Main Components |
|---|---|
| Engine Area | Cooling system, ignition system, fuel injectors |
| Suspension | Shock absorbers, springs, control arms |
| Braking System | Brake pads, calipers, rotors |
| Transmission | Gearbox, clutch, drive shafts |
| Electrical System | Battery, alternator, wiring |
Engine Components Breakdown
The engine consists of various interconnected elements that work together to ensure optimal performance and functionality. Understanding these components can help in identifying potential issues and maintaining overall efficiency.
Main Elements
- Cylinder Block: The core structure that houses critical components and maintains the stability of the entire system.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: Converts the vertical movement of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves, synchronizing with the crankshaft.
Additional Key Components
- Oil Pump: Ensures proper lubrication of all moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
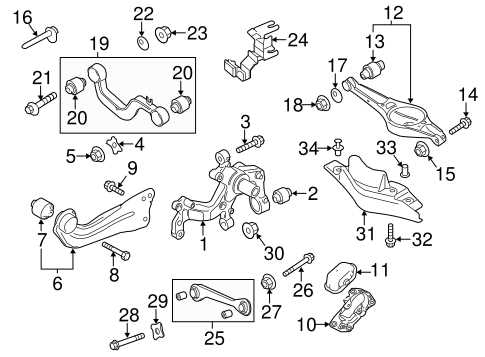
- Suspension System Diagram
The suspension system plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride, absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces while maintaining the vehicle’s balance. It consists of several key components working together to provide comfort and safety. Understanding the layout and functionality of this system helps in identifying potential issues and maintaining overall vehicle performance.
Component Function Shocks/Struts Absorb bumps and maintain tire contact with the road. Control Arms Connect the wheels to the vehicle’s frame, allowing smooth vertical movement. Ball Joints Provide a pivot point between the wheels and suspension. Sway Bar Reduces body roll during turns and maintains stability. Springs Support the vehicle’s weight and control ride height. Interior Parts Layout
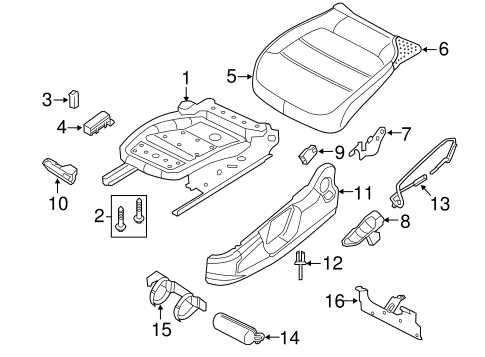
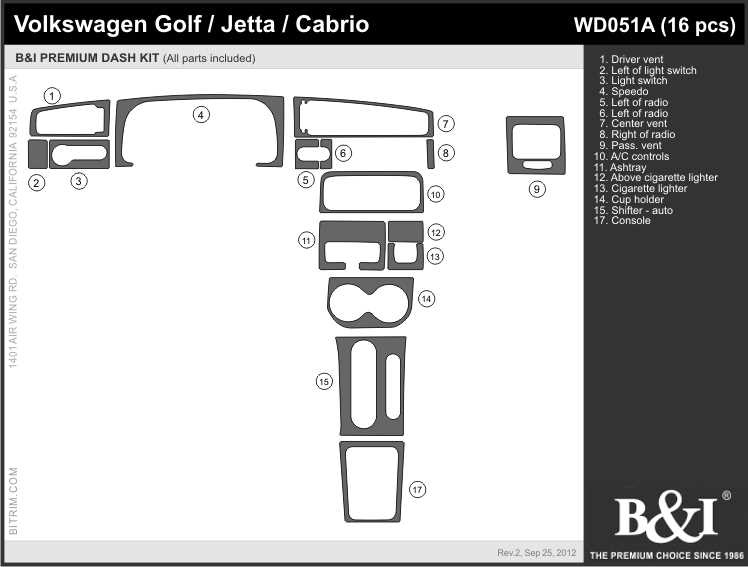
The arrangement of elements inside the vehicle is crucial for ensuring both comfort and functionality. This section highlights the overall structure of the interior, where each component has been designed to offer convenience and practicality. Understanding the placement of key features will help optimize the experience within the cabin.
Key Components Overview
- Dashboard Configuration: The central control area provides easy access to essential controls, including climate and media functions.
- Seating Arrangement: Designed for maximum comfort, the seats offer ergonomic support and adjustability for both the driver and passengers.
- Storage Compartments: Multiple
Brake System Components
The braking system is essential for safe vehicle operation, ensuring the ability to slow down and stop effectively. Understanding the different parts of this system helps in maintaining its performance and reliability.
- Brake Pedal: This is the component the driver uses to initiate the braking process. It transmits force to other parts of the system.
- Brake Calipers: These house the brake pads and are responsible for applying pressure to slow down the wheels.
- Brake Pads: Positioned inside the calipers, they press against the rotors to create friction, slowing the vehicle.
- Rotors: These metal discs are attached to the wheels and provide the surface for the brake pads to press against, generating the necessary friction to stop the vehicle.
- Brake Lines: These carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, ensuring hydraulic
Electrical System Overview
The electrical system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of various components and features. This intricate network consists of various elements that work together to provide energy and control to essential systems, enhancing the overall performance and safety of the automobile.
Key components of the electrical system include:
- Battery: Acts as the primary power source, storing electrical energy for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories.
- Alternator: Charges the battery while the engine runs, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity to the vehicle’s systems.
- Fuses: Protect electrical circuits from overload, preventing potential damage to components.
- Wiring Harness: Connects various electrical parts, facilitating the flow of electricity throughout the vehicle.
- Control Modules: Manage and regulate the operation of various electrical systems, including the engine management and infotainment systems.
Understanding these components and their functions is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring reliability and efficiency in everyday driving scenarios.
Cooling System Parts
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in an automobile’s engine. It comprises various components that work in harmony to dissipate heat, ensuring the engine runs efficiently. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repair, which helps prolong the lifespan of the vehicle.
Component Description Radiator Facilitates heat exchange by dissipating heat from the coolant into the atmosphere. Thermostat Regulates coolant flow to maintain the engine’s temperature by opening and closing at specific temperatures. Water Pump Circulates coolant throughout the cooling system, ensuring consistent flow and heat transfer. Coolant Reservoir Stores excess coolant and provides a source for the system, allowing for proper fluid levels. Hoses Flexible conduits that transport coolant between various components of the cooling system. Transmission Diagram and Parts
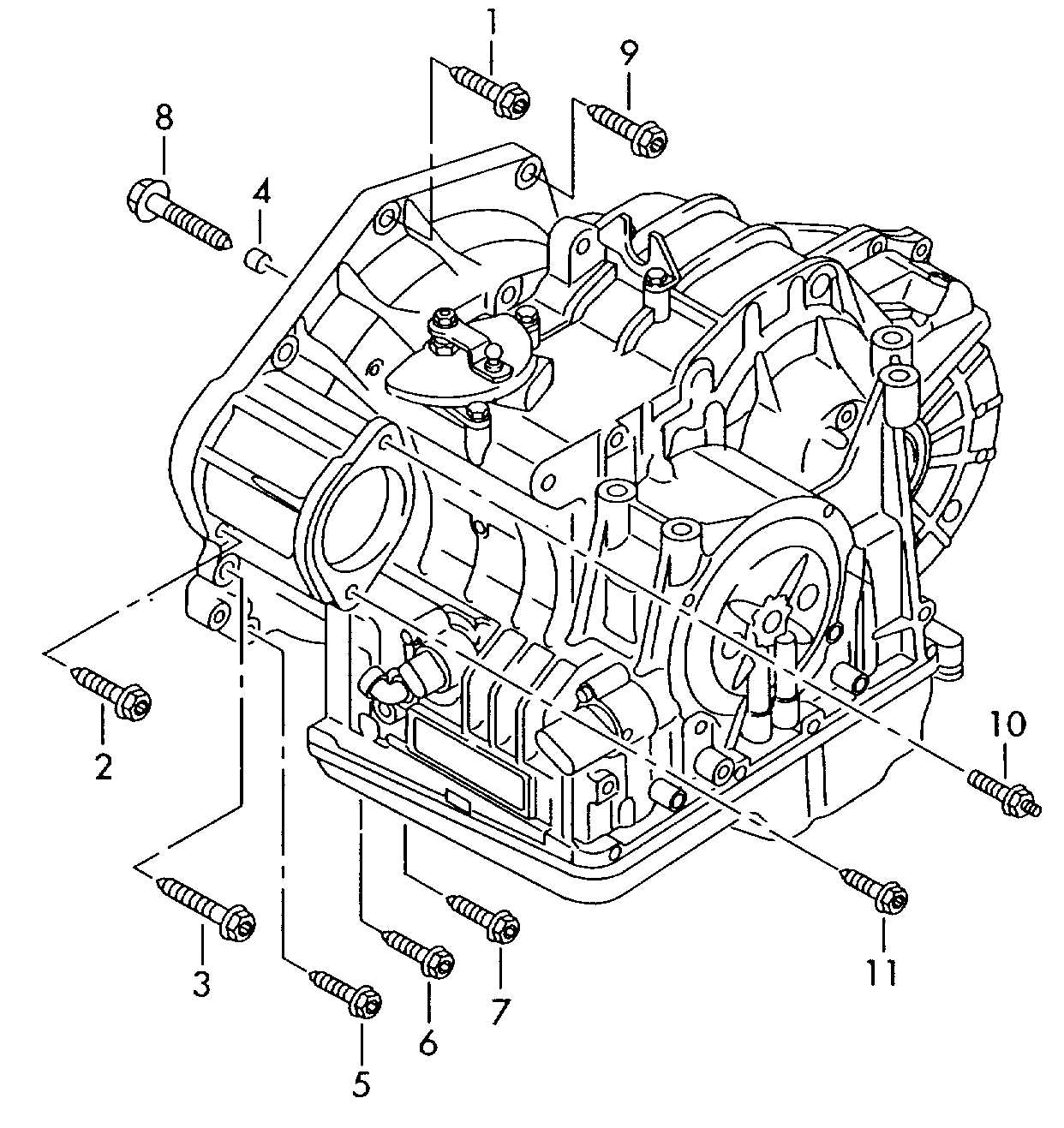
The transmission system is a crucial component that facilitates the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, enabling efficient movement of the vehicle. Understanding its structure and functionality is essential for maintenance and repair, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the automotive system.
Key Components of the Transmission System
- Gearbox: The primary housing that contains the gears and mechanisms for power transfer.
- Clutch: This component engages and disengages the engine from the drivetrain, allowing for smooth gear shifts.
- Torque Converter: A fluid coupling that allows the engine to continue running while the vehicle is stationary.
- Shifter: The control used by the driver to select different gear positions.
- Transmission Fluid: A vital lubricant that ensures smooth operation and cooling of the transmission system.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Inadequate fluid levels can lead to overheating. Regular checks and maintenance are necessary.
- Worn gears can cause shifting problems; replacing them promptly is crucial.
- Clutch slippage may indicate the need for adjustment or replacement to restore performance.
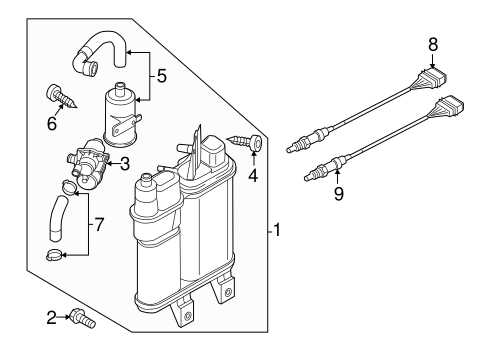
Fuel System Components
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of a vehicle. This intricate assembly is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine while maintaining the necessary pressure and flow. Understanding the various elements involved in this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Fuel Tank: The primary storage unit for fuel, designed to hold a specific volume while preventing leaks.
- Fuel Pump: An essential component that transfers fuel from the tank to the engine. It can be mechanical or electric, depending on the vehicle’s design.
- Fuel Filter: This part ensures that impurities and contaminants are removed from the fuel before it reaches the engine, protecting critical components.
- Fuel Injectors: Devices that atomize fuel and deliver it directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for efficient combustion.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses or pipes that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors, maintaining pressure and preventing leaks.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator: This component regulates the pressure of the fuel delivered to the engine, ensuring consistent performance across various driving conditions.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, vehicle owners can better appreciate the importance of regular maintenance and prompt repairs when issues arise within the fuel delivery system.
Exhaust System Layout
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in managing engine emissions and enhancing performance. Its design influences how exhaust gases exit the engine and the overall efficiency of the vehicle. A well-structured system not only minimizes harmful emissions but also contributes to a quieter ride.
In a typical layout, the exhaust system consists of several key components, including the manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler. Each element is strategically placed to ensure optimal flow and reduction of back pressure, allowing for smoother engine operation. The manifold collects gases from the engine’s cylinders, directing them towards the catalytic converter, which transforms harmful substances into less toxic emissions.
Following this, the exhaust gases travel through the piping to the muffler, designed to reduce noise levels while maintaining efficient flow. This entire configuration not only aids in compliance with environmental regulations but also enhances the driving experience by promoting effective power delivery and performance.
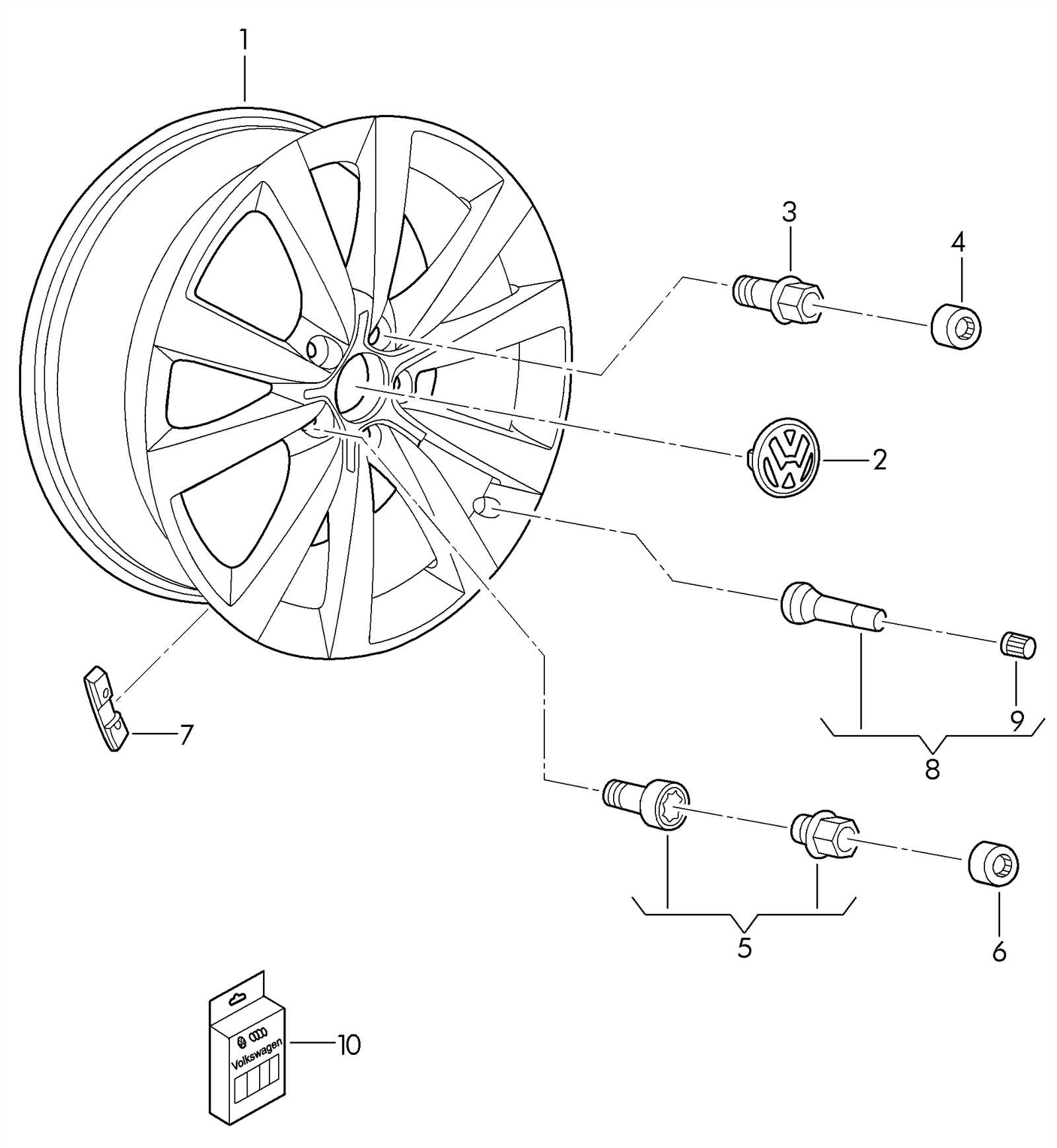
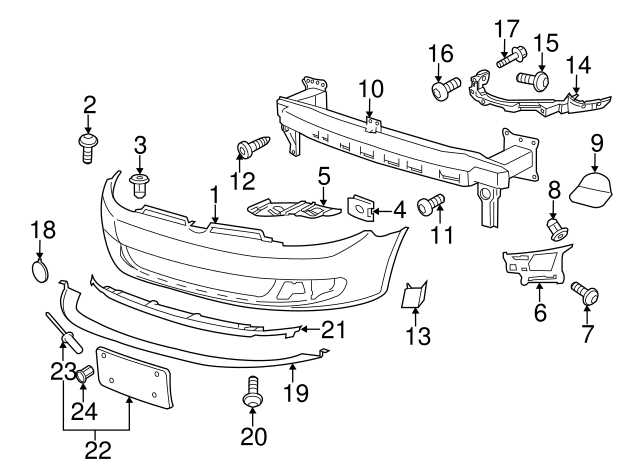
Exterior Body Parts Diagram
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the various components that make up the outer structure of a vehicle. Understanding these elements is crucial for both maintenance and repair tasks, ensuring that each part is functioning optimally to protect and enhance the vehicle’s aesthetics and performance.
Component Description Hood The hinged cover that rests over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance and repairs. Bumper A protective bar positioned at the front and rear of the vehicle to absorb impact during collisions. Fender The panel that surrounds the wheel area, designed to protect the body from debris kicked up by the tires. Door The movable barrier that allows entry and exit to the cabin, available in various styles including coupe and sedan configurations. Trunk Lid The cover for the storage compartment located at the rear, providing access for cargo loading. Windshield The glass panel at the front of the vehicle, crucial for visibility and protecting occupants from wind and debris. Roof The top structure of the vehicle that contributes to its overall shape and stability. Steering Mechanism Components
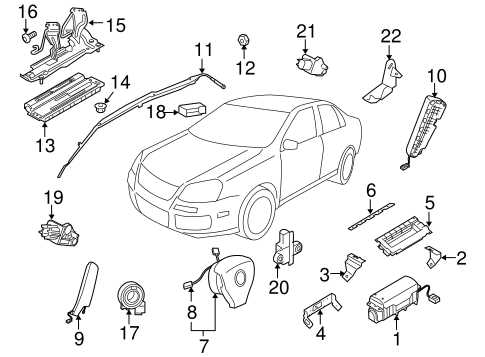
The steering system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring precise maneuverability and stability. It comprises various elements that work together seamlessly to provide the driver with control over the direction of the vehicle. Understanding these components is essential for effective maintenance and repair, contributing to the overall performance and safety of the automobile.
At the core of the steering mechanism lies the steering wheel, which the driver uses to initiate changes in direction. This input is transmitted through a series of linkages and gears, including the steering column and rack and pinion system. These components translate the rotational movement of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels, facilitating responsive handling.
Additionally, the tie rods connect the steering rack to the wheels, ensuring that any adjustments made by the driver are effectively relayed to the front axle. The power steering pump enhances this process by providing hydraulic assistance, making it easier to turn the wheel, especially at lower speeds. Moreover, the steering knuckles serve as pivot points for the wheels, allowing for smooth turning and improved maneuverability.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to prevent steering issues, such as play in the wheel or unresponsive handling. Ensuring that each part functions correctly not only enhances the driving experience but also promotes safety on the road.
Lighting and Signal Parts
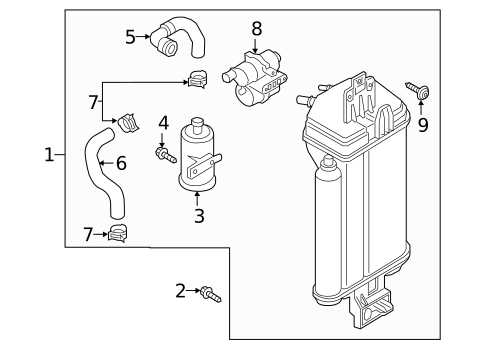
Effective illumination and signaling systems are crucial for safe vehicle operation, enhancing visibility and communication with other road users. Understanding the various components involved helps ensure optimal functionality and maintenance.
Key Components
- Headlamps
- Taillights
- Turn Signal Lights
- Brake Lights
- Fog Lights
- Daytime Running Lights
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect all lighting elements for functionality.
- Replace any burned-out bulbs promptly to ensure visibility.
- Keep lenses clean and free of obstructions for maximum brightness.
- Check electrical connections to avoid malfunctions.