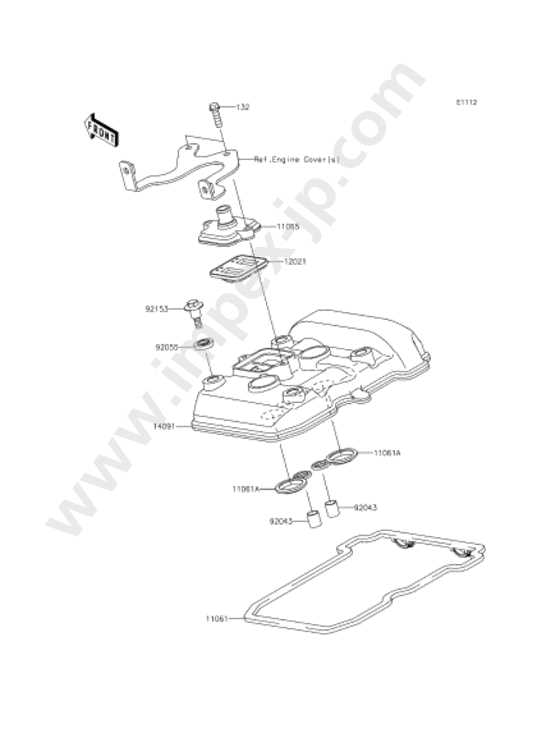
In the world of high-speed motorcycles, the intricate design and engineering of each component play a crucial role in overall performance and reliability. Whether you are a seasoned rider or an enthusiastic newcomer, gaining insight into the various elements that constitute these machines can enhance your riding experience and maintenance skills. This section delves into the essential building blocks that make up these powerful vehicles, offering a comprehensive view of their functionality and interrelation.
From the engine to the braking system, every aspect is meticulously crafted to ensure optimal performance. Understanding how these parts work together not only improves your knowledge but also empowers you to make informed decisions when it comes to upgrades and repairs. Each piece contributes to the bike’s agility, speed, and handling, making it imperative for riders to familiarize themselves with the mechanical layout.
Moreover, having a clear visual representation of these components can aid in troubleshooting and enhancing the overall riding experience. Whether you are looking to replace a specific element or simply wish to explore the technological marvel behind your machine, comprehending the configuration of these integral parts is essential for every motorcycle enthusiast.
The engine assembly is a crucial component of any high-performance motorcycle, acting as the heart that drives the machine forward. Comprehending its structure and function is essential for both maintenance and performance enhancement. This section delves into the various elements that constitute the engine assembly, their interrelationships, and their roles in the overall operation.
Key components of the engine assembly include:
- Crankshaft: Converts linear motion from the pistons into rotational motion.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, compressing the fuel-air mixture.
- Cylinders: Houses the pistons and facilitates combustion.
- Camshaft: Regulates the timing of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Valves: Control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out.
- Oil Pump: Ensures lubrication throughout the engine components.
Each part works in unison to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance of these components is vital for longevity and efficiency.
Understanding the interplay between these elements can lead to improved tuning and overall performance enhancements. Regular inspection and familiarity with the assembly can aid in diagnosing potential issues before they escalate.
Detailed Frame and Chassis Insights
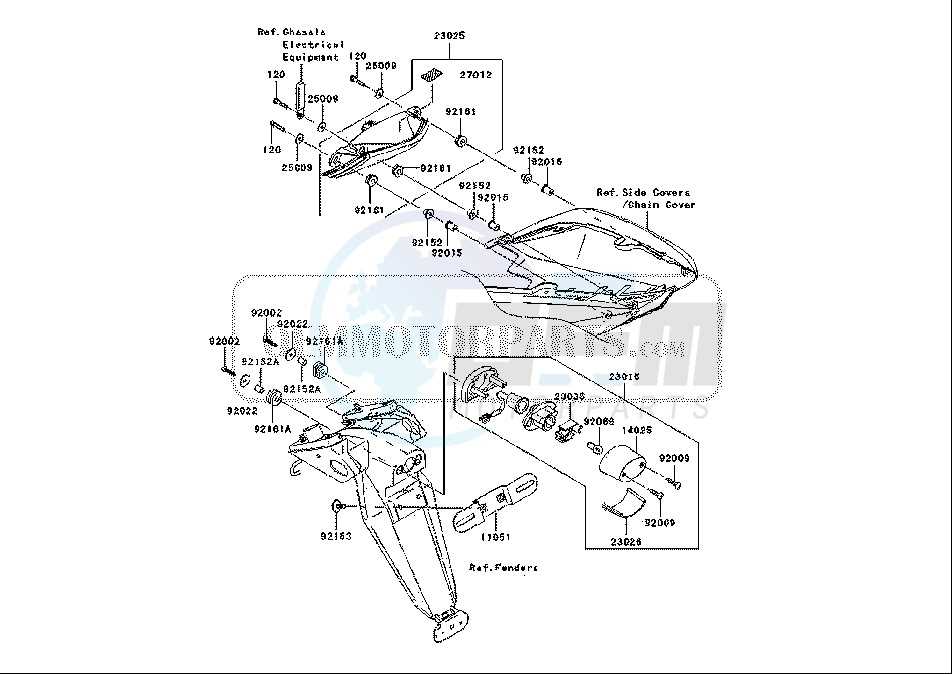
Understanding the intricate design of a motorcycle’s structure is crucial for both enthusiasts and professionals. The frame serves as the backbone, providing stability and support, while the chassis components play a significant role in the overall performance and handling. A well-engineered framework not only enhances the rider’s experience but also ensures safety and durability.
The layout of the frame affects the motorcycle’s agility, responsiveness, and comfort. Various materials are employed in construction, each contributing unique properties such as weight reduction and increased strength. Here, we explore the key elements that define the framework and chassis, highlighting their importance in achieving optimal performance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame | The primary structure that supports all other components, providing rigidity and stability. |
| Swingarm | Connects the rear wheel to the frame, allowing for suspension movement while maintaining structural integrity. |
| Subframe | A secondary structure that supports the seat and rear components, often designed for weight savings. |
| Forks | The front suspension system that connects the front wheel to the frame, crucial for steering and stability. |
| Footpegs | Provide a point of contact for the rider, essential for control and comfort during rides. |
| Handlebars | The steering mechanism that allows the rider to navigate and control the motorcycle’s direction. |
Each of these components interacts seamlessly to create a harmonious balance between performance and safety. Careful consideration of their design and integration is essential for maximizing the potential of any high-performance machine.
Brake System and Components Explained

The braking system of a high-performance motorcycle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and control. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system can enhance your knowledge of vehicle maintenance and improve your riding experience. Each component works in harmony to provide effective deceleration, making it essential for riders to be familiar with their functions and interactions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Brake Lever | Acts as the control interface for the rider, initiating the braking process. |
| Master Cylinder | Generates hydraulic pressure when the brake lever is pulled, sending fluid to the calipers. |
| Brake Lines | Transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers. |
| Brake Caliper | Houses the brake pads and applies force to the rotor when hydraulic pressure is received. |
| Brake Pads | Friction material that makes contact with the rotor to create stopping power. |
| Brake Rotor | Metal disc that rotates with the wheel; brake pads clamp onto it to slow down the bike. |
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Prevents wheel lockup during heavy braking, enhancing stability and control. |
Each element of the braking mechanism is vital for optimal performance. Regular maintenance and understanding the role of these components can significantly contribute to both safety and enjoyment on the road.
Electronics and Wiring Diagram Overview
This section delves into the intricate web of electronic components and their connections within a high-performance motorcycle. Understanding the layout and functionality of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. The arrangement of wires, connectors, and control units plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Key Components
The following table outlines some essential electronic components commonly found in advanced motorcycle systems:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| ECU (Engine Control Unit) | Regulates engine performance and efficiency. |
| Ignition Module | Controls the ignition timing for optimal combustion. |
| ABS Unit | Prevents wheel lock-up during braking. |
| Sensor Array | Monitors various parameters like speed, temperature, and throttle position. |
Wiring Layout
The wiring layout connects these components, facilitating communication and power distribution throughout the machine. A thorough understanding of this network helps technicians diagnose issues and enhance the performance of the vehicle.
Suspension Parts and Functionality
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride. It absorbs shocks from uneven surfaces, maintaining tire contact with the ground and enhancing overall handling. Understanding the components involved helps riders appreciate their significance in performance and safety.
Key Components
At the core of any suspension system are the forks and shock absorbers. Forks serve to guide the front wheel, while shock absorbers mitigate the impact of bumps. Together, these elements work to provide stability and comfort during acceleration, braking, and cornering.
Functionality and Adjustments
The functionality of the suspension system can be adjusted to suit various riding styles and conditions. Compression and rebound settings allow riders to customize how the system responds to terrain changes, enhancing grip and maneuverability. Regular maintenance and adjustments are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Fuel System Layout and Parts
The fuel system plays a critical role in the overall performance and efficiency of a high-performance motorcycle. It is designed to deliver the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal combustion and power generation. Understanding the arrangement and components of this system is essential for maintenance and modifications.
Transmission and Gear Mechanism Details
The efficiency of a motorcycle’s performance heavily relies on its transmission and gear mechanism. This intricate system plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth acceleration and optimal speed. Understanding the components and their functions can enhance both maintenance and performance tuning.
Key Components
At the heart of the transmission system are the gears, each designed to facilitate specific ratios that allow for varying levels of torque and speed. The primary components include the input shaft, output shaft, and the gear clusters. Synchronizers are also essential as they help align the gears during shifting, providing a seamless transition and reducing wear.
Functionality and Operation
The operation of the gear mechanism is initiated when the rider engages the clutch, disconnecting the engine from the wheels. This action allows for smooth gear selection without jarring. Once the appropriate gear is chosen, the clutch is released, re-engaging the engine’s power. This process is vital for achieving the desired speed and efficiency, making it crucial for riders to understand and master gear shifting techniques.
In summary, a well-functioning transmission and gear mechanism not only contribute to the overall performance of a motorcycle but also enhance the riding experience by providing better control and responsiveness.
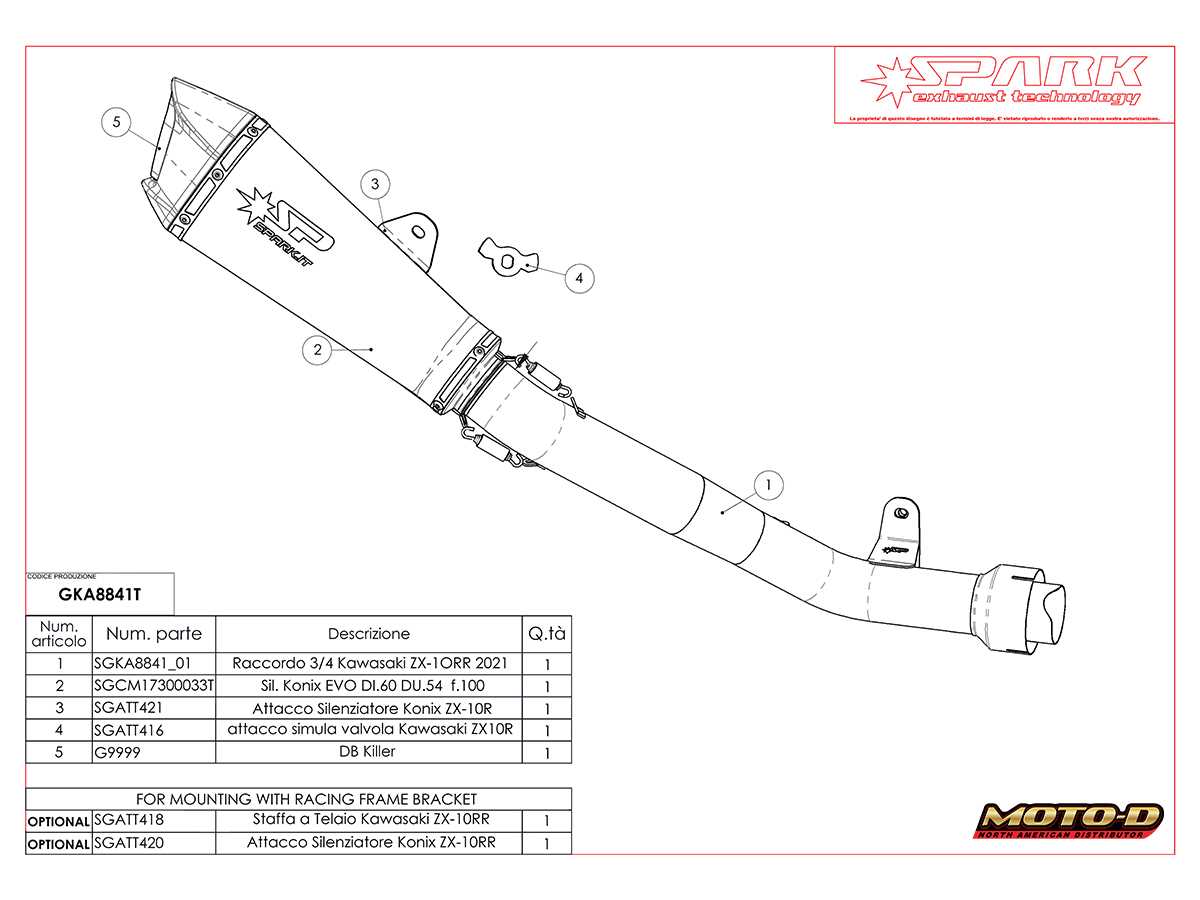
Exhaust System Components Breakdown
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance and ensuring efficient expulsion of gases. Understanding its various elements is essential for both maintenance and enhancement of overall functionality.
Header Pipes: These are the initial sections of the exhaust system, responsible for collecting gases from the engine’s cylinders. Their design significantly influences backpressure and power delivery.
Collector: The collector merges the exhaust flow from multiple header pipes into a single path. This component aids in balancing the exhaust flow and reducing turbulence, contributing to smoother engine operation.
Mid-Pipe: Serving as the transition piece, the mid-pipe connects the collector to the muffler. It often incorporates bends to navigate the bike’s chassis while maintaining optimal flow characteristics.
Muffler: This component serves a dual purpose–reducing noise and improving exhaust flow. Various designs exist, including baffled and straight-through types, each offering unique sound and performance attributes.
Exhaust Tips: The final section of the system, exhaust tips not only direct the gases away from the bike but also contribute to its aesthetic appeal. They come in various styles, allowing for personalization.
Each component of the exhaust system works in harmony to enhance performance, sound, and efficiency. Familiarity with these parts enables enthusiasts to make informed decisions regarding upgrades and maintenance.
Wheels and Tires Specifications
This section delves into the essential characteristics of the wheel and tire assembly, a crucial component for any high-performance motorcycle. Understanding these specifications ensures optimal handling, stability, and safety while enhancing the overall riding experience.
Wheel Dimensions
The wheel diameter and width are key factors that influence both performance and aesthetics. Typically, larger diameters improve acceleration and handling, while wider wheels enhance grip and stability. Material composition also plays a vital role, with lightweight alloys often used to reduce unsprung weight and improve responsiveness.
Tire Characteristics
Tire specifications include aspects such as profile, tread pattern, and rubber compound. A lower profile tire offers improved cornering capabilities, while a suitable tread pattern provides necessary traction in varying conditions. The rubber compound affects grip levels, durability, and performance in both wet and dry environments, making it essential to choose tires that match riding style and conditions.
Maintenance Tips for ZX10R Parts
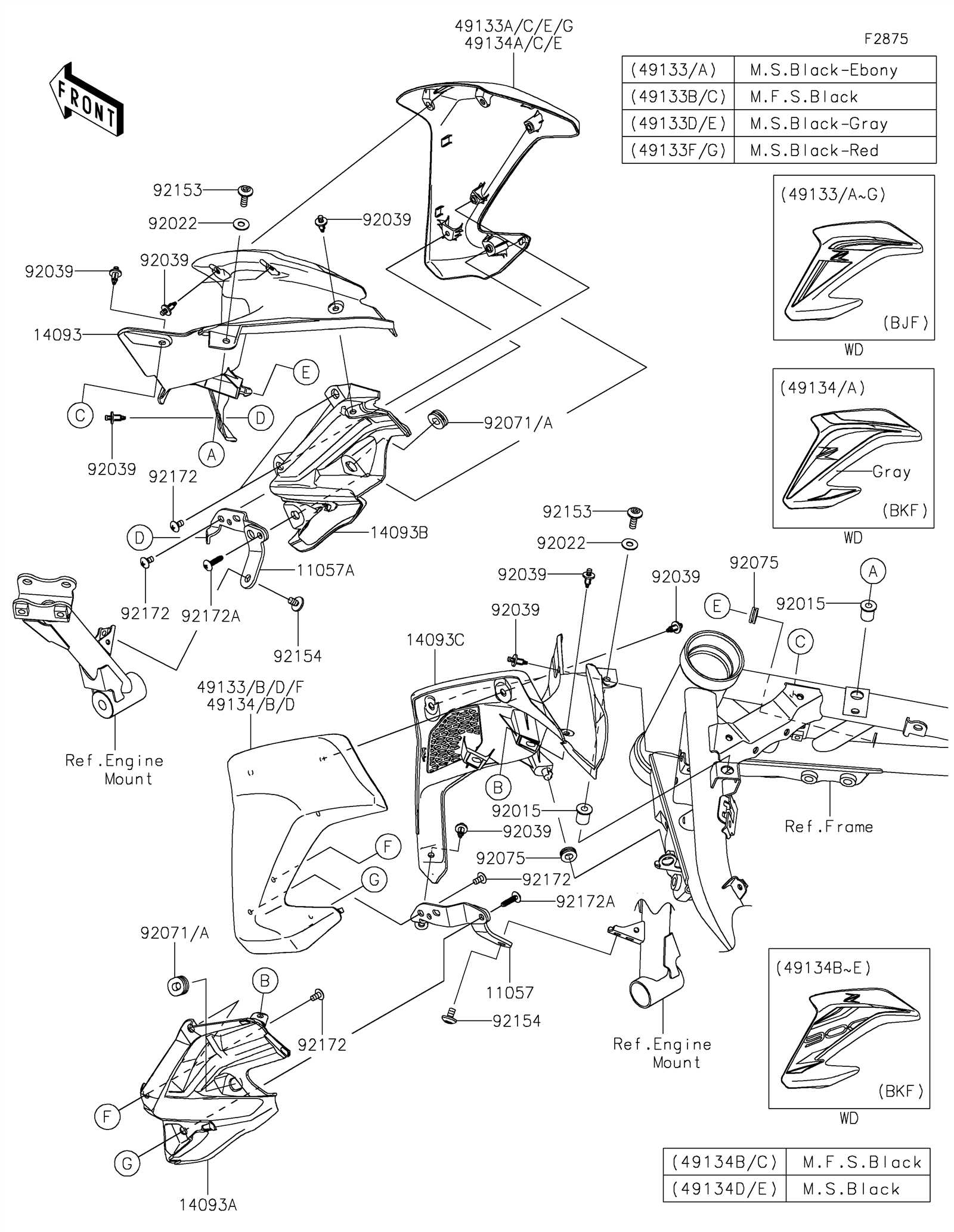
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your motorcycle components. By adhering to a systematic maintenance routine, riders can prevent premature wear and ensure that every aspect of their machine operates seamlessly. Below are key recommendations that can help enhance the durability and efficiency of various elements of your bike.
| Component | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|
| Brakes | Check pads for wear and replace them when they are thin. Regularly inspect brake fluid levels and replace fluid annually. |
| Chain | Keep the chain clean and lubricated. Adjust tension according to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| Oil System | Change engine oil every 3,000 miles or as recommended. Use high-quality oil that meets the required specifications. |
| Tires | Check tire pressure weekly and inspect for uneven wear. Replace tires that show signs of damage or excessive tread wear. |
| Electrical | Inspect battery terminals for corrosion and ensure connections are tight. Replace the battery every few years or as needed. |
Implementing these practices will not only enhance safety but also elevate the overall riding experience. Consistent attention to these details can save time and money in the long run, allowing you to enjoy your machine to the fullest.