
Understanding the internal layout and structure of machinery is crucial for maintaining and optimizing performance. This section will guide you through the essential elements and layouts that define the core of industrial equipment, ensuring clarity and precision in recognizing various components.
When dealing with complex systems, visual aids play an integral role in simplifying otherwise intricate configurations. The layout of mechanical systems is carefully organized to enhance both the machine’s efficiency and ease of maintenance.
In this guide, you’ll find detailed representations of critical mechanical sections, aiding in both identification and servicing. These illustrations serve as a vital resource for both professionals and enthusiasts seeking to improve their understanding of the system’s internal workings.
Components Overview
In this section, we will explore the essential elements that make up this compact track loader, providing a closer look at the internal and external systems responsible for its efficient performance. Understanding how each component functions together is key to ensuring optimal operation and longevity.
Main Operational Systems
The machine’s functionality relies on several core systems, including the hydraulic mechanism, which powers the lifting and digging capacities. Additionally, the cooling system is vital for maintaining proper temperature levels, preventing overheating during heavy-duty tasks. Both of these elements work in unison to ensure smooth and reliable operation in various conditions.
Chassis and Drive Mechanism
The drive system is a fundamental part of the machine’s mobility, ensuring powerful and precise movements across different terrains. The robust undercar
Engine Parts Breakdown and Description
In this section, we will explore the essential components of a typical engine, highlighting their functions and how they work together to ensure smooth operation. Understanding these elements is key to maintaining and servicing the engine effectively.
- Cylinder Block: The core structure that houses various other engine components, providing stability and support during operation.
- Pistons: Move within the cylinders, converting the pressure generated by combustion into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: Transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational movement, which drives the machinery.
- Valves: Control the intake of air and fuel, as well as the expulsion of exhaust gases, ensuring proper engine breathing.
- Camshaft: Synchronizes the timing of the valve operations, controlling their opening and closing as the engine runs.
- Power Source: Supplies energy to the entire system.
- Wiring Harness: Connects various elements, ensuring proper signal transmission.
- Control Module: Manages electrical signals and system operations.
- Sensors: Monitor conditions and provide feedback to the control module.
- Actuators: Convert electrical signals into mechanical movement.
- Fuel Tank: This component stores the fuel and is usually constructed from durable materials to withstand various environmental conditions.
- Fuel Pump: The pump is responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring consistent fuel flow.
- Fuel Filter: This part removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel, protecting the engine and enhancing its longevity.
- Fuel Injectors: These components atomize the fuel and deliver it into the engine’s combustion chamber, promoting efficient combustion.
- Fuel Lines: The lines transport fuel between different components, ensuring a secure and leak-free pathway.
- Filters: Regularly inspect and replace air, oil, and fuel filters to ensure optimal operation and prevent clogging.
- Belts: Check for cracks or signs of wear in belts; replacing them can help maintain efficiency and prevent unexpected failures.
- Hydraulic Hoses: Monitor hoses for leaks or damage. Timely replacement is crucial for maintaining hydraulic pressure and system performance.
- Blade Edges: For machinery equipped with cutting or digging tools, regularly sharpening or replacing blade edges is essential for effective operation.
- Battery: Batteries should be checked periodically for charge capacity and corrosion. Replacing old batteries can prevent starting issues.
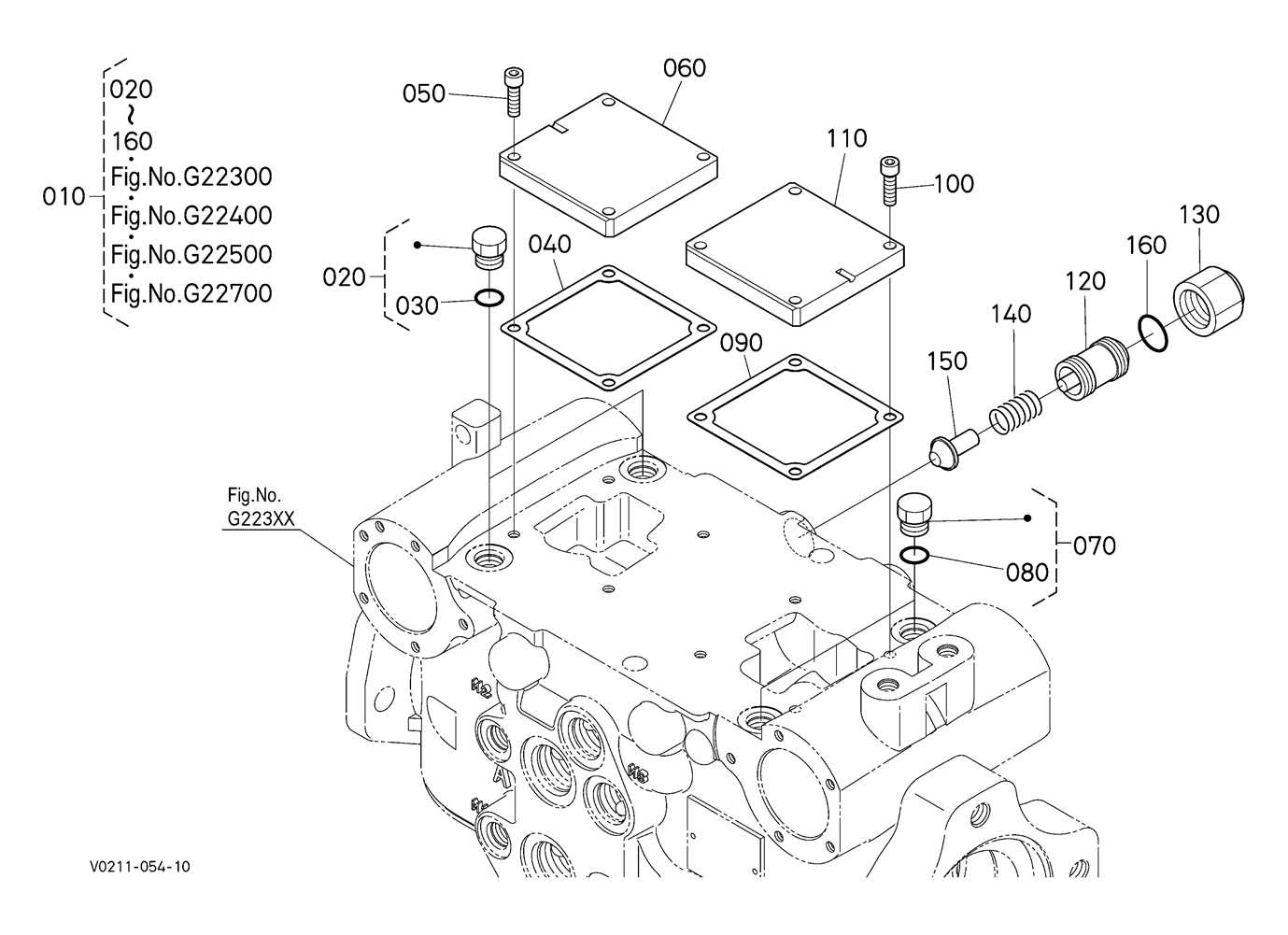
Hydraulic System Components Explanation
The hydraulic system is an essential part of modern machinery, ensuring smooth and efficient operation through the control of fluid pressure. Understanding the various elements that make up this system helps operators maintain and troubleshoot it effectively. These components work together to generate, regulate, and distribute hydraulic energy, which powers various mechanical functions.
Main Elements of the Hydraulic System
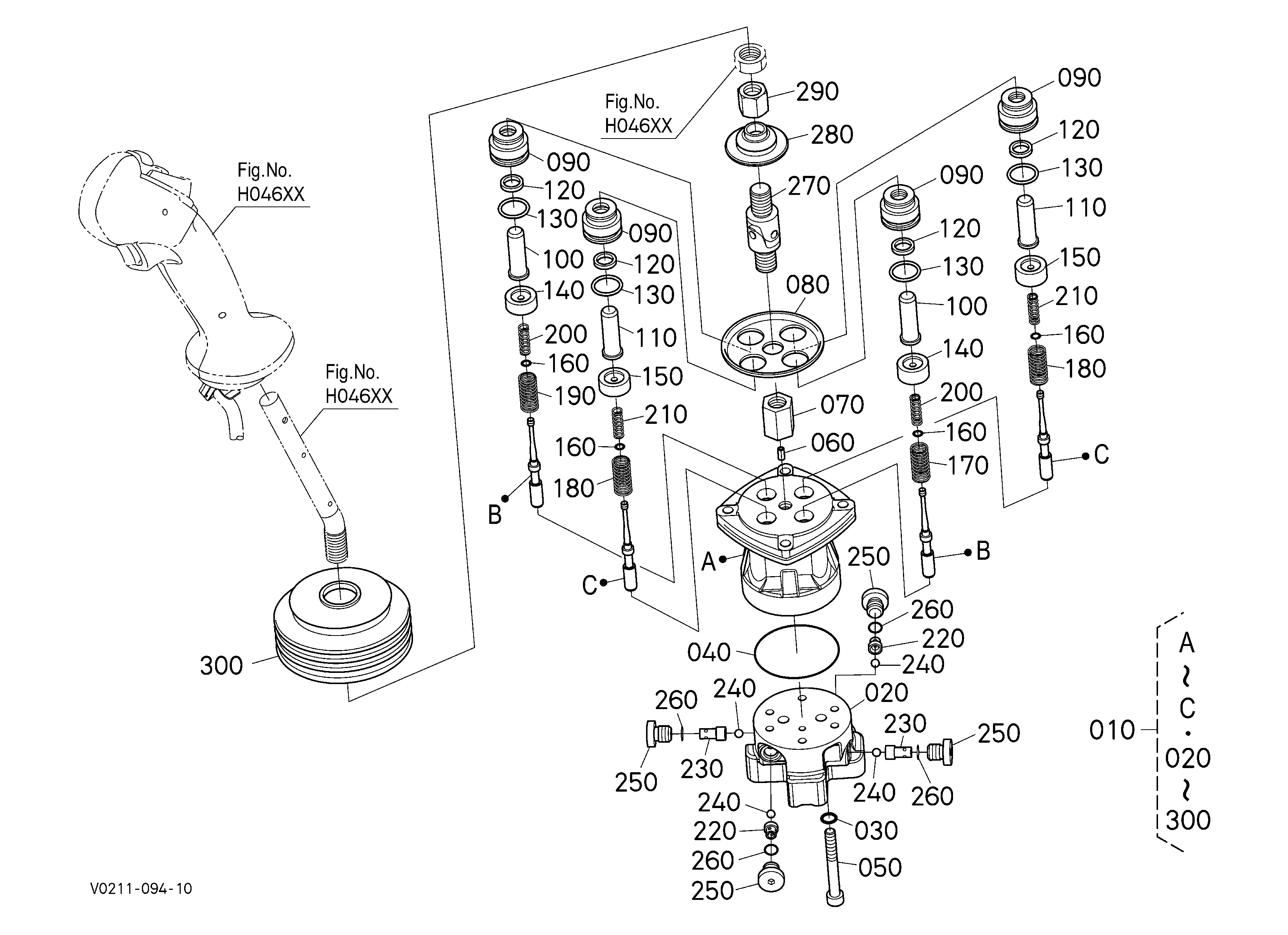
The core components include pumps, valves, cylinders, and motors. The pump is responsible for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, pushing the fluid through the system. Valves manage the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring that it reaches the right components at the right time. Cylinders convert the hydraulic energy into mechanical force, allowing movement, while motors drive rotational motion for various functions.
Additional System Elements
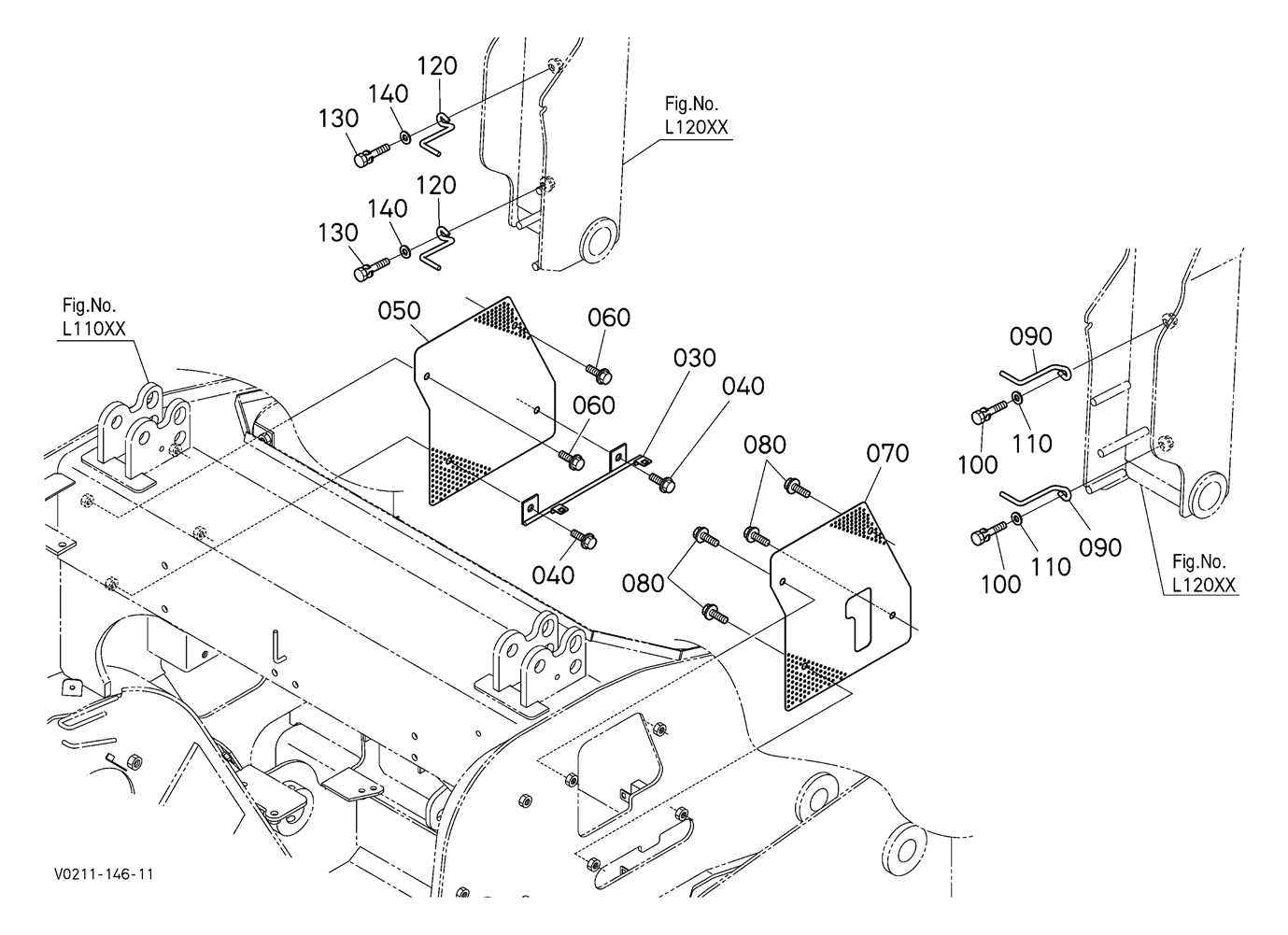
Track and Undercarriage Detailed Diagram
The track system and undercarriage play a crucial role in the operation and stability of compact machines. Understanding the structure of these components ensures smoother handling, reduced wear, and better performance. A well-maintained undercarriage contributes to extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
Track System Overview: The track system includes multiple elements that work together to provide traction and support, even on challenging terrains. From tension adjusters to track rollers, each component has its own function in ensuring mobility.
Undercarriage Key Components: The undercarriage consists of various mechanical parts that interact to absorb impact and provide a stable base. These include the track frame, rollers, and the idler, which together support the machine’s weight and ensure smooth movement.
Cab Interior Parts and Functions
The operator’s cabin is designed for comfort, efficiency, and control. Inside, key elements contribute to a seamless working experience, ensuring that all necessary features are easily accessible and simple to operate. The arrangement of controls, instruments, and seating is optimized to provide maximum functionality without sacrificing operator comfort.
Primary controls include levers, pedals, and buttons for managing various machine operations. These components are positioned strategically to reduce fatigue during long work hours. The seat is adjustable, providing ergonomic support, while the dashboard features indicators and gauges that allow the operator to monitor performance effortlessly.
Additional elements, such as ventilation systems, lighting, and storage compartments, are also essential for maintaining a pleasant working environment. These features are designed with practicality in mind, ensuring that everything within the cabin serves a clear purpose to enhance both comfort and efficiency during operation.
Cooling System Structure and Parts
The cooling system is an essential component of any machinery, ensuring optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. This system comprises various elements that work together to maintain the ideal thermal conditions, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.
At the core of the cooling mechanism is the radiator, which facilitates heat exchange by transferring excess heat from the engine coolant to the surrounding air. This process is vital for maintaining the engine’s efficiency and preventing damage due to extreme temperatures.
The water pump plays a crucial role by circulating the coolant throughout the system. By ensuring a constant flow, it helps regulate temperatures and allows for efficient heat dissipation. Additionally, thermostats are integrated to monitor and control the coolant temperature, enabling the system to respond dynamically to varying operational conditions.
Hoses and connectors facilitate the movement of coolant between different parts, ensuring that all components receive the necessary thermal management. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are vital for the system’s reliability and effectiveness.
In summary, understanding the structure and function of the cooling system is essential for maintaining machinery performance. By ensuring all components work harmoniously, operators can prevent overheating and enhance the durability of the equipment.
Electrical System Overview and Key Elements
The electrical system plays a crucial role in the functionality and efficiency of modern machinery. Understanding the components and their interactions is essential for optimal performance and maintenance. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental aspects of the electrical setup and highlights key elements that contribute to its effectiveness.
Key components of an electrical system include:
In addition to these components, understanding the layout and integration of the electrical system is vital. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements can prevent issues and enhance the longevity of the machinery.
Fuel System Components and Layout
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of heavy machinery. It is designed to store, filter, and deliver fuel to the engine, allowing for optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the layout and individual components of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components of the Fuel System
Layout Considerations
In a well-designed fuel system, components are strategically arranged to facilitate easy access for maintenance and repairs. Proper routing of fuel lines minimizes the risk of leaks and ensures optimal flow rates. Additionally, the placement of filters and pumps should allow for straightforward inspection and replacement, enhancing the overall reliability of the system.
Control Panel Components and Their Roles
The control panel is an essential part of any machinery, serving as the interface between the operator and the various functions of the equipment. Understanding the different elements within this assembly is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality and user experience.
Displays are vital for providing real-time information about the machine’s status, including performance metrics and alerts. These visual indicators help operators monitor essential parameters effectively.
Switches facilitate manual control over various functions, allowing the operator to activate or deactivate specific systems as needed. This hands-on approach ensures quick adjustments during operation.
Knobs and Dials are designed for fine-tuning settings, offering a tactile means to adjust performance levels. Their ergonomic design enhances user experience by allowing precise control.
Indicators inform the operator of critical conditions, such as low fuel or maintenance requirements. By providing immediate feedback, they help in preventing operational issues and ensuring safety.
Understanding these components and their respective functions empowers users to operate the machinery effectively, enhancing productivity and longevity.
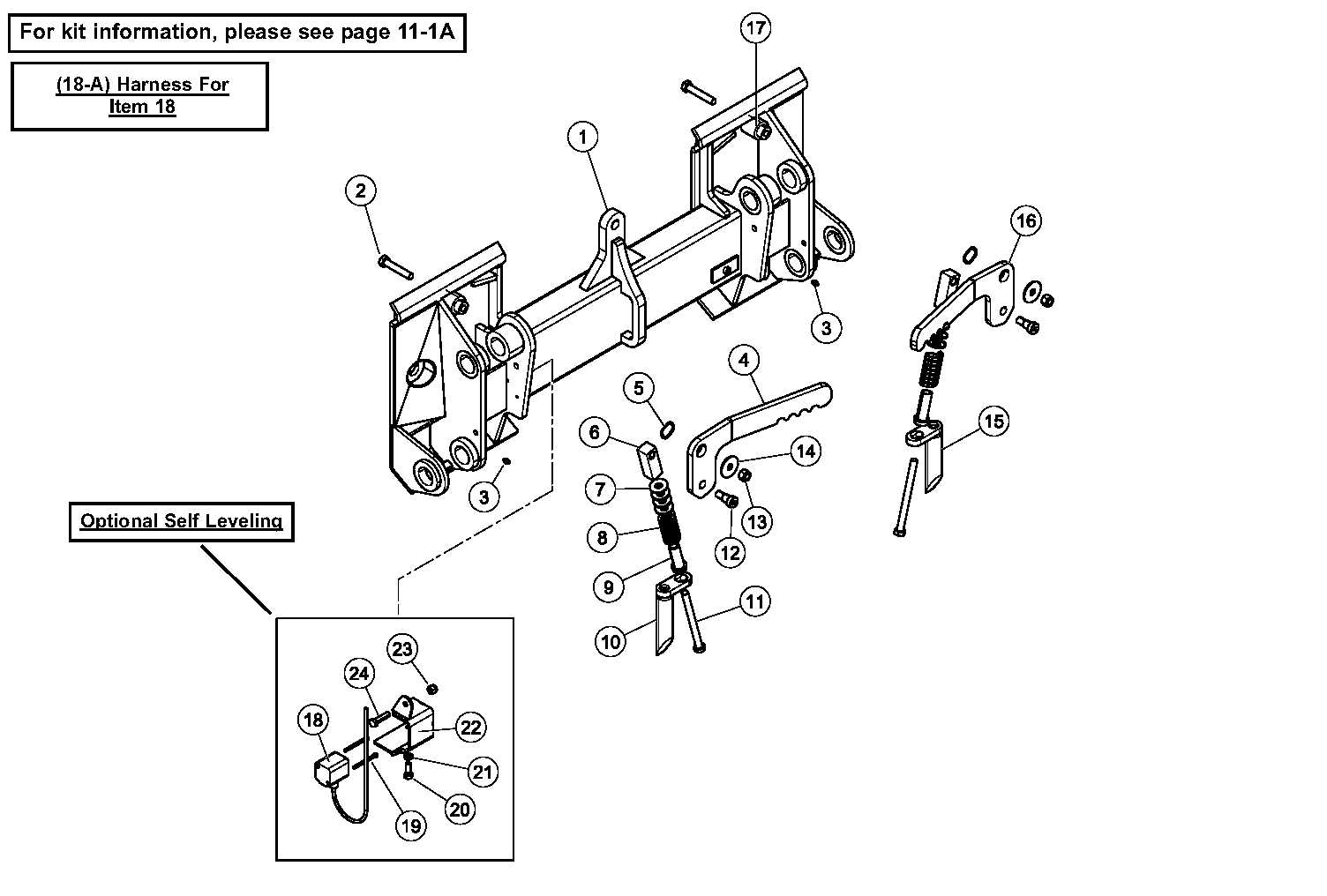
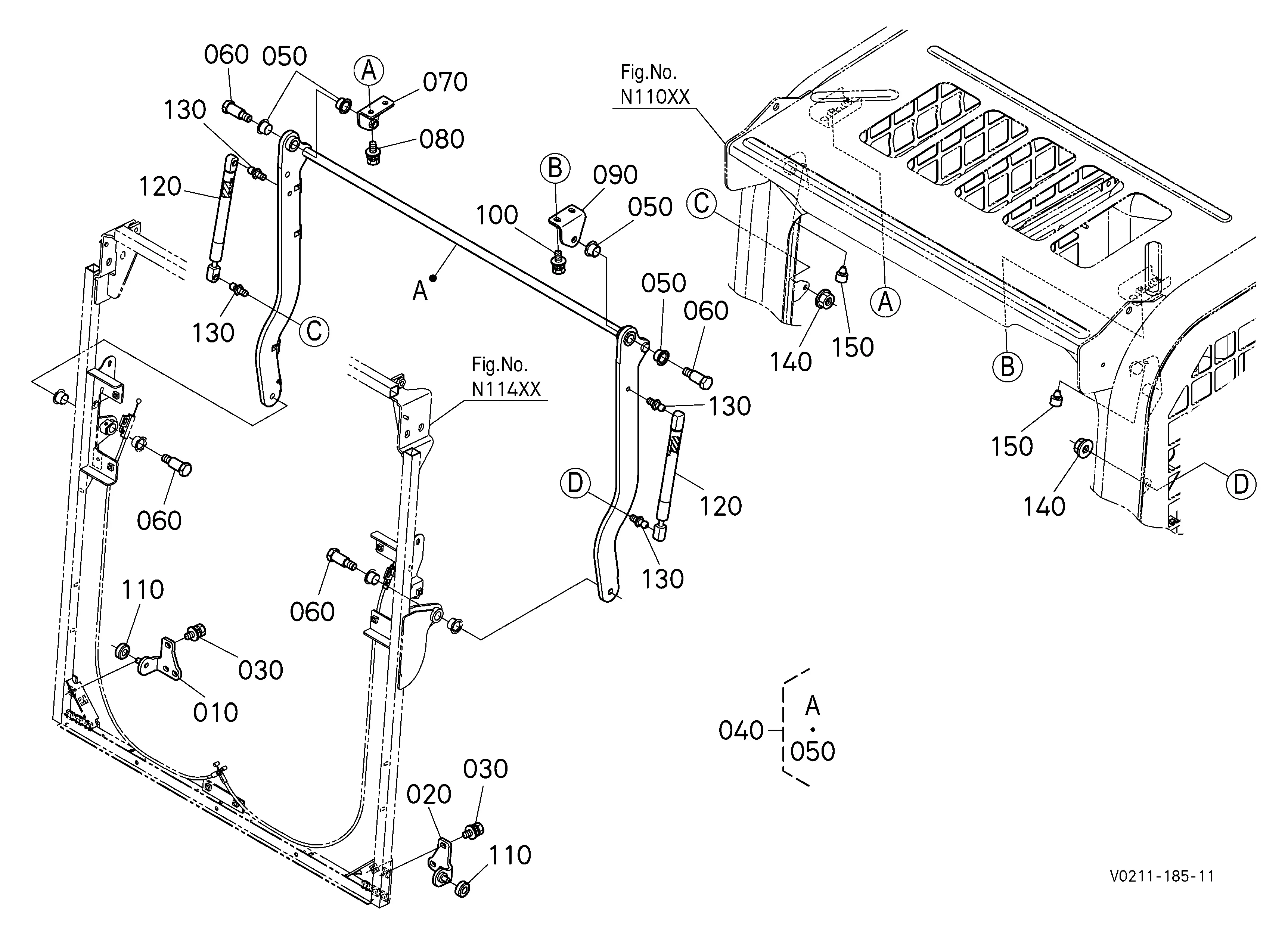
Loader Arms and Linkage Parts Description
The loader arms and their associated linkage components play a crucial role in the overall functionality of compact machinery. These elements are designed to enhance the lifting capacity and maneuverability, allowing for efficient operation in various tasks such as digging, lifting, and transporting materials. Understanding the structure and arrangement of these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Functionality of Loader Arms
Loader arms are pivotal in connecting the vehicle to the attachment implements. Their robust construction ensures that heavy loads can be lifted and transported safely. The design often includes a range of motion that enables operators to reach various heights and angles, maximizing efficiency during operation.
Linkage Mechanisms
The linkage systems facilitate the movement between the loader arms and the main body of the machine. These mechanisms are composed of several joints and pivot points that allow for smooth articulation. Regular inspection of these components is vital to prevent wear and ensure seamless operation, ultimately contributing to the longevity of the equipment.
Maintenance Parts and Replacement Guide
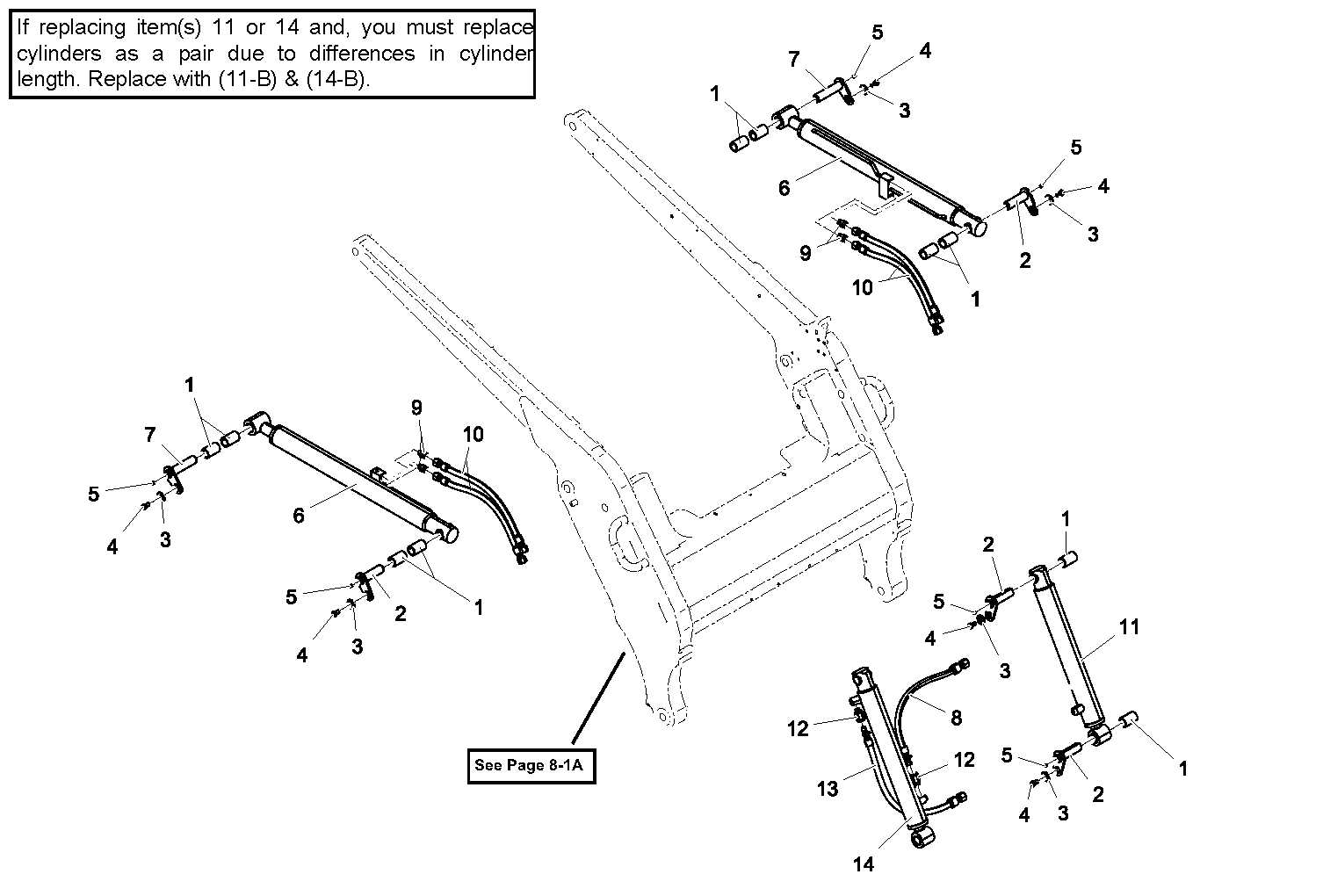
This section provides essential information regarding the upkeep and replacement components necessary for optimal performance of machinery. Understanding which elements require regular attention can significantly enhance longevity and efficiency.
Regular maintenance involves inspecting various elements, such as filters, belts, and fluids, to ensure they are functioning correctly. Timely replacement of worn or damaged components helps prevent breakdowns and costly repairs.
It is crucial to refer to the equipment’s manual for specific maintenance schedules and recommended replacement intervals. Utilizing high-quality components that meet the manufacturer’s specifications is vital for maintaining operational integrity.
In addition to routine inspections, keeping an inventory of commonly used replacement items can streamline the maintenance process. This proactive approach reduces downtime and ensures the machinery remains in peak condition.
Common Wear Items and Suggested Replacements
In any machinery, certain components are prone to wear and tear due to regular usage and exposure to varying conditions. Identifying these items and replacing them proactively can enhance performance and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Below are some commonly affected parts along with recommendations for replacements.
By routinely monitoring these items and addressing replacements as needed, users can ensure smoother operation and mitigate the risk of more significant breakdowns.