The efficient operation of a high-performance engine depends on the seamless integration of various mechanical and electrical components. Understanding how each part contributes to the overall functioning is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. In this section, we delve into the intricate details of the engine’s design, offering insights into the role of each piece within the system.
Systematic analysis of engine configurations helps in diagnosing potential issues and optimizing functionality. By carefully studying the layout and connections of each part, enthusiasts and professionals can achieve a deeper understanding of how these elements interact to produce power and efficiency. The exploration of these components reveals key factors that contribute to an engine’s durability and reliability.
Component identification and function are essential for anyone working on engine repair or maintenance. Whether you’re troubleshooting performance issues or planning upgrades, having a clear overview of the structure enables more effective decision-making. This comprehensive guide will help you familiarize yourself with the key components that ensure smooth operation and longevity.
Overview of Mercury Optimax 150
This engine is designed to deliver high performance and reliability, making it an ideal choice for boating enthusiasts. With its innovative technology and engineering, it offers a balance of power, fuel efficiency, and durability. The unit is built to withstand various water conditions, providing smooth operation for both recreational and professional users.
The advanced features include an efficient fuel delivery system, ensuring optimal engine performance and reduced emissions. Its robust construction ensures longevity, even under demanding conditions. Whether for speed or fuel economy, this engine excels in meeting diverse boating needs, providing a seamless experience on the water.
Key Components of the Engine
The internal mechanisms of a marine propulsion system are comprised of several vital elements that work together to ensure efficient performance and reliability. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall function, with specific parts handling different processes, from fuel intake to exhaust expulsion. Understanding these fundamental units allows for proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring longevity and optimal functionality of the engine.
The core of the engine is the power unit, responsible for generating the energy needed to drive the propeller. It works in conjunction with the fuel system, which regulates the flow and mixture of fuel for combustion. The ignition system is another critical element, providing the necessary spark to ignite the fuel, while the cooling system ensures that the engine does not overheat during operation.
A well-maintained exhaust system is essential for efficient expulsion of gases, while the lubrication system minimizes wear and tear by reducing friction between moving parts. The electrical system provides power to essential components such as sensors and controls. Each of these parts must function in harmony to deliver the power and performance expected from a high-quality engine.
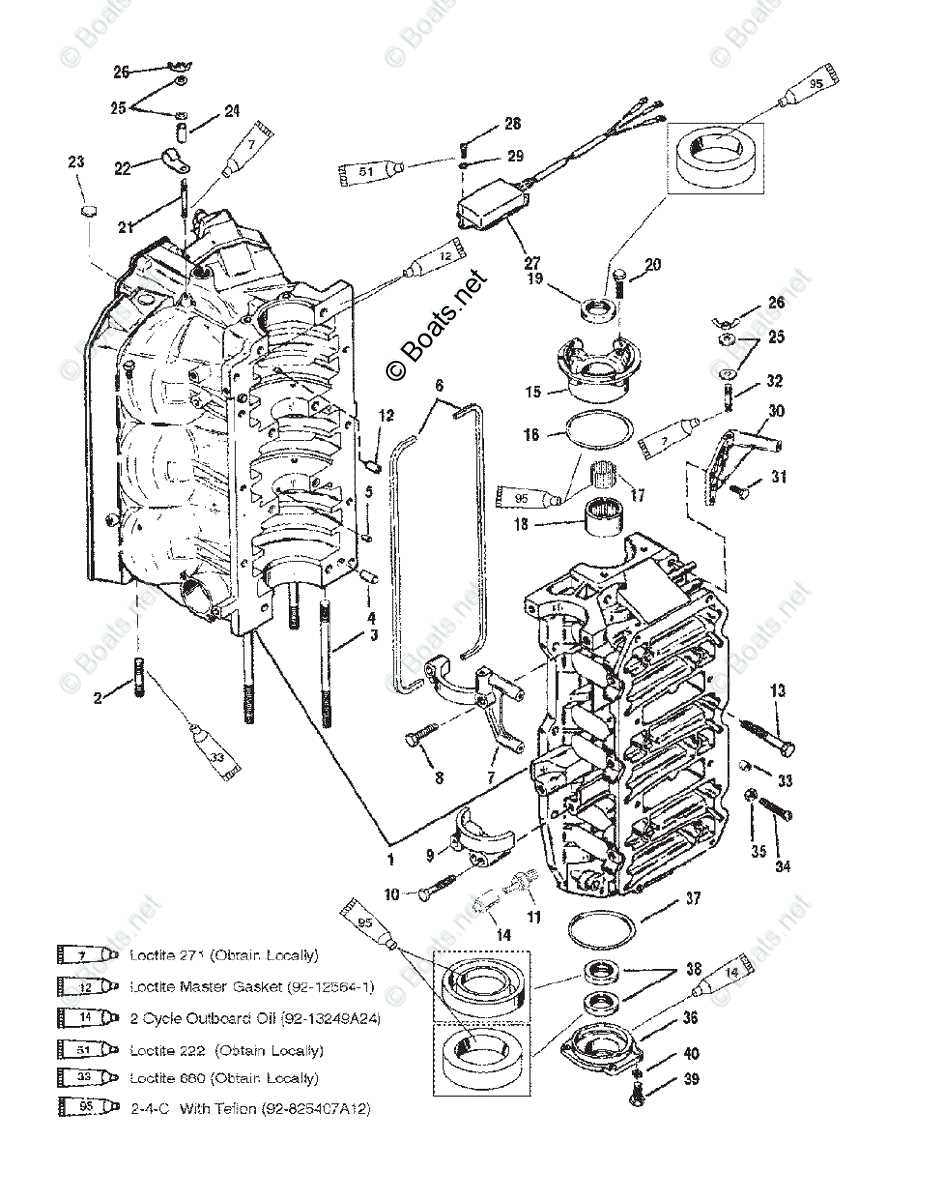
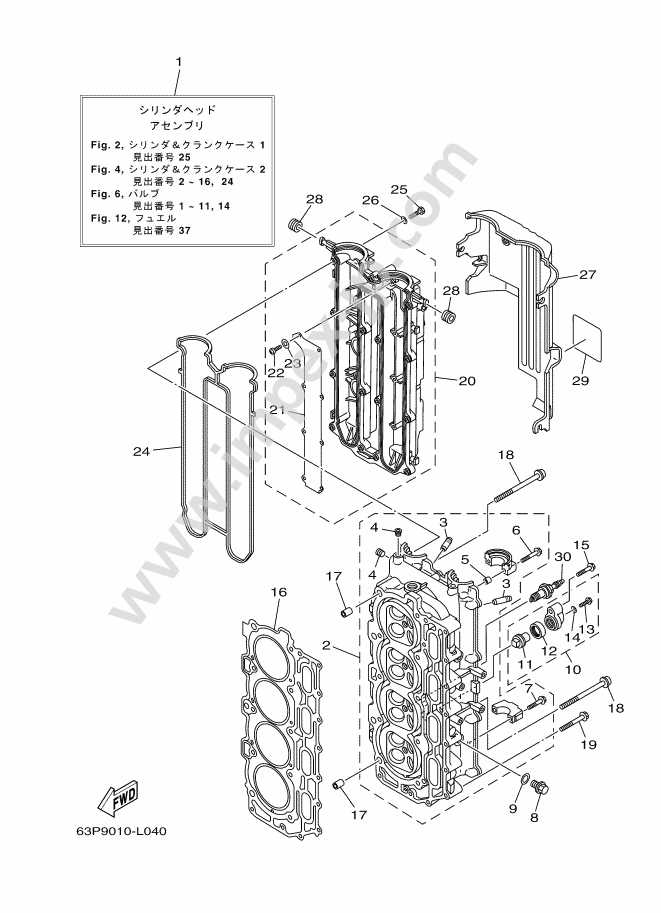
Understanding the Powerhead Assembly
The powerhead is a critical component of marine engine systems, housing several essential elements that contribute to overall engine performance. It serves as the central unit, integrating the core mechanisms that drive the boat’s movement. The structure is designed to support high levels of operation and withstand various environmental stresses. Key elements within this assembly are strategically placed to ensure efficient functioning and optimal performance over extended periods.
This section explores the key components within the powerhead, explaining their roles and interactions. It will also delve into the importance of maintaining these components for reliable engine function, highlighting common issues and troubleshooting practices.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | The main structure of the powerhead, housing the cylinders and other critical components like pistons and connecting rods. |
| Crankshaft | Transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion to drive the propeller. |
| Cylinder Head | Seals the top of the cylinder, containing vital parts such as valves and camshaft for air intake and exhaust control. |
| Water Pump | Circulates cooling water to prevent the engine from overheating during operation. |
| Fuel System | Delivers the fuel-air mixture into the cylinders, crucial for combustion and engine power. |
| Exhaust System | Manages the expulsion of exhaust gases, ensuring optimal performance and emissions control. |
Understanding the assembly’s design is key for anyone looking to enhance engine longevity and performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to avoid unexpected failures and ensure the system operates smoothly under various conditions.
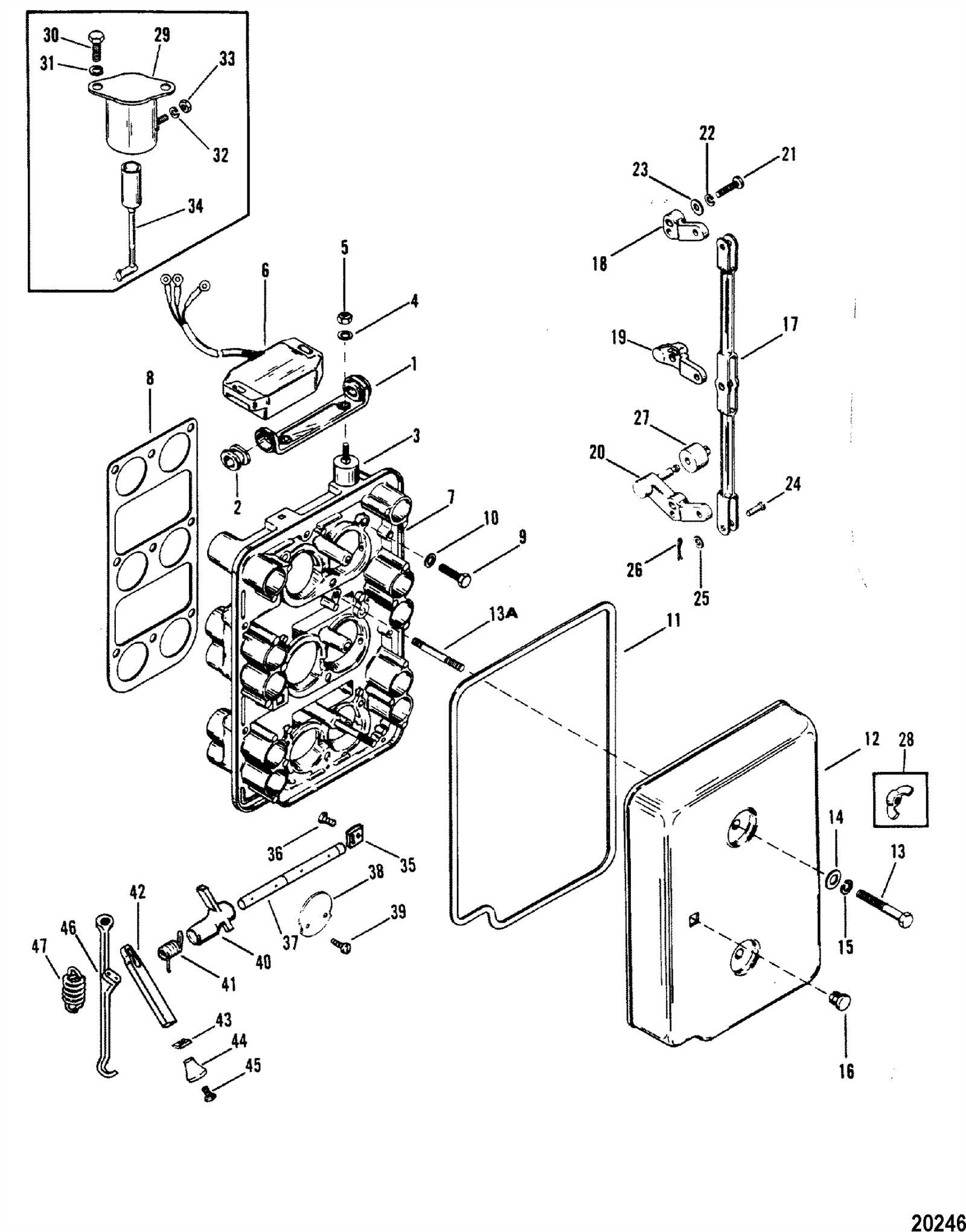
Fuel System and Fuel Components
Efficient fuel delivery is crucial for the optimal performance of marine engines. The components responsible for ensuring smooth fuel flow are designed to maintain engine stability, reliability, and longevity. Each part plays a specific role in regulating fuel intake, filtration, and distribution to ensure the engine operates at its peak efficiency.
Key Elements of the Fuel Delivery System
- Fuel Pump: This component is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. It maintains consistent pressure to ensure proper fuel flow.
- Fuel Injectors: These precision devices inject fuel into the combustion chamber at the right time and in the correct quantity, optimizing fuel combustion.
- Fuel Filter: A critical part that removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine, preventing blockages and ensuring clean fuel delivery.
- Fuel Tank: The container that stores fuel before it is sent to the engine. It must be kept clean and properly sealed to avoid contamination.
- Fuel Lines: These are the pathways that transport fuel from the tank to the engine components, often requiring regular maintenance to avoid cracks or leaks.
Maintaining Fuel System Integrity
Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system are essential for ensuring engine performance and preventing costly repairs. It’s important to check the fuel filters and lines for wear, as well as monitor the fuel pump’s pressure levels. Additionally, ensuring that the fuel is free from contaminants will prolong the life of the engine and improve overall efficiency.
Ignition System Parts Breakdown
The ignition mechanism is a crucial part of the engine’s functionality, responsible for starting the power generation process. This section delves into the various components that work together to ensure a seamless spark creation and distribution, fueling the engine’s performance. Understanding these components is key to both diagnosing issues and performing necessary repairs to maintain optimal engine operation.
Key Components of the Ignition System
At the heart of the system lies the spark plug, which ignites the fuel mixture by generating a high-voltage spark. The ignition coil plays an equally important role, converting low-voltage electricity into the necessary high-voltage needed to power the spark plug. Additionally, the flywheel serves as the mechanical drive that assists in timing the ignition cycle, working in tandem with the stator to produce electrical power for the system.
Timing and Control
The ignition system is highly dependent on precise timing, which is regulated by the control module. This module receives input from various sensors, ensuring that the ignition occurs at exactly the right moment. A malfunction in any of these components can result in improper timing, leading to performance issues such as misfires or inefficient combustion.
Exploring the Exhaust and Cooling System
The exhaust and cooling mechanisms of an engine are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage. These systems work in tandem to regulate the temperature and manage the expulsion of gases produced during operation. Understanding their design and functionality is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The exhaust system is responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine, ensuring that they do not interfere with its operation. It consists of various components, such as the manifold and the muffler, which help in reducing noise and controlling emissions. Proper functioning of this system is vital to the overall health of the engine.
Cooling components play an equally important role by preventing the engine from overheating. This system utilizes water and air to dissipate excess heat, with key elements like thermostats, water pumps, and heat exchangers managing the flow and distribution of coolant. A failure in any of these parts can lead to a significant drop in performance or even cause engine failure.
Both of these systems need regular inspection and maintenance to ensure that all components are working together seamlessly. Whether it’s replacing worn-out seals or flushing out old coolant, keeping these systems in top condition is essential for long-term engine reliability.
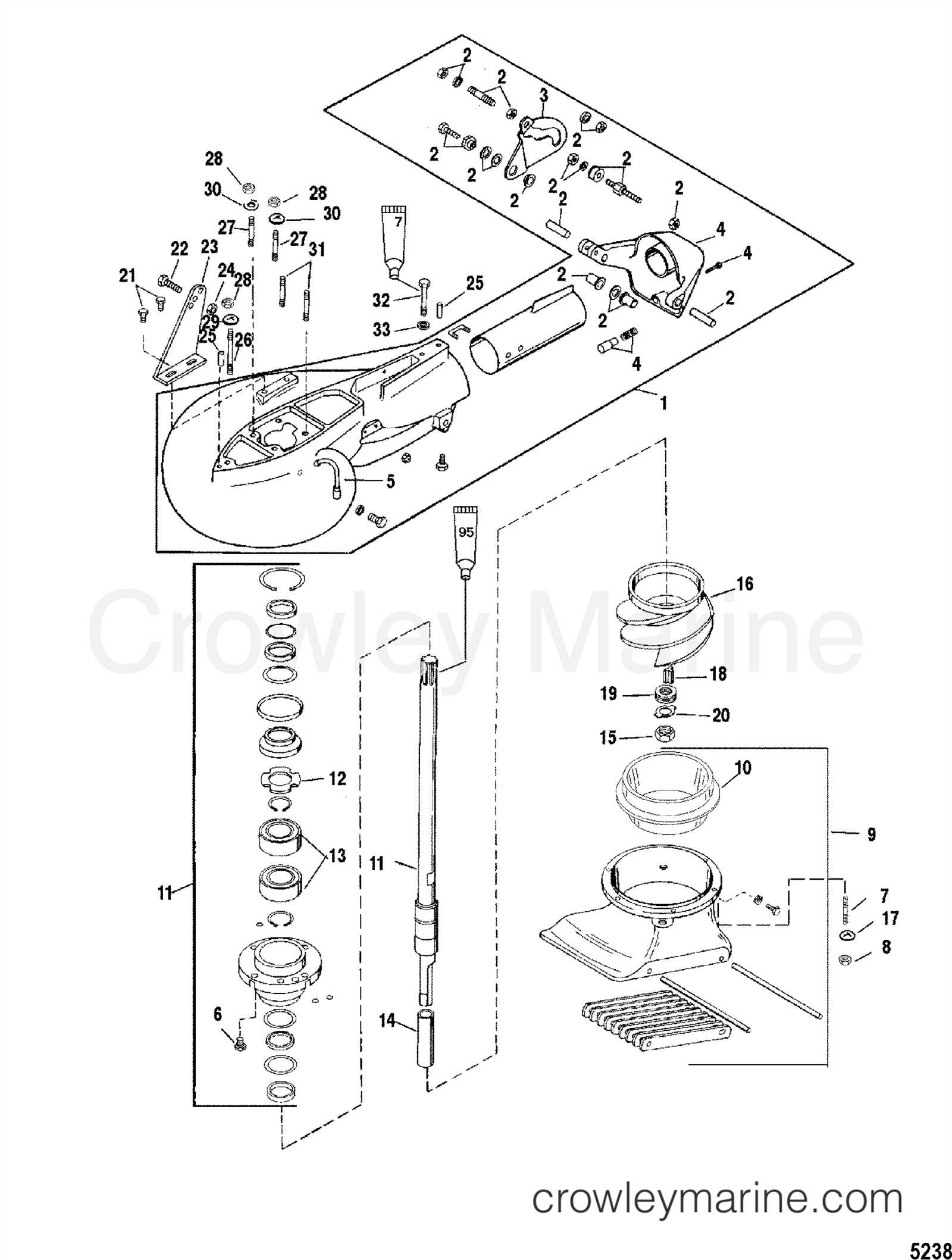
Internal Parts of the Lower Unit
The lower unit of a marine engine is a crucial component that houses various mechanisms responsible for transferring power from the engine to the propeller. It contains several essential parts that work in unison to ensure smooth operation and efficiency. These components are strategically placed to optimize performance and protect the engine from wear and tear, especially in harsh aquatic environments.
Key Components
The internal components of the lower unit include the gear assembly, shaft, bearings, and seals. These parts are designed to withstand high torque and pressure while maintaining reliability under continuous use. Proper maintenance of these elements is vital for extending the lifespan of the unit and preventing potential failures.
Functionality and Maintenance
Each part within the lower unit serves a distinct role in maintaining the engine’s performance. The gear assembly is responsible for transmitting power, while the shaft connects the internal systems to the propeller. Regular inspection and lubrication are necessary to ensure these parts are functioning optimally, preventing damage and maintaining smooth operation on the water.
Transmission and Gearcase Overview
The system responsible for transferring power from the engine to the propeller is an integral part of any watercraft. It plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient movement by adjusting the gear ratio according to the vessel’s speed and load. This mechanism involves a series of interconnected components that work in unison to provide smooth and controlled propulsion, even under varying conditions.
Transmission systems in marine engines are designed to handle the demands of different water environments, ensuring that the power generated by the engine is optimally transferred. The primary function of the transmission is to shift the gears, allowing for both forward and reverse motion, as well as neutral positioning. These systems often include a clutch that engages or disengages the engine from the drive mechanism, providing smooth transitions and reducing strain on the engine.
The gearcase houses the gears that manage the rotation of the propeller. It is a critical component, often sealed to prevent water ingress while ensuring that the gears remain lubricated for smooth operation. Depending on the design, some gearcases incorporate multiple gear sets to handle various operating conditions, enabling the vessel to function optimally across a range of speeds and conditions. Regular maintenance of this system is essential for preserving its efficiency and extending the lifespan of the vessel’s propulsion system.
Hydraulic and Steering System Features
The hydraulic and steering components play a crucial role in the functionality and responsiveness of marine propulsion systems. These systems ensure smooth and precise control, offering an enhanced driving experience. The integration of hydraulic systems allows for effortless maneuvering, making it a key feature in modern watercraft design.
Hydraulic Pump and Steering Mechanism
The hydraulic pump is responsible for providing the necessary fluid pressure to enable efficient steering. It works by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, ensuring a consistent flow of fluid to the steering actuator. This setup reduces the physical effort needed to turn the wheel or helm, making the steering process more effortless.
- Provides smoother handling and greater precision.
- Minimizes manual effort required for steering adjustments.
- Reduces wear on mechanical steering components.
Steering Cylinder and Linkage
The steering cylinder is a vital element that allows the boat to change direction. It is connected to the helm through a series of hydraulic hoses and linkages, which enable the cylinder to move the rudder or drive system. The cylinder’s responsiveness is critical to the overall maneuverability of the vessel, ensuring swift turns and improved stability.
- Improves overall vessel stability and responsiveness.
- Ensures accurate control in various water conditions.
- Reduces the effort needed for sharp turns or high-speed navigation.
Electrical System Wiring and Connections
The electrical setup of a high-performance engine is a critical element for ensuring smooth operation. Proper wiring and secure connections are necessary to maintain functionality and prevent failures. The various components involved rely on accurate wiring for communication and power transmission, ensuring the system works efficiently across a wide range of conditions.
Wiring layout plays a vital role in the overall system’s stability, providing the necessary connections for sensors, ignition systems, and power management. A well-organized wiring structure allows easy identification of components for maintenance or troubleshooting, minimizing the risk of errors. Incorrect or loose connections can lead to malfunctions, affecting the performance and reliability of the engine.
The system is designed to withstand harsh conditions, with robust insulation and protection measures to prevent damage from water, vibrations, and extreme temperatures. Understanding the connection types and their placements can significantly improve the efficiency of repairs or upgrades. Each connection has a specific function, ensuring the system operates at peak performance when required.
Routine Maintenance and Component Care
Regular upkeep and proper handling of each system element are essential to maintaining peak performance. By adhering to scheduled inspections and addressing minor issues before they become major problems, owners can ensure the longevity and efficiency of their equipment. This process involves more than just cleaning; it requires careful attention to the small parts and mechanisms that contribute to overall function.
To achieve optimal reliability, routine procedures should focus on key areas such as:
- Fluid levels and quality control
- Inspection of seals and gaskets
- Cleaning of air and fuel systems
- Examination of electrical connections
- Verification of moving components for wear and tear
Each component must be carefully evaluated for signs of stress or damage, with particular attention given to areas that undergo frequent operation. Regular lubrication and timely replacement of worn-out parts are fundamental steps in keeping everything functioning smoothly.
Troubleshooting Common Engine Issues
When experiencing engine difficulties, understanding the common problems that arise can significantly streamline the diagnostic process. Identifying symptoms early on allows for quicker resolutions and more efficient repairs. From performance loss to starting issues, knowing where to focus attention is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Engine Not Starting: If the engine fails to start, it could be due to fuel delivery issues, electrical malfunctions, or a worn-out starter motor. Check the fuel system for blockages or leaks and ensure the battery is fully charged. Additionally, inspect the ignition system to confirm proper spark generation.
Overheating: Overheating is a common issue, often caused by insufficient coolant flow or a clogged cooling system. Inspect the radiator, hoses, and water pump for any signs of leaks or damage. Ensure the thermostat is functioning correctly and replace it if necessary.
Unstable Idling: An erratic idle could be a sign of dirty fuel injectors, air intake problems, or issues with the idle control valve. Cleaning or replacing the fuel injectors and inspecting the air intake system for blockages or leaks may resolve this issue.
Power Loss: If there is a noticeable decrease in engine power, it could indicate a clogged air filter, faulty spark plugs, or a problem with the fuel system. Inspecting and replacing the air filter, spark plugs, and checking fuel pressure can help restore normal power levels.
By addressing these common issues promptly, engine performance can be maintained at its peak, ensuring longevity and reliability.