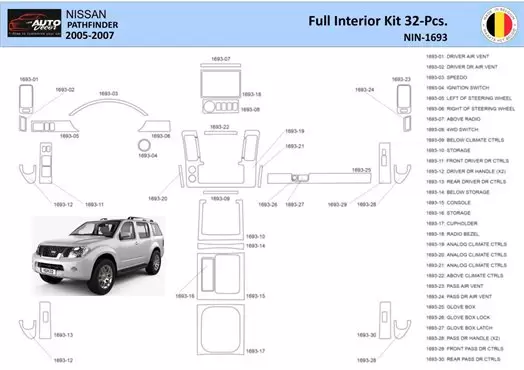
The intricate assembly of any off-road vehicle is crucial for its performance and longevity. A comprehensive overview of the various elements involved reveals how each component plays a significant role in the overall functionality. Familiarizing oneself with these elements enhances the understanding of the vehicle’s design and operational capabilities.
Visual aids are invaluable tools in grasping the configuration of these essential parts. By examining a detailed schematic, one can gain insights into the connections and interactions between different sections. This knowledge not only assists in maintenance and repairs but also empowers enthusiasts to make informed decisions regarding upgrades and modifications.
In essence, understanding the arrangement of these components is vital for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of off-road vehicles. Whether for routine upkeep or more extensive modifications, this foundational insight can significantly enhance one’s experience with their 4×4.
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of the essential components that constitute a specific vehicle model. Knowledge of these elements is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and modifications, enabling vehicle owners to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Key Components
- Engine Assembly
- Transmission Unit
- Suspension System
- Brake Mechanism
- Electrical System
Importance of Understanding Components
Recognizing the various elements of a vehicle enhances troubleshooting capabilities and supports informed decision-making during repairs. Furthermore, this knowledge aids in identifying compatible accessories and upgrades to improve functionality and aesthetics.
Understanding the Parts Diagram Layout
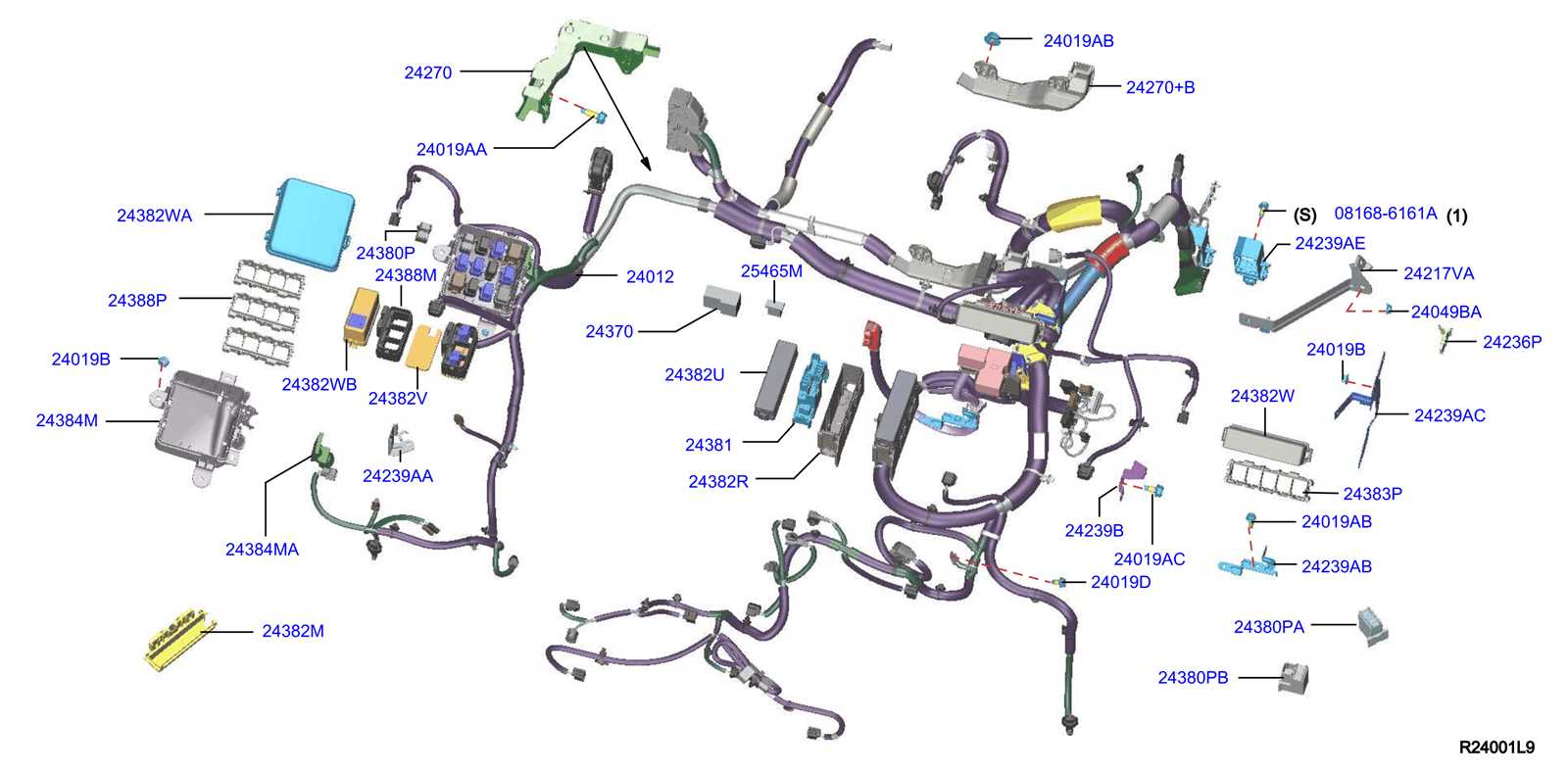
The layout of a component schematic serves as a visual guide to the various elements within a mechanical assembly. It simplifies the process of identifying each part and its corresponding placement within the system. By familiarizing oneself with this layout, one can better understand the relationships between different components and their functions.
Typically, these schematics are organized in a clear and logical manner, allowing for easy navigation and comprehension. Each section is labeled meticulously, indicating specific groups of components that work together. Utilizing distinct colors and shapes helps in distinguishing between different types of elements, making the overall interpretation more intuitive.
Understanding how to read these schematics is essential for maintenance and repairs. It enables individuals to locate parts quickly, assess their condition, and determine the necessary actions for replacement or servicing. Therefore, mastering the layout of a component schematic is invaluable for anyone involved in mechanical work.
Common Components of the Pathfinder
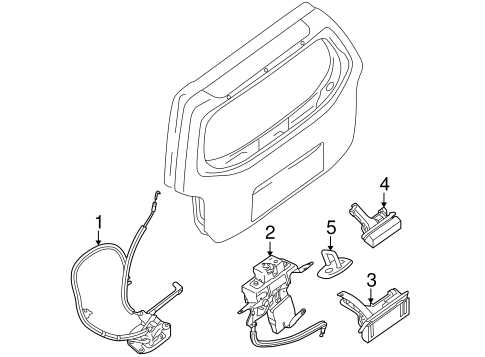
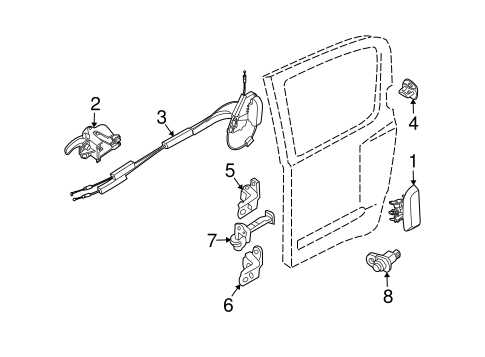
This section provides an overview of the essential elements found in the vehicle, highlighting their significance and functionality. Understanding these components can aid in maintenance, repairs, and overall vehicle knowledge.
Key Elements
- Engine: The core power unit that drives the vehicle.
- Transmission: The mechanism that transmits power from the engine to the wheels.
- Suspension: The system that supports the vehicle’s weight and absorbs shocks from the road.
- Braking System: A crucial safety feature that slows down or stops the vehicle.
- Electrical System: Powers all electronic components and systems within the vehicle.
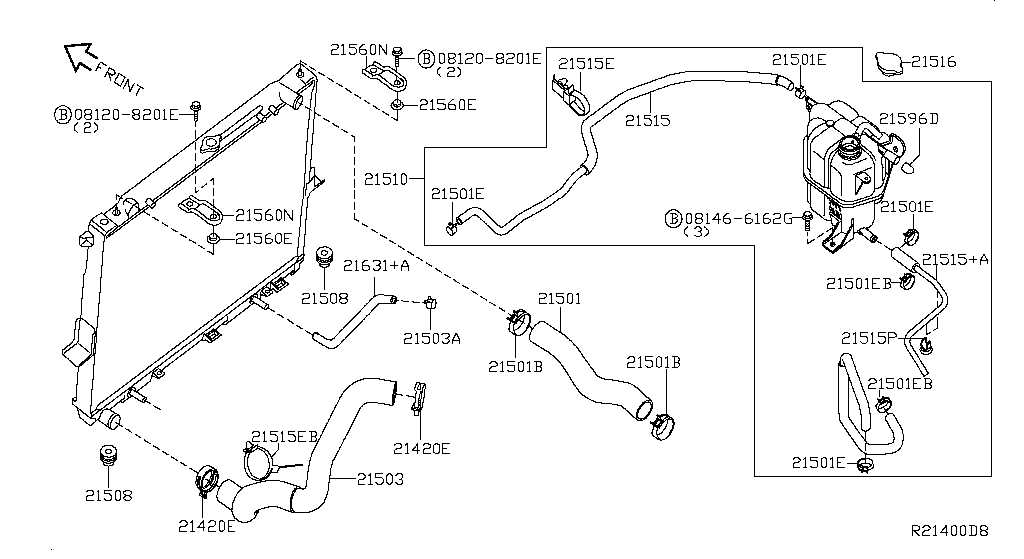
Additional Components
- Fuel System: Responsible for delivering fuel to the engine.
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal engine temperature to prevent overheating.
- Exhaust System: Reduces harmful emissions and noise produced by the engine.
- Steering Mechanism: Allows for control and direction of the vehicle.
Engine Assembly Breakdown Explained
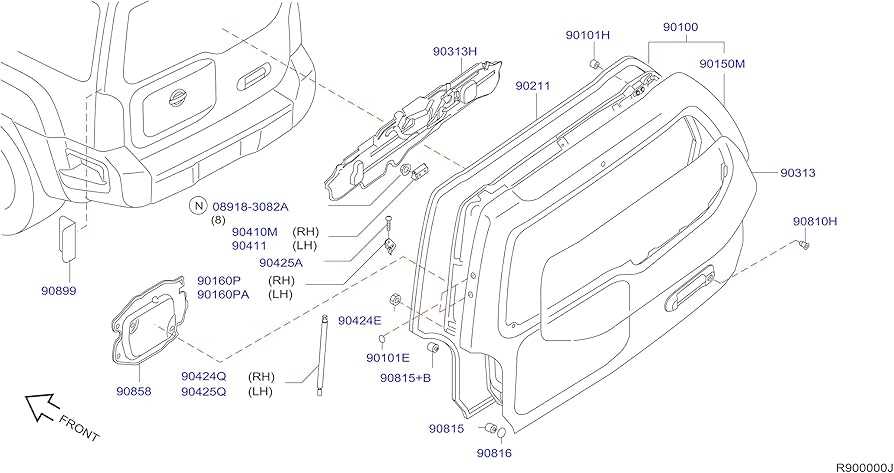
The intricate structure of an engine is essential for understanding how various components function together to produce power. This section will delve into the organization of key elements within the engine assembly, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Core Components: The main constituents include the cylinder block, cylinder head, and crankshaft. Each part is meticulously designed to perform specific tasks, such as housing combustion chambers and facilitating the conversion of linear motion into rotational energy.
Supporting Elements: Additional components like pistons, connecting rods, and timing belts play crucial roles in ensuring efficient operation. These parts must work in harmony to maintain the engine’s cycle and optimize performance.
Understanding the layout and function of each component is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. A comprehensive grasp of the engine assembly can aid in diagnosing issues and enhancing overall vehicle reliability.
Transmission System Parts Overview
The transmission system plays a vital role in the overall functionality of a vehicle, ensuring the efficient transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This complex assembly comprises various components that work in unison to enable smooth gear shifts and optimal performance. Understanding these elements can enhance maintenance practices and contribute to better vehicle longevity.
Key Components of the Transmission System

- Torque Converter: Facilitates the transfer of power from the engine by converting engine torque into hydraulic pressure.
- Transmission Fluid: Essential for lubrication, cooling, and ensuring smooth operation of the transmission.
- Gear Set: Comprises various gears that determine the vehicle’s speed and torque output.
- Valve Body: Acts as the control center, directing fluid to different components based on the transmission’s operation.
- Shifter Assembly: Enables the driver to select different gears, connecting the driver’s input with the transmission’s response.
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the transmission system is crucial for preserving its performance and extending its lifespan. Key practices include:
- Routine checks of transmission fluid levels and quality.
- Periodic inspection of the torque converter for signs of wear or damage.
- Regular assessment of the gear set to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
- Prompt attention to any unusual noises or shifting issues that may indicate problems.
By understanding the fundamental components and their functions, vehicle owners can take proactive steps to maintain their transmission systems effectively.
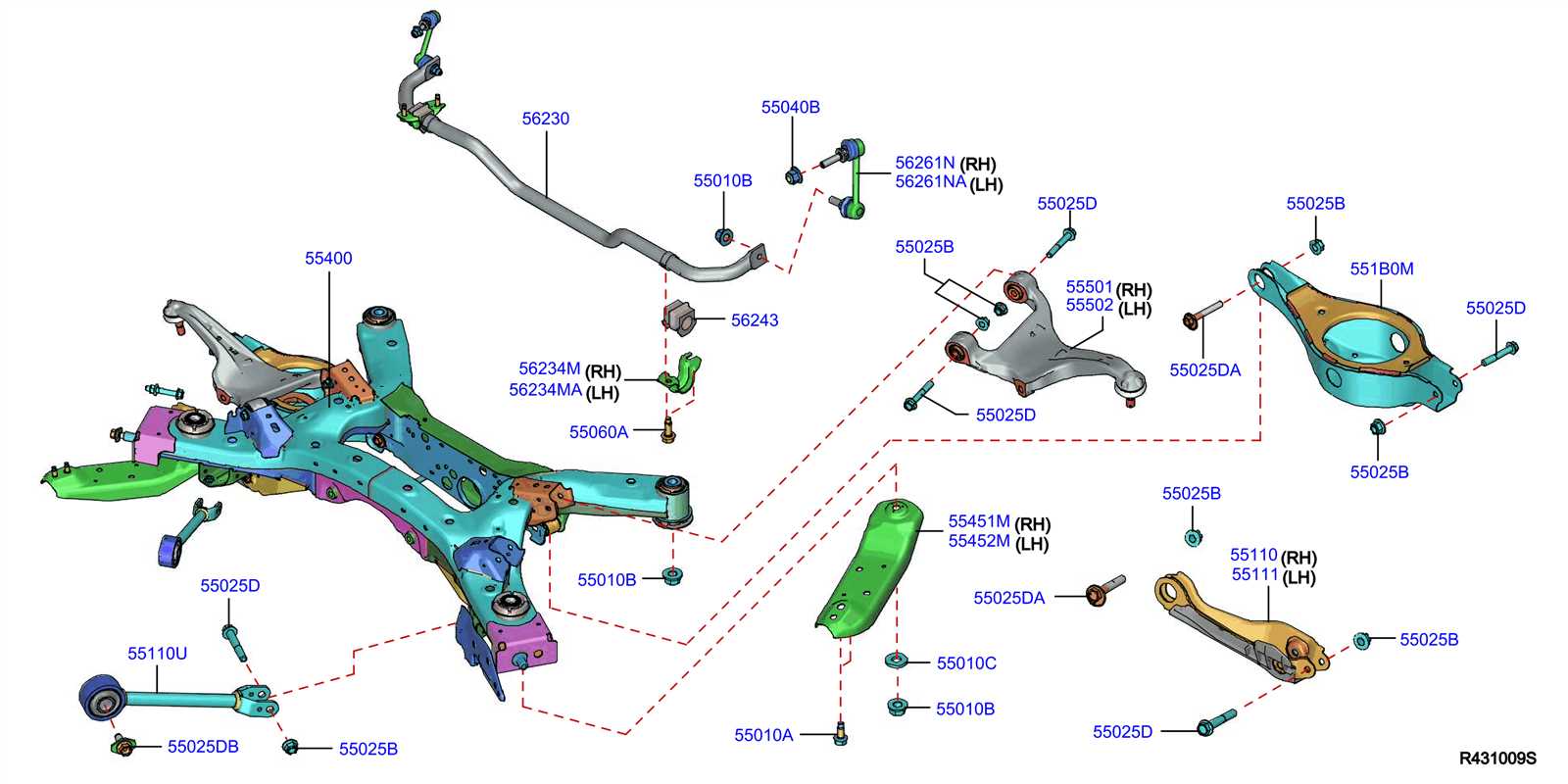
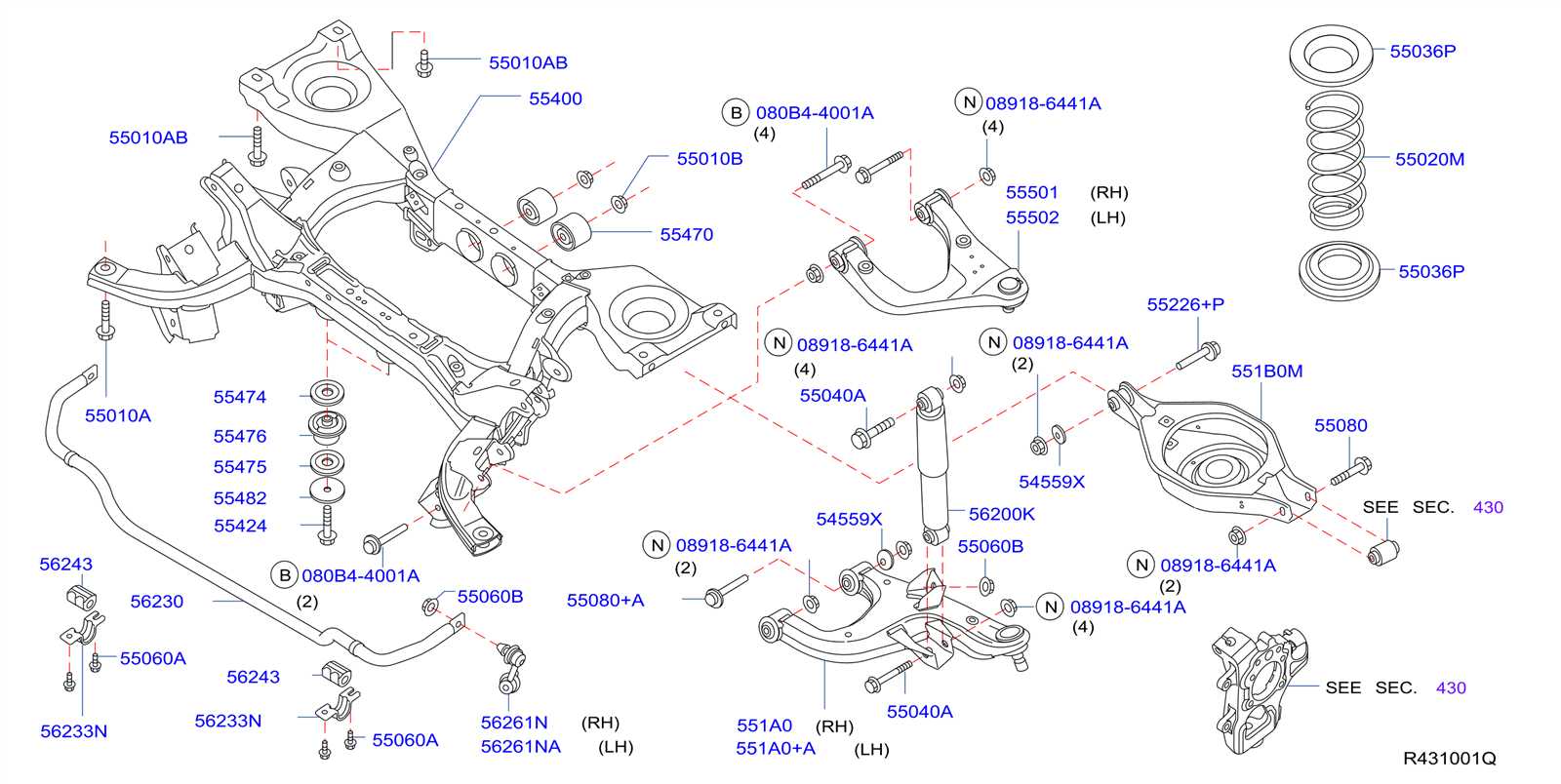
Suspension and Steering Elements
The suspension and steering systems play a crucial role in ensuring a vehicle’s stability, handling, and overall ride quality. These components work together to provide comfort to occupants while maintaining control during various driving conditions. Understanding the different elements involved in these systems can help in diagnosing issues and enhancing performance.
Key Components of the Suspension System
The suspension system consists of several vital parts that contribute to its functionality. These include shock absorbers, springs, control arms, and stabilizer bars. Each element is designed to absorb shocks from the road and maintain the vehicle’s alignment, which ultimately influences the driving experience.
Steering Mechanism Overview
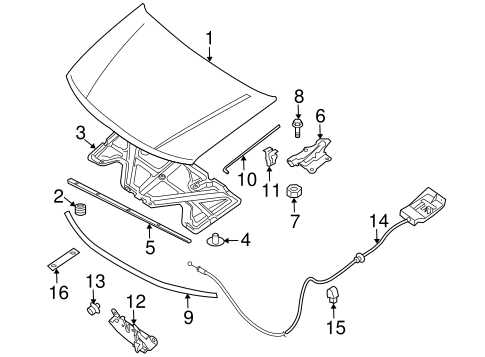
The steering mechanism is essential for maneuvering the vehicle. It comprises components such as the steering wheel, rack and pinion, and tie rods. This system allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle effectively, ensuring precision and responsiveness during turns and lane changes.
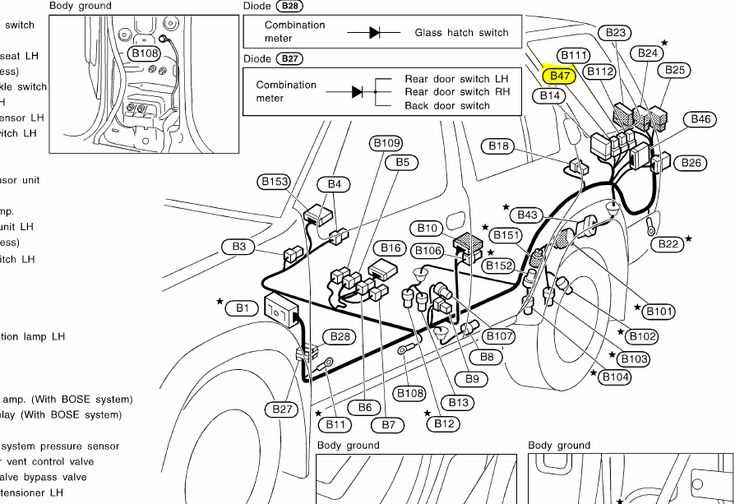
Electrical System Components Listed
This section provides an overview of the essential components that constitute the electrical framework of the vehicle. Understanding these elements is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting of the system.
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter Motor
- Fuse Box
- Relays
- Wiring Harness
- Ignition Switch
- Headlight Assembly
- Taillight Assembly
- Instrument Cluster
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the vehicle’s electrical system, ensuring reliable operation of essential features such as lighting, starting, and power distribution.
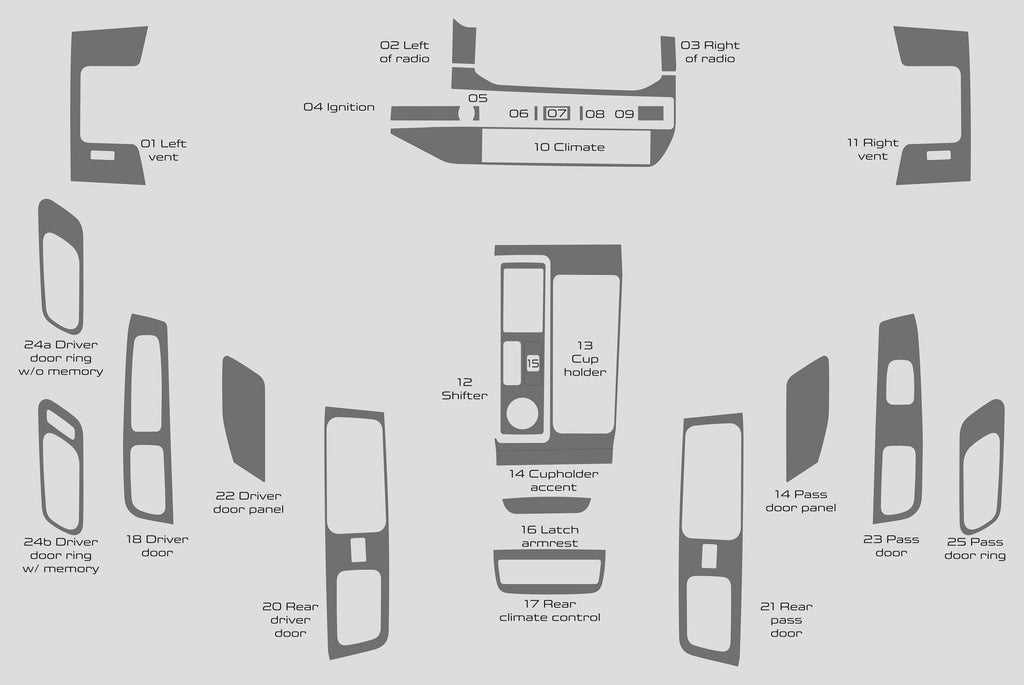
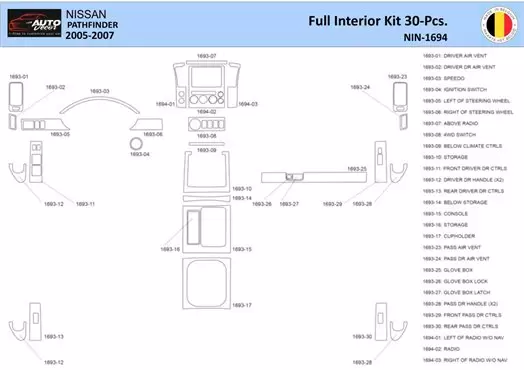
Interior Parts and Accessories Explained
Understanding the components and enhancements within the cabin of a vehicle is essential for both maintenance and personalization. This section will delve into various elements that contribute to the overall comfort and functionality of the interior space, offering insights into their roles and potential upgrades.
Key interior components include:
- Seating: Different types of seats offer varying levels of comfort and support, with options ranging from basic fabric to premium leather.
- Dashboard: The control center for numerous functions, it houses gauges, displays, and controls that keep the driver informed and in command.
- Trim and Upholstery: The aesthetic aspects of the interior, which can be customized with various materials and colors to enhance the visual appeal.
- Storage Solutions: Includes compartments, consoles, and pockets designed to keep the cabin organized and clutter-free.
- Lighting: Interior illumination not only enhances visibility but also contributes to the overall ambiance of the space.
Accessories available for enhancement can include:
- Floor Mats: Protect the flooring and add style, available in various materials and designs.
- Sunshades: Help regulate cabin temperature and protect interior surfaces from UV damage.
- Sound Systems: Upgrades for audio quality can significantly enhance the driving experience.
- Technology Add-ons: Navigation systems and Bluetooth connectivity improve functionality and convenience.
- Custom Fit Accessories: Tailored items that provide additional convenience, such as seat covers and organizers.
By exploring these components and accessories, vehicle owners can ensure that their interior space not only meets their needs but also reflects their personal style.
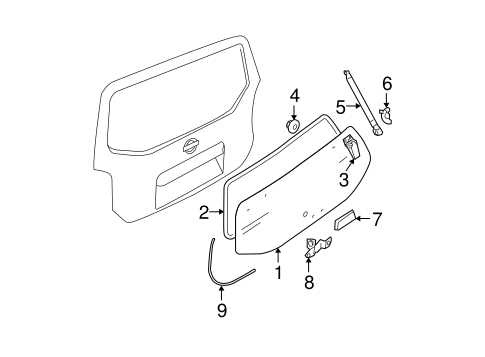
Brake System Detailed Analysis
The braking mechanism is a critical component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. This section delves into the intricacies of the braking assembly, examining its various elements and their functions.
Components Overview: The braking system consists of multiple parts, each playing a vital role in deceleration and stopping. Key components include brake pads, rotors, calipers, and master cylinders. Understanding the interaction among these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Working Principles: The primary function of the braking assembly is to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. When the brake pedal is engaged, hydraulic pressure activates the calipers, pressing the pads against the rotors. This process significantly slows down or halts the vehicle’s movement.
Common Issues: Various factors can affect the efficiency of the braking system, including wear and tear, fluid leaks, and air in the hydraulic lines. Regular inspections are crucial to identify potential problems early and maintain optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips: To ensure longevity and reliability, it is essential to adhere to a regular maintenance schedule. This includes checking brake fluid levels, inspecting pads for wear, and replacing components as necessary. Proper care can enhance the overall functionality and safety of the braking mechanism.
Maintenance Tips for Key Parts
Ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle involves regular attention to its essential components. Proper care and timely interventions can prevent major issues and enhance overall performance. This section offers valuable insights into maintaining crucial elements that contribute to a smooth driving experience.
1. Engine Care
- Regularly check and change the oil to maintain optimal lubrication.
- Inspect air filters and replace them as needed to ensure efficient airflow.
- Monitor fluid levels, including coolant and transmission fluid, and top them off when necessary.
2. Brake System Maintenance
- Inspect brake pads and rotors for wear and replace them as needed to ensure safety.
- Check brake fluid levels and quality, replacing it if it appears contaminated.
- Listen for unusual sounds when braking, which may indicate underlying issues.