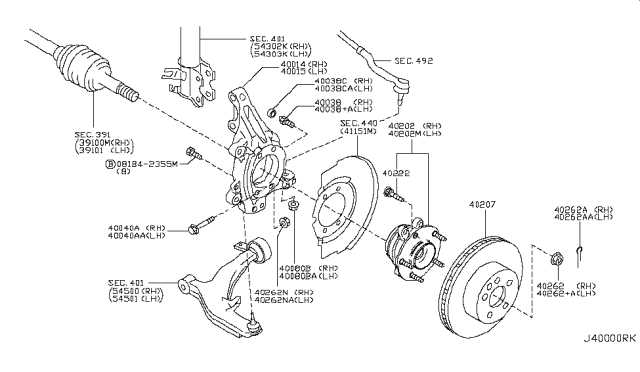
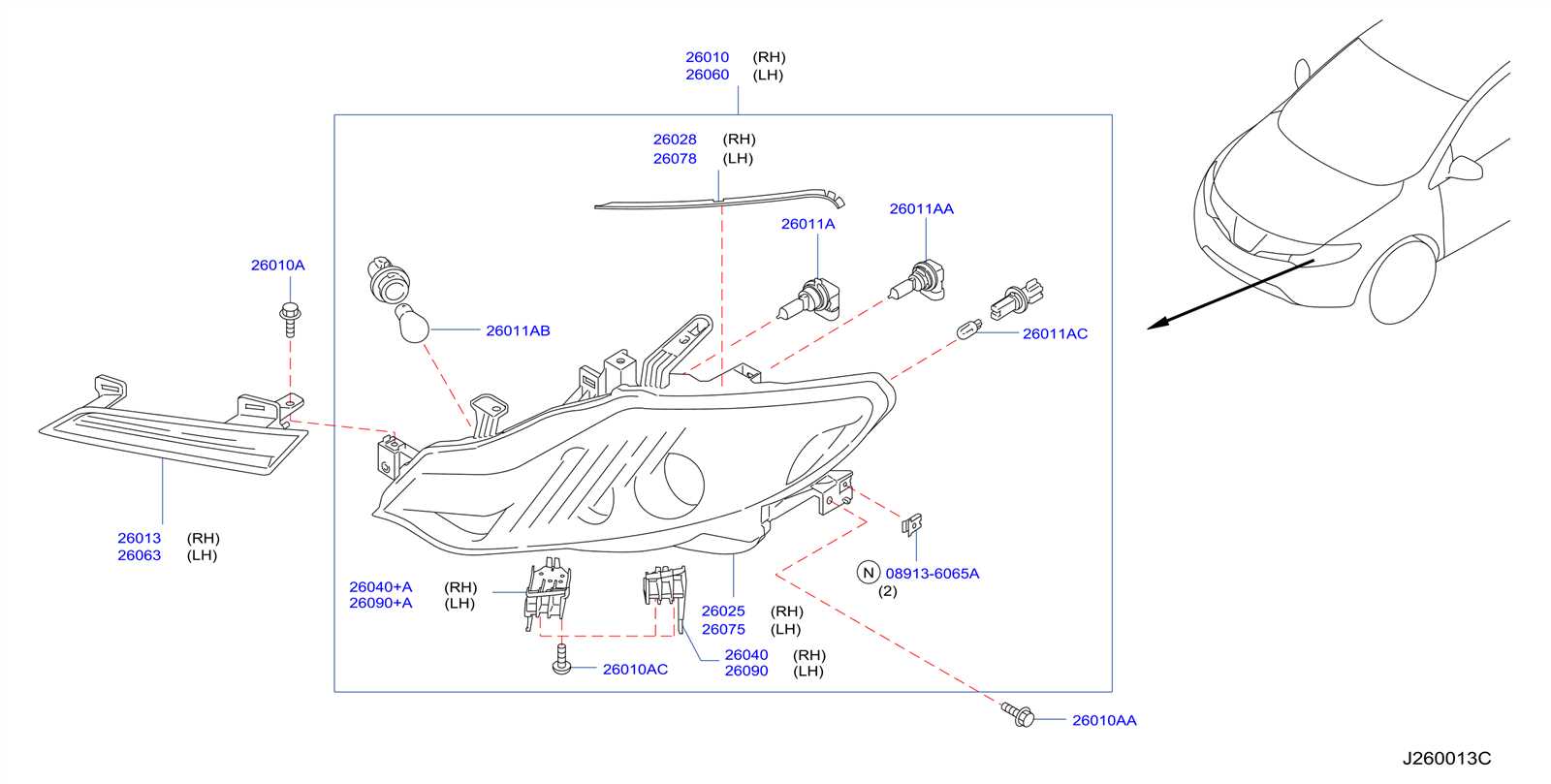
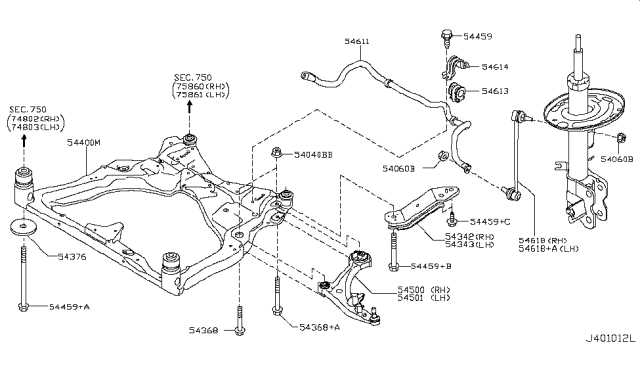
The brake system is a critical component in ensuring the safety and control of your vehicle. It involves several key elements that work together to slow down and stop the car efficiently. By learning about the various components and their functions, you can better understand how this system operates and why regular maintenance is crucial.
The braking system consists of various elements, each performing a specific role. These components work in unison to ensure that when you press the brake pedal, your vehicle responds appropriately. Below is an outline of the primary parts:
| Component |
Function |
| Brake Caliper |
Houses the brake pads and uses hydraulic pressure to squeeze them against the rotor. |
| Brake Rotor |
The metal disc that the brake pads clamp onto, slowing the rotation of the wheels. |
| Brake Pads |
Friction material that presses against the rotor, generating the necessary force to reduce speed. |
| Brake Fluid |
Hydraulic fluid that transfers force from the brake pedal to the calipers. |
Electrical System Connections and Functions
The electrical system in vehicles serves as a vital network that ensures the proper functioning of various components. This intricate setup not only powers essential features but also facilitates communication between different parts, ensuring that each element operates in harmony. Understanding these connections is crucial for diagnosing issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Wiring Harness and Circuitry

The wiring harness acts as the central nervous system, linking multiple electrical components. Each wire within the harness has a specific function, ranging from powering lights to controlling advanced infotainment systems. Proper insulation and routing are essential to prevent interference and ensure reliability. A malfunction in any part of the circuitry can lead to widespread failures, making it imperative to regularly inspect these connections.
Fuse and Relay Functions
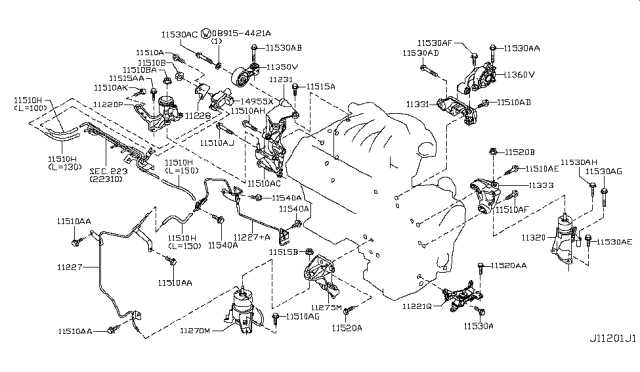
Fuses and relays play a critical role in protecting the electrical system from overloads and short circuits. Fuses serve as sacrificial components, designed to break the circuit when excessive current flows, thereby preventing damage to sensitive devices. On the other hand, relays act as switches, allowing low-current signals to control high-current circuits, which is essential for safety and efficiency. Understanding the location and function of these elements aids in effective troubleshooting and repair.
Fuel System Components Breakdown
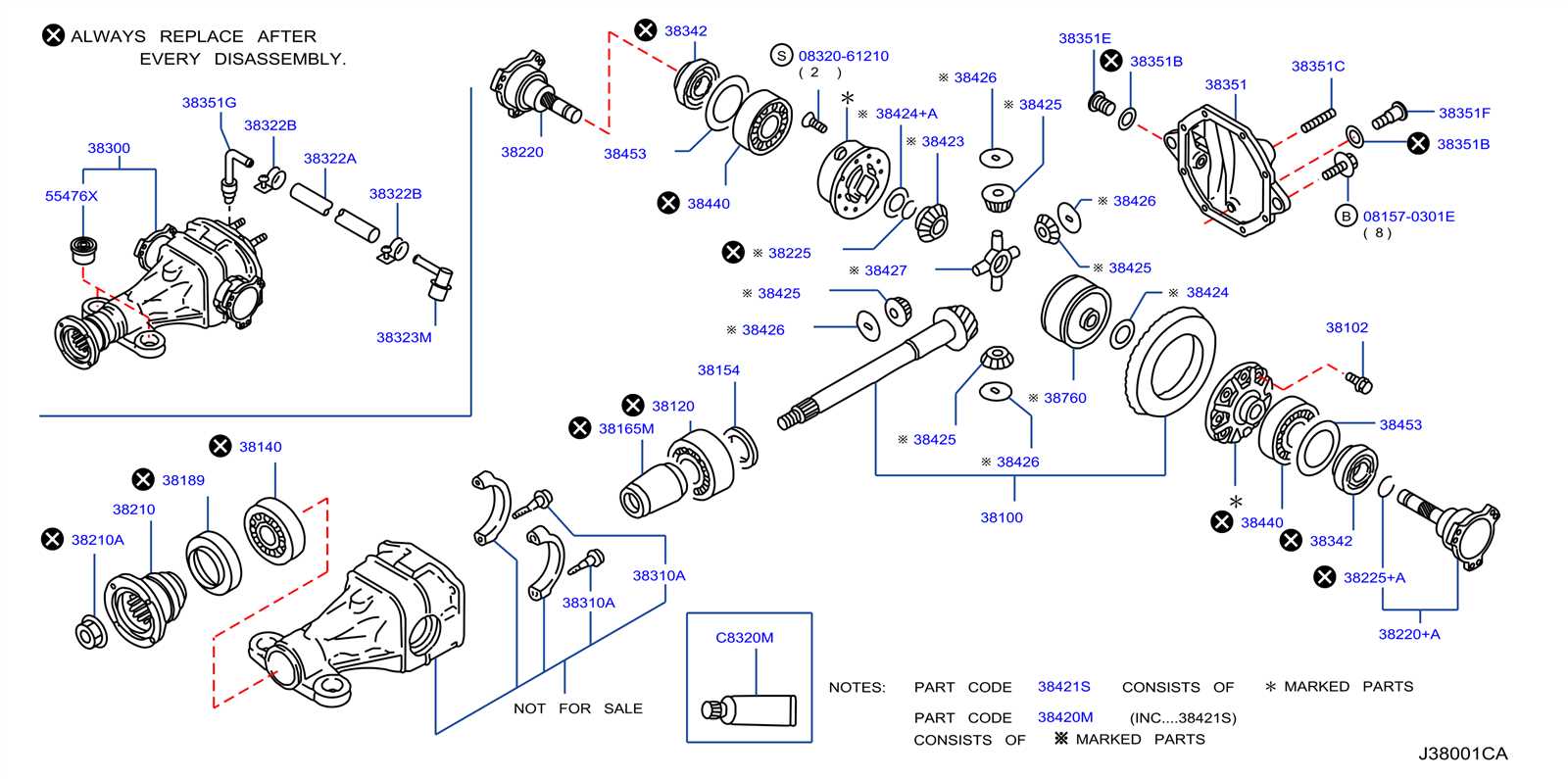
The fuel system in modern vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. This section delves into the essential elements that make up this vital system, highlighting their functions and interconnections. Understanding these components is key to maintaining and troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank serves as the reservoir for storing the gasoline or diesel, providing a steady supply to the engine. It is designed to withstand various environmental conditions while ensuring safety and reliability.
Fuel Pump: This component is responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine. It generates the necessary pressure to ensure that fuel reaches the injection system, and its efficiency is critical for smooth operation.
Fuel Filter: The filter’s primary role is to remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it enters the engine. Regular replacement of this component is essential to prevent damage to the fuel injectors and engine components.
Fuel Injectors: These precision devices deliver the appropriate amount of fuel into the combustion chamber at the right moment. Their performance directly impacts fuel efficiency and emission levels, making them vital for the overall health of the engine.
Fuel Pressure Regulator: This component maintains optimal fuel pressure within the system, ensuring consistent performance during varying engine conditions. It adjusts the fuel supply according to the engine’s demands.
Fuel Lines: These conduits transport fuel from the tank to the engine. They must be durable and resistant to pressure and temperature changes to prevent leaks and ensure a reliable supply of fuel.
Understanding the various elements of the fuel system is essential for any vehicle owner. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance vehicle performance and longevity.
Cooling System Components and Their Arrangement
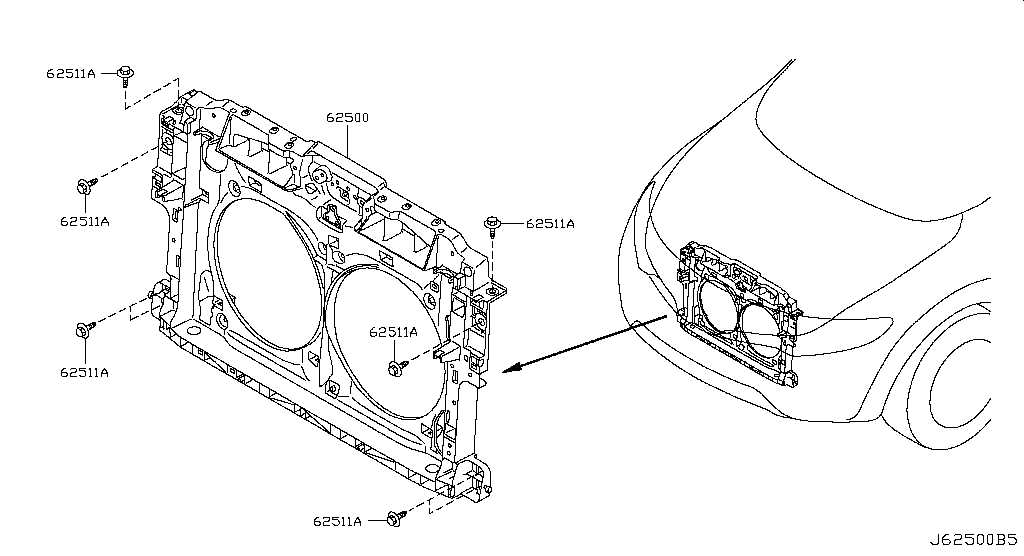
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance. This system comprises various elements that work together to regulate the temperature of the engine and other critical components. Understanding the layout and functionality of each element can greatly aid in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance.
Key Components

Essential elements of the cooling mechanism include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fans. The radiator is responsible for dissipating heat from the engine coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant through the engine and radiator. The thermostat regulates the coolant flow, allowing the engine to reach its optimal operating temperature before directing excess heat to the radiator. Cooling fans assist in maintaining airflow through the radiator, particularly at low speeds or during idle conditions.
Placement and Accessibility
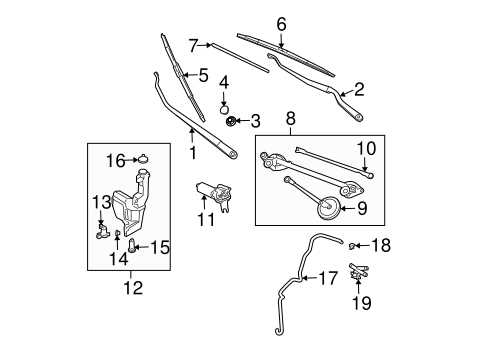
Typically, the radiator is positioned at the front of the engine bay, ensuring maximum airflow. The water pump is often mounted on the engine block, facilitating direct circulation of the coolant. The thermostat is situated between the engine and the radiator, providing easy access for replacement. Cooling fans are usually located behind the radiator, ensuring efficient air movement when needed. Proper arrangement of these components is vital for effective heat management and overall system reliability.
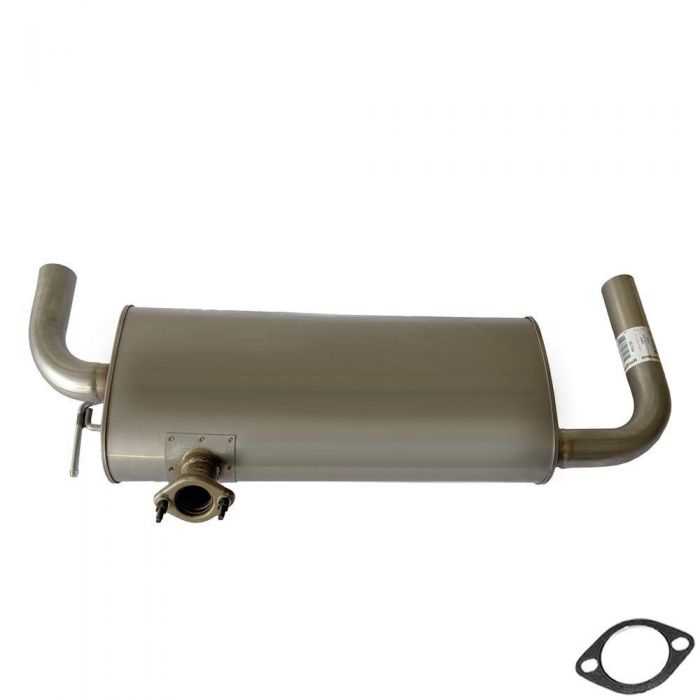
Exhaust System Overview
The exhaust assembly plays a critical role in a vehicle’s operation, ensuring optimal performance and emission control. It channels harmful gases produced during combustion away from the engine, helping to maintain engine efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Key Components
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: Converts harmful pollutants into less harmful emissions through chemical reactions.
- Muffler: Reduces engine noise and controls exhaust flow.
- Exhaust Pipes: Transport exhaust gases from the manifold through the system to the tailpipe.
- Oxygen Sensors: Monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases, providing feedback to the engine control unit for optimal fuel efficiency.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and upkeep of the exhaust system are vital for ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently. Neglecting this system can lead to performance issues, increased emissions, and potential safety hazards.
- Check for leaks or damage regularly.
- Ensure the catalytic converter is functioning correctly to minimize pollution.
- Listen for unusual noises that may indicate muffler or pipe issues.
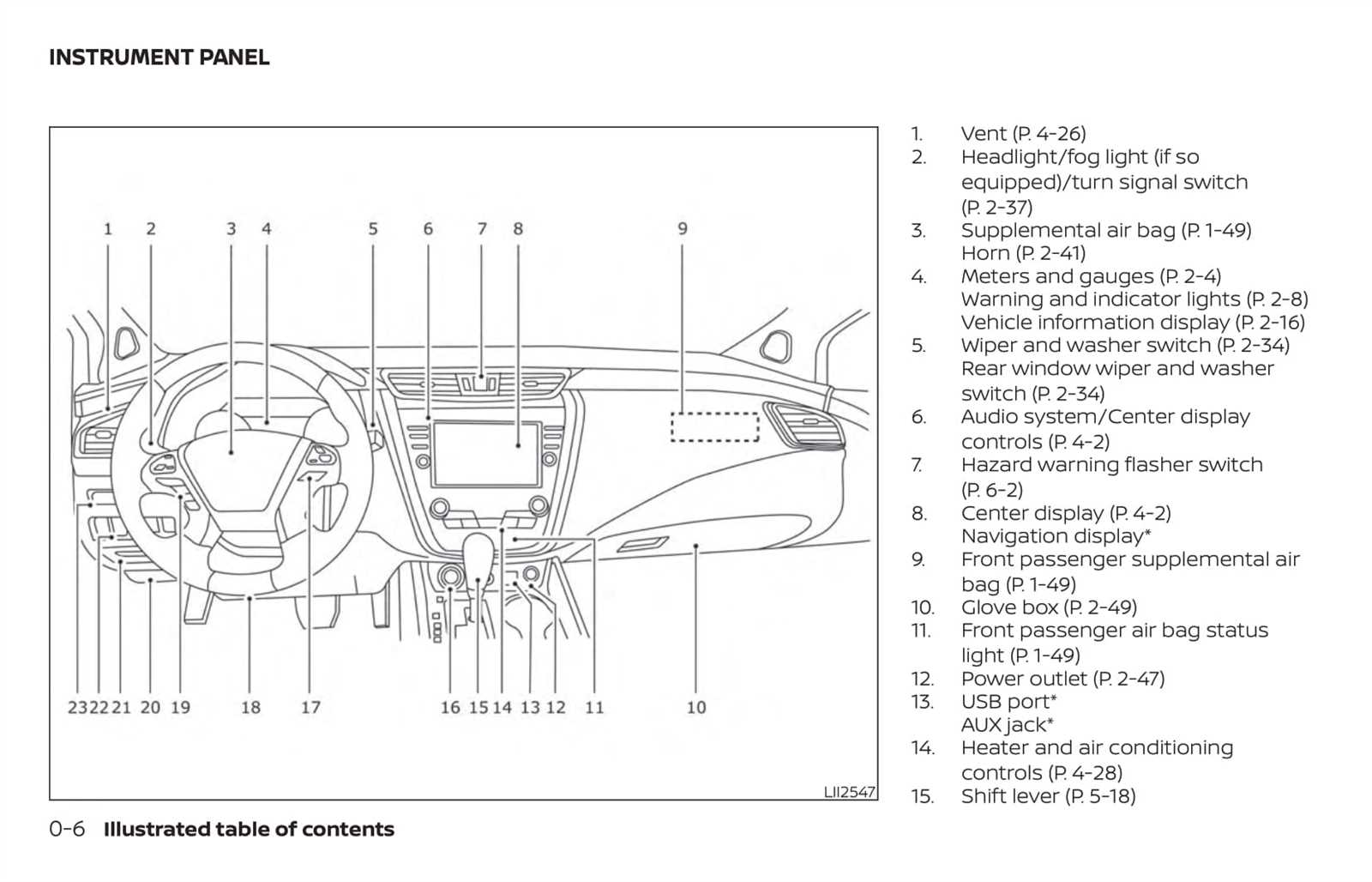
Interior Mechanisms and Controls
The functionality and comfort of a vehicle’s interior largely depend on its various mechanisms and control systems. These components play a vital role in enhancing the driving experience by providing ease of access and intuitive operation. From seating adjustments to climate control, the integration of these systems ensures that drivers and passengers can enjoy a customized environment while on the road.
One of the primary aspects of the interior setup includes the seating mechanisms, which allow for adjustments to accommodate different body types and preferences. Controls for lumbar support and seat position are typically user-friendly, ensuring that drivers can achieve optimal comfort effortlessly. Additionally, the inclusion of electronic controls further simplifies these adjustments, allowing for precise customization.
The climate control system is another crucial feature, enabling occupants to maintain a pleasant atmosphere regardless of external weather conditions. This system often incorporates intuitive controls for temperature regulation, air distribution, and fan speed, ensuring that every passenger can enjoy their desired level of comfort.
Furthermore, the integration of infotainment systems has revolutionized how drivers interact with their vehicles. These systems typically feature touch screens and voice recognition technology, allowing for seamless navigation and media access. The controls are strategically placed for easy reach, promoting safety and convenience.
Finally, safety features, such as advanced driver-assistance systems, are essential in modern interiors. These controls may include options for lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and parking aids, all designed to enhance driver confidence and vehicle security. Collectively, these interior mechanisms and controls contribute significantly to the overall functionality and user experience of contemporary vehicles.
Exterior Body Parts and Structure
The outer shell of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. It not only enhances the visual appeal but also provides protection to the internal components while contributing to aerodynamics and overall structural integrity. Understanding the various elements that comprise this exterior framework is essential for maintenance and repair.
The framework includes components such as the fenders, bumpers, doors, and hoods, each serving a specific purpose. Fenders shield the wheels and prevent debris from scattering, while bumpers absorb impact during minor collisions. Doors provide access to the interior, and the hood covers the engine, safeguarding it from external elements.
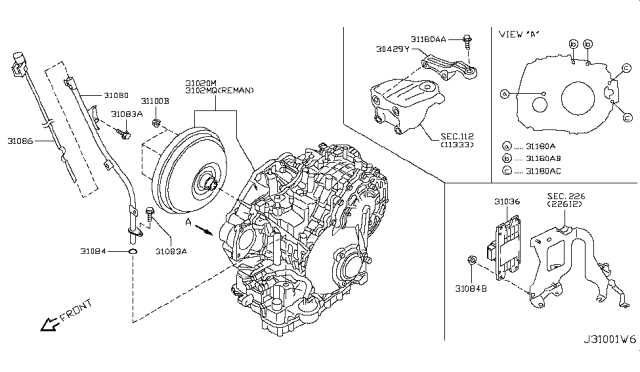
Steering System Components and Operation
The steering mechanism is a vital aspect of any vehicle, enabling the driver to control direction and navigate effectively. This system is composed of several integral elements that work in unison to provide a smooth and responsive driving experience. Understanding these components and their functionality is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
Key Components
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver, allowing for manual control of the vehicle’s direction.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear, housing various electrical components.
- Steering Gearbox: Translates the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels.
- Linkage Components: Various rods and joints that connect the steering gearbox to the wheel assembly, enabling precise movement.
- Power Steering System: Assists the driver by using hydraulic or electric actuators to reduce the effort needed to turn the wheel.
Operational Mechanics
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering column transmits this motion to the steering gearbox. The gearbox converts the rotation into linear motion, directing the linkage components, which in turn move the wheels. In vehicles equipped with power steering, hydraulic fluid or electrical energy enhances this process, making it easier to maneuver the vehicle, especially at low speeds.
Regular maintenance of the steering system components is crucial for safety and performance. Checking for wear and tear, fluid levels, and ensuring proper alignment can significantly enhance the driving experience and extend the lifespan of the steering mechanism.
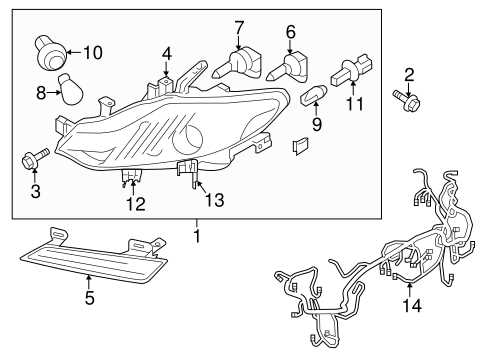
Lighting and Signal Assembly Explained

The lighting and signal assembly plays a crucial role in enhancing vehicle safety and visibility on the road. It encompasses various components that facilitate effective communication between drivers and pedestrians, ensuring that intentions are clearly conveyed. This section delves into the intricacies of these assemblies, highlighting their significance and functionality.
Within the assembly, several key elements work in tandem:
- Headlights: These illuminate the road ahead, enabling safe navigation during low-light conditions.
- Turn Signals: These indicate directional changes, allowing other road users to anticipate movements.
- Brake Lights: These signal when the vehicle is decelerating, alerting those behind to reduce their speed.
- Fog Lights: Designed for use in adverse weather conditions, these improve visibility when visibility is significantly reduced.
- Tail Lights: These serve as a rear warning to other drivers, enhancing safety during nighttime driving.
Understanding the components of the lighting and signal assembly is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s functionality. Regular inspections and prompt replacements of faulty elements ensure that the system operates efficiently, thereby enhancing overall safety on the roads.
In summary, the lighting and signal assembly is an integral part of vehicle safety. By effectively communicating the vehicle’s movements and intentions, these components contribute significantly to road safety.