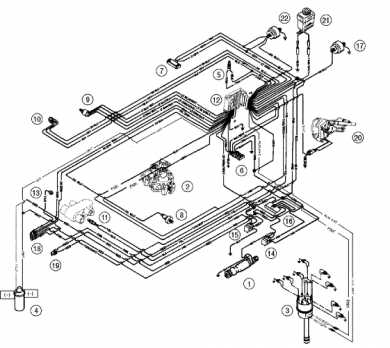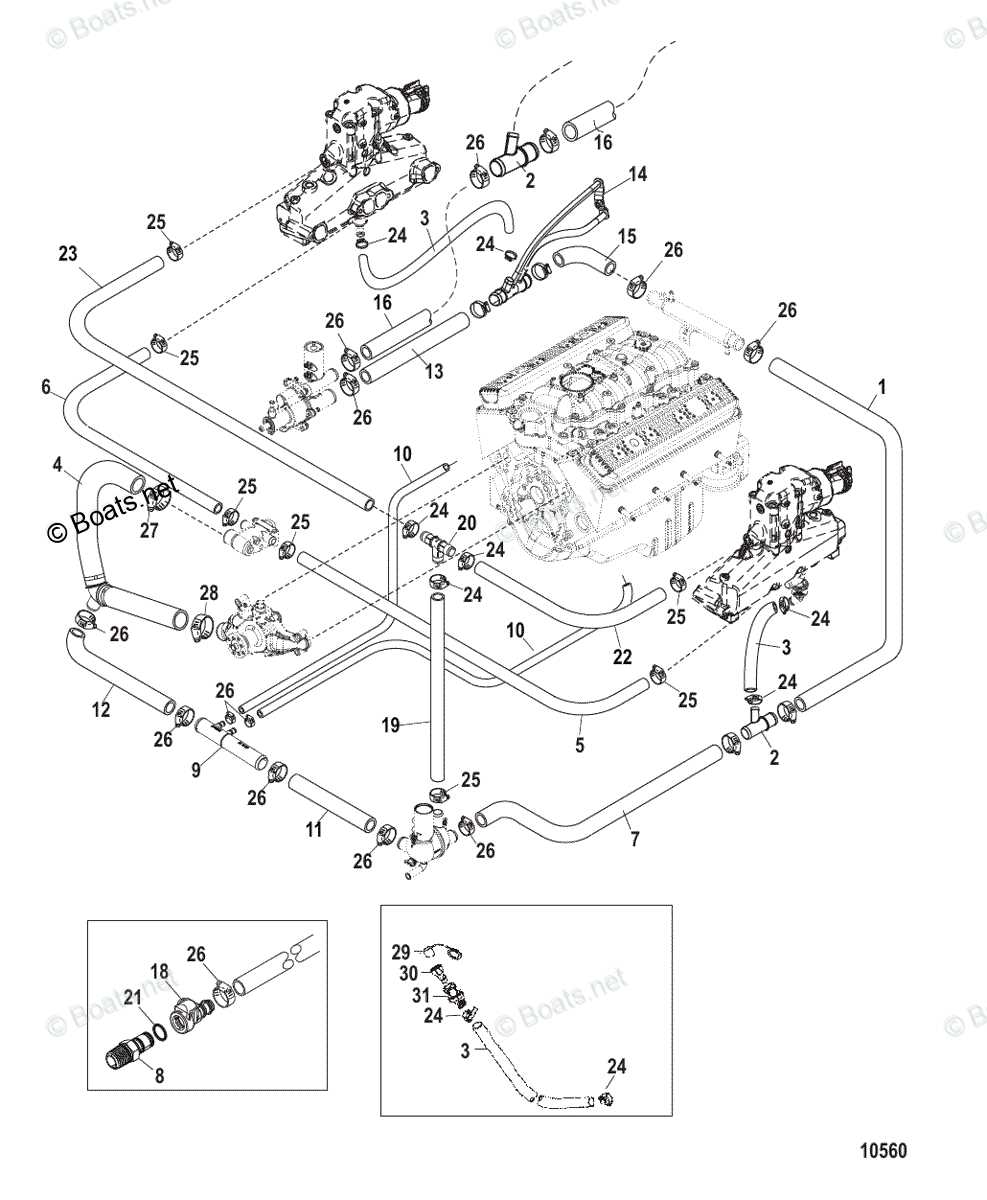
When working with high-performance marine engines, it’s crucial to understand how various elements function together. The internal combustion system and related assemblies demand precision and proper maintenance to ensure smooth operation on the water. With numerous elements involved, a clear understanding of their roles can significantly improve the engine’s performance and longevity.
Each element within the power unit has a specific task, contributing to both the propulsion and the safety of the vessel. Knowing the connections between the fuel delivery system, ignition components, and cooling mechanisms can help in troubleshooting and maintaining the entire structure effectively.
Delving into the detailed layout of such a powertrain, it’s important to grasp how different components interact.
Understanding the Engine Components of MerCruiser 5.7
The internal structure of this power unit consists of various interconnected systems, all working in harmony to deliver performance. Each section plays a vital role in ensuring efficient fuel combustion, cooling, and overall operation, making it essential to understand how these elements contribute to the motor’s functionality.
Main Mechanical Sections
The core elements include mechanical systems responsible for power generation, fuel management, and air intake. These systems work together to optimize the flow of energy, ensuring that the machine operates smoothly across different conditions. Components such as the crankshaft and camshaft synchronize motion, facilitating the necessary mechanical precision.
Auxiliary Systems

Additional components, including the cooling and exhaust setups, provide essential support. The cooling system prevents overheating by circulating fluids, while the exhaust removes combustion byproducts. Together, these auxiliary systems enhance the longevity and reliability of the motor, helping to maintain optimal performance over time.
Key Parts in the 1998 Model
In this section, we will explore the critical components that make this engine configuration reliable and powerful. Each element works together to ensure optimal performance and durability, highlighting the efficiency and engineering that sets this system apart.
Engine Block
The core structure houses all moving parts, serving as the foundation for the motor. Crafted from robust materials, it is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring longevity and smooth operation. This essential component supports various systems that contribute to overall functionality.
Cooling System
Maintaining optimal operating temperature is crucial for engine efficiency. This cooling setup consists of multiple channels that help regulate heat, ensuring the motor remains within safe operating limits during prolonged use. Without proper heat management, performance and reliability would be compromised.
Essential Maintenance for Optimum Performance
Regular upkeep is critical to ensure the longevity and smooth operation of any marine engine. Consistent attention to key components helps prevent costly repairs and keeps your system running efficiently in various conditions. Following a structured maintenance plan ensures that your vessel is always ready for the demands of the open water.
Regular Inspections
Thorough visual checks should be part of your routine to identify potential issues before they become serious. Look for signs of wear or corrosion on essential parts, ensuring everything is properly lubricated and secured.
- Inspect belts and hoses for cracks or looseness.
- Check fluid levels, including oil and coolant, ensuring they are within recommended ranges.
- Examine filters and replace them at regular intervals to maintain efficiency.
Cooling System Elements and Their Function
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal temperature and preventing overheating during operation. Each component in this system plays a role in regulating and dispersing heat, ensuring the engine performs efficiently over extended periods. Below, we outline the key elements of this system and how they contribute to temperature control.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant through the engine and heat exchanger, ensuring consistent cooling flow. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermostat | Regulates the engine’s temperature by controlling when coolant is released from
Fuel Delivery System and Key Components
The fuel supply system is essential for ensuring smooth operation by efficiently transferring the necessary fluid from the reservoir to the combustion chamber. This process relies on a network of interconnected parts working together to maintain proper flow and pressure, contributing to optimal performance. Understanding these components allows for better diagnostics and maintenance. Main Elements of the Fuel Transfer SystemThe primary elements responsible for fuel transport include various devices and lines that manage flow, ensuring precise distribution. These elements are designed to maintain consistent pressure and protect against leaks, making them critical for uninterrupted functioning. Overview of Key Components
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the engine, contributing to its efficiency and performance characteristics. Proper understanding and inspection of these elements are key for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the engine system. Lubrication System and Oil FlowThe lubrication system plays a crucial role in maintaining the operational efficiency of an engine by ensuring that moving components are adequately coated with oil. This process minimizes friction, reduces wear, and facilitates optimal performance. Understanding the flow of oil within this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. The primary functions of the lubrication system include:
Oil flows through various passages and channels, which are designed to deliver it efficiently to critical areas. The following components are integral to this flow:
Regular maintenance of the lubrication system is vital to ensure longevity and performance. Key practices include:
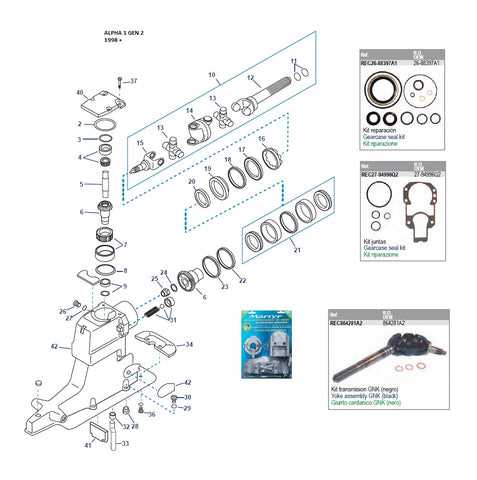
By understanding the lubrication system and its oil flow, operators can better maintain their engines and enhance their operational reliability. Drive System Overview and Key PartsThe drive mechanism of a marine engine is crucial for transforming power into motion. This system comprises various components that work harmoniously to ensure efficient propulsion and steering. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and optimal performance of the vessel. Key components of the drive mechanism include:
Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the propulsion system. Regular inspection and maintenance of these parts can lead to improved reliability and longevity of the entire setup. TThis section focuses on an essential component often associated with marine engines. Understanding its function and the related elements can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the overall system. Exploring its characteristics provides valuable insights into maintenance and optimization strategies. Functionality OverviewThe discussed element plays a crucial role in the engine’s operation. It facilitates the efficient conversion of fuel into energy, contributing to the overall efficiency of the vessel. Proper functionality ensures optimal power delivery and helps prevent potential issues that could arise from wear or malfunction. Key ComponentsSeveral critical elements work in tandem to support the primary function. Below is a brief overview of these components, illustrating their significance in maintaining overall system performance.
|