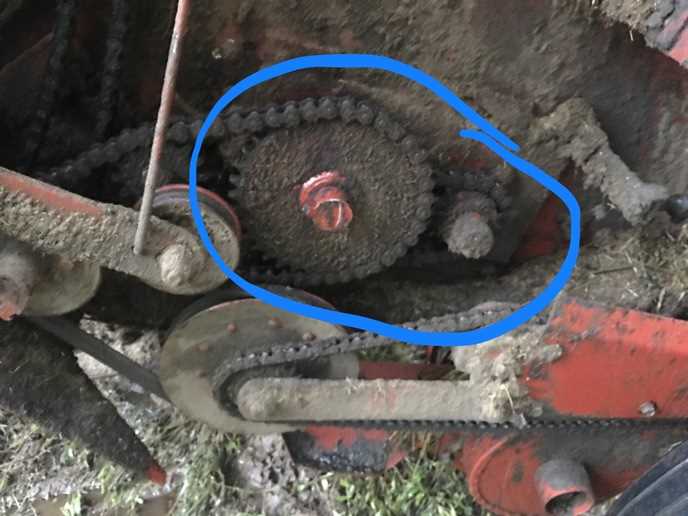

Modern agricultural machinery is designed with precision, ensuring reliability and efficiency in the field. For those involved in maintaining or repairing such equipment, having a clear understanding of the internal structure is essential. Knowing how each component interacts and where it fits into the overall assembly can greatly enhance the repair process.
Exploring detailed layouts can simplify the identification of specific mechanical elements, ensuring smooth operation and timely replacements. It allows users to visualize how different sections connect, providing a comprehensive view of the equipment’s mechanics. This deeper insight can be a crucial tool for anyone aiming to keep their machinery in optimal working condition.
By familiarizing oneself with such detailed breakdowns, operators can quickly pinpoint areas requiring attention, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity. This knowledge serves as a valuable resource, whether for routine upkeep or addressing unexpected issues, ensuring the machinery remains dependable across seasons.
Understanding the Structure of the 530 Model
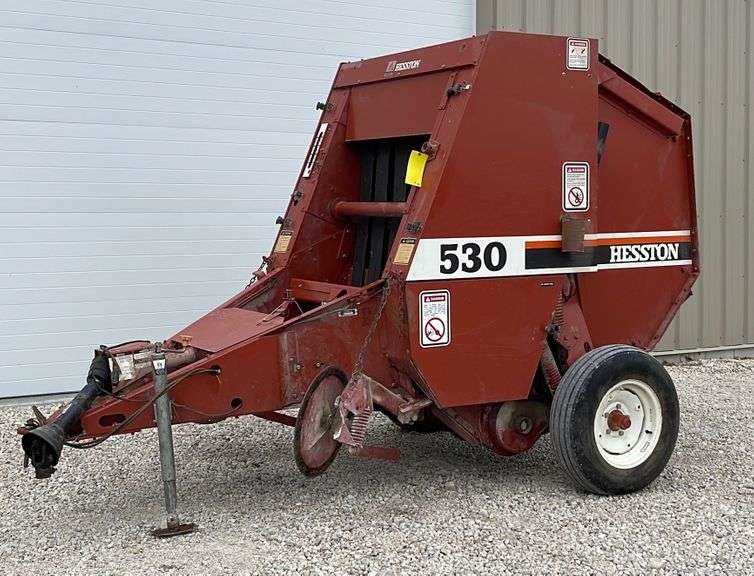

The design of this agricultural equipment is built around functionality and efficiency, providing a reliable solution for a variety of tasks. Its framework is crafted to handle substantial workloads, ensuring durability and consistent performance in different field conditions. By examining its key components and how they interact, one can appreciate the engineering that makes it suitable for demanding agricultural needs.
Core Framework and Durability: The machine’s robust skeleton is engineered to withstand continuous use, making it an essential asset for maintaining operations. Its metal frame provides stability, ensuring that all mechanisms function smoothly, even when subjected to tough environments. This sturdy foundation is crucial for long-term reliability.
Mechanical Coordination: Inside, a complex system of gears and levers works in harmony, managing the flow and handling of materials. This coordination allows for seamless processing, reducing the strain on individual components. Each element plays a critical role in achieving efficient operations, making it a highly optimized piece of machinery.
Adjustable Systems for Versatility: A key feature of this model is its ability to adapt to various field conditions. Adjustable settings allow users to modify the operation, ensuring optimal results regardless of terrain or material density. This adaptability is especially important for maintaining productivity across diverse agricultural needs.
Key Components in the Round Baler
This section provides an overview of the essential mechanisms and assemblies that ensure efficient performance in agricultural baling equipment. These elements work together to gather, compress, and secure plant material into compact, cylindrical bundles, optimizing the harvesting process.
Primary Mechanisms
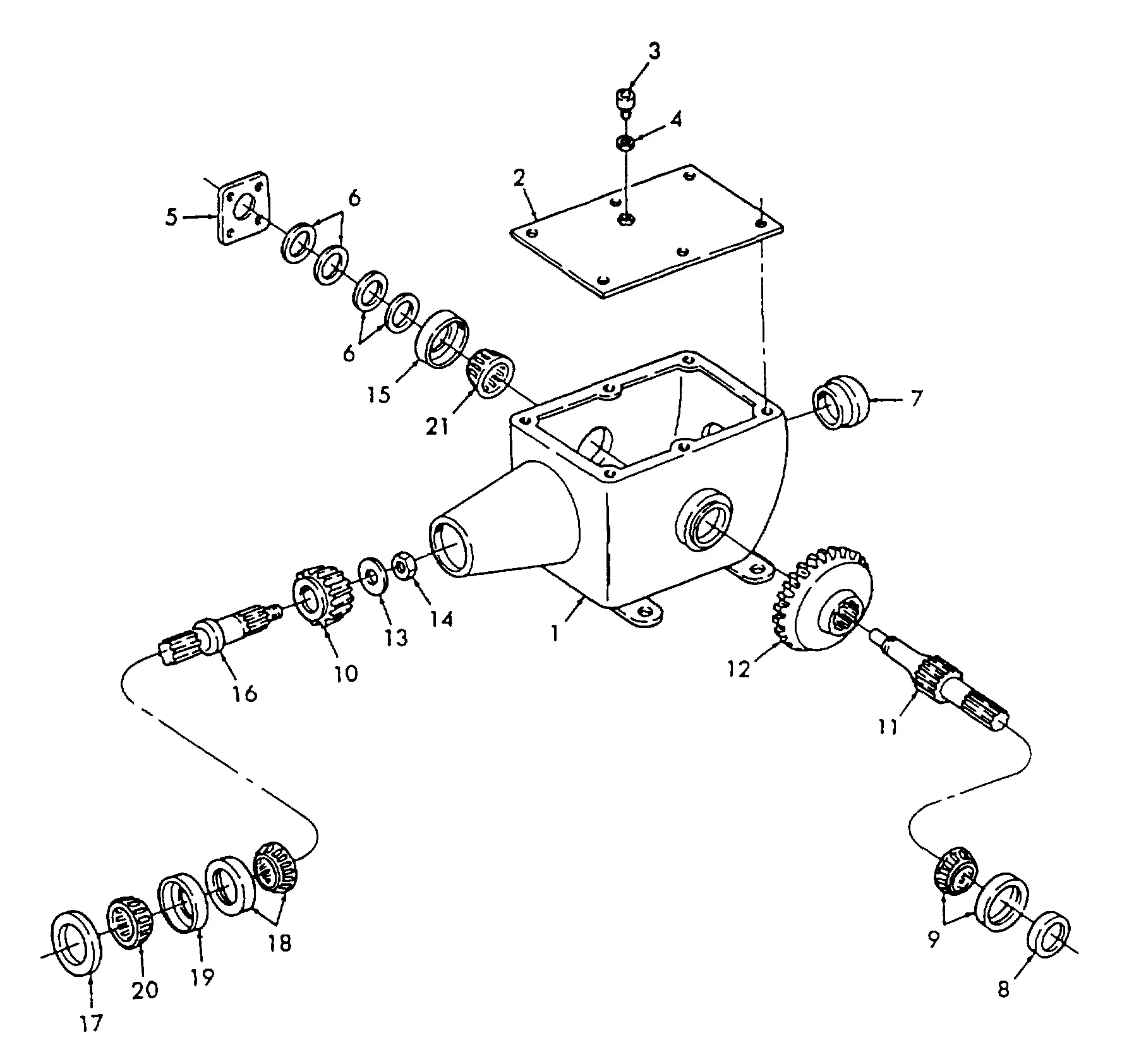
- Pickup Assembly: This element gathers the crop from the ground and directs it into the machine. It uses rotating tines to lift and feed the material into the next stage.
- Compression Chamber: The core part of the equipment where the material is rolled into a dense form. It operates with belts or rollers that rotate, compacting the content to achieve a uniform shape.
- Wrapping System: This mechanism applies layers of material around the bundle to maintain its shape and prevent moisture ingress, ensuring long-term preservation of the contents.
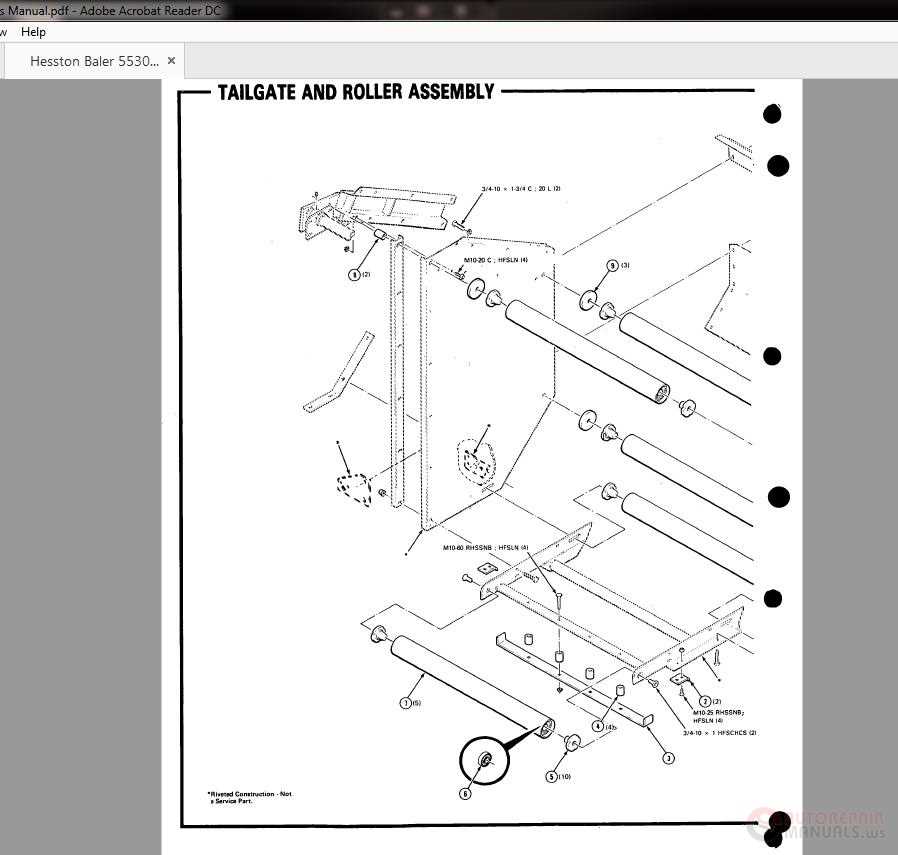
Support Systems
- Hydraulic Controls: These components adjust various settings such as pressure and rolling speed, allowing for precise operation based on different crop conditions.
- Tensioners: Used to regulate the tightness of belts or chains within the machine, ensuring consistent compression during the rolling process.
- Monitoring Se
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Keeping machinery in top shape is essential for extending its lifespan and ensuring reliable operation. Regular attention to various components can prevent unexpected issues and enhance overall efficiency. Below are some key practices to keep your equipment running smoothly.
Inspect Regularly: Frequent checks of the equipment’s moving parts are crucial. Look for signs of wear or potential damage to avoid complications during operation. Addressing minor issues early can save time and reduce repair costs.
Lubrication Is Key: Proper lubrication minimizes friction between moving parts, reducing heat buildup and preventing premature wear. Use the recommended oils or greases and apply them according to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the best results.
Check Fluid Levels: Maintaining correct fluid levels is vital for smooth functioning. Regularly check and replenish hydraulic fluids, coolant, and other essential liquids. This helps maintain optimal pressure and prevents overheating during heavy-duty tasks.
Keep It Clean: Dirt and debris can clog filters, damage seals, and impede proper airflow. Clean the exterior and interior components to ensure that dust and other particles do not affect performance. Regular cleaning extends the life of various systems.
Replace Worn Parts: Over time, some components may wear out due to regular use
Replacing Worn Parts in the Baler

Maintaining a well-functioning agricultural machine is crucial for optimal performance during harvest. Over time, certain components can experience wear and tear, which may impact the efficiency of the machine. Timely replacement of these elements can extend the lifespan of the equipment and ensure smooth operation.
Identifying Commonly Affected Areas

Some elements of the machinery are more prone to wear due to constant motion and pressure. Recognizing the signs of deterioration in these areas helps to prevent breakdowns during critical use. Regular inspection allows operators to spot issues before they lead to larger mechanical problems.
Key Components to Monitor and Replace
Several essential elements should be checked periodically for wear. Below is an overview of typical components that may require attention:
Component Signs of Wear Recommended Action Belt Cracking or fraying Replace immediately to avoid slippage Bearings Unusual noise or heat buildup Swap out to maintain smooth rotation Common Issues and How to Fix Them

Maintaining agricultural equipment can present various challenges over time. Regular use, exposure to different weather conditions, and the nature of heavy-duty tasks can all contribute to wear and tear. Identifying these challenges and knowing how to address them can extend the lifespan of your machine and improve its efficiency.
Frequent Malfunctions and Their Solutions
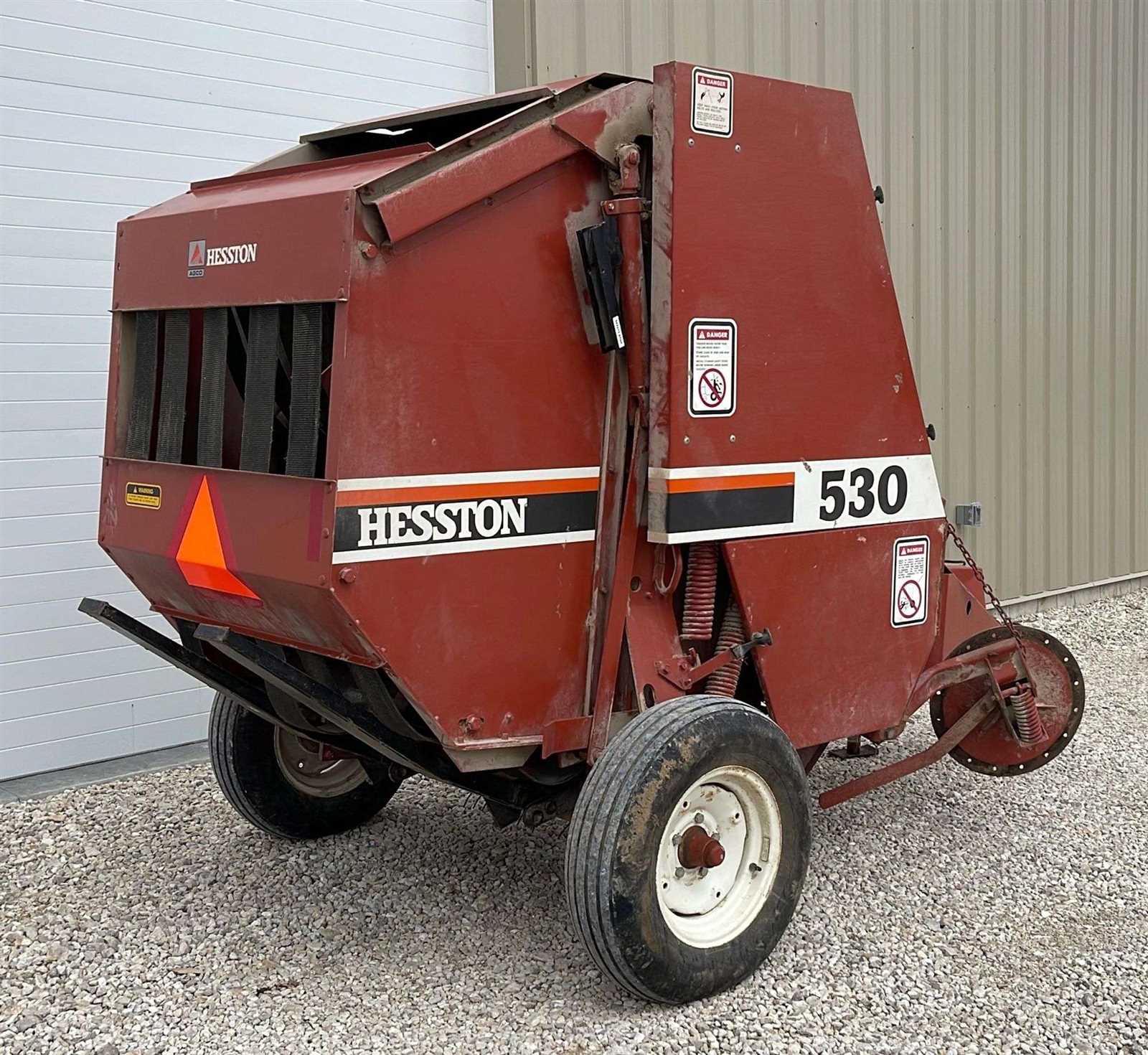

One of the most common problems involves the mechanism responsible for picking up and processing materials. Issues like jamming or uneven feeding can disrupt the entire process. To resolve this, it’s essential to inspect the intake system for any blockages or worn-out parts. Cleaning out debris and replacing any damaged components can often restore functionality.
Maintenance Tips to Prevent Wear

Proactive maintenance plays a crucial role in avoiding costly repairs. Regular lubrication of moving parts helps to prevent rust and ensures smooth operation. It is also important to monitor tension settings in the mechanical systems to ensure optimal performance. Adjustments should be made according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent excessive strain on the components.
Note: Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent larger breakdowns and save time and resources in the long run.
Guide to the Hydraulic System
The hydraulic mechanism is a vital component in machinery, utilizing fluid power to perform various tasks with precision and efficiency. This system converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, allowing for the seamless operation of numerous functions within the equipment. Understanding the intricacies of this setup is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
Components of the Hydraulic System
- Hydraulic Fluid: The lifeblood of the system, providing the necessary force for movement.
- Pumps: Devices that create pressure within the system, facilitating fluid movement.
- Actuators: Mechanisms that convert hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy to execute tasks.
- Valves: Components that control the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid.
- Reservoir: A storage unit for hydraulic fluid, ensuring a consistent supply.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check fluid levels to ensure the system operates efficiently.
- Inspect hoses and connections for signs of wear or leakage.
- Replace filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to prevent contamination.
- Monitor the performance of pumps and actuators for any irregularities.
- Consult the operational manual for specific maintenance guidelines.
Belt Tension Adjustments for Consistency
Maintaining the proper tightness of conveyor belts is crucial for optimal performance and reliability in machinery operations. Proper adjustments ensure that the belts operate smoothly, preventing slippage and wear, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs. Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential for achieving consistent functionality and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
To effectively manage belt tension, follow these steps:
Step Description 1 Identify the appropriate tension specifications as per the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure compliance with operational standards. 2 Utilize a tension gauge or measuring device to assess the current tightness of the belt, noting any discrepancies from the recommended settings. 3 Make necessary adjustments using the appropriate tools, such as tensioning screws or levers, to achieve the specified tightness. 4 After adjustments, run the machine at idle to check for vibrations or unusual sounds that may indicate improper tension. 5 Regularly inspect and re-evaluate the tension at scheduled intervals to ensure sustained performance and address any emerging issues proactively. Adhering to these practices will help maintain the efficiency and reliability of the machinery, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures and enhancing overall productivity.
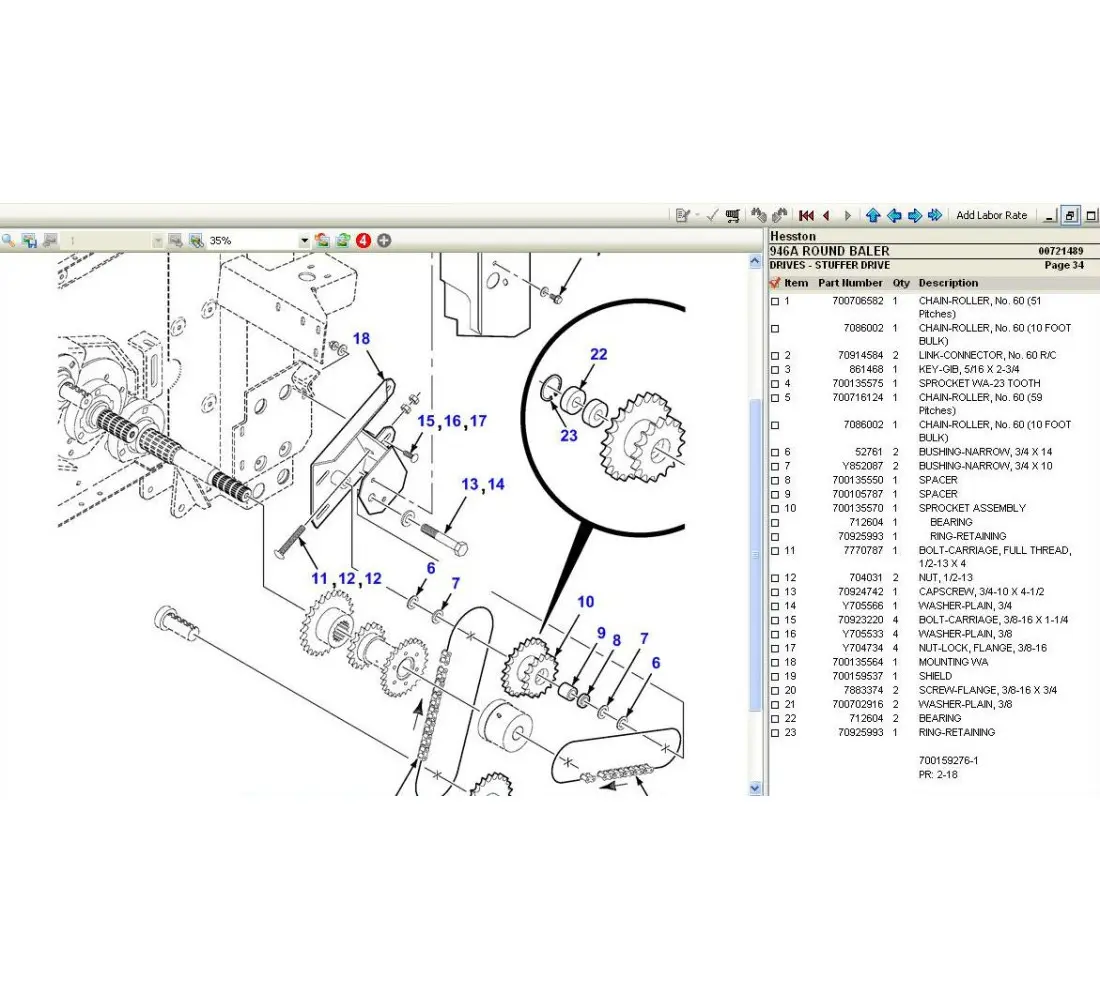
Roller and Chain Mechanisms Explained
Roller and chain systems serve as fundamental components in various mechanical applications, providing efficient movement and transmission of power. These mechanisms are designed to convert rotational motion into linear movement, ensuring seamless operation across a range of machinery. Their structure typically involves interlinked components that facilitate reliable and smooth functioning, making them essential in agricultural equipment and other machinery.
Understanding the Functionality
At the core of roller and chain systems lies the interplay between rollers and interconnected links. Rollers reduce friction and wear while enabling smoother movement along a designated path. As the chain engages with sprockets, it transmits torque from one part of the mechanism to another. This dynamic interaction not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of the components involved.
Applications in Machinery
These mechanisms find extensive usage in various types of machinery, particularly in sectors requiring precision and reliability. In agricultural devices, roller and chain systems contribute significantly to the efficiency of operations, ensuring that energy is effectively transferred where needed. Their versatility allows them to be adapted for different tasks, ranging from simple movements to complex operations in larger equipment.
Identifying Signs of Wear and Tear
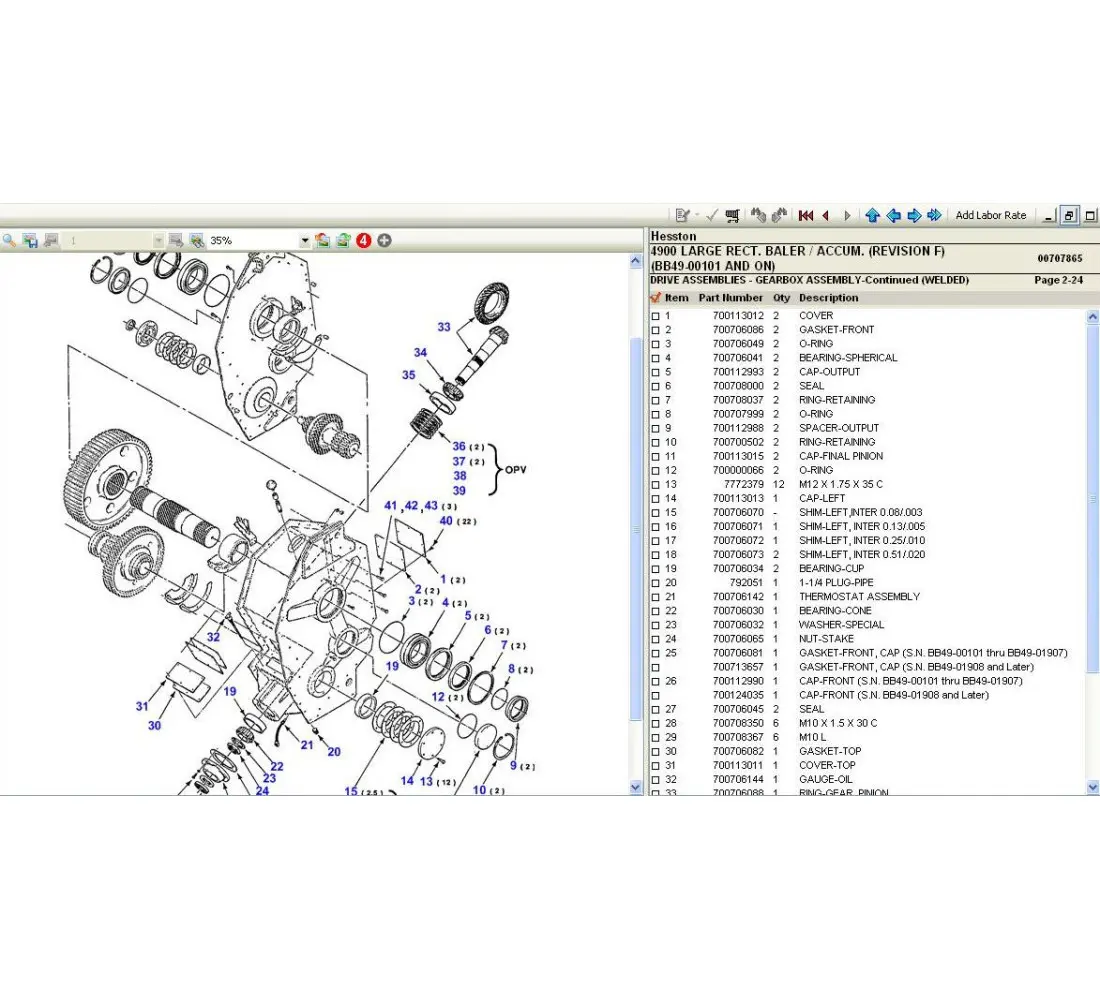
Recognizing the early indications of deterioration is essential for maintaining equipment functionality and extending its lifespan. By observing the condition of various components, operators can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure optimal performance. Regular inspections play a crucial role in detecting subtle changes that may signal the need for repair or replacement.
Common indicators of wear include unusual noises, vibrations, and changes in performance. Components may exhibit signs of rust, cracking, or discoloration, which can point to underlying issues. Additionally, any irregularities in movement or alignment can suggest that adjustments or maintenance are necessary. Proactive attention to these factors can lead to timely interventions, preserving the reliability of machinery.
It is also important to monitor fluid levels and conditions, as leaks or contamination can significantly impact overall operation. Keeping a close watch on these elements allows for early detection of potential problems. By prioritizing routine evaluations and remaining vigilant for any discrepancies, operators can effectively mitigate the risks associated with equipment wear.
Electrical Components and Wiring Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical elements and their configurations in agricultural machinery. Understanding these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal functionality and longevity of the equipment.
Key Electrical Elements
- Battery: Stores energy for starting and powering electrical systems.
- Alternator: Generates electrical power while the engine is running.
- Wiring Harness: Connects various electrical parts, facilitating power distribution.
- Fuse: Protects circuits from overload by breaking the connection if current exceeds safe levels.
- Relays: Act as switches to control higher current devices using low current signals.
Wiring Configuration Tips
- Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for wiring configurations.
- Use appropriate gauge wires to prevent overheating and ensure efficient power transfer.
- Secure connections with connectors to avoid loose contacts that can cause failures.
- Regularly inspect wiring for wear, fraying, or damage to prevent electrical issues.
- Label wires during installation or repair to simplify future maintenance.
Maintaining the integrity of the electrical systems is crucial for reliable operation. Regular checks and understanding of the components will lead to better performance and reduced downtime.
Troubleshooting Pickup and Feeding Issues

Addressing challenges with collection and feed mechanisms is essential for ensuring optimal performance of harvesting equipment. Identifying the root causes of these complications can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce downtime during operation. This section outlines common problems and potential solutions to help maintain smooth functionality.
Issue Possible Causes Solutions Poor Collection Blocked pickup tines or worn components Inspect and clean tines; replace worn parts Inconsistent Feeding Improper speed settings or uneven load Adjust speed settings and balance load Jamming Debris buildup or damaged feed rollers Clear debris and check for roller damage Uneven Crop Flow Incorrect alignment or worn drive components Realign components and replace as needed By systematically addressing these issues, operators can enhance the performance and reliability of their machinery. Regular maintenance checks and prompt attention to emerging problems will lead to improved harvesting efficiency.
Essential Spare Parts for Emergencies
In any machinery operation, having a well-stocked inventory of critical components is crucial for minimizing downtime during unforeseen events. Preparedness can significantly enhance efficiency and maintain workflow when unexpected issues arise. Understanding the importance of readily available replacements ensures smooth operations and quick resolutions.
Key elements to consider include items that are commonly subject to wear and tear. Components such as belts, bearings, and seals play a vital role in the overall functionality and performance of the machinery. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent larger issues from developing, ultimately saving time and resources.
Another category of essential replacements consists of electrical and hydraulic components, which are often the first to fail under stress. Having spare fuses, relays, and hydraulic hoses on hand can significantly reduce downtime during emergencies. Investing in a selection of these crucial components ensures that operations can swiftly resume, regardless of the situation.
Lastly, maintaining a supply of tools and maintenance equipment is equally important. Having the right instruments readily available allows for quick repairs and adjustments, facilitating immediate responses to any mechanical failures. This proactive approach to inventory management not only enhances productivity but also boosts overall reliability in operations.