
In today’s world, efficient temperature regulation is essential for comfort in both residential and commercial spaces. A thorough understanding of the various elements that contribute to this technology can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. Knowing the function and interaction of each component empowers users to ensure optimal performance.
Visual representations serve as valuable tools in comprehending the intricate relationships between these elements. By breaking down complex systems into more manageable visual guides, individuals can better grasp how each piece fits into the overall functionality. This clarity promotes effective communication and facilitates a deeper appreciation of how temperature control operates.
Furthermore, recognizing the individual roles of each segment allows for informed decision-making regarding repairs and upgrades. This knowledge not only aids in prolonging the lifespan of the system but also contributes to energy efficiency, ultimately resulting in cost savings. Thus, understanding the components and their interconnections is crucial for anyone involved in managing indoor climate solutions.
Understanding Air Conditioner Components
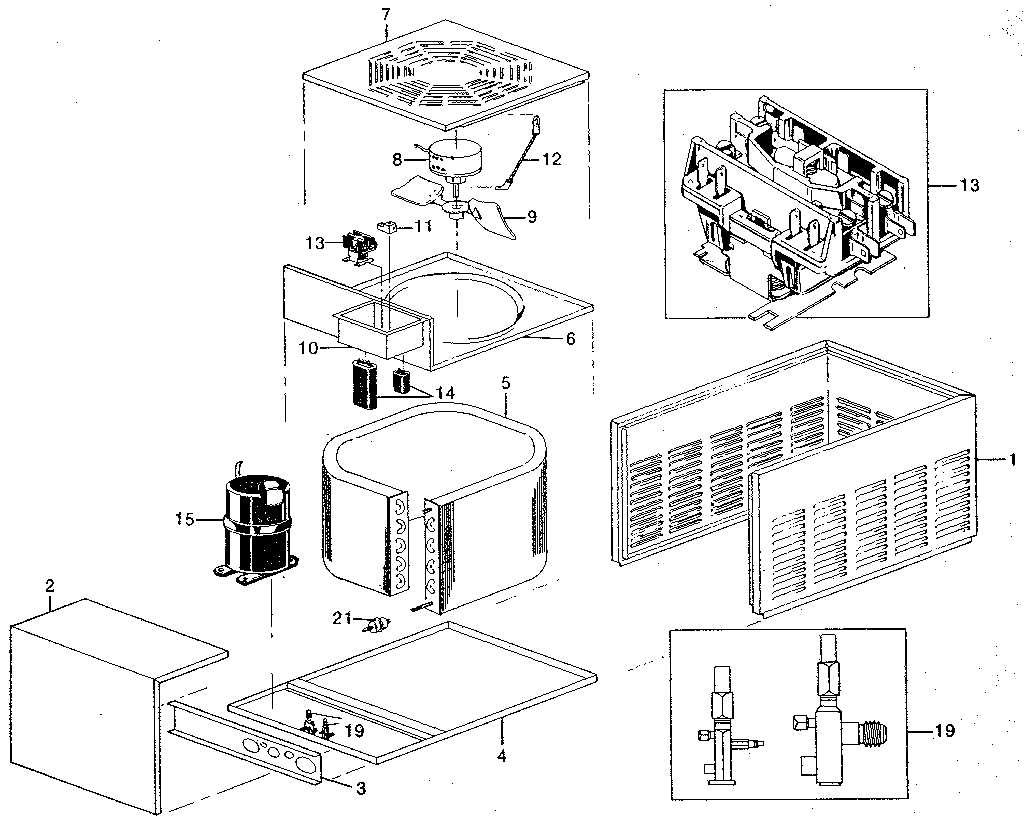
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the effective operation of a cooling system. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring comfort and efficiency. Gaining knowledge about these elements helps in better maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Elements
- Compressor: This device is responsible for circulating the refrigerant throughout the system, maintaining pressure and flow.
- Condenser: This component dissipates heat absorbed by the refrigerant, allowing it to transition back into a liquid state.
- Evaporator: Located indoors, this element absorbs heat from the surrounding air, facilitating cooling.
- Expansion Valve: This part regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, controlling the cooling process.
Supporting Components
- Fan: Essential for air circulation, this element helps distribute cooled air throughout the space.
- Filter: This accessory removes dust and debris from the air, ensuring clean airflow and maintaining system efficiency.
- Thermostat: This device monitors and regulates the desired temperature within the environment.
Essential Parts of an AC Unit
Understanding the core components of a cooling system is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring efficient performance, contributing to overall comfort in indoor environments. Familiarity with these key elements can help in troubleshooting and optimizing functionality.
Key Components
Among the main elements are the compressor, evaporator, and condenser, which work in harmony to facilitate heat exchange and maintain desired temperatures. Additionally, the expansion device is integral to the cooling cycle, regulating refrigerant flow and ensuring optimal efficiency.
Overview of Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Pumps refrigerant and increases its pressure |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the indoor environment |
| Condenser | Releases heat to the outside atmosphere |
| Expansion Device | Controls refrigerant flow and pressure |
How Air Conditioning Systems Function
The operation of climate control systems involves several key components working in harmony to provide a comfortable indoor environment. These systems are designed to manage temperature, humidity, and air quality, ensuring a pleasant atmosphere for occupants.
At the core of these systems is the refrigeration cycle, which relies on the principles of thermodynamics. A refrigerant circulates through various components, absorbing heat from the interior and expelling it outside. This process begins with the evaporator, where the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas as it absorbs heat from the surrounding air.
The gaseous refrigerant then travels to the compressor, where its pressure and temperature increase. This high-pressure gas moves to the condenser, where it releases heat and transforms back into a liquid state. Once condensed, the refrigerant returns to the expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature before re-entering the evaporator to repeat the cycle.
Throughout this process, fans and ducts facilitate the movement of air, distributing cooled or heated air effectively throughout the space. Sensors and controls monitor conditions, allowing for adjustments to maintain desired comfort levels. This intricate interplay of components ensures that occupants enjoy a stable and pleasant indoor environment.
Refrigeration Cycle Explained
The refrigeration cycle is a fundamental process that enables the transfer of heat from one location to another, thereby creating a cooler environment. This cycle involves several stages, each playing a crucial role in the overall function of the system. Understanding these stages can help in appreciating how cooling systems operate effectively.
Key Stages of the Process
At the heart of the cycle is the transformation of a refrigerant, a fluid specifically designed for this purpose. Initially, this substance absorbs heat from the surroundings, evaporating into a gas. This phase is followed by compression, where the gas is pressurized, increasing its temperature. The next step involves the condensation process, during which the gas releases the absorbed heat, reverting to a liquid state. Finally, the liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature, ready to begin the cycle anew.
Importance of Each Phase
Each stage of the refrigeration cycle is interconnected and essential for maintaining an efficient cooling effect. The absorption of heat allows the system to lower temperatures effectively, while compression and condensation ensure that the refrigerant can continue to function optimally. This harmonious operation not only enhances comfort but also contributes to energy efficiency.
Indoor and Outdoor Unit Differences
Understanding the distinctions between the internal and external components of a cooling system is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each unit has unique characteristics and functions that contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
Functionality
- Internal Unit: Primarily responsible for circulating chilled air within the space. It contains the evaporator coil, which absorbs heat from the indoor environment.
- External Unit: Essential for expelling heat absorbed from the interior. This unit houses the compressor, which increases the pressure of the refrigerant, and the condenser coil, which releases heat to the outside atmosphere.
Components
- Internal Unit:
- Evaporator coil
- Blower fan
- Filters
- External Unit:
- Compressor
- Condenser coil
- Expansion valve
Each unit plays a pivotal role in the functionality of the entire system. Understanding their differences allows for better troubleshooting, maintenance, and ultimately, a more efficient operation.
Importance of the Compressor
The compressor serves a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and functionality of cooling systems. Acting as the heart of the mechanism, it circulates refrigerant, facilitating the transfer of heat. This essential component ensures that the desired temperature is achieved and maintained, contributing to overall comfort and energy efficiency.
Without a properly functioning compressor, the entire system would be rendered ineffective. It compresses the refrigerant, raising its pressure and temperature before moving it to the condenser. This process allows for efficient heat exchange, crucial for cooling environments effectively. The reliability of the compressor directly impacts the performance and longevity of the entire system.
Moreover, regular maintenance of this component is crucial for optimal operation. Neglecting the compressor can lead to higher energy consumption and potential breakdowns, resulting in costly repairs and decreased performance. Understanding its significance allows users to appreciate the complexity and necessity of this crucial element in cooling technology.
Role of the Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil plays a crucial function in cooling systems, facilitating the transfer of heat from the surrounding environment to the refrigerant within. This component is essential for the efficient operation of the entire system, as it creates a cold surface that absorbs heat effectively.
When warm air passes over the coil, the refrigerant inside absorbs the heat, causing it to evaporate and transform into a gas. This process lowers the temperature of the air that circulates back into the space, providing comfort and relief from heat. Additionally, the evaporator coil helps maintain optimal humidity levels, enhancing indoor air quality by removing excess moisture.
Regular maintenance of the evaporator coil is vital to ensure its longevity and efficiency. Any buildup of dirt or debris can hinder its ability to absorb heat, leading to reduced performance and increased energy consumption. Thus, keeping this component clean and in good working order is essential for the overall effectiveness of the cooling mechanism.
Condenser Coil: Key Functions
The condenser coil serves a vital role in the overall functioning of a cooling system. Its primary objective is to facilitate the release of heat absorbed from the surrounding environment, thus maintaining optimal temperatures within the designated area. This component efficiently converts refrigerant vapor back into liquid form, enabling the entire cycle to proceed smoothly.
Heat Dissipation: One of the main responsibilities of the condenser coil is to dissipate heat. As the refrigerant passes through the coil, it releases the heat it has gathered, allowing the fluid to cool down. This process is essential for the system’s efficiency and effectiveness.
Phase Change: The coil also plays a crucial role in the phase change of the refrigerant. As the vaporized refrigerant flows through the coil, it loses heat and transitions into a liquid state. This phase change is fundamental for the refrigeration cycle, ensuring the proper functioning of the overall system.
Pressure Regulation: Additionally, the condenser coil helps in regulating the pressure of the refrigerant. By controlling the flow and temperature of the fluid, it ensures that the system operates within the required pressure range, optimizing performance and preventing potential damage.
In summary, the condenser coil is indispensable in maintaining the functionality and efficiency of cooling systems. Its ability to dissipate heat, facilitate phase changes, and regulate pressure significantly contributes to the effectiveness of the entire operation.
Thermostat’s Role in Temperature Control
The thermostat serves as a critical component in managing and regulating the environment’s thermal conditions. It plays a vital part in ensuring that a comfortable atmosphere is maintained within a given space by responding to temperature fluctuations.
This device operates based on the principle of sensing and adjusting the surrounding temperature, which enables it to perform several essential functions:
- Monitoring: The thermostat continuously tracks the current temperature, providing real-time data for adjustments.
- Regulating: Upon detecting changes in temperature, it activates or deactivates the system to achieve the desired level of warmth or coolness.
- Energy Efficiency: By maintaining optimal conditions, the thermostat helps to minimize energy consumption, leading to reduced utility costs.
- User Control: Many models allow users to set specific temperatures, offering customizable comfort based on individual preferences.
Ultimately, the thermostat not only enhances comfort but also promotes energy conservation, making it an indispensable element in maintaining a pleasant indoor environment.
Significance of the Expansion Valve
The expansion valve plays a crucial role in the efficiency and performance of cooling systems. Its primary function is to regulate the flow of refrigerant, ensuring optimal operation and energy consumption. This component is essential for maintaining the desired temperature and enhancing the overall functionality of the system.
Key reasons for the importance of the expansion valve include:
- Flow Regulation: It controls the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator, which directly impacts the system’s cooling capacity.
- Pressure Management: By lowering the pressure of the refrigerant, it facilitates the phase change from liquid to gas, maximizing heat absorption.
- Energy Efficiency: A well-functioning expansion valve optimizes the cooling cycle, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs.
- System Protection: It prevents excessive refrigerant flow, which can cause damage to other components and lead to system failure.
In conclusion, the expansion valve is vital for the efficient operation of cooling systems. Its role in regulating refrigerant flow and pressure significantly influences the performance and longevity of the overall setup.
Air Filters: Maintenance and Function
Filters play a crucial role in the efficiency and longevity of climate control systems. They are designed to trap dust, allergens, and other particles, ensuring clean airflow. Regular upkeep of these components is vital for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Proper maintenance of filtration elements enhances not only air quality but also the overall system functionality. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved indoor air quality by reducing pollutants.
- Enhanced energy efficiency, leading to lower utility bills.
- Extended lifespan of the entire system.
- Prevention of system malfunctions and costly repairs.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure optimal operation, follow these maintenance guidelines:
- Check filters monthly, especially during peak usage seasons.
- Replace or clean disposable filters as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Consider using high-efficiency filtration for better particle capture.
- Keep the surrounding area clean to minimize dirt entry.
By adhering to these practices, users can significantly enhance the functionality and efficiency of their climate control systems.
Electrical Components Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the vital electrical elements that contribute to the operation of a cooling system. Understanding these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, as they play a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality.
Key components include various switches, sensors, and relays that facilitate the system’s performance. Each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall efficiency of the unit. Below is a summary of these essential elements:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Regulates temperature by controlling the cooling cycle. |
| Capacitor | Stores electrical energy and assists in starting motors. |
| Compressor | Pumps refrigerant through the system and maintains pressure. |
| Relay | Controls the electrical flow to various components. |
| Fan Motor | Circulates air within the system and promotes heat exchange. |
Each of these elements works together to ensure the efficient operation of the entire system, highlighting the importance of regular inspections and maintenance for long-term reliability.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Understanding typical challenges associated with climate control systems can significantly enhance their performance and longevity. Identifying symptoms early and applying the correct solutions can prevent extensive damage and costly repairs. Below are frequent problems users may encounter along with practical guidance to address them.
| Issue | Possible Causes | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient cooling | Low refrigerant, blocked filters, or dirty coils | Check and replace filters, clean coils, and verify refrigerant levels. |
| Noisy operation | Loose components or debris in the system | Tighten any loose parts and remove debris from the unit. |
| Frequent cycling | Incorrect thermostat settings or dirty sensors | Adjust thermostat settings and clean or replace sensors as needed. |
| Unpleasant odors | Mold or mildew growth, or debris accumulation | Clean the system thoroughly and consider using a dehumidifier. |
| Water leaks | Clogged drainage system or damaged components | Inspect drainage for blockages and check for any damaged parts. |