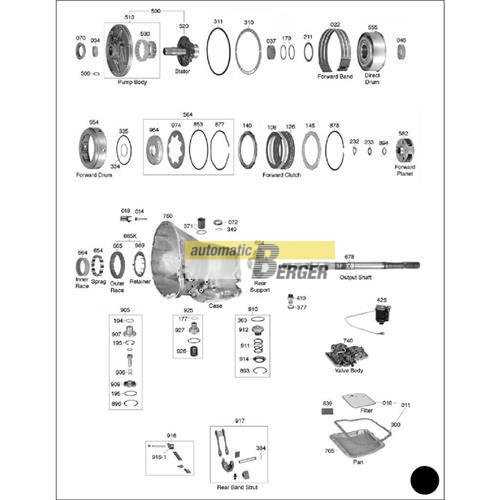
The intricate system of modern transmissions relies on a variety of interconnected elements that ensure smooth operation and durability. Understanding the structure and organization of these essential components provides valuable insights for maintenance and repair.
Detailed visual layouts are key tools for identifying individual elements and their placement within the transmission system. Such representations assist technicians and enthusiasts alike in recognizing potential issues and planning upgrades or replacements effectively.
Each component serves a distinct purpose in the seamless transfer of power, from input mechanisms to control modules. A clear understanding of these systems allows for more efficient troubleshooting and ensures optimal performance under various conditions.
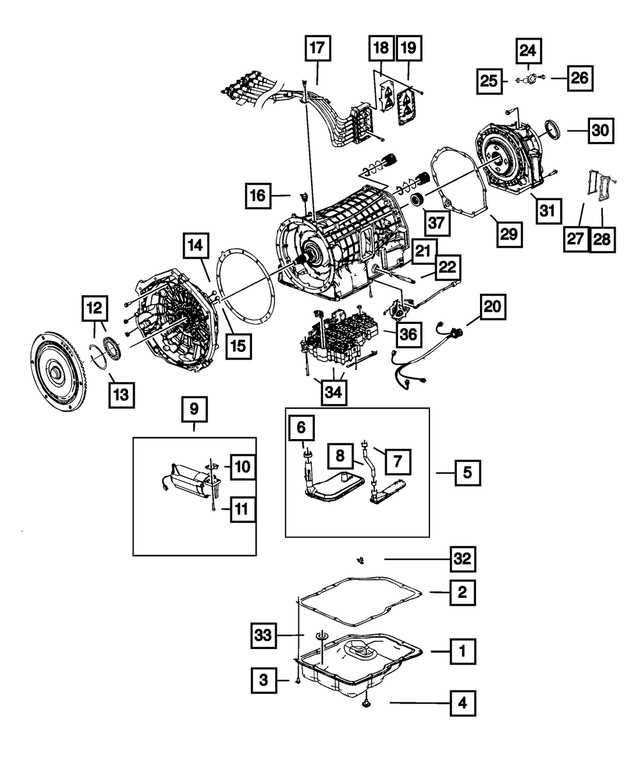
Allison 1000 Parts Diagram
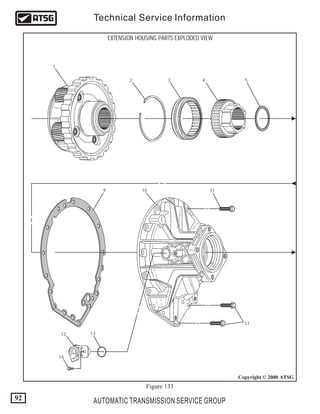
A detailed view of the internal components provides valuable insights into how the system operates. Understanding the arrangement and function of each element is essential for maintenance, troubleshooting, and ensuring smooth operation.
The structure consists of various interconnected modules, each playing a specific role. These elements are designed to work together seamlessly, ensuring efficient power transfer and reliable performance under different conditions.
Key assemblies include control units, fluid circuits, and mechanical linkages. Proper synchronization among these segments is critical to maintaining peak efficiency. Regular inspections of the individual sections help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Each segment serves a unique purpose, contributing to the system’s overall durability and adaptability. Mastering the layout of the internal setup is a crucial step in performing timely repairs and optimizing functionality.
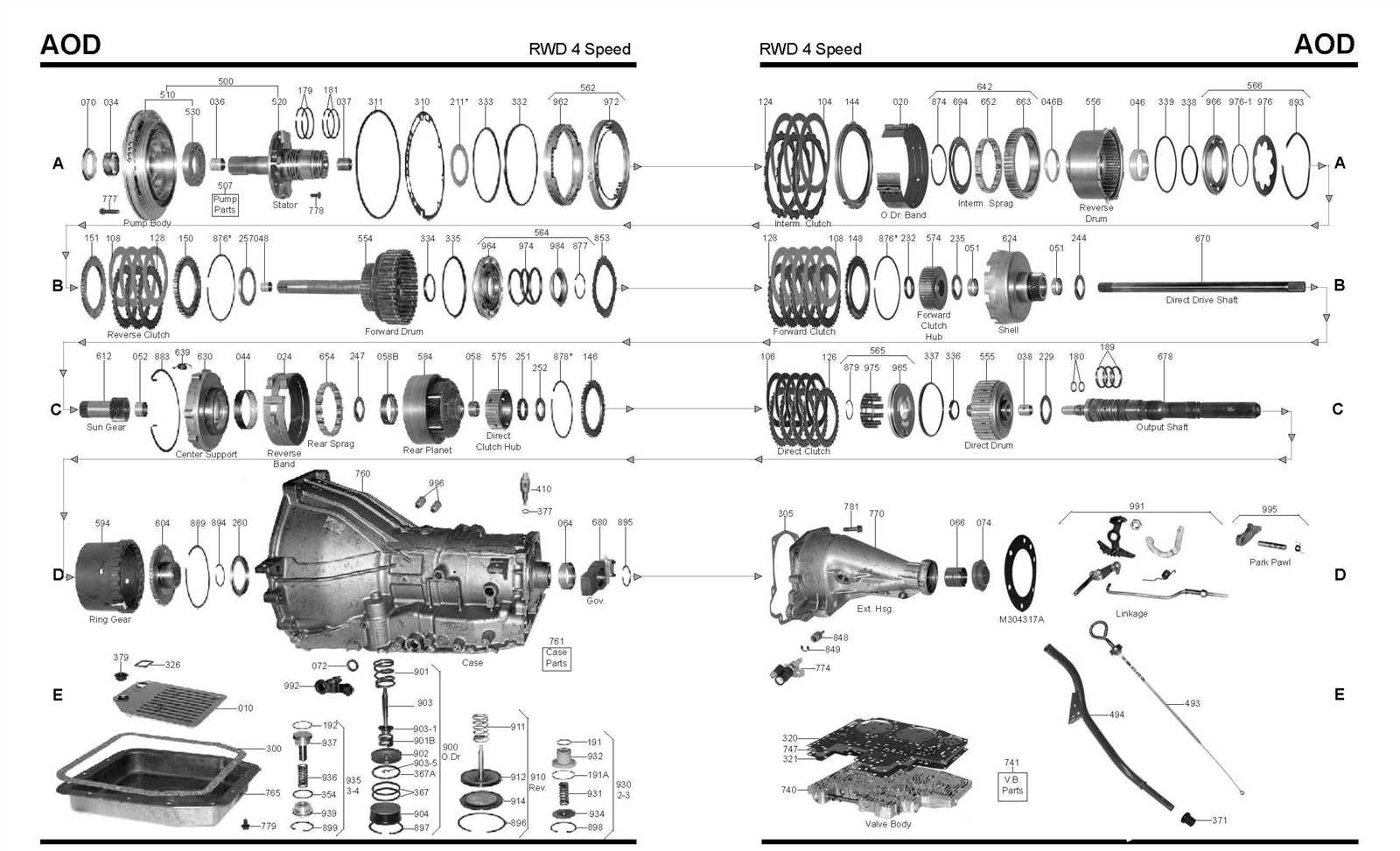
Transmission Assembly Overview
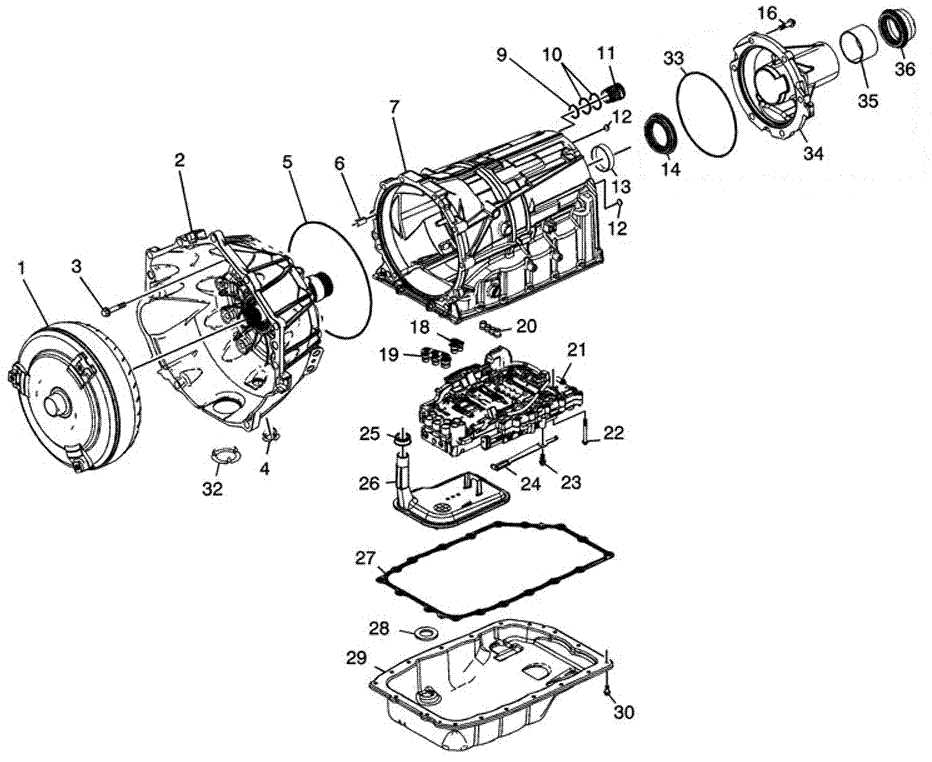
The transmission assembly ensures efficient power delivery from the engine to the drivetrain, enabling smooth gear transitions and optimized performance across various driving conditions. This complex system integrates multiple interconnected components, each contributing to the seamless operation of the vehicle.
Main Components and Functions
- Torque Converter: Acts as a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission, allowing the engine to rotate independently of the transmission during idling.
- Planetary Gear Sets: Provide different gear ratios, facilitating smooth acceleration and deceleration.
- Valve Body: Directs hydraulic fluid to various clutches and brakes, managing gear shifts automatically.
- Clutch Packs and Bands: Control the engagement of gears to maintain proper transmission operation.
Maintenance Considerations
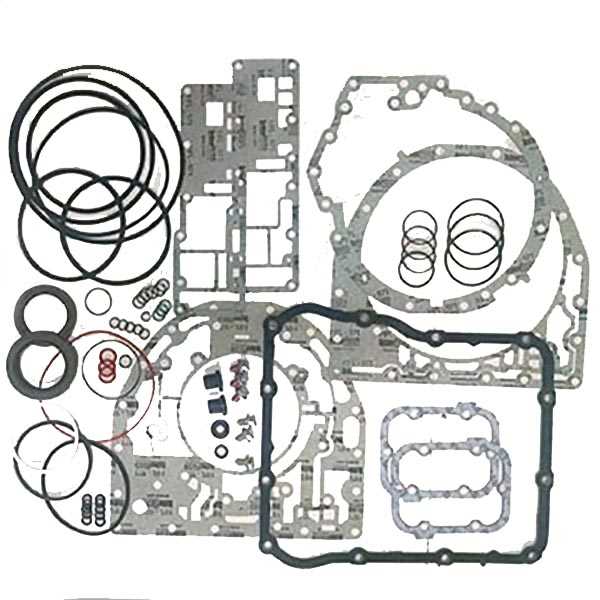
- Regular fluid checks and replacements ensure
Main Components and Their Functions
This section focuses on the essential elements that contribute to the smooth and efficient operation of a transmission system. Understanding the role of each component ensures better maintenance and performance management.
Key Mechanical Elements
- Torque Converter: Transfers engine power to the transmission, allowing smooth acceleration and deceleration.
- Planetary Gears: Control speed and torque by engaging different gear ratios as needed.
- Pump: Circulates transmission fluid to keep the system lubricated and cool.
- Valve Body: Acts as the control center, directing fluid flow to manage gear shifts.
Electronic Control Components
- Control Module: Processes signals from sensors to regulate gear shifts and optimize performance.
- Solenoids:
Fluid Flow and Circuit Paths
Understanding how fluids move through interconnected channels and control circuits is essential for maintaining optimal system performance. The proper distribution of hydraulic or transmission fluids ensures smooth operation by reducing friction and regulating pressure across various components.
Key Flow Channels and Routes
Fluid travels through designated pathways that control pressure levels and direct movement between essential modules. These paths are precisely engineered to ensure balanced flow, avoiding blockages or pressure build-up that could lead to operational failures.
Main Control Functions and Circuits
The fluid circuit system relies on valves, pumps, and sensors to monitor and adjust the flow rate according to real-time needs. This regulation helps maintain consistent output by rerouting fluids as needed to different sections of the machinery.
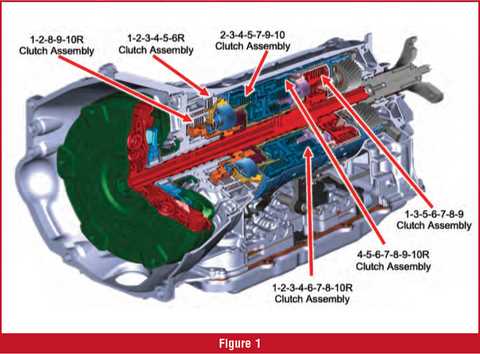
Component Function Clutch Pack Arrangement
The configuration of clutch packs plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth gear transitions and efficient torque distribution. Proper alignment and sequencing of friction and steel plates within these assemblies contribute to the transmission’s ability to handle varying loads and speeds.
Component Description Friction Plate Provides the necessary grip to transfer torque while engaging gears. Steel Plate Maintains structural integrity and ensures even pressure distribution. Piston Applies hydraulic pressure to compress the plates for smooth engagement. Return Spring Facilitates disengagement by releasing pressure when shifting is complete. Sealing Ring Prevents hydraulic fluid leakage and ensures consistent pressure levels. Torque Converter Breakdown
The torque converter is a vital component in the transmission system, responsible for transferring engine power to the drivetrain. It serves as a hydraulic coupling, enabling smooth acceleration and deceleration while allowing the engine to run at an optimal speed. Understanding the inner workings of this device can help diagnose performance issues and facilitate effective maintenance.
Components of a Torque Converter
A torque converter consists of several essential parts that work together to ensure efficient power transfer. Each component plays a crucial role in the converter’s functionality, contributing to overall vehicle performance.
Component Description Stator Redirects fluid returning from the turbine to improve efficiency. Turbine Transmits power from the engine to the transmission by converting hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. Impeller Draws in fluid from the transmission and converts it into rotational energy. Lock-Up Clutch Engages at higher speeds to create a direct connection between the engine and the transmission. Functionality and Benefits
The torque converter allows for smooth gear shifts and enhances fuel efficiency by reducing engine load during acceleration. Additionally, it compensates for variations in engine speed, ensuring consistent power delivery to the wheels. By understanding the structure and purpose of each part, vehicle owners can better appreciate the importance of this hydraulic component in their vehicles.
Valve Body Structure
The valve body serves as a crucial component within automatic transmission systems, playing a vital role in the regulation and distribution of hydraulic pressure. This structure houses a network of valves that direct fluid flow, ultimately influencing the shifting process and overall performance of the transmission.
Components Overview
At its core, the valve body comprises various elements, including valves, channels, and gaskets. Each of these parts works collaboratively to manage the hydraulic pressure essential for gear changes. Valves act as gates, controlling the passage of fluid based on the transmission’s operational needs, while channels provide the pathways through which the fluid travels.
Functionality and Importance
Proper functionality of the valve body is critical for maintaining smooth gear transitions and optimizing engine performance. An efficient valve body ensures that the hydraulic pressure is applied accurately, reducing wear on other components and enhancing the longevity of the entire system. Thus, understanding its structure and function is key to diagnosing potential issues and ensuring effective maintenance.
Electrical Connections and Sensors
The integration of electrical connections and sensors is crucial for the optimal functioning of modern transmission systems. These components play a vital role in monitoring various parameters and ensuring seamless communication between different systems. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these connections is essential for effective diagnostics and maintenance.
Types of Sensors

Sensors utilized in transmission systems can be categorized based on their function and measurement capabilities. Common types include speed sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors. Each type serves a distinct purpose, providing critical data that aids in the performance analysis and decision-making processes of the vehicle’s operation.
Importance of Electrical Connections
Reliable electrical connections are fundamental for the accurate transmission of signals between sensors and control units. Properly configured connections ensure that data is transmitted without interference, facilitating real-time adjustments to optimize performance. Regular inspections and maintenance of these connections are necessary to prevent malfunctions and enhance overall system reliability.
Cooling System Integration
The integration of a cooling system is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of transmission systems. This component plays a critical role in regulating temperatures, thereby preventing overheating and maintaining efficient operation.
Effective cooling solutions encompass various elements that work together seamlessly. Key components of the cooling system include:
- Radiators
- Coolant pumps
- Thermostats
- Cooling lines
Each of these parts contributes to the overall functionality:
- Radiators: Dissipate heat from the fluid, ensuring that the system operates within a safe temperature range.
- Coolant Pumps: Circulate the cooling fluid throughout the system, facilitating efficient heat transfer.
- Thermostats: Regulate the flow of coolant based on temperature, helping maintain the ideal operating conditions.
- Cooling Lines: Transport the coolant between various components, ensuring a continuous flow of heat exchange.
Proper integration of these elements is vital for maximizing efficiency and preventing failures. Regular maintenance and inspection of the cooling system can significantly enhance reliability and performance in demanding conditions.
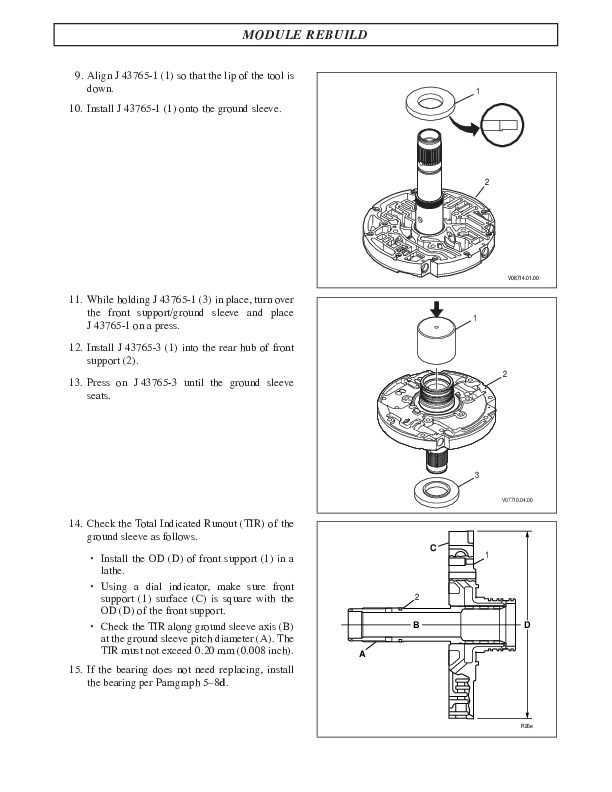
Common Wear Points and Repairs

Understanding the typical areas of wear and potential repairs is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality in automatic transmission systems. Certain components are more prone to degradation over time due to constant use and exposure to varying conditions. Identifying these wear points can lead to proactive measures that enhance longevity and performance.
Frequent Areas of Concern
Several key components require attention, as they often experience significant stress. Among these are clutches, seals, and valve bodies, which play essential roles in the system’s operation. Regular inspections can help detect early signs of wear, allowing for timely interventions.
Recommended Repair Strategies
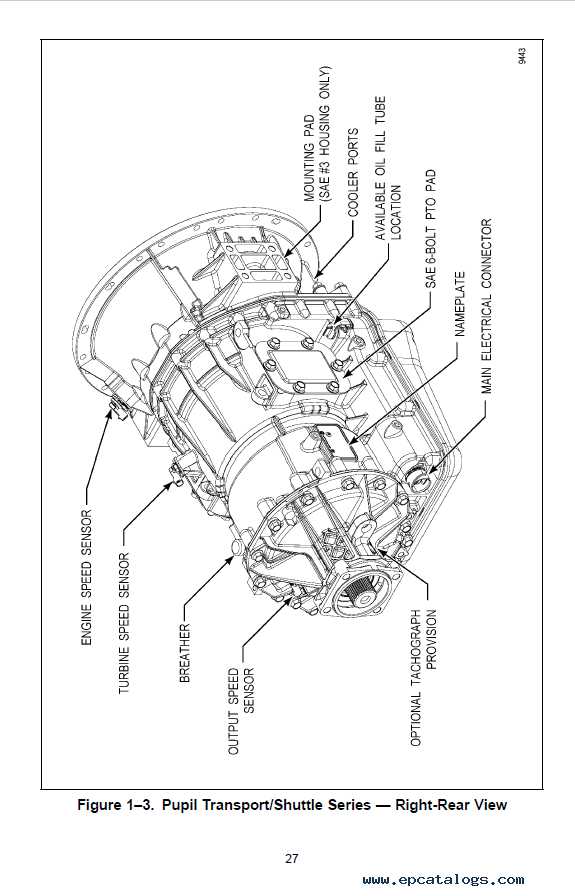
Addressing wear effectively often involves replacement or rebuilding of affected parts. Utilizing quality components for repairs can restore functionality and improve reliability. Additionally, performing routine maintenance checks can prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures.
Component Common Issue Recommended Action Clutch Plates Slipping or grabbing Replace or resurface Seals Leaks Replace Valve Body Shifting problems Rebuild or replace Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure optimal performance and extended lifespan of your machinery, regular upkeep is essential. Implementing effective maintenance practices can prevent unexpected failures and enhance overall efficiency. This section outlines key recommendations to help you maintain your equipment in peak condition.
Routine Inspections
Conducting frequent checks is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of wear, leaks, or unusual noises. Early detection can save you time and money in the long run.
Fluid Management
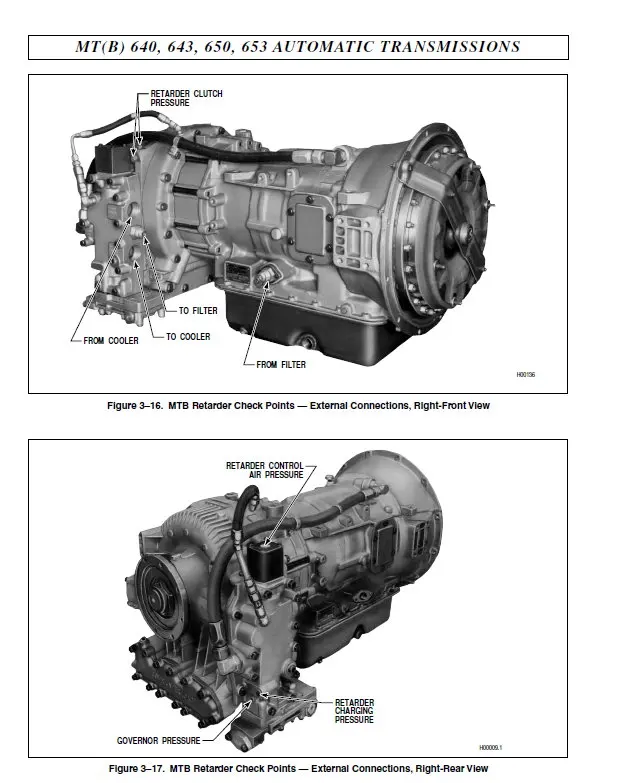
Proper fluid management is vital for ensuring smooth operation. Regularly check and replace fluids as recommended by the manufacturer. Maintaining the correct fluid levels helps to lubricate components effectively and reduces friction, which can lead to wear and tear.