
Delving into the intricate world of vintage timekeeping instruments reveals a fascinating array of elements that work harmoniously to mark the passage of time. Each segment plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal of these remarkable devices. Appreciating the complexity of these mechanisms enriches our understanding of historical craftsmanship and innovation.
In this section, we will explore the various components that make up these remarkable creations. By examining the relationships and functions of each element, we can gain insights into the artistry and precision that define these mechanical wonders. Through careful study, enthusiasts can better appreciate the beauty and engineering that has transcended generations.
Whether you are a collector, restorer, or simply an admirer, understanding these components is essential for grasping the full essence of these treasured timepieces. The knowledge gained here will not only enhance your appreciation but also empower you to engage more meaningfully with the world of horological craftsmanship.
Understanding Antique Clock Components
Delving into the intricacies of timekeeping mechanisms unveils a fascinating world of craftsmanship and engineering. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to the harmonious operation of the device. An exploration of these components reveals their unique characteristics and the importance of their interaction.
Fundamentally, the structure comprises several essential elements that govern the movement and accuracy of the timepiece. Understanding these components not only enhances appreciation for their historical significance but also aids in restoration and maintenance efforts.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Movement | Drives the entire mechanism, controlling the passage of time. |
| Escapement | Regulates the movement of gears, ensuring accurate time intervals. |
| Gear Train | Transmits power from the movement to the hands, translating energy into motion. |
| Dial | Displays time, often embellished with intricate designs. |
| Winding Mechanism | Allows for the manual or automatic winding of the energy source. |
Key Elements of Clock Mechanisms
The intricate design of timekeeping devices relies on several fundamental components that work in harmony to ensure accurate measurement of time. Understanding these essential elements is crucial for anyone interested in the mechanics behind these fascinating instruments.
Movement: At the heart of any timekeeping device is the movement, which serves as the driving force. This mechanism converts energy into motion, enabling the device to track the passage of time with precision.
Gear Train: The gear train consists of a series of interlocking wheels that transmit energy from the movement to the hands. Each gear is meticulously designed to maintain the correct ratio, allowing for smooth movement and accurate readings.
Escapement: This component regulates the release of energy from the movement, controlling the speed at which the gears turn. It creates a rhythmic motion, essential for dividing time into equal segments.
Balance Wheel: The balance wheel works in conjunction with the escapement to maintain consistent timekeeping. Its oscillation ensures that the movement remains steady, preventing any discrepancies in time measurement.
Dial: The dial displays the time and is often adorned with numerals or markers. Its design can vary significantly, reflecting both functionality and artistry, and serves as the interface between the mechanism and the observer.
Understanding these key elements is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of timekeeping devices, as they collectively contribute to the overall functionality and reliability of these remarkable creations.
Types of Antique Clock Movements
The intricate mechanisms that power timekeeping devices have evolved significantly over the years. Each type of mechanism reflects the craftsmanship and technological advancements of its era, showcasing a variety of designs and functionalities.
Below are some notable categories of these mechanisms:
- Mechanical Movements: These are powered by a winding system, typically using weights or springs. They rely on gears and escapements to regulate time accurately.
- Quartz Movements: Utilizing a battery as a power source, these mechanisms offer precise timekeeping through the oscillation of quartz crystals. They are less common in historical devices but became prevalent in the 20th century.
- Weight-Driven Movements: This type employs gravity to drive the mechanism. The weights descend gradually, unwinding a cord or chain that activates the gears, making it suitable for large timekeeping structures.
- Spring-Driven Movements: These utilize a tightly coiled spring, which, when released, powers the gears. This design allows for a more compact form, often seen in smaller devices.
- Regulator Movements: Designed for accuracy, these mechanisms are often used in laboratory settings or precise timekeeping devices. They typically feature a pendulum or balance wheel for stability.
Understanding these diverse mechanisms provides insight into the artistry and engineering that define these timekeeping treasures, reflecting their historical significance and evolution over time.
Materials Used in Clock Construction
The construction of timekeeping devices involves a variety of materials that contribute to their functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Each element serves a distinct purpose, influencing both the performance and the overall design. Understanding these materials provides insight into the craftsmanship and engineering behind these intricate mechanisms.
Traditionally, the selection of materials has been guided by their properties, availability, and the desired characteristics of the final product. The interplay of different substances not only affects the mechanical efficiency but also enhances the visual elements, making these devices both practical and beautiful.
| Material | Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Corrosion-resistant, malleable | Gear wheels, movement components |
| Steel | Strong, durable | Pinions, levers |
| Wood | Natural beauty, insulation | Cases, decorative elements |
| Glass | Transparent, fragile | Faces, protective coverings |
| Plastic | Lightweight, versatile | Modern casings, dials |
By blending these diverse materials, artisans create unique pieces that not only measure time but also tell stories of their craftsmanship and the era in which they were made. The careful choice of substances reflects both the technical requirements and the aesthetic aspirations of the makers.
Functions of Clock Gears Explained
The intricate mechanisms found within timekeeping devices play a crucial role in their overall functionality. Understanding how these components interact reveals the complexity behind measuring and displaying time. Each element contributes uniquely to the seamless operation of the entire system.
Here are some primary functions of these essential components:
- Power Transmission: Gears facilitate the transfer of energy from one part to another, ensuring that the entire system operates smoothly.
- Speed Regulation: By varying the size and arrangement of the gears, manufacturers can control the speed at which the mechanism moves, allowing for accurate timekeeping.
- Direction Change: Gears can alter the direction of movement, allowing for the synchronization of various elements within the device.
- Force Multiplication: A smaller gear can turn a larger gear, amplifying force and enhancing the efficiency of the mechanism.
In conclusion, the interplay of these functions ensures that the timepiece operates effectively, showcasing the remarkable ingenuity behind its design.
Recognizing Different Clock Faces
The variety of timekeeping dials can be quite fascinating, as each design reflects unique styles and functionality. Identifying these displays is essential for enthusiasts and collectors alike, as it can enhance appreciation for the craftsmanship involved.
One common type is the analog face, which features hour and minute hands moving around a circular background. These often include numerals or markers to indicate the passage of time. In contrast, digital displays present time in a numerical format, offering a modern touch and often more straightforward readability.
Some designs incorporate ornamental elements, such as floral motifs or geometric patterns, enhancing aesthetic appeal. Additionally, multi-functional faces may show not only time but also additional information, such as date or weather conditions, showcasing the evolution of timekeeping technology.
Lastly, it is important to consider the historical context of these faces, as different periods favored specific styles and materials. Understanding these variations can lead to a deeper appreciation for the artistry and innovation behind each timekeeping device.
Importance of Pendulums in Clocks
Pendulums play a crucial role in the functionality and accuracy of timekeeping devices. Their unique design allows for a consistent swing, which contributes to the precise measurement of time. By maintaining a steady rhythm, these components ensure that the entire mechanism operates smoothly and reliably.
Mechanics of Time Measurement
The oscillation of a pendulum serves as a natural regulator in timekeeping mechanisms. This rhythmic movement establishes a predictable interval that translates into the passage of time. The longer the swing, the more accurate the timing, making the length of the pendulum essential in achieving optimal performance.
Influence on Design and Innovation
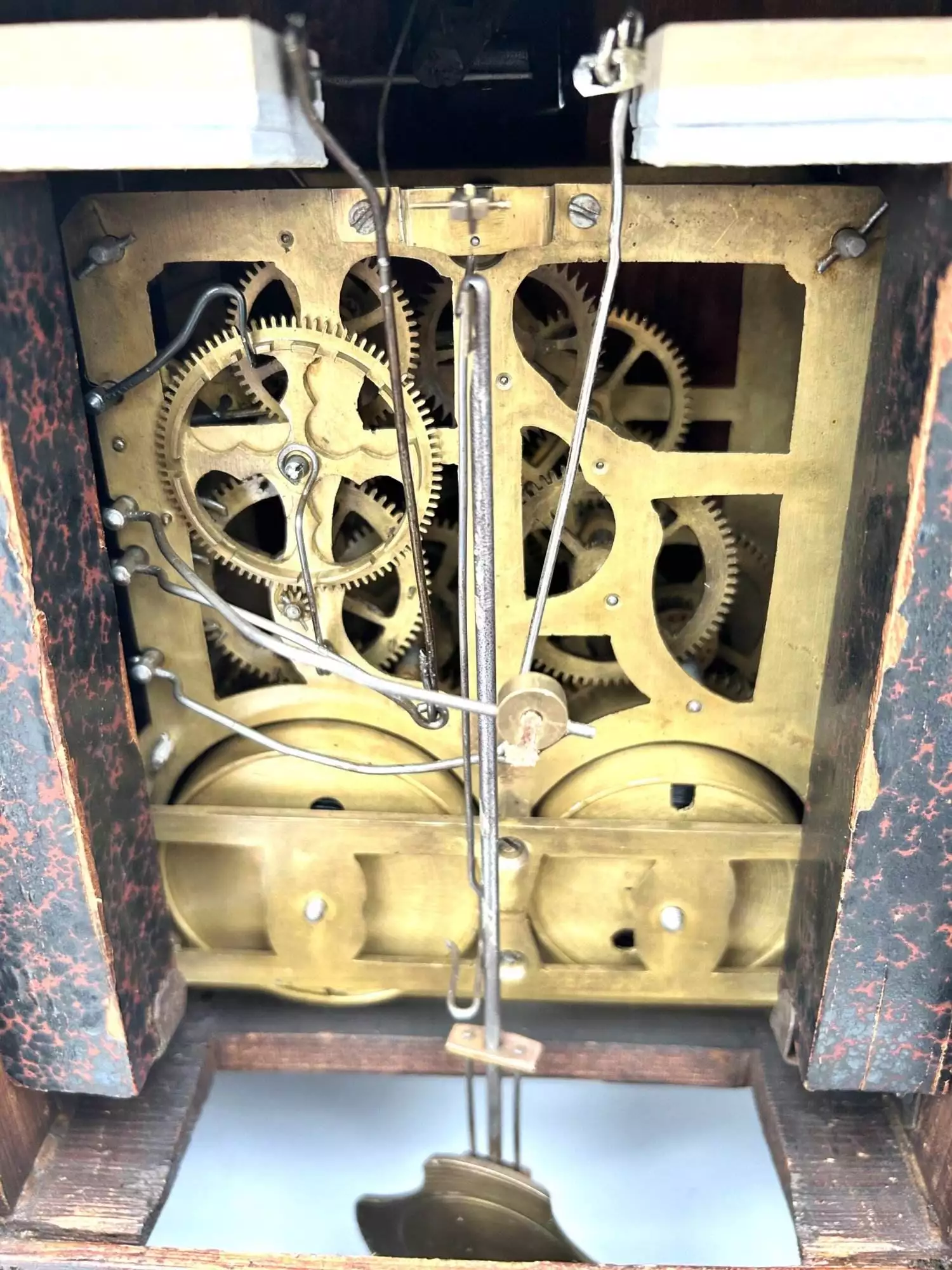

Throughout history, the incorporation of pendulums has significantly influenced the evolution of timekeeping devices. Their introduction marked a turning point in engineering, prompting innovations that enhanced accuracy and reliability. This development not only improved existing designs but also paved the way for new creations in horology.
How to Identify Clock Hands
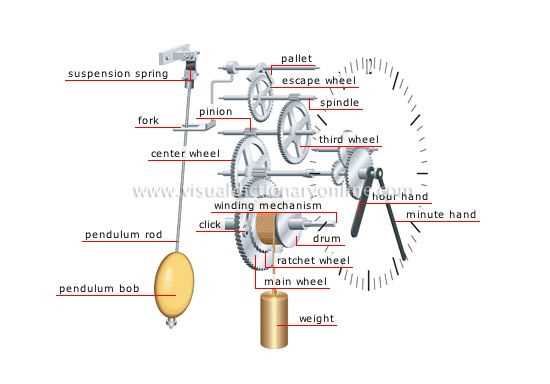
Recognizing the components that indicate time on a timekeeping device is essential for maintenance and restoration. These elements, crucial for functionality, vary in design and size, influencing both aesthetic appeal and precision. Understanding their characteristics can significantly aid in repairs and replacements.
Typically, there are three primary indicators used to show the hours, minutes, and sometimes seconds. Each type has unique features that differentiate them from one another. Below is a table outlining common types of indicators, along with their distinguishing attributes.
| Indicator Type | Length | Shape | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hour Indicator | Short | Thick | Metal, Wood |
| Minute Indicator | Longer | Thin | Metal, Brass |
| Second Indicator | Very Long | Fine | Metal, Plastic |
By familiarizing yourself with these features, you can more easily identify the components responsible for displaying time, enhancing your understanding and capability in caring for such devices.
Understanding the Role of Escapements
Escapements play a crucial part in the functionality of timekeeping devices, acting as the mechanism that regulates the release of energy. Their primary function is to maintain a consistent flow of power, which is essential for accurate measurement. This component serves as the bridge between the drive mechanism and the timekeeping element, ensuring that the movement operates smoothly and effectively.
How Escapements Work
The operation of escapements relies on a delicate balance of forces. They interact with the gear system to control the speed at which energy is released. By doing so, they allow for precise time intervals to be measured, which is fundamental to the overall performance of the mechanism. The intricate design of these components ensures that the mechanism functions reliably over extended periods.
Types of Escapements
Various designs of escapements exist, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Some of the most notable types include:
| Type | Characteristics | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor Escapement | Simple design, used widely in traditional devices | Reliable and easy to maintain |
| Swiss Lever Escapement | Precision engineering, allows for greater accuracy | Ideal for high-quality timekeeping |
| Detent Escapement | Used in marine chronometers, offers stability | Excellent for navigation and accuracy in harsh conditions |
Exploring the Dial and Its Features
The face of a timekeeping device serves as a crucial interface between the mechanism and the user. This component not only displays the passage of time but also embodies the craftsmanship and aesthetic elements of its era. Understanding its characteristics can enhance appreciation for its design and functionality.
One of the most striking features of the dial is the arrangement of numerals or markers, which indicate the hours and sometimes minutes. These indicators may vary in style, from elegant Roman numerals to simple Arabic digits, reflecting the cultural influences of the time. Additionally, the material and finish of the dial can greatly affect its visual appeal, with options ranging from polished metals to intricate painted surfaces.
Another important aspect is the presence of decorative elements such as patterns or motifs, which can tell a story about the period in which the timekeeping device was crafted. Some faces incorporate unique features like sub-dials, which may indicate secondary functions, while others showcase exquisite craftsmanship in their hands or embellishments.
Furthermore, the protective cover, typically made of glass or crystal, plays a vital role in safeguarding the dial from dust and damage. The clarity and quality of this material can enhance the overall aesthetic, allowing for unobstructed views of the intricate details beneath.
In summary, examining the face of a timekeeping device reveals a wealth of information about its design, craftsmanship, and historical context. Each element, from the numeral layout to decorative touches, contributes to the overall character and charm of this fascinating component.
Common Issues with Clock Parts
When dealing with timekeeping mechanisms, various complications can arise that affect their functionality. Understanding these issues can help in maintaining the precision and longevity of these intricate devices. Below are some frequent challenges that enthusiasts may encounter.
1. Mechanical Malfunctions
One of the primary concerns involves mechanical failures that can disrupt the flow of time. This can occur due to a buildup of dust or grime, which may hinder the smooth operation of gears and levers. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent such obstructions. Additionally, worn-out components may require replacement to restore accurate timekeeping.
2. Power Source Issues
Another common problem relates to the energy supply. Whether powered by a battery or a winding mechanism, any irregularities in the power source can lead to inconsistent performance. Ensuring that batteries are fresh or that the winding mechanism is functioning correctly is crucial for optimal operation. A careful inspection of connections and potential leaks is advisable to avoid power-related disruptions.
Maintenance Tips for Antique Clocks
Caring for historical timepieces requires attention and understanding of their unique mechanisms. Regular upkeep not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also ensures their longevity. Here are some essential practices to maintain these cherished relics effectively.
Regular Cleaning

Dust and debris can accumulate within the intricate workings of these timekeepers, affecting their performance. Utilize a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe the exterior surfaces. For the internal components, it is advisable to consult a professional who specializes in vintage mechanisms, as improper cleaning can lead to damage.
Humidity and Temperature Control
Environmental factors significantly influence the condition of these delicate devices. Maintain a stable climate, avoiding extreme fluctuations in temperature and humidity. Ideally, the surroundings should be kept at a consistent level, as excessive moisture can cause wood to warp and metals to corrode.
Resources for Clock Restoration
Restoring timepieces can be an enriching pursuit, combining historical appreciation with practical skills. Various resources are available for enthusiasts, ranging from literature and online communities to specialized workshops and suppliers. These tools can aid in understanding the intricacies of mechanisms and techniques necessary for successful restoration.
Literature and Guides
Books and manuals focusing on restoration techniques serve as essential references for those seeking to deepen their knowledge. They often cover topics such as disassembly, cleaning, and reassembly, providing step-by-step instructions that help beginners and experienced restorers alike. Additionally, these texts may include illustrations and case studies that offer valuable insights into different restoration challenges.
Online Communities and Forums
Engaging with online platforms allows restorers to connect with others who share their passion. Forums and social media groups provide spaces for exchanging ideas, asking questions, and sharing experiences. These communities can be incredibly supportive, offering advice and encouragement while helping individuals navigate the complexities of restoring intricate timekeeping devices.