Understanding the internal structure of maintenance tools is crucial for ensuring their proper function and longevity. Each element in the machinery plays a specific role, and knowing how these elements interact can simplify troubleshooting and upkeep. A detailed layout provides a visual representation of the various mechanisms involved, making it easier to identify and replace faulty components.
Having a clear map of the inner workings allows users to perform maintenance with greater efficiency. Whether you are dealing with electrical systems, pneumatic setups, or mechanical assemblies, each section of the device serves a critical function. Proper knowledge of these systems ensures that repairs are carried out smoothly, minimizing downtime.
Without the right reference, even minor issues can become complicated. A well-organized diagram helps to streamline the repair process, guiding users to the correct parts. By familiarizing yourself with the equipment’s layout, you can ensure timely interventions and better performance over time.
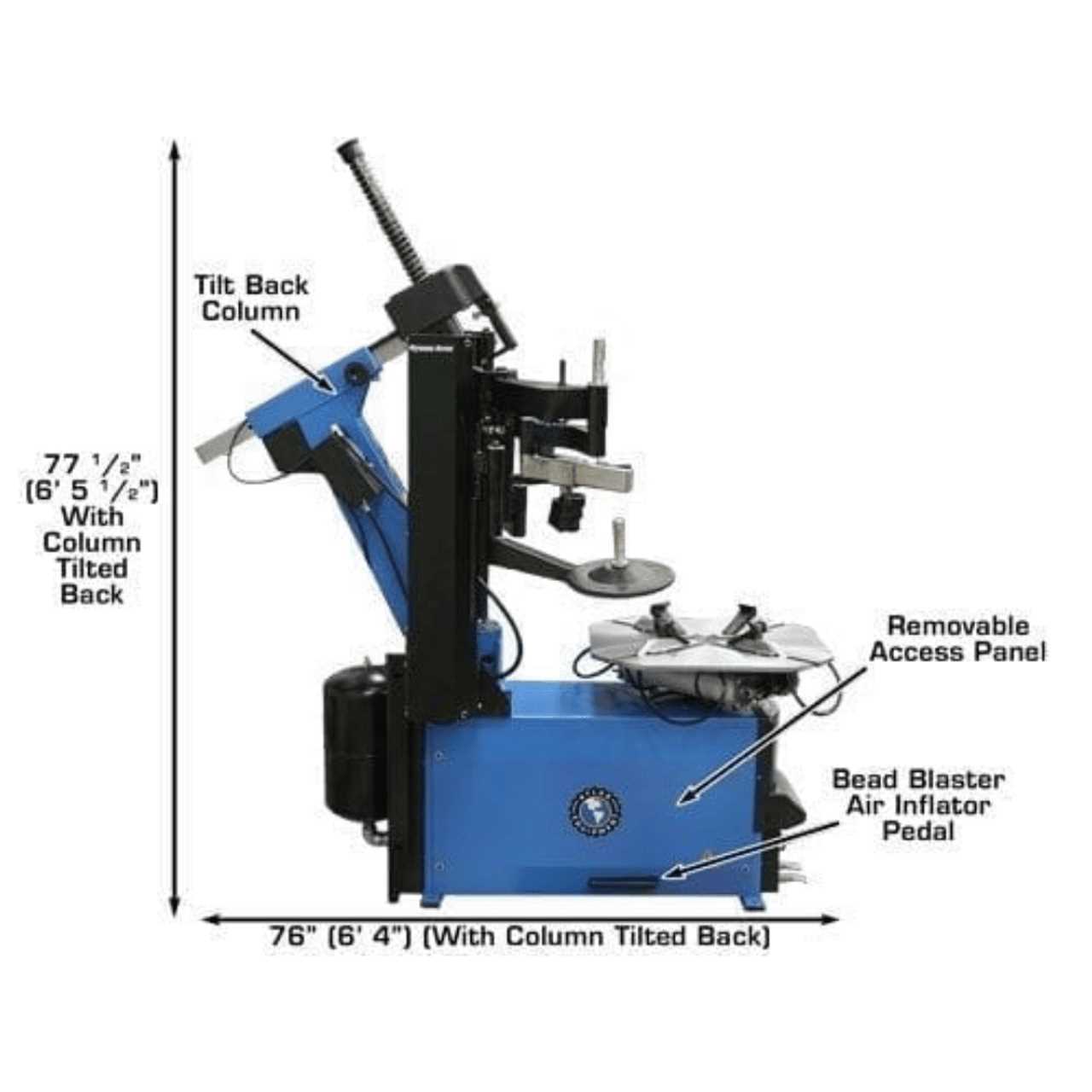
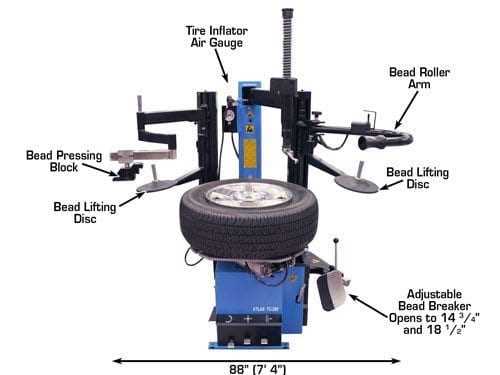
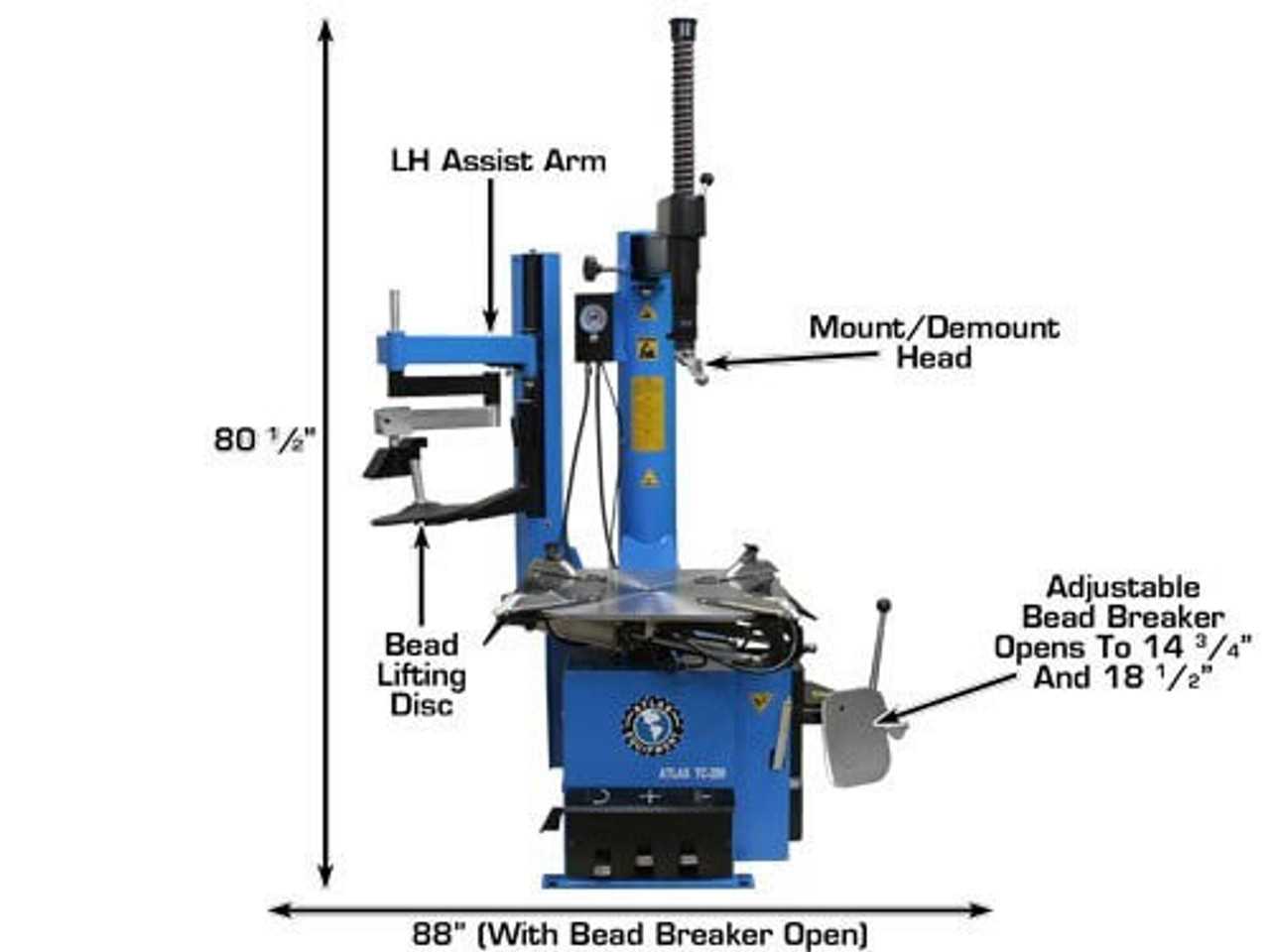
Understanding the Atlas Tire Changer
The machine designed for handling automotive wheels is an essential tool in many workshops. It streamlines the process of removing and fitting various types of rubber casings onto metal rims, ensuring safety and efficiency for mechanics. A clear comprehension of how it operates and its key functions is crucial for proper use.
- Operational mechanics: How the machine handles the removal and installation of casings.
- Main features: Including its rotating table and arm system for seamless operations.
- Safety protocols: Ensuring safe handling during usage to prevent damage to both equipment and wheels.
Each component of the equipment works in unison to facilitate a smooth workflow, reducing manual labor and increasing accuracy. Familiarity with the controls and setup greatly improves the efficiency of any wheel servicing process.
Key Components of the Tire Changer
Understanding the essential mechanisms within the equipment helps improve its operation and maintenance. This section provides a breakdown of the most crucial elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient functionality.
One of the primary features is the platform, which supports the item during the process. It provides stability and ensures that the object remains securely in place. Another vital part is the clamp system, designed to firmly hold and adjust the object throughout different stages. Additionally, the arm mechanism plays a critical role, guiding the motion and applying the necessary force for the operation.
Each of these elements contributes significantly to the overall performance, allowing the equipment to function seamlessly under various conditions. Keeping these components in optimal condition ensures longevi
How the Air System Functions
The pneumatic mechanism operates by channeling compressed air through a series of valves and hoses, creating the necessary pressure to perform various tasks. This system relies on an efficient flow of air, ensuring that the equipment functions smoothly and consistently. Proper airflow regulation is essential for maintaining stable performance and achieving desired outcomes.
Air Intake and Distribution plays a critical role, as it ensures the incoming air is filtered and directed to the appropriate channels. The air is then managed by pressure regulators, which adjust the amount of force applied to different components, ensuring smooth transitions during operation.
Additionally, air release mechanisms are incorporated to safely expel excess pressure, preventing overloading of the system. These features contribute to maintaining durability and ensuring operational safety during intensive use.
Foot Pedal Control Mechanism Explained
The foot pedal control system plays a crucial role in regulating various functions within the equipment. It provides an efficient way to manage different tasks without manual interference, ensuring smooth operation and user convenience. The mechanism behind this control allows for precise actions, responding immediately to the operator’s input through foot pressure.
- Activation of different mechanical processes is initiated by the foot pedal.
- Each pedal corresponds to a specific function, making it easier to multitask efficiently.
- Pressure sensitivity ensures that the operator can finely adjust the force needed for operation.
To maintain the system’s efficiency, regular inspection of the pedal and its internal components is essential. This helps prevent wear, ensuring that the mechanism remains responsive and accurate during use.
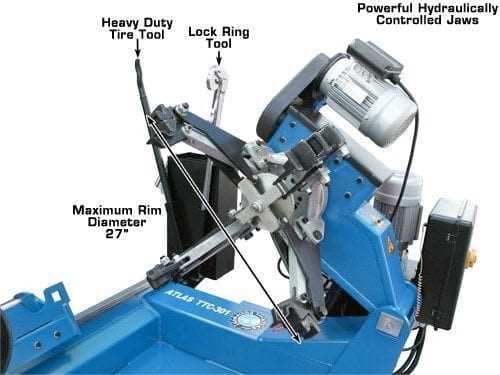
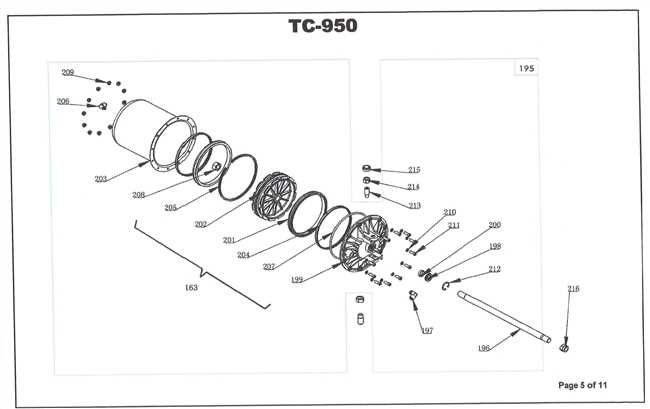
Bead Breaker Parts Overview
The mechanism responsible for separating the bead from the rim is essential in ensuring smooth operation. A collection of interconnected components works together to apply sufficient pressure, effectively loosening the rubber from the metal edge without causing damage.
- Hydraulic Cylinder: A vital component that delivers the necessary force, driven by fluid pressure, to perform the separation task efficiently.
- Foot Pedal: This allows the operator to control the application of pressure, engaging the system with precision during the removal process.
- Arm Assembly: The structural support that guides the movement and positioning of the tool, ensuring accurate placement for optimal results.
- Pusher Block: Positioned to make direct contact with the rubber, this part pushes against the bead, creating the necessary force for detachment.
- Return Spring: After the action is complete, this element helps reset the system, ensuring that the device returns to its original
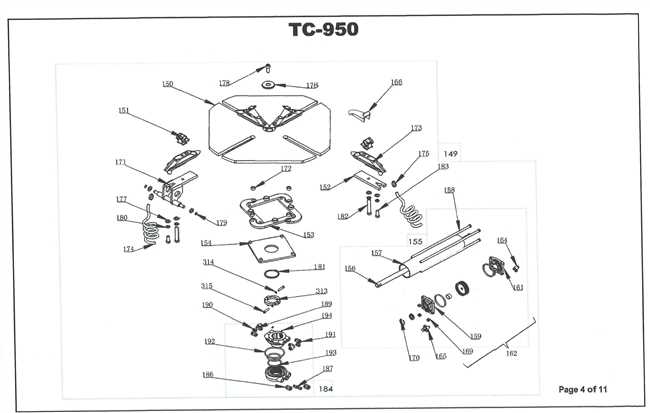
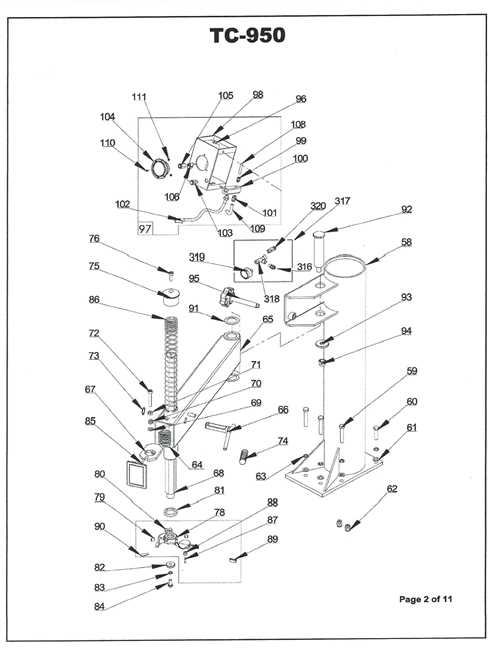
Mounting Head Assembly Details
The mounting head assembly is a crucial component in the operation of wheel servicing equipment. This assembly plays a significant role in securely attaching and detaching the wheel from the rim, ensuring optimal performance and safety during the process. Understanding its structure and function is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Assembly
This assembly typically consists of several key elements, each contributing to its overall effectiveness:
Component Description Mounting Arm Provides leverage for easy attachment and removal of the wheel. Clamping Mechanism Secures the wheel in place during the servicing process. Head Pad Protects the rim from damage during mounting. Pivot Joint Allows for flexible movement of the mounting arm. Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and maintenance of the mounting head assembly are vital for prolonging its lifespan. Ensure that all components are free from debris and wear, and lubricate moving parts as needed to maintain smooth operation.
Common Wear and Tear Areas
In any equipment used for wheel servicing, certain components are prone to deterioration over time due to frequent use and mechanical stress. Understanding these areas can help in maintaining optimal functionality and prolonging the lifespan of the machinery.
Drive Mechanism: The drive assembly is often subjected to significant strain, leading to potential wear. Regular inspection of the gears and belts can prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Clamping System: This area experiences constant pressure and friction. It is essential to check for signs of fatigue or damage, as compromised clamps can affect performance.
Hydraulic Components: Leaks and decreased pressure in hydraulic systems can lead to inefficiency. Monitoring fluid levels and seals will ensure that the equipment operates smoothly.
Electrical Connections: Over time, wiring may corrode or fray. Ensuring connections are secure and free from debris will minimize electrical issues that could disrupt operation.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn components can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of the machine.
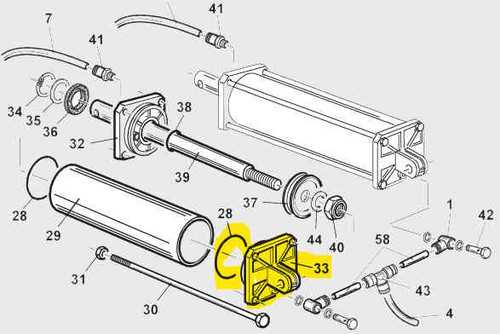
Hydraulic Cylinder Breakdown
The hydraulic cylinder is a crucial component in the operation of equipment designed for manipulating wheels and rims. Understanding its structure and function is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Hydraulic Cylinder
- Outer casing: Provides structural integrity and houses internal components.
- Piston: Transforms hydraulic pressure into mechanical force.
- Seals: Prevent fluid leakage and maintain pressure.
- Ports: Allow fluid to enter and exit the cylinder.
Common Issues and Solutions

- Leakage: Inspect seals and replace them if damaged.
- Inconsistent movement: Check for obstructions and ensure proper fluid levels.
- Piston damage: Examine the piston for wear and replace if necessary.
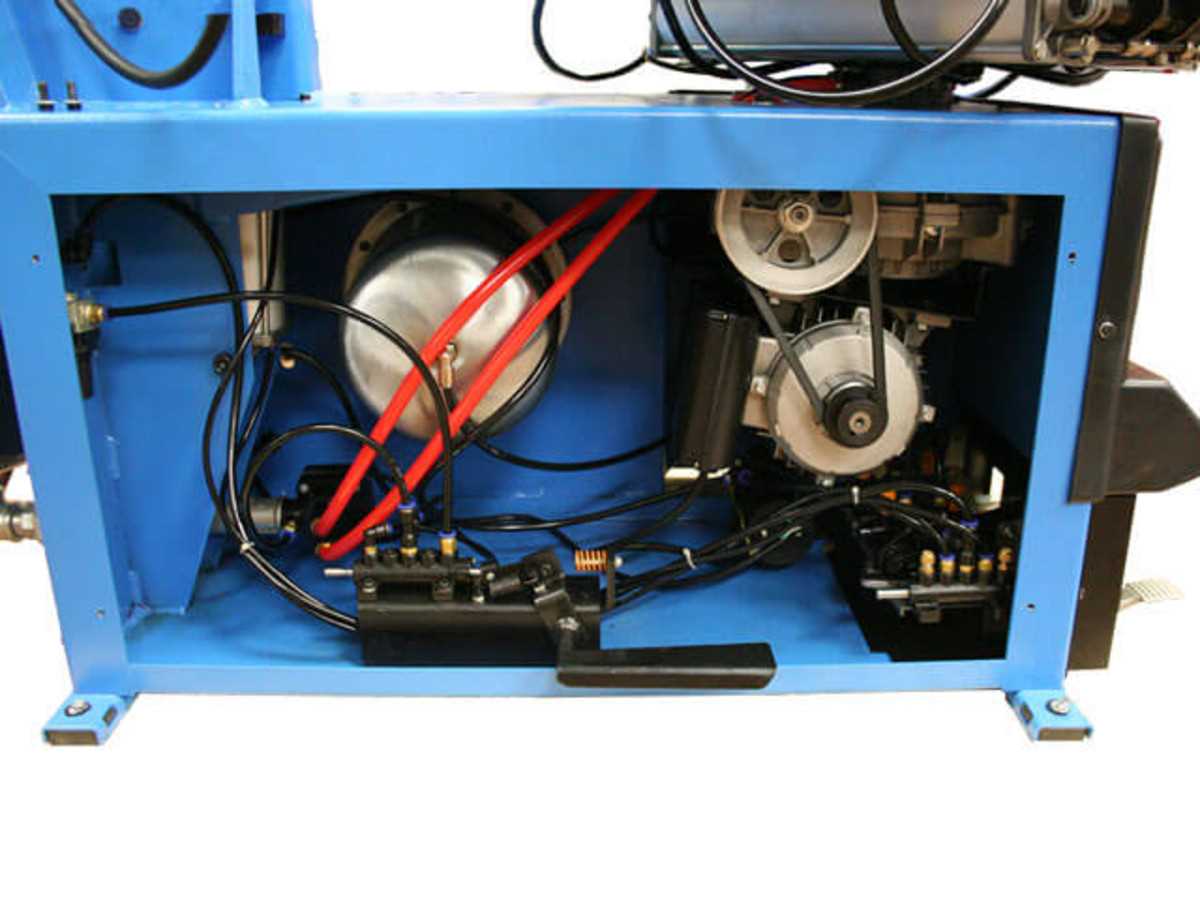
Electrical System and Safety Features
The electrical framework of the equipment is designed to enhance operational efficiency while ensuring user safety. This system integrates advanced technology to monitor performance and manage various functions seamlessly.
Components of the Electrical Framework
Key elements of the electrical setup include sensors, controllers, and wiring harnesses. These components work together to facilitate smooth operation and minimize the risk of malfunction. Regular maintenance and inspections of these parts are essential for optimal performance.
Safety Mechanisms
Safety mechanisms are integral to the device, designed to protect users during operation. Features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and fault detection systems are incorporated to mitigate hazards. Understanding these safety features is crucial for ensuring a safe working environment.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Use
Proper upkeep of your equipment is essential for ensuring its longevity and efficiency. By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, you can prevent wear and tear, minimize downtime, and enhance performance over time.
Regular Inspections
Conduct frequent evaluations to identify any signs of wear or damage. Checking components for cracks, rust, or loose fittings can help you address issues before they escalate. Timely detection is key to maintaining functionality.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Keep moving parts well-lubricated to reduce friction and prolong lifespan. Regularly clean surfaces to remove debris and grime, which can hinder performance. Using the appropriate lubricants and cleaning agents will contribute to the overall efficiency of your machinery.
Replacement Options for Critical Parts
When maintaining essential equipment, ensuring that key components are available for replacement is crucial. Several alternatives exist that can restore functionality and enhance performance, enabling operators to work efficiently without significant downtime.
Types of Available Alternatives
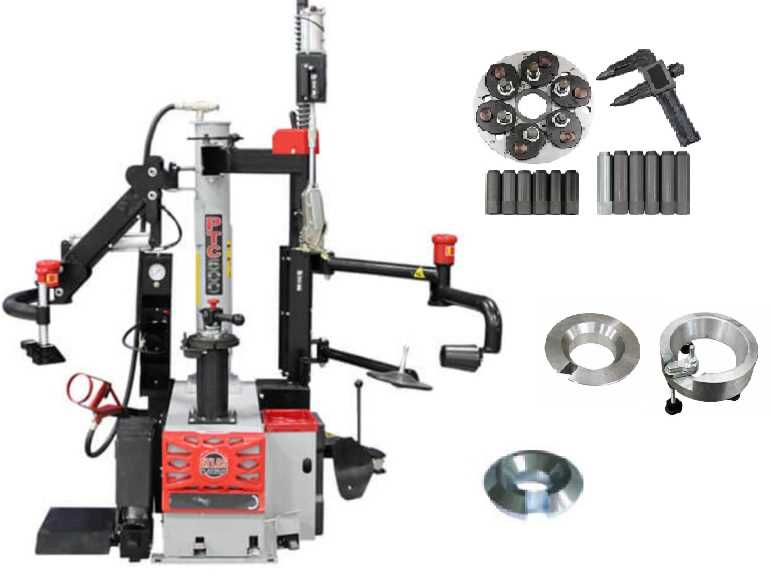

Various sources provide quality substitutes for vital components. These include original manufacturer parts, aftermarket options, and refurbished items, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Selecting the right type depends on factors like budget, availability, and the specific needs of the equipment.
Comparison Table of Replacement Options

Option Type Advantages Disadvantages OEM Components Guaranteed compatibility and quality Higher cost Aftermarket Alternatives Often more affordable Quality may vary Refurbished Parts Cost-effective and environmentally friendly May have limited warranty