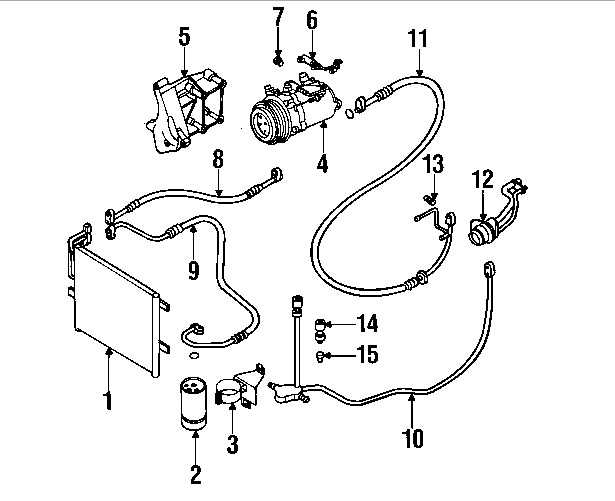
Modern climate solutions in vehicles are designed to maintain comfort through precise temperature management. These systems consist of multiple interconnected elements, each performing essential roles to ensure a stable and pleasant cabin environment. Understanding how these components align and function together offers valuable insights into system performance.
At the heart of these mechanisms are various modules responsible for regulating airflow, cooling, and heating. Key elements are often concealed under the dashboard, with hoses, compressors, and valves forming an intricate web. Every connection plays a vital role, from regulating refrigerant flow to managing fan speed.
A closer look at how individual components fit into the larger network helps identify potential issues and aids in repairs. Having a clear view of the arrangement allows technicians to quickly assess which sections may require attention, streamlining diagnostics and maintenance tasks.
Comprehensive Overview of Climate System Components
The modern climate regulation setup relies on a network of interconnected elements working together to maintain comfortable interior conditions. Each unit plays a critical role in ensuring consistent airflow, temperature adjustment, and humidity control, creating an efficient environment for occupants.
Core Elements of the Air Regulation System
The central cooling and heating module serves as the foundation of the entire assembly. This unit ensures the circulation of treated air, balancing temperatures through internal exchanges. Filters embedded within the flow path remove impurities, keeping the air clean and breathable throughout the operation.
Key Fluid and Control Mechanisms
Circulatory networks transport special fluids to facilitate temperature regulation, driven by a compressor that maintains optimal pressure levels. Valves and sensors work in tandem to monitor and adjust airflow, preventing irregularities. The seamless interaction between these components ensures steady climate control, regardless of external conditions.
Main Unit Responsible for Airflow Control
This essential module ensures the movement and distribution of cooled or heated air throughout the cabin. It adjusts airflow direction and intensity, creating a comfortable interior environment. Its functionality is crucial for maintaining an even temperature and eliminating window fog during various driving conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Control Assembly | Regulates fan speed and air direction settings. |
| Vent Control Actuator | Adjusts air pathways by opening or closing internal flaps. |
| Temperature Mixer | Blends warm and cool air for precise climate regulation. |
| Fan Motor | Drives air circulation through the ducts. |
Thermal Exchange Core Functions in Cooling
The effectiveness of maintaining temperature balance relies on systems designed to transfer heat between different environments. This process ensures stable internal conditions by redirecting excess warmth away and allowing cooler air to circulate efficiently. Understanding these mechanisms highlights their importance in sustaining overall operational stability.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Absorption | Captures unwanted thermal energy from components or surroundings for redirection. |
| Fluid Circulation | Enables continuous movement of liquid or gas to enhance heat transfer. |
| Heat Dissipation | Releases accumulated warmth into the environment to prevent overheating. |
| Pressure Regulation | Ensures optimal flow by maintaining stable internal pressure levels. |
| Temperature Monitoring | Tracks thermal variations to prevent inefficiencies and enable quick adjustments. |
Piping Layouts for Refrigerant Distribution
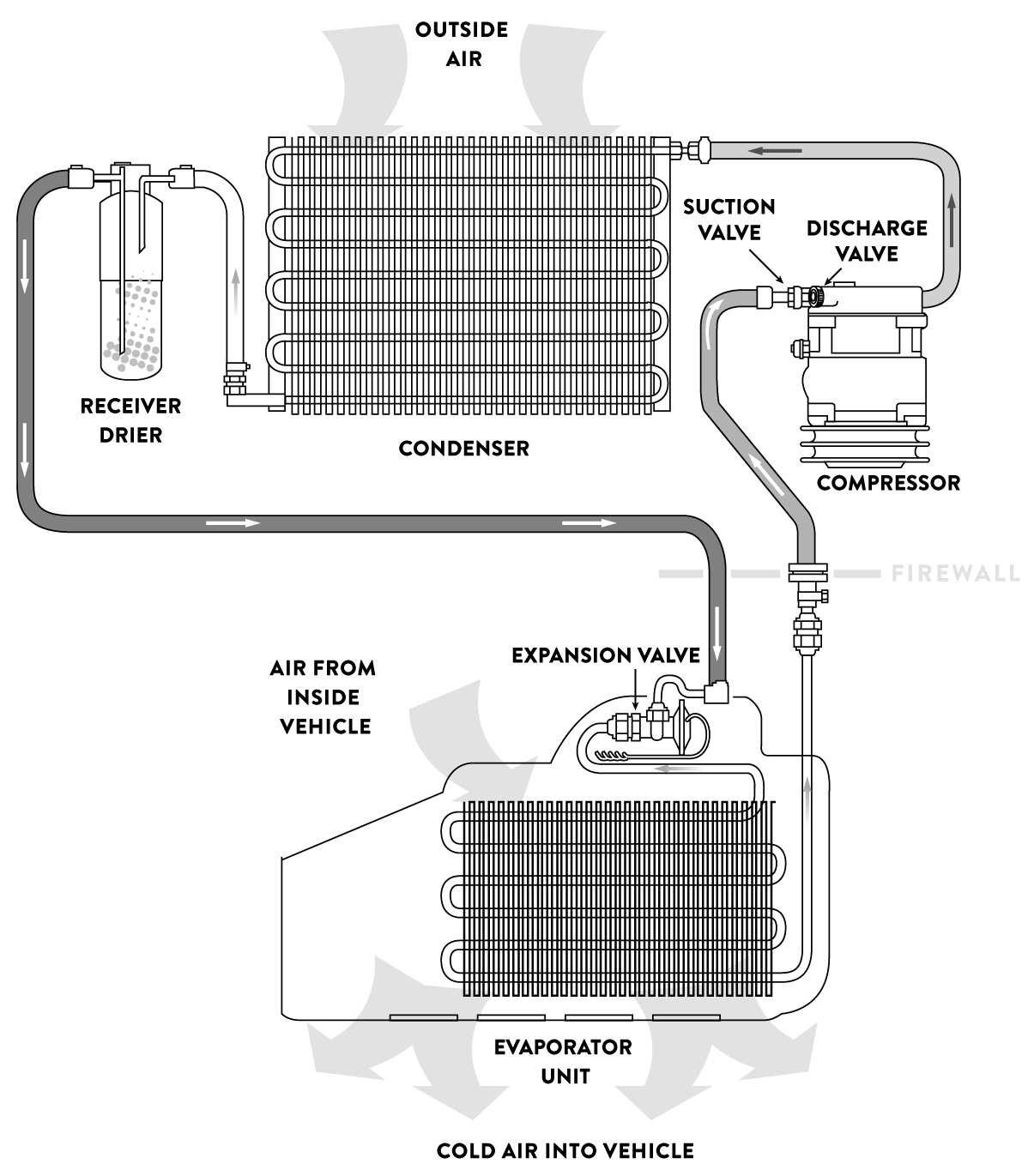
Effective refrigerant flow within climate regulation systems relies on well-planned tube arrangements that connect various components. These layouts ensure a smooth transfer of coolant, maximizing efficiency while preventing blockages or pressure drops.
Main Circulation Routes
Primary circulation routes link the compressor, condenser, and evaporator, forming a closed-loop system. Strategic positioning of these tubes minimizes energy loss and maintains steady pressure, promoting optimal cooling. Precision in route length and connections is crucial for uninterrupted performance.
Branching and Connections
Branch networks distribute the cooling agent to multiple areas through secondary pathways. The use of fittings and joints allows the main flow to divide efficiently, ensuring that each segment receives an adequate supply. Proper insulation of these lines is essential to prevent condensation and maintain thermal stability.
Key Sensors Monitoring Temperature Shifts
Accurate monitoring of environmental changes is essential for maintaining stable performance. Specific modules are employed to track fluctuations, ensuring that every shift is promptly identified and adjustments are made as needed to avoid inefficiencies.
Thermal sensors are critical for detecting heat variations, helping to regulate systems efficiently by providing real-time data. When temperature levels drift beyond optimal ranges, these components trigger responses to restore balance.
Another key element includes pressure-sensitive devices that detect irregularities caused by changing conditions. These modules interact with the broader framework to ensure that each component operates within the recommended limits, preventing potential issues from escalating.
Combined efforts of these sensors create a synchronized network that enhances stability, preserves functionality, and minimizes the risk of performance decline over time.
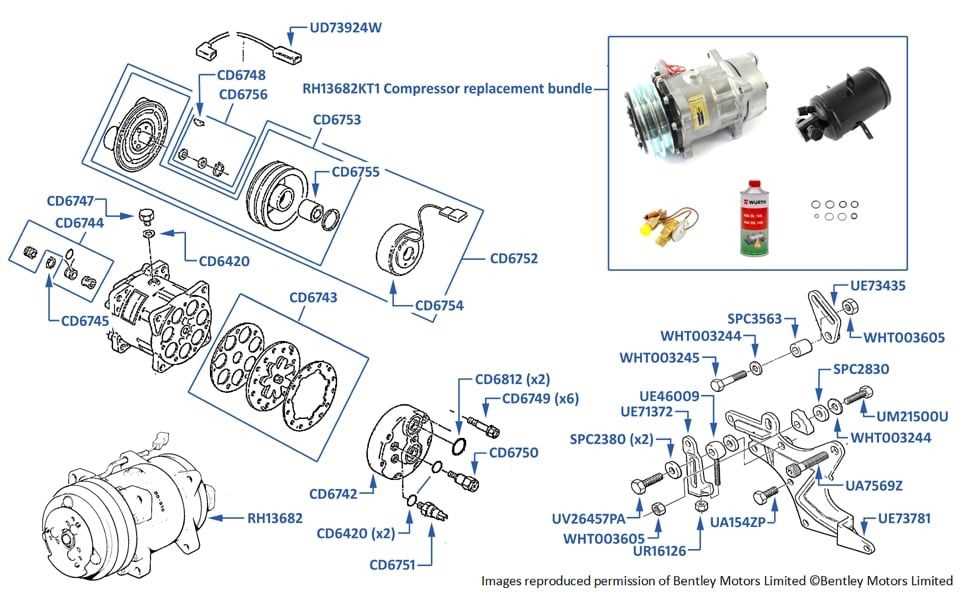
Compressor Role in Pressure Regulation

The compressor serves as a pivotal component in maintaining the proper balance of pressure within a cooling system. By compressing the refrigerant, it transforms the substance from a low-pressure gas into a high-pressure vapor, facilitating the circulation of refrigerant throughout the system.
This transformation is crucial, as it enables the effective transfer of heat. When the refrigerant is compressed, its temperature rises, allowing it to release heat efficiently as it moves through the condenser. This process is essential for the overall functionality of the system, ensuring that the desired cooling effect is achieved.
Moreover, the compressor helps to regulate pressure fluctuations that may occur during operation. By adjusting its speed and output, it can maintain a consistent pressure level, which is vital for optimal performance and energy efficiency. In essence, the compressor plays an integral role in the system’s ability to operate smoothly and effectively.
In summary, understanding the compressor’s function in pressure regulation provides insights into how cooling systems maintain their efficiency and effectiveness, highlighting its significance in overall system performance.
Control Interfaces and User Settings
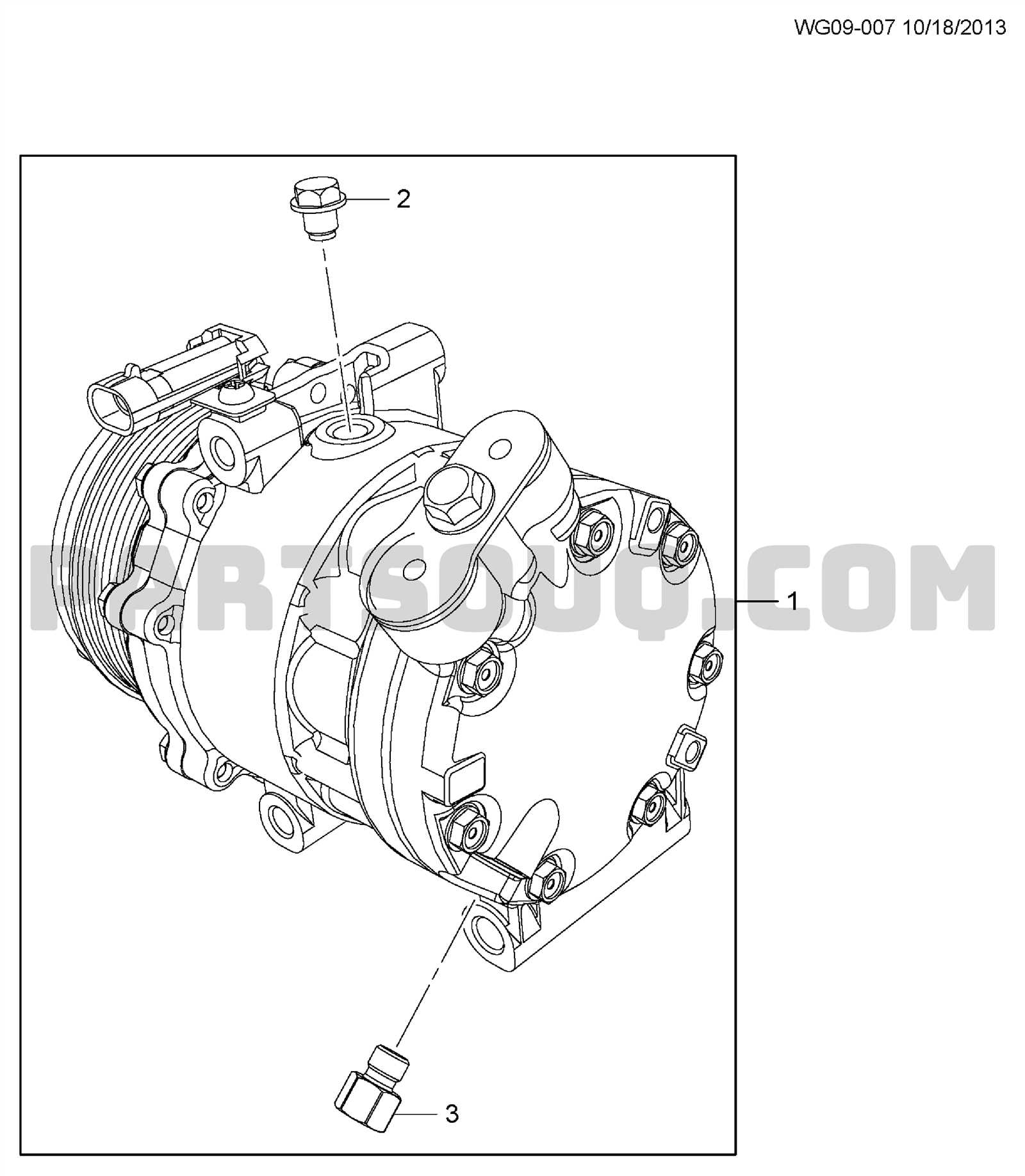
The interaction between a user and the system is essential for optimal functionality and convenience. Control mechanisms serve as the bridge, allowing individuals to customize settings and manipulate features to meet their preferences. This section explores the various elements involved in these interactions, emphasizing their significance in enhancing the overall experience.
Customization Options
Users often benefit from a range of customization features that enable them to adjust settings according to their specific needs. These options may include temperature regulation, airflow direction, and operational modes, each designed to enhance comfort. By tailoring these functionalities, individuals can create an environment that suits their personal preferences.
Feedback Mechanisms
Effective feedback mechanisms play a crucial role in informing users about the current state of the system. Visual indicators, audible alerts, and tactile responses provide essential information, ensuring that individuals are aware of adjustments and system statuses. Such feedback enhances user confidence and facilitates informed decision-making.
Filtration Units Ensuring Air Quality
In various mechanical systems, the role of filtration mechanisms is pivotal for maintaining the purity of circulating air. These components work diligently to eliminate unwanted particles and contaminants, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of the system. Effective filtration not only ensures optimal functionality but also contributes to the longevity of the entire assembly.
The effectiveness of these units can be gauged through their ability to capture a range of pollutants, including dust, pollen, and other airborne debris. Understanding the characteristics of these mechanisms is essential for maintaining a healthy environment within the operational context.
| Filtration Type | Efficiency (%) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| HEPA Filters | 99.97 | General Air Purification |
| Activated Carbon Filters | 85.0 | Odor Removal |
| Electrostatic Filters | 90.0 | Fine Particulate Capture |
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of these filtration units are crucial to sustain their performance. Monitoring their condition can prevent potential issues, ensuring that the system continues to operate at peak efficiency.
Valves Managing Refrigerant Flow Rate

Regulating the flow of cooling agents is a critical function in temperature control systems. These mechanisms ensure optimal performance by managing the amount of refrigerant that circulates within the system. Proper modulation of this flow is essential for maintaining efficiency and effectiveness in the cooling process.
Types of Flow Control Mechanisms
Several types of devices are employed to control the movement of cooling agents. Each type serves a specific purpose, with designs that allow for precise adjustments in flow rates. Among them, some utilize pressure differentials, while others rely on electronic controls to achieve the desired level of refrigerant movement.
Importance of Proper Functioning
Ensuring that these flow regulation devices operate correctly is vital for the longevity of the entire system. Any malfunction can lead to improper cooling performance, increased energy consumption, or even system failure. Regular maintenance and timely replacements of these components help in sustaining an efficient cooling environment.
Electrical Circuitry for Component Coordination
The effective functioning of interconnected mechanisms relies heavily on the intricate web of electrical pathways that facilitate communication among various elements. Understanding these circuits is essential for ensuring seamless operation, as each component requires precise signals to perform its designated tasks. A comprehensive grasp of how these circuits are structured and how they interact with one another is crucial for diagnosing and enhancing overall system performance.
Within this context, the configuration of electrical connections plays a pivotal role. Each link must be meticulously designed to allow the flow of current while minimizing resistance and potential disruptions. By analyzing the arrangements and their functionalities, one can gain insights into optimizing performance and troubleshooting issues that may arise in the coordination of different elements.
| Component | Function | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|
| Relay | Controls high-current devices | Normally Open (NO) |
| Sensor | Detects specific parameters | Analog/Digital |
| Actuator | Executes physical movement | Direct Current (DC) |
| Fuse | Protects circuit from overload | Standard |
By mastering the principles of electrical connectivity and the roles of each component, one can ensure that the entire system operates smoothly and efficiently. This knowledge not only aids in the assembly and maintenance of these intricate setups but also empowers users to make informed decisions when modifications or repairs are necessary.
Indicators and Alerts for Fault Detection
Monitoring systems play a crucial role in identifying issues within operational mechanisms. These systems are designed to provide real-time feedback, allowing for prompt diagnosis and resolution of potential malfunctions. Through various signals and notifications, users can quickly ascertain the status of the equipment and take necessary actions to maintain optimal functionality.
| Indicator Type | Description | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Warning Light | Illumination signifies a minor fault or maintenance requirement. | Inspect and address the issue during the next service. |
| Error Code Display | Specific alphanumeric codes indicating particular failures. | Refer to the manual to interpret the code and resolve the issue. |
| Buzzer Alert | An audible notification signaling an urgent concern. | Immediately check the system for possible faults. |
| Temperature Gauge | Displays the operational temperature range. | Monitor for abnormalities and cool the system if overheating occurs. |
| Fluid Level Indicator | Monitors the levels of essential fluids. | Refill fluids as needed to ensure proper operation. |
Maintenance Tips to Extend System Life
Ensuring the longevity of your climate control system involves regular upkeep and attention to detail. By following a few essential guidelines, you can help prevent premature wear and enhance the overall efficiency of the equipment. Simple practices can make a significant difference in performance and durability.
Regular Inspections
Conducting routine examinations of the system components is crucial. Look for any signs of wear, leakage, or damage. Addressing issues promptly can prevent more severe problems down the line.
Cleaning and Airflow Management

Keeping the airflow paths clear is vital for optimal functioning. Regularly clean or replace filters to maintain efficient airflow, which helps reduce strain on the system.
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect Components | Monthly | Check for signs of wear or damage. |
| Clean Filters | Every 1-3 Months | Replace if heavily soiled. |
| Check Refrigerant Levels | Annually | Ensure proper levels for efficiency. |
| Professional Service | Every 1-2 Years | Schedule comprehensive maintenance. |