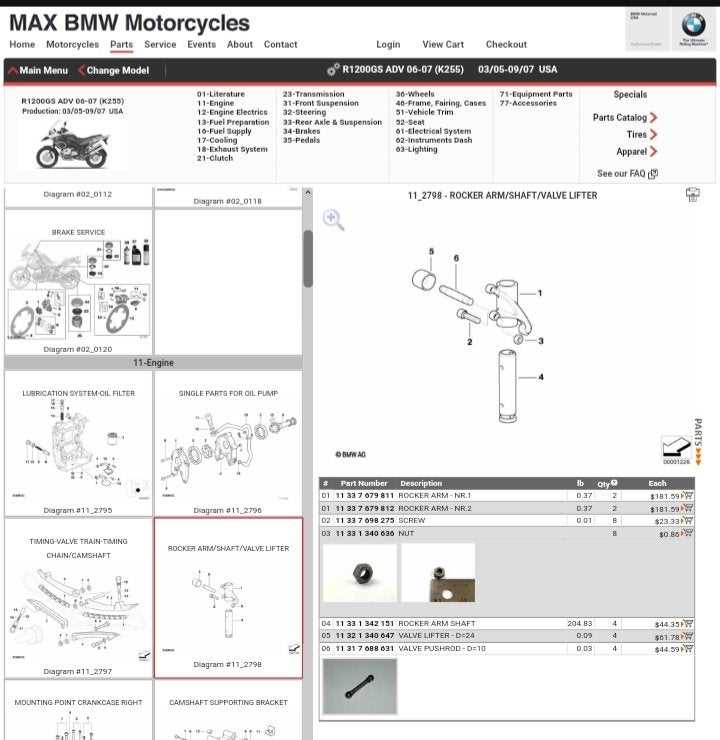
Understanding the structure of individual elements in a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. A detailed look at various components helps riders ensure that every part functions seamlessly, contributing to a smooth and safe journey.
This guide provides insights into the layout and connections between key mechanical and electrical elements. With an organized view, enthusiasts can quickly identify necessary components and improve efficiency when performing routine checks or repairs.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or an owner seeking to deepen your knowledge, having a clear reference for the arrangement of essential systems is invaluable. This approach not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the vehicle.
Bmw GS 1200 Parts Diagram
This section explores the detailed layout of individual components found in one of the most popular dual-sport motorcycles. Understanding how various elements interact ensures easier maintenance and better performance management.
Component Categories Overview
- Engine System: Key elements responsible for power generation and smooth operation, including cylinders, valves, and exhausts.
- Electrical Setup: Components like the battery, alternator, and wiring ensure proper power distribution.
- Suspension: Front forks and rear shocks play essential roles in stability and handling across terrains.
Importance of a Clear Layout
Engine Components Overview
The heart of any motorcycle lies in its engine, composed of multiple interconnected elements that ensure efficient operation. These components are carefully designed to convert fuel into mechanical energy, providing the necessary power to drive the vehicle forward. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and performance under varying conditions.
Primary Engine Elements
The essential parts include a cylinder block, crankshaft, and piston assembly, working in unison to create combustion. The combustion chamber ensures precise fuel ignition, while the crankshaft transfers the generated energy to the transmission system. Proper synchronization of these components is vital to achieve optimal output and durability.
Supporting Systems and Their Functions
A range of auxiliary systems supports engin
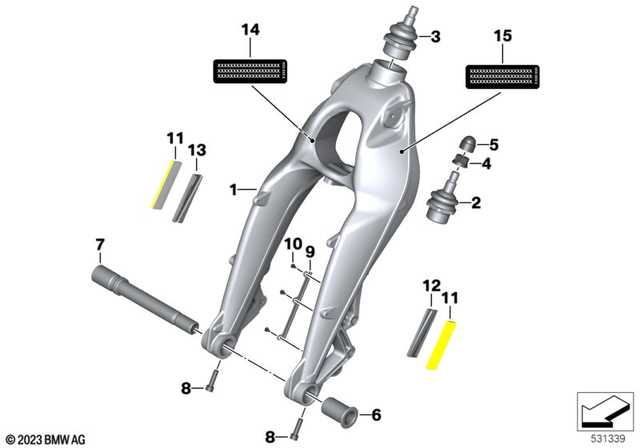
Suspension System Structure
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth ride and maintaining stability on various surfaces. It balances the vehicle by distributing weight evenly and absorbing shocks from uneven terrain. Properly functioning components enhance handling, traction, and comfort for both short commutes and long journeys.
Key Components
The system consists of several interconnected parts designed to work in harmony. Springs and dampers absorb vertical movement, while control arms guide the wheels’ motion. Additionally, bushings reduce friction, and stabilizers limit body roll during turns.
System Interaction
The elements of the suspension operate together to adjust to road conditions dynamically. Shocks
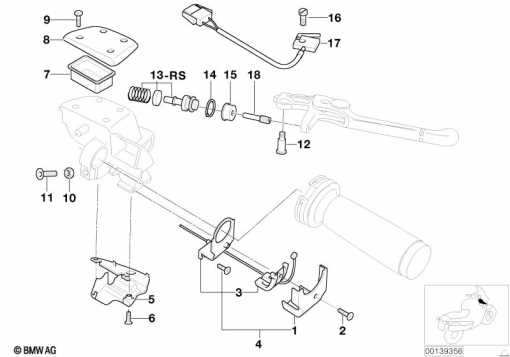
Electrical Wiring Layout
The structure of an electrical system ensures efficient operation by connecting various components through a network of wires and connectors. This layout provides seamless communication between elements, supporting functions such as lighting, sensors, and control modules.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuse Box | Protects circuits from overloads by breaking the connection when needed. |
| Relay Switches | Enable or di
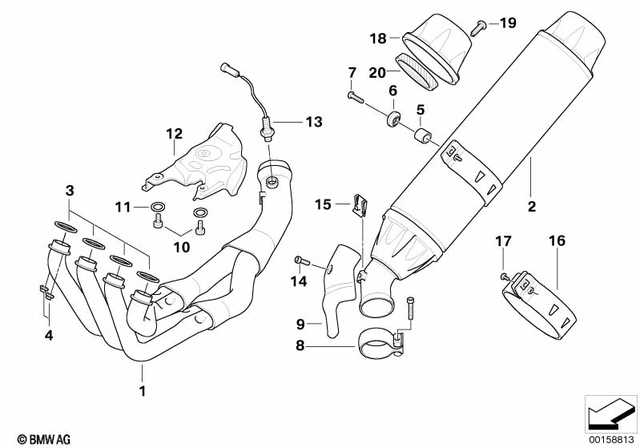
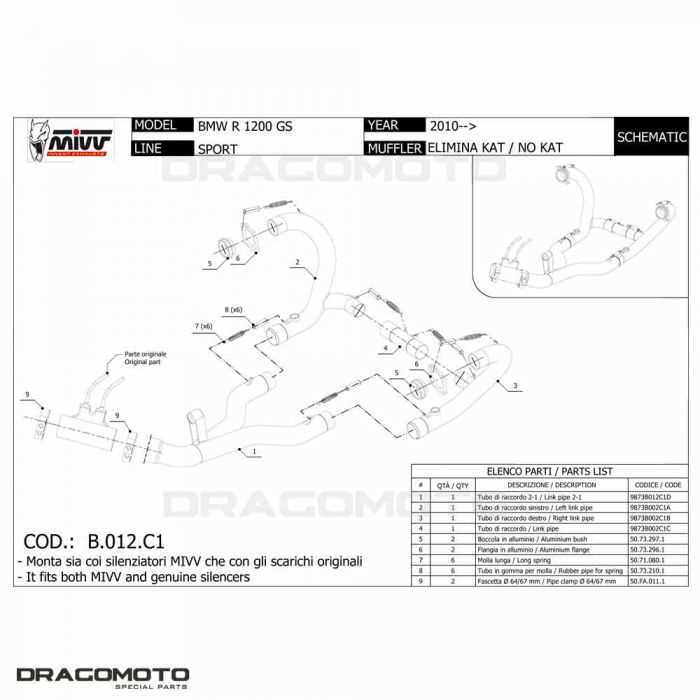
Exhaust System BreakdownThe exhaust system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of a motorcycle. Understanding its components and functionality can significantly enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. This section delves into the essential elements of the exhaust assembly, providing insights into their interconnections and significance. Key components of the exhaust assembly include:
Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust assembly are essential for optimal performance. Addressing issues such as rust, leaks, or blockages can prevent costly repairs and enhance the longevity of the entire system. Brake System ComponentsThe braking system of a motorcycle is crucial for ensuring safety and performance during operation. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for maintenance and repairs. Each component plays a specific role in the overall functionality, contributing to the effective deceleration and control of the vehicle. Main Elements of the Brake System
Additional Features
Fuel System ConfigurationThe fuel system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of a motorcycle, ensuring optimal combustion and engine efficiency. A well-designed fuel system not only enhances power output but also contributes to smoother operation and fuel economy. Understanding the components and their arrangement can aid in maintaining and troubleshooting issues effectively.
Understanding the configuration of the fuel system helps in diagnosing potential issues and optimizing performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of each component can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the motorcycle. Cooling System Details
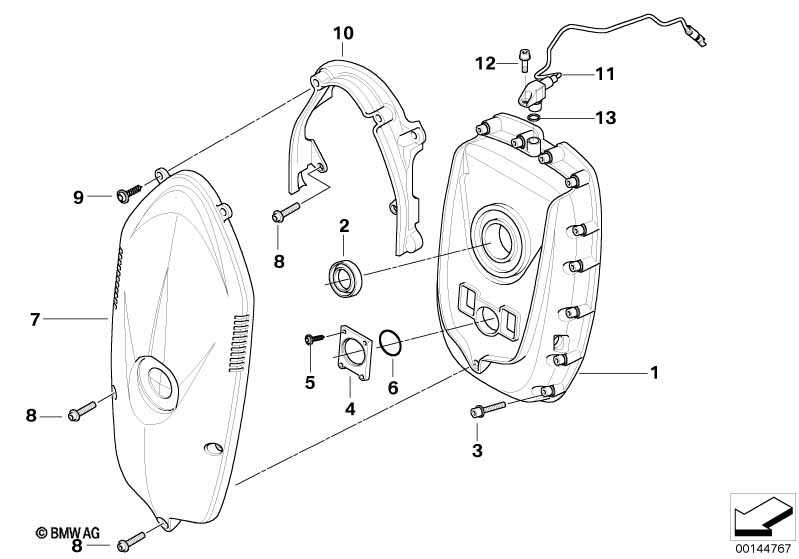
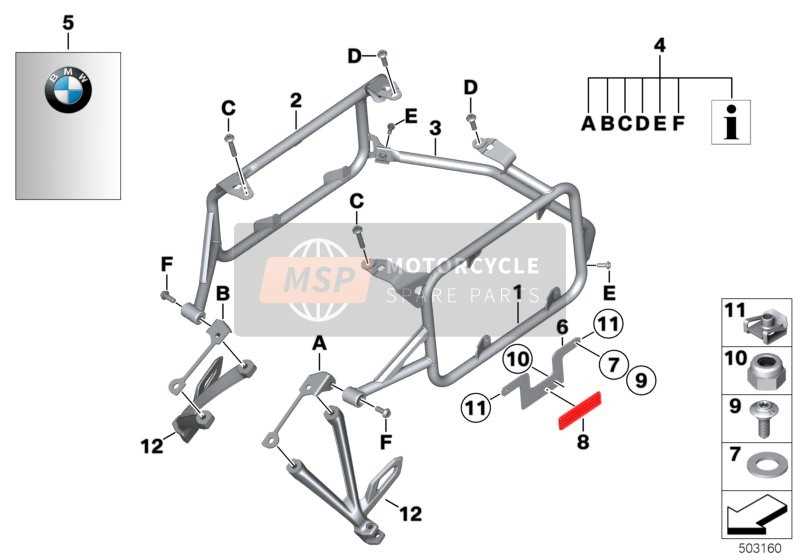
The cooling mechanism in a motorcycle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, ensuring efficient performance and longevity. This system is designed to regulate heat generated during operation, preventing overheating and related damage. Key Components of this system typically include a radiator, water pump, and various hoses. The radiator acts as a heat exchanger, dissipating excess heat from the coolant fluid. The water pump circulates the coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring a constant flow to manage temperatures effectively. Proper maintenance of the cooling system is essential for reliable operation. Regular checks for leaks, ensuring fluid levels are adequate, and inspecting the condition of hoses can prevent potential failures and costly repairs. Understanding the function and upkeep of this system is vital for any motorcycle enthusiast. Frame and Body PanelsThe structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of a motorcycle are significantly influenced by its chassis and outer coverings. These components not only provide essential support for various parts but also contribute to the overall design and functionality of the vehicle. Understanding their configuration is vital for both maintenance and customization. Key elements of the chassis and exterior include:
Each of these elements plays a crucial role in ensuring the motorcycle’s durability and performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential for safe operation and to preserve the bike’s aesthetic qualities. Transmission and Clutch AssemblyThe transmission and clutch assembly is a crucial component of a motorcycle’s drivetrain, playing a vital role in the efficient transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This assembly allows for smooth gear shifting and optimal performance during various riding conditions. At its core, the transmission consists of a series of gears that facilitate different speed ranges, enabling the rider to adapt to various terrains and driving styles. The clutch, on the other hand, acts as a mechanism that engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing the rider to change gears seamlessly. Understanding the intricate relationship between these elements is essential for maintaining the overall functionality of the vehicle. Regular inspection and maintenance of the transmission and clutch assembly can prevent potential issues, ensuring a smooth riding experience. Proper adjustments and timely replacements of worn components are key to prolonging the life of this essential system. Lighting and Dashboard Elements
The illumination and control displays of a motorcycle play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and enjoyable riding experience. These components not only provide visibility during low-light conditions but also communicate essential information to the rider, enhancing overall functionality and comfort. Types of Lighting
Dashboard Features
|