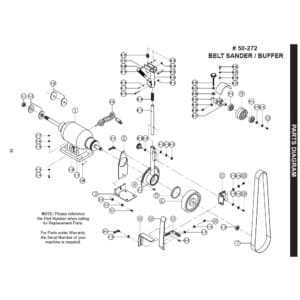
In many fields, visual representations are key to simplifying complex structures. These illustrations help to clarify how individual sections relate to one another, providing a clear understanding of how everything fits together. By exploring these visual tools, we can better grasp how different elements function as a cohesive whole.
Breaking down larger systems into smaller, manageable elements enables a deeper comprehension of their overall purpose. Each piece, while distinct, plays a vital role in ensuring the system operates smoothly. Through careful examination, one can uncover the significance of each element and its contribution to the bigger picture.
These visual layouts are particularly useful for gaining insight into the arrangement of key elements within various constructs. They offer a simple way to organize information, making it easier to follow and interpret the relationships between the individual components.
Understanding the Components of Diagrams
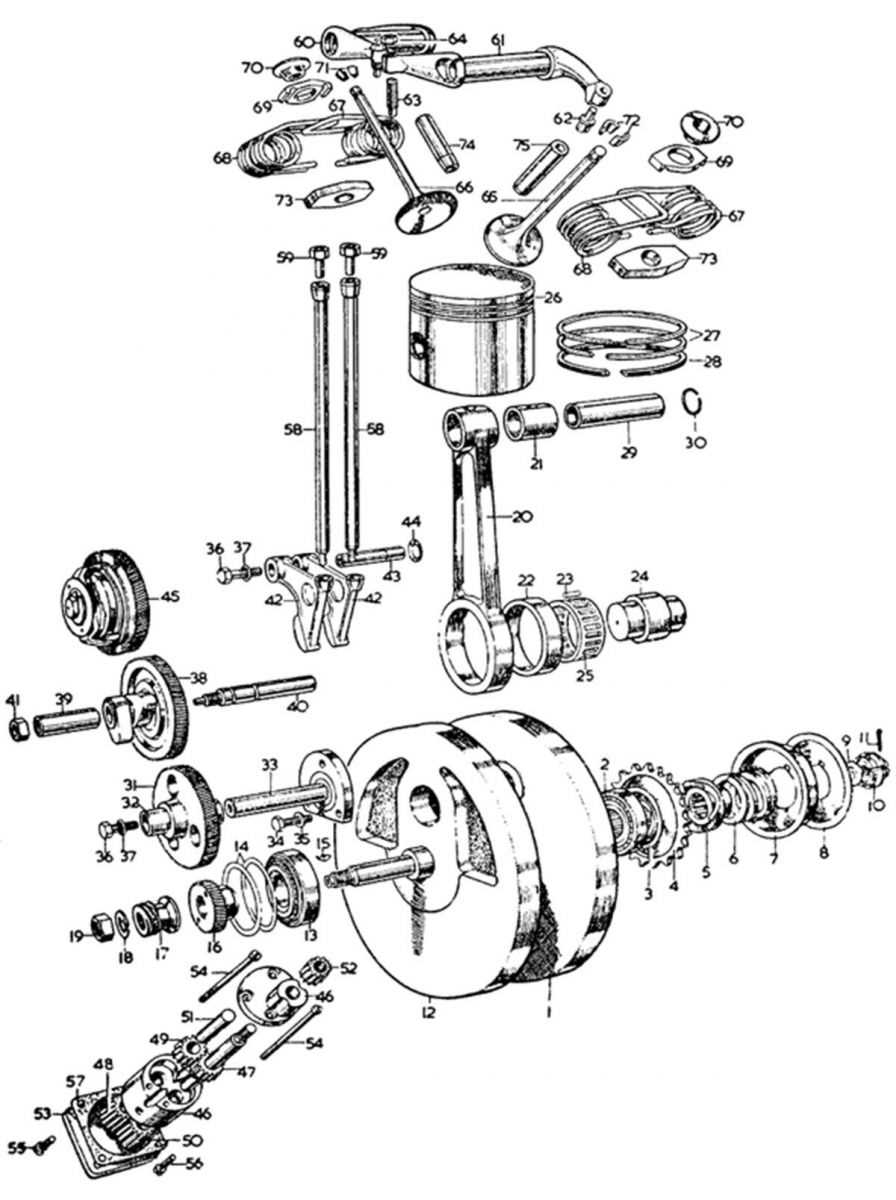
When examining visual representations of information, it’s essential to recognize how individual elements come together to convey a complete picture. Each element plays a distinct role in building a cohesive structure that allows for clear communication of ideas, processes, or relationships.
Below is an outline of key elements often found in these visual tools:
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Shapes | Used to represent objects, actions, or ideas, providing a visual shorthand for understanding complex concepts. |
| Lines | Connect different components, showing relationships or pathways between them. |
| Text | Labels and annotations that offer additional details or clarify meanings of other visual elements. |
| Arrows | Indicate direction or sequence, guiding the viewer through a specific flow or process. |
Main Elements in Visual Representations

Visual representations serve as a method to convey information in a structured and clear manner. They are essential tools for illustrating complex concepts, simplifying data, and highlighting relationships. Understanding the fundamental components that make up these visual structures is key to interpreting and creating them effectively.
Key Components
- Shapes: Various geometric forms are used to represent distinct items or ideas. They often symbolize different categories or steps within a broader framework.
- Lines and Arrows: These are used to indicate connections, direction, or flow between different elements. Arrows typically suggest movement or progress.
- Text Labels: Descriptive titles or annotations provide clarity, ensuring that each section or connection is easily understood.
Organizational Features
- Sections: Dividing the visual into distinct areas helps in organizing related elements together, making the information more digestible.
- Color Coding: Different hues are often applied to highlight key areas or differentiate between various sections, adding emphasis or aiding in grouping related information.
Breaking Down Diagram Sections
Understanding how different visual components interact within a larger structure is essential for clarity and communication. Each area within a visual layout serves a unique function, helping to convey information in an organized and efficient manner.
- Headers: Often placed at the top, these help identify the main focus or title of the visual representation.
- Labels: These text elements ensure clarity, giving names or descriptions to various segments of the visual.
- Lines and Arrows: These directional markers guide the viewer’s attention, linking distinct sections or showing the flow between them.
- Blocks: Segmented areas that are grouped together based on their relevance to a specific topic or function.
- Color Coding: Used to differentiate and categorize, colors play a key role in making content easier to digest visually.
By recognizing the purpose and relationship of each section, it becomes simpler to navigate and understand the overall presentation.
Key Features of Diagram Structures
When examining the composition of visual representations, certain core elements consistently stand out, contributing to the overall clarity and purpose of the design. These components work together to convey information in a structured and meaningful way, allowing users to grasp complex ideas quickly and efficiently.
Organizational Patterns
One of the most important characteristics is the way information is arranged. Properly structured layouts ensure logical flow and coherence, enabling viewers to easily follow the intended message. Hierarchical relationships often help distinguish key points from supporting details, which enhances understanding.
Visual Cues
Another essential feature is the use of markers and shapes to guide attention. These indicators, whether through distinct outlines, colors, or symbols, create a visual hierarchy that directs focus to the most important sections. Additionally, the choice of spacing and alignment significantly affects readability and overall perception.
Analyzing Different Diagram Components
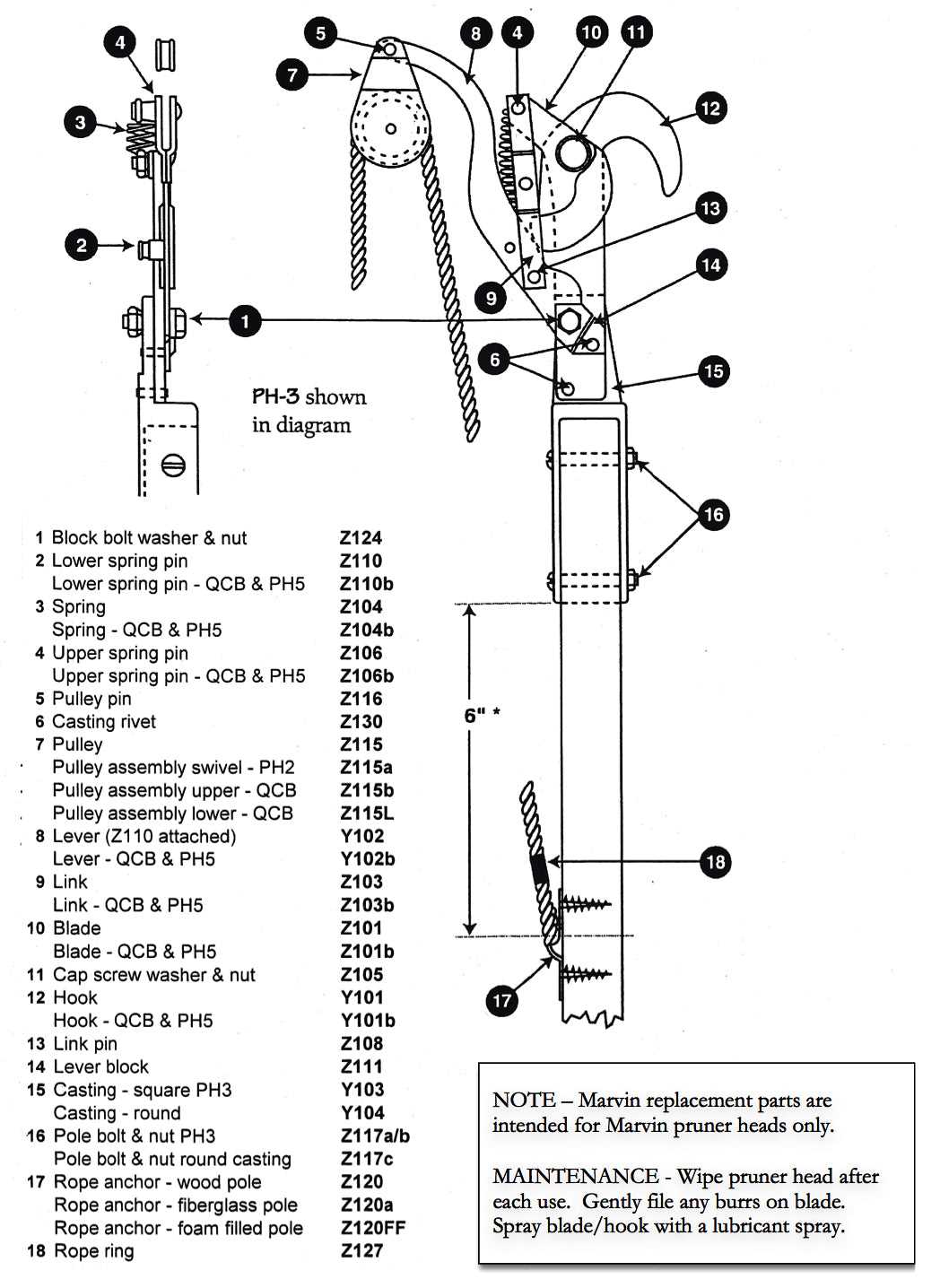
Understanding the essential building blocks of a visual representation is crucial for interpreting and utilizing its structure effectively. These individual elements each serve a specific purpose in conveying information, contributing to the overall clarity and functionality of the graphic. By identifying how each component interacts within the whole, one can gain deeper insights into the relationships and data being presented.
Key Elements of Visual Representations
When breaking down a complex visual, it’s important to focus on the role of each section. Some areas may highlight key data points, while others organize these points into understandable patterns. The arrangement of these segments often reflects the importance or hierarchy of information, guiding the viewer’s attention where it’s most needed.
Connecting and Organizing Information
Another critical aspect is how various sections are linked together. These connections illustrate relationships, dependencies, or flow, which help in understanding the overall purpose. By examining the placement and connections of these elements, one can better grasp how the information fits together logically.
How Labels Enhance Diagrams
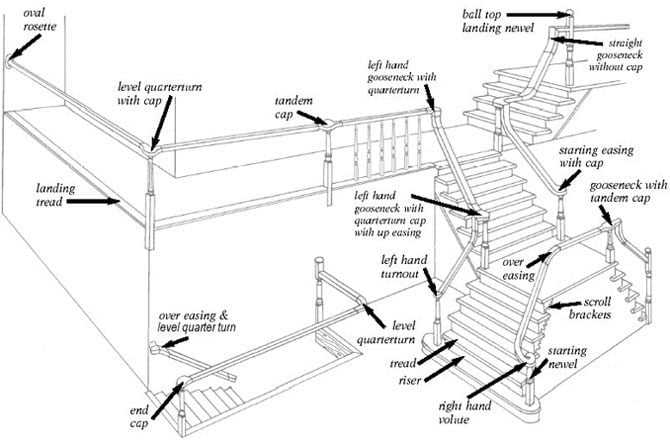
Effective labeling is crucial for improving comprehension and communication in visual representations. Labels serve as signposts, guiding the viewer through the information presented, ensuring clarity and reducing confusion. By providing context and meaning, they transform complex images into understandable narratives.
Clarity and Understanding
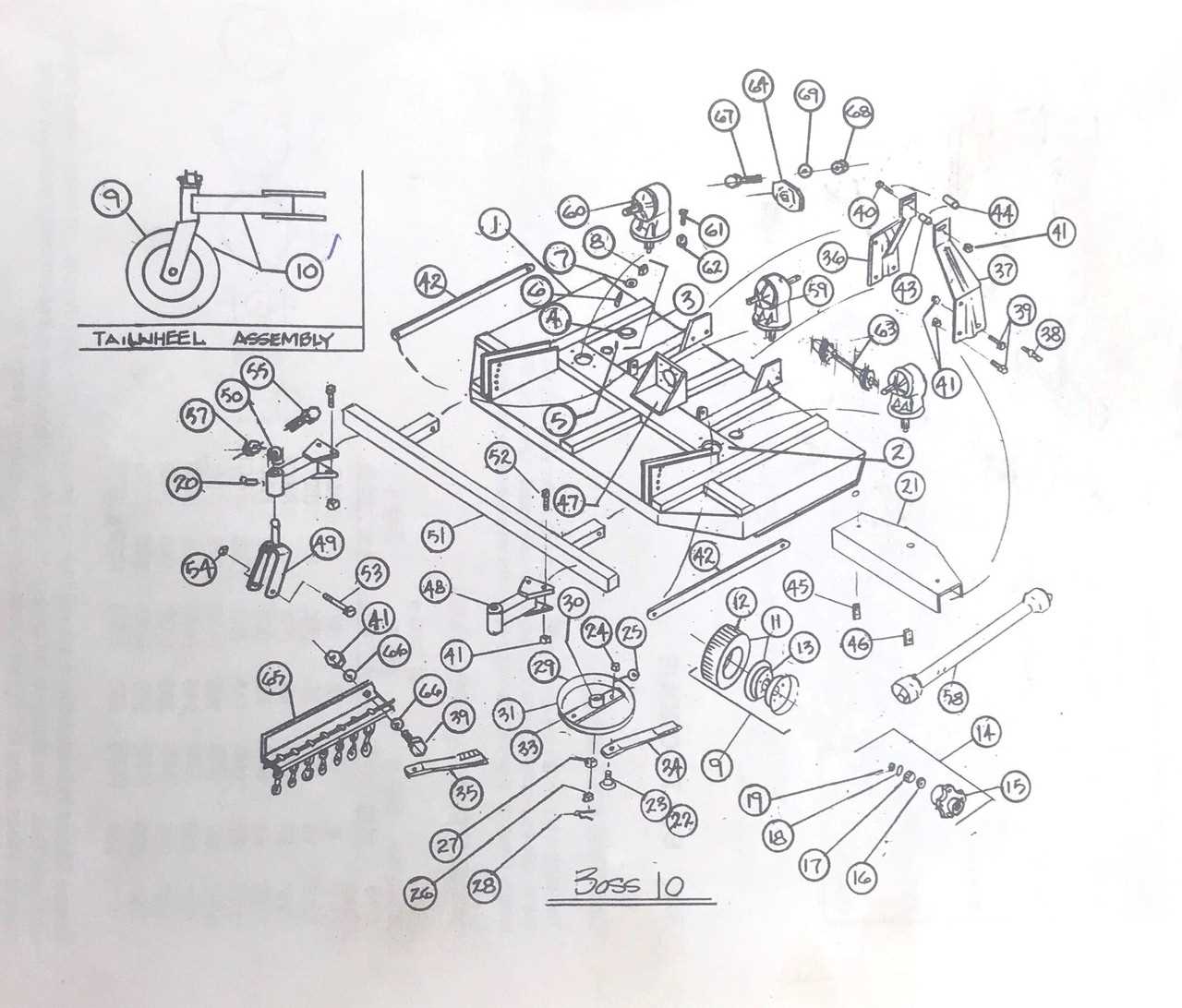
Labels contribute significantly to the clarity of visual aids. They help in the following ways:
- Identify key elements, making it easier for the audience to understand the relationships between components.
- Simplify intricate information by breaking it down into digestible pieces.
- Provide essential details that might not be evident from visuals alone.
Enhancing Engagement
Incorporating labels can also enhance viewer engagement. This is achieved through:
- Encouraging interaction by prompting viewers to explore the content more deeply.
- Facilitating discussions by providing a common language for referencing specific aspects.
- Supporting educational efforts by reinforcing learning through repetition and clarity.
Diagram Layouts and Their Importance
The arrangement of visual elements plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively. Properly organized layouts enhance clarity, making complex concepts more accessible to the audience. Understanding the significance of structure helps in presenting ideas in a way that is both engaging and informative.
Effective organization allows for a logical flow of information, guiding viewers through the content seamlessly. This structured approach not only aids comprehension but also fosters retention of the presented material. When elements are strategically positioned, the audience can easily identify relationships and hierarchies, which ultimately leads to a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Furthermore, thoughtfully designed layouts can greatly influence the overall aesthetic appeal of the presentation. An appealing arrangement captivates attention and encourages viewers to engage with the content. A well-crafted visual organization not only enhances the overall quality of the presentation but also reflects professionalism and attention to detail.
Visual Symbols in Diagrams
In visual representations, symbols serve as essential tools for conveying complex information in a clear and concise manner. These graphical elements help simplify intricate concepts, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the relationships and functions within the depicted system. By utilizing various shapes, lines, and colors, one can create an intuitive understanding that transcends language barriers.
Types of Symbols
Different categories of symbols exist, each designed to represent specific ideas or functions. Understanding these categories can enhance the effectiveness of visual communication. Below is a table highlighting some common symbol types and their meanings:
| Symbol Type | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Circle | Indicates a process or activity |
| Square | Represents a storage element or container |
| Arrow | Denotes direction or flow of information |
| Diamond | Signifies a decision point |
Importance of Clarity
Clarity in visual symbols is paramount for effective communication. When symbols are universally recognized and appropriately utilized, they can significantly reduce misunderstandings. Ensuring consistency in symbol usage across various contexts helps maintain a coherent visual language, facilitating smoother interactions and comprehension.
Connections and Flows in Diagram Design
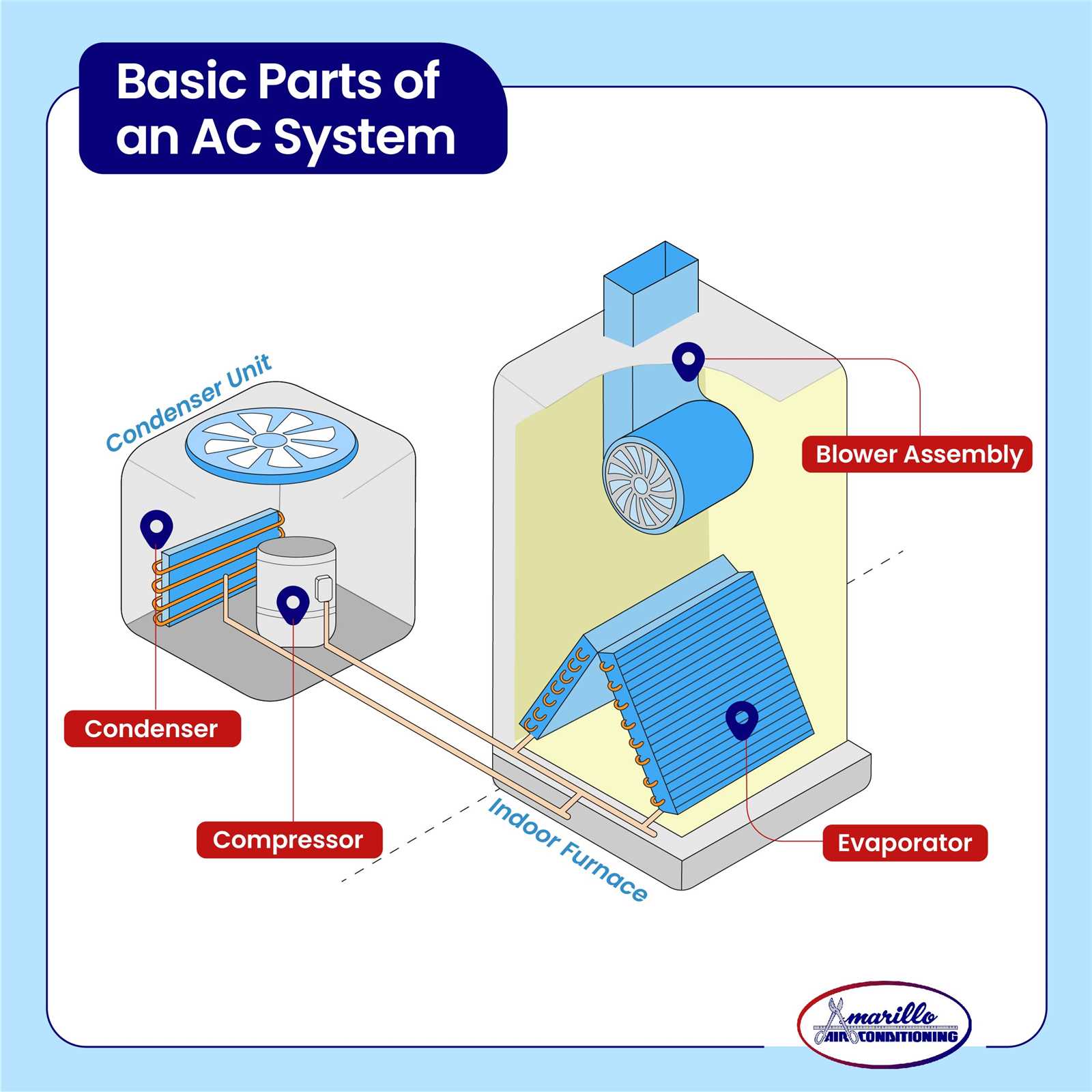
Creating effective visual representations requires a deep understanding of how elements interact and communicate. The arrangement of these components significantly influences the overall clarity and effectiveness of the visual model. Understanding the relationships and pathways between different elements is crucial for conveying information accurately and efficiently.
Understanding Interconnections
Interconnections serve as the backbone of any visual representation. Recognizing how different elements relate to each other allows for a seamless flow of information. Key aspects include:
- Establishing clear pathways for interaction.
- Identifying key nodes that serve as focal points.
- Utilizing directional indicators to guide the viewer’s understanding.
Enhancing Information Flow
Optimizing the flow of information is vital for ensuring that the audience can easily grasp the intended message. Consider the following techniques:
- Prioritize essential connections to avoid clutter.
- Utilize varying line styles to denote different types of relationships.
- Incorporate color coding to enhance differentiation among elements.
By focusing on the interconnections and information flow, creators can design more effective and comprehensible visual models that facilitate better understanding and engagement.
Shapes and Their Roles in Diagrams
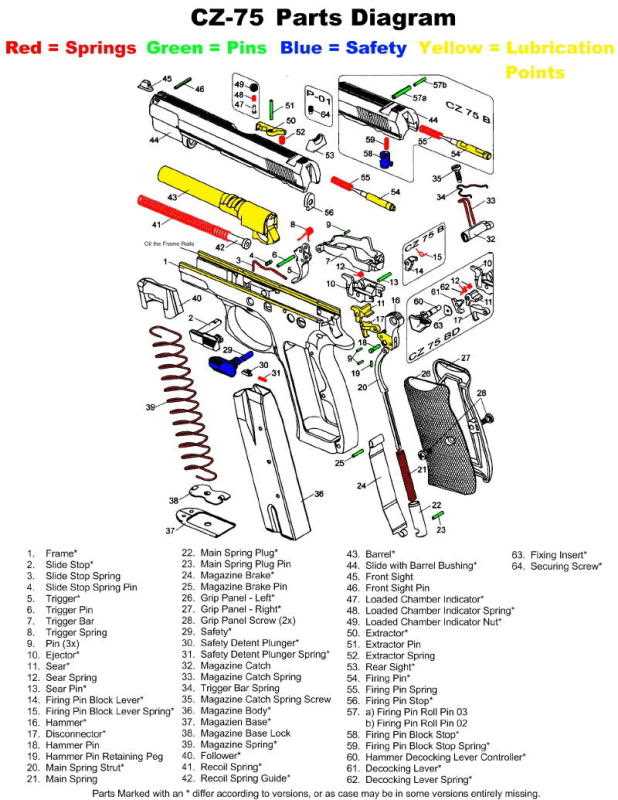
In visual representations, various forms serve distinct functions, contributing to clarity and understanding. Each type of shape conveys specific meanings, guiding the viewer through the information presented. Recognizing the significance of these forms enhances interpretation and facilitates effective communication.
Common Shapes and Their Meanings
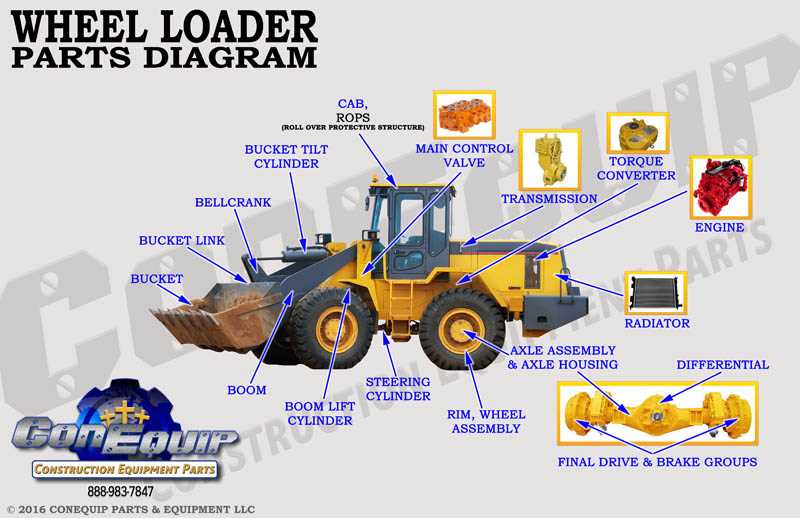
| Shape | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Circle | Represents unity, completeness, or a cycle. |
| Square | Indicates stability, structure, and reliability. |
| Triangle | Symbolizes change, direction, or action. |
| Rectangle | Conveys organization, processes, or systems. |
| Diamond | Signifies decision points or alternative paths. |
Using Shapes Effectively
To maximize comprehension, it is essential to utilize these forms strategically. Consistent use of specific shapes can establish a visual language, allowing viewers to navigate complex information with ease. Additionally, combining various shapes can create intricate narratives that enhance the overall understanding of the concept being conveyed.
Text Annotations in Diagram Interpretation
Text annotations serve as essential tools for enhancing understanding and clarity within visual representations. They provide context, emphasize key information, and guide the viewer’s interpretation. By integrating descriptive elements, these notations help convey complex ideas succinctly and effectively.
Effective communication through written notes is vital for ensuring that the intended message is accurately understood. Annotations can highlight specific components, illustrate relationships, or present additional data that enriches the overall narrative. Their strategic placement aids in directing attention to critical areas, facilitating a more comprehensive analysis.
Moreover, the use of concise language and clear terminology is crucial in making these notations accessible. This practice not only supports engagement but also fosters a deeper connection with the visual content. In essence, well-crafted textual elements play a pivotal role in transforming abstract concepts into relatable insights, bridging the gap between visual representation and cognitive comprehension.