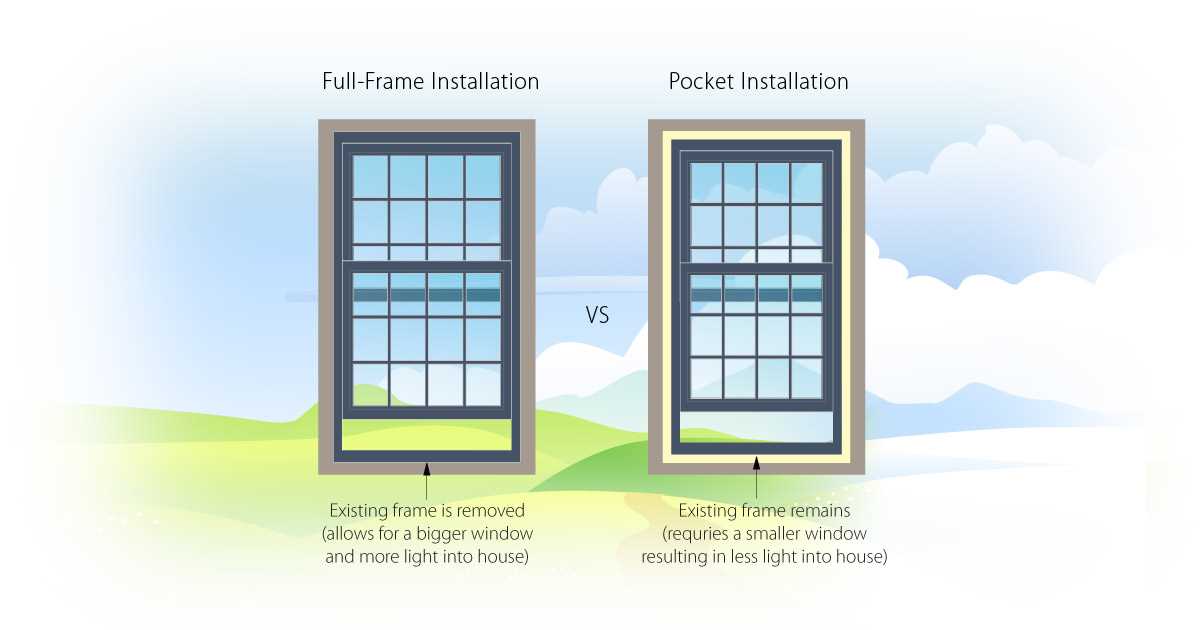
The structure surrounding openings plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. An in-depth examination of these elements reveals how they interact to create a seamless barrier against external conditions while enhancing the beauty of a building.
By exploring the various elements involved, we can uncover their individual purposes and contributions. Each component serves not only to support the overall design but also to ensure energy efficiency and protection from the elements.
Through a detailed look at these integral features, we can ultimately appreciate how they work together. This understanding is essential for anyone involved in design, construction, or renovation, providing insight into the best practices for maintaining and enhancing the integrity of structures.
Understanding Window Components
In any structure, the elements that create openings play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Each element contributes to the overall performance, offering various benefits such as insulation, protection, and style. By examining these components, one can appreciate how they work together to enhance the living experience.
Frames serve as the foundational structure, providing stability and support. Sashes are the moving sections that allow for ventilation, while glazing ensures clarity and thermal efficiency. Additional features, such as weather stripping and locks, enhance security and energy conservation.
Understanding these individual components ultimately leads to informed choices regarding maintenance, replacement, or new installations. This knowledge empowers homeowners to create comfortable and inviting spaces, tailored to their needs.
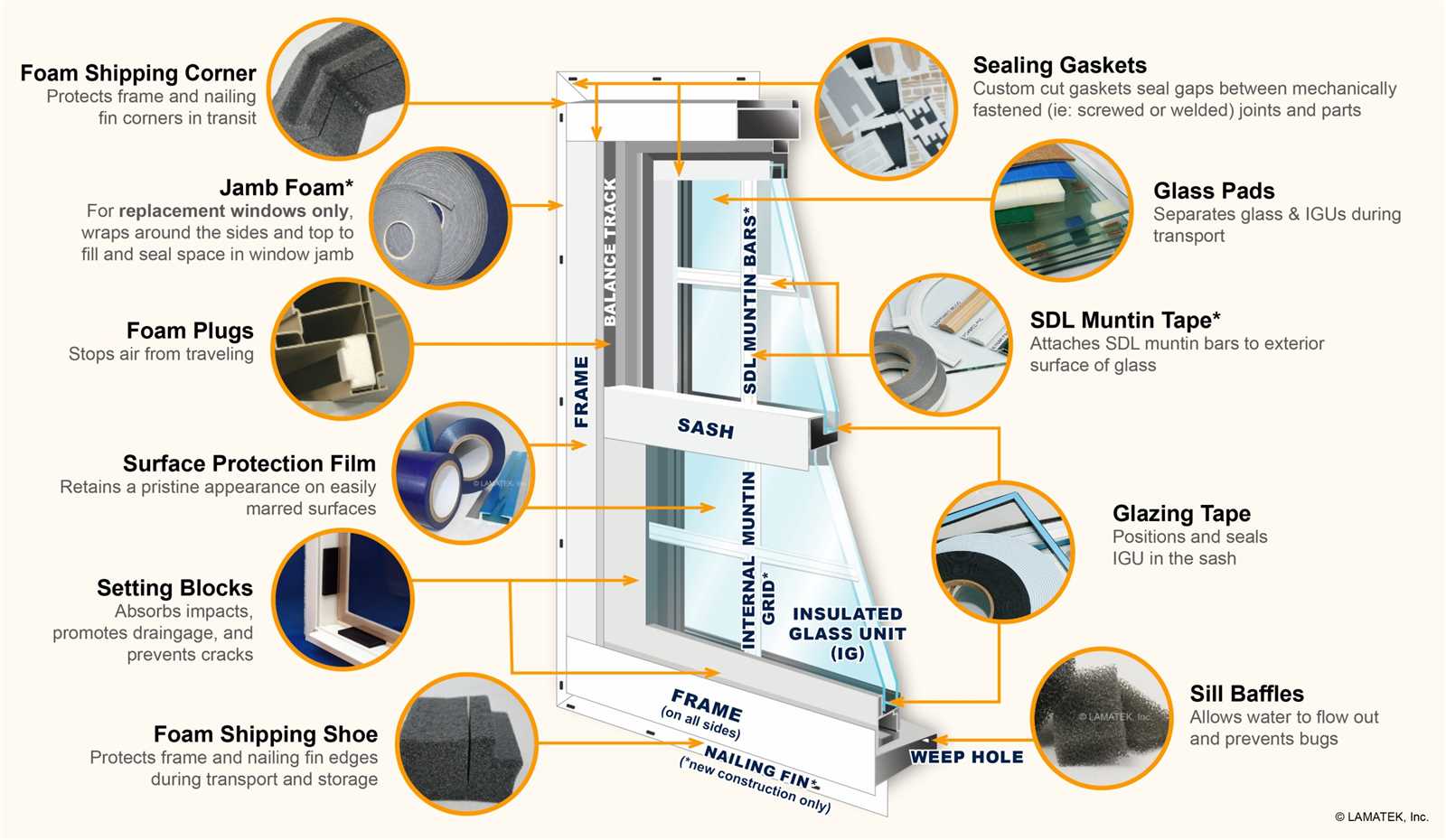
Basic Parts of a Window
Understanding the fundamental components that make up an opening is essential for anyone interested in construction, home improvement, or design. Each element plays a crucial role in functionality, aesthetics, and energy efficiency, contributing to the overall performance of the structure.
Key Components
- Frame: The sturdy structure that supports the entire assembly and holds all other elements together.
- Sash: The movable part that typically contains the glazing, allowing for operation and ventilation.
- Glazing: The transparent material that provides visibility and insulation, often made of glass or other materials.
- Seal: The material used to prevent air and water infiltration, ensuring energy efficiency and comfort.
- Hardware: The mechanisms that enable operation, such as locks, hinges, and handles.
Additional Elements
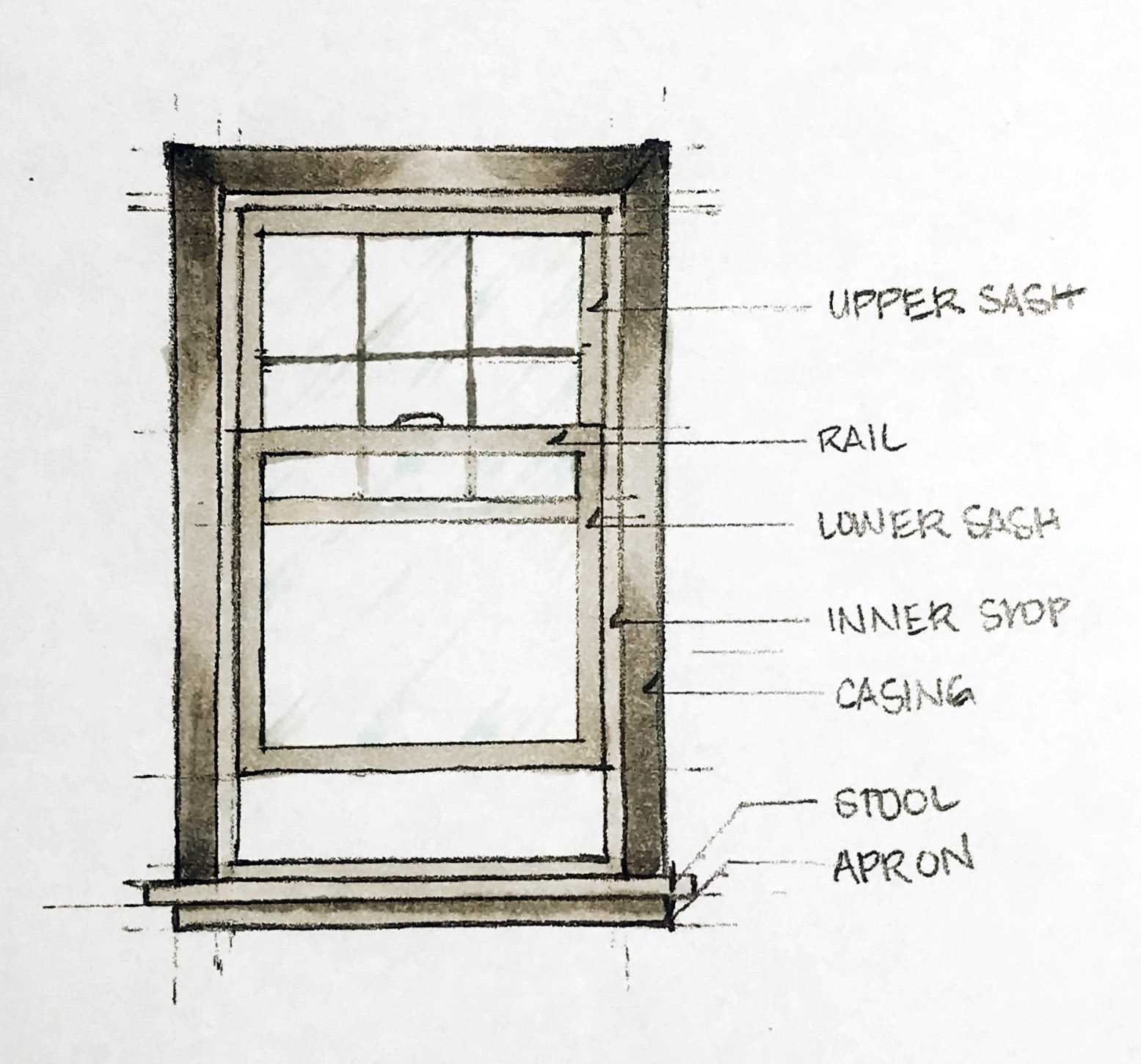
- Casing: The decorative trim that covers the gaps between the frame and the surrounding structure.
- Sill: The horizontal surface at the bottom that directs water away from the interior.
- Head: The upper horizontal member that caps the opening.
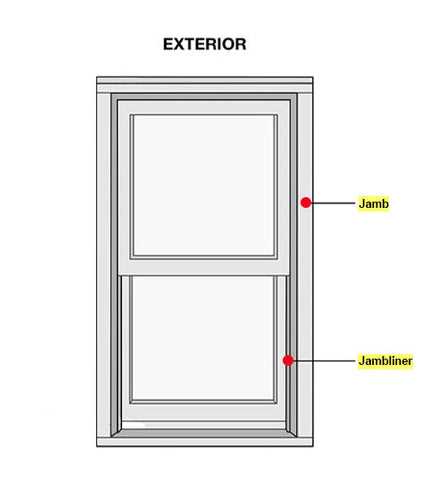
- Jamb: The vertical sides that support the frame and sash.
Common Materials Used in Windows
In the construction and design of openings, various substances play a crucial role in enhancing durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these materials helps in making informed decisions for both functionality and style.
Popular Materials
| Material | Properties | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Natural, Insulating | Classic appearance, good thermal performance | Requires maintenance, susceptible to rot |
| Vinyl | Synthetic, Low maintenance | Energy efficient, affordable | Limited color options, can warp in extreme heat |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, Strong | Modern look, durable | Poor insulation, can be prone to condensation |
| Fiberglass | Composite, High strength | Excellent insulation, low expansion | Higher initial cost, limited availability |
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the appropriate substance for your openings involves considering various factors, including climate, design preferences, and budget. Each option offers unique benefits and drawbacks, making it essential to evaluate them carefully to achieve the desired outcome.
How Windows Operate Mechanically
Understanding the mechanics behind these structures reveals the intricate interplay of components that allow for functionality and efficiency. Various elements work together to ensure seamless operation, enabling users to control light, airflow, and insulation effectively.
Components and Functions
Key elements include frames, sashes, and moving mechanisms that facilitate opening and closing. These components are designed to work in harmony, ensuring stability and ease of use while contributing to the overall durability of the assembly.
Movement Mechanisms
Different styles utilize distinct movement systems, such as sliding, casement, or awning functions. Each mechanism employs specific hardware and design principles to optimize performance and meet user needs, ultimately enhancing convenience and functionality.
Types of Window Frames Explained
There are several structures that serve as the foundation for openings in walls, offering both stability and aesthetic appeal. Each variation brings its unique qualities, affecting durability, maintenance, and thermal performance. Understanding these options can help in making informed decisions regarding materials and functionality.
| Material | Features | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Offers natural insulation and a classic appearance but requires regular upkeep to prevent deterioration. | ||||||||||
| Vinyl | A low-maintenance choice that is resistant to moisture and doesn’t need painting, making it a popular modern option. | ||||||||||
| Aluminum | Known for its strength and slim design,
Benefits of Energy-Efficient WindowsImproving your home’s efficiency not only enhances comfort but also reduces long-term costs. With advanced insulation and modern designs, you can significantly cut down on energy consumption, creating a more sustainable and cost-effective living space. Cost Savings Over TimeChoosing efficient solutions can lead to notable reductions in heating and cooling expenses. These innovations prevent air leakage and maintain a steady indoor temperature, minimizing the need for constant adjustments to your climate control system. Over time, this can result in considerable savings on utility bills. Environmental ImpactEnergy-efficient installations contribute to a greener planet by reducing the overall demand for power. This decrease in energy consumption lowers greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change while also conserving natural resources. By making such choices, you play a part in promoting a healthier environment for future generations. Identifying Window Styles and DesignsUnderstanding various types of architectural openings is essential for selecting the right design for any building. Each style offers unique characteristics, whether it’s about enhancing aesthetics or improving functionality. This section covers popular styles and their distinctive features to help you make informed choices. Popular Design Variations
Choosing the Right Design for Your Space
|
| Tool | Purpose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measuring Tape | For taking accurate dimensions before any adjustments or replacements. | ||
| Putty Knife | Used to apply or remove putty or sealant around frames. | ||
| Utility Knife | Ideal for cutting through caulk, old paint,
Choosing the Right Window GlazingSelecting the appropriate glazing material is crucial for ensuring long-lasting performance and energy efficiency. Different types of glazing offer unique benefits, making it essential to evaluate your specific needs and preferences. Below are some factors to consider when making your choice:
|