
In the realm of musical expression, certain instruments stand out due to their unique construction and sound production. This article seeks to explore the intricate assembly of one such wind instrument, providing clarity on its individual segments and their functions. By gaining insight into its layout, musicians can enhance their appreciation and mastery of the instrument.
The organization of this brass creation is essential for producing its characteristic tones. Each section plays a crucial role in sound generation and overall playability. By delving into these components, we can uncover the ultimate relationship between design and acoustics, facilitating a deeper understanding for both learners and seasoned players alike.
As we navigate through the various segments, it becomes apparent that each element contributes to the instrument’s versatility and range. Whether you are an aspiring musician or a curious enthusiast, recognizing these key features will enhance your engagement with this magnificent brass creation.
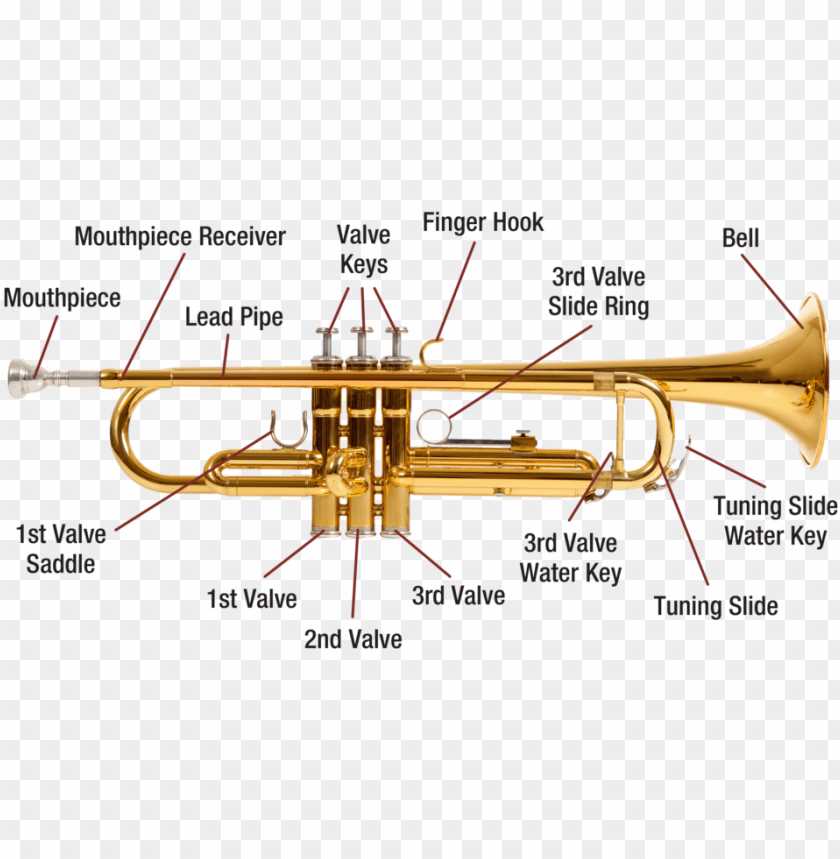
Understanding the French Horn Anatomy
Exploring the structure of this brass instrument reveals a fascinating interplay of components that contribute to its unique sound. Each segment is meticulously designed to enhance resonance and tonal quality, creating an intricate system that musicians must master. By delving into these elements, one gains insight into how they work together to produce rich, melodic notes.
The tubing of the instrument is coiled to facilitate easier handling while also influencing sound projection. This configuration allows for a variety of pitches, each shaped by the length and width of the passages. Additionally, the bell, which flares outward, plays a critical role in sound dispersion, affecting both volume and timbre.
Valves are essential mechanisms that enable players to alter the pitch by redirecting air through different lengths of tubing. Understanding how these valves function enhances a musician’s ability to navigate complex compositions, ensuring precision and clarity in performance.
The mouthpiece, often overlooked, is a vital element that directly impacts the player’s comfort and the instrument’s overall sound quality. Its shape and material can significantly affect tone production, making it a crucial consideration for any musician seeking to refine their craft.
By comprehensively examining the structure of this brass instrument, one can appreciate the artistry and engineering that contribute to its distinctive voice, empowering musicians to express a wide range of emotions through their performances.
Essential Components of the French Horn
This section explores the fundamental elements that contribute to the design and functionality of this unique brass instrument. Each component plays a crucial role in shaping the sound and ease of play, creating a harmonious blend that defines its character.
Main Elements
- Bell: The flared end that amplifies sound.
- Body: The coiled tubing that influences pitch and tone.
- Mouthpiece: The part where the player blows to produce sound.
- Valves: Mechanisms that alter the pitch and facilitate smoother transitions.
Additions and Modifications
- Handstop: Used to modify the instrument’s sound.
- Braces: Support structures that ensure stability and comfort.
- Tuning slides: Adjustments for fine-tuning the pitch.
How to Read a French Horn Diagram
Understanding the layout and components of a brass instrument is crucial for musicians seeking to enhance their skills. This section will guide you through the essentials of interpreting visual representations that detail the various sections of the instrument, enabling better familiarity and proficiency.
Begin by identifying the key elements displayed in the illustration. Each segment usually corresponds to a specific function or feature that contributes to the overall mechanics of sound production. Familiarizing yourself with these features can greatly aid in both practice and performance.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Bell | The flared end that amplifies sound. |
| Valve | Controls airflow and alters pitch. |
| Fingers’ keys | Used to change notes and create melodies. |
| Tubing | Connects various components and affects tonal quality. |
By becoming familiar with these features and their functions, players can effectively interpret how to utilize their instrument to achieve desired musical outcomes. Practicing with these visuals in mind will enhance both comprehension and performance capabilities.
Common Repairs for French Horn Parts
Maintaining the integrity of brass instruments is crucial for optimal performance. Over time, various issues can arise, necessitating attention and repair. Understanding the common types of fixes can help musicians ensure their instrument remains in peak condition.
Valve Issues: Problems with valves are frequent. These may include sticking or leaks, which can be resolved by cleaning or replacing worn components.
Slide Alignment: Misalignment of slides can affect tone and intonation. Regular adjustment and lubrication are essential to maintain smooth operation.
Dents and Bumps: Physical damage can occur, leading to altered sound quality. Skilled technicians can often remove these imperfections without compromising the instrument’s finish.
Felt and Cork Replacement: Over time, the felt and cork in various mechanisms wear out. Replacing these components ensures precise action and a reliable playing experience.
By addressing these common repairs promptly, musicians can prolong the life of their instrument and enhance their overall performance.
Different Types of French Horns Explained
In the world of brass instruments, there exists a variety of designs, each tailored for unique musical styles and performance contexts. Understanding these variations can greatly enhance a musician’s ability to choose the right instrument for their artistic expression and technical needs.
Single and Double Models
Among the most common designs are the single and double models. The single variant typically features a simpler construction, making it lighter and easier to handle, which is ideal for beginners. In contrast, the double version incorporates an additional tube, providing a broader range and richer tones. This complexity allows for greater versatility, catering to both classical and contemporary repertoires.
Variations in Key and Size
In addition to basic models, instruments also differ in key and size. Some versions are pitched in F, while others are in B♭, affecting the overall sound and playing style. Moreover, smaller instruments, like the descant variant, are often favored for their agility and bright tone, making them suitable for specific musical genres.
Importance of Proper Maintenance Practices
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of any musical instrument hinges on effective upkeep strategies. Regular care not only enhances sound quality but also preserves the overall integrity of the instrument.
Benefits of Regular Care
- Improved sound clarity and tonal richness.
- Extended lifespan of the instrument.
- Early detection of potential issues, preventing costly repairs.
Essential Maintenance Practices
- Routine cleaning to remove moisture and debris.
- Regular inspection for wear and tear.
- Proper storage to avoid environmental damage.
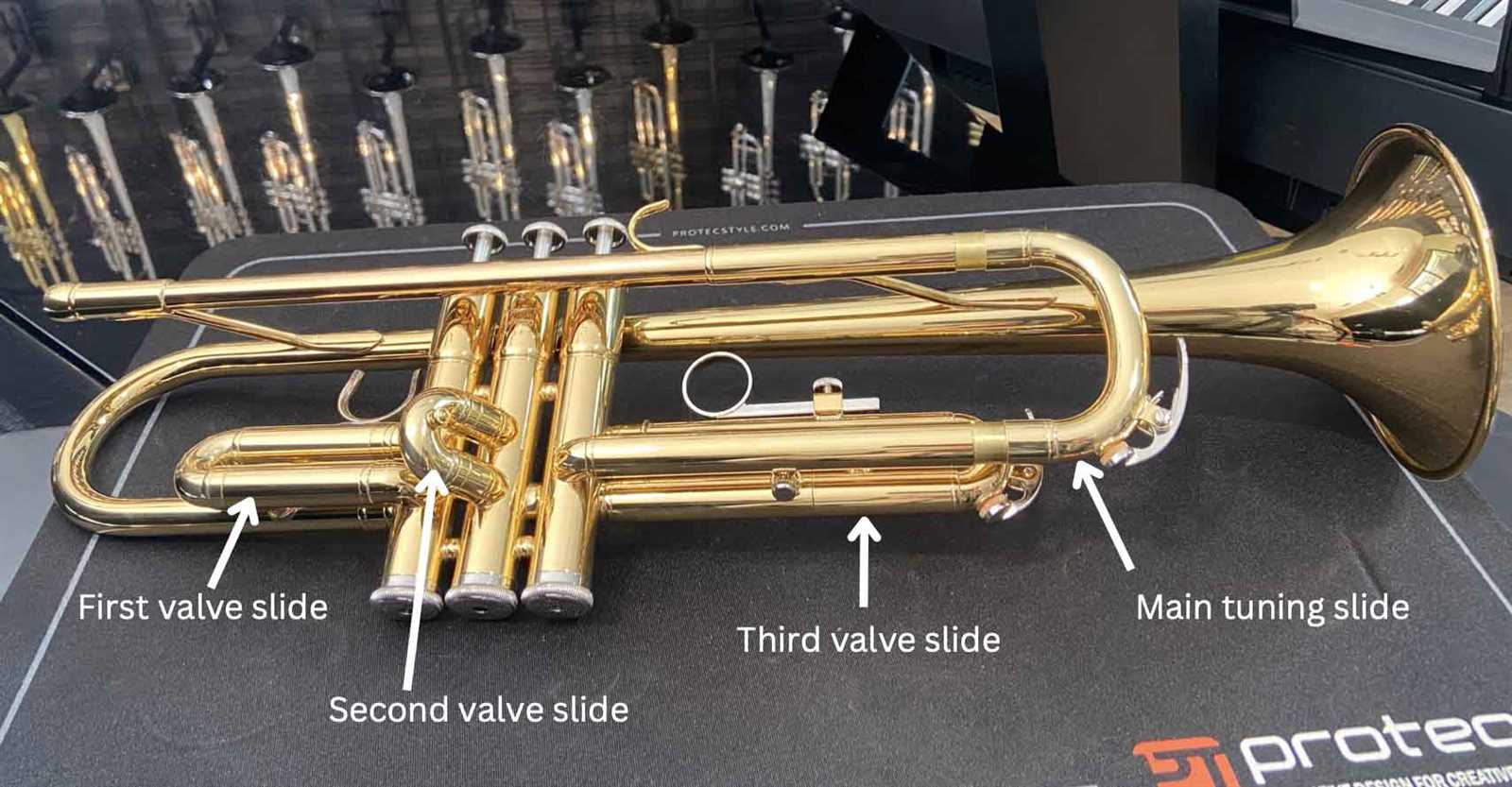
Identifying French Horn Valves and Tubes
Understanding the components of this brass instrument is essential for both players and enthusiasts. Each element contributes to the overall sound and functionality, making familiarity with their arrangement crucial for effective playing and maintenance.
Key Components Overview
The instrument features several distinct sections, each with a unique role in producing music. The tubes vary in length and curvature, affecting pitch and tone, while the valves control airflow, allowing for different notes to be played.
Table of Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Valves | Mechanisms that redirect air through various tubing configurations to change pitch. |
| Main Tubing | The primary pathway for airflow, influencing the overall sound quality. |
| Braces | Support structures that maintain the instrument’s shape and stability. |
| Bell | The flared end that projects sound outward, significantly shaping the tone. |
Sound Production in French Horns
The creation of sound in this brass instrument involves a harmonious blend of airflow and resonance within its intricate structure. Players manipulate various techniques to produce distinct tones, harnessing both physical skill and the instrument’s unique design.
Mechanics of Sound Generation
When a musician blows air into the mouthpiece, vibrations are initiated. These vibrations travel through the coiled tubing, where they interact with the instrument’s shape, amplifying and modifying the sound.
Factors Influencing Tone Quality
Numerous elements affect the richness of the sound, including the player’s embouchure, the instrument’s materials, and its overall configuration. Mastery of these factors is essential for achieving the desired auditory experience.
| Factor | Influence on Sound |
|---|---|
| Embouchure | Determines vibration control |
| Material | Affects resonance and timbre |
| Configuration | Shapes the overall sound projection |
Comparing Single and Double Horns
When exploring the world of brass instruments, one may encounter two distinct types that offer unique characteristics and playability. Understanding their differences can enhance a musician’s experience and choice in repertoire.
Key Differences
- Design: The single variant typically has a simpler structure, while the double version features an additional set of tubing for greater versatility.
- Range: The double variant provides a wider tonal range, allowing for more complex musical passages.
- Weight: The single version is generally lighter, making it easier for prolonged playing sessions.
- Intonation: The double design often offers improved intonation across different registers.
Choosing the Right Instrument

Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on personal preference, playing style, and the specific demands of the music being performed. Aspiring musicians should delve into each type to find the one that best suits their needs.
Choosing the Right Horn for You
Selecting the appropriate instrument is crucial for any aspiring musician. The choice can significantly influence your playing experience, sound quality, and overall enjoyment. Understanding your unique needs and preferences will help you make an informed decision.
Consider Your Skill Level
Beginner players may benefit from a more forgiving model, while experienced musicians might seek advanced features. Testing various options can provide insight into what feels most comfortable.
Material and Build Quality
The construction and materials used in an instrument affect tone and durability. Brass is common, but variations exist that can enhance sound quality. It’s essential to choose one that resonates with your style.