
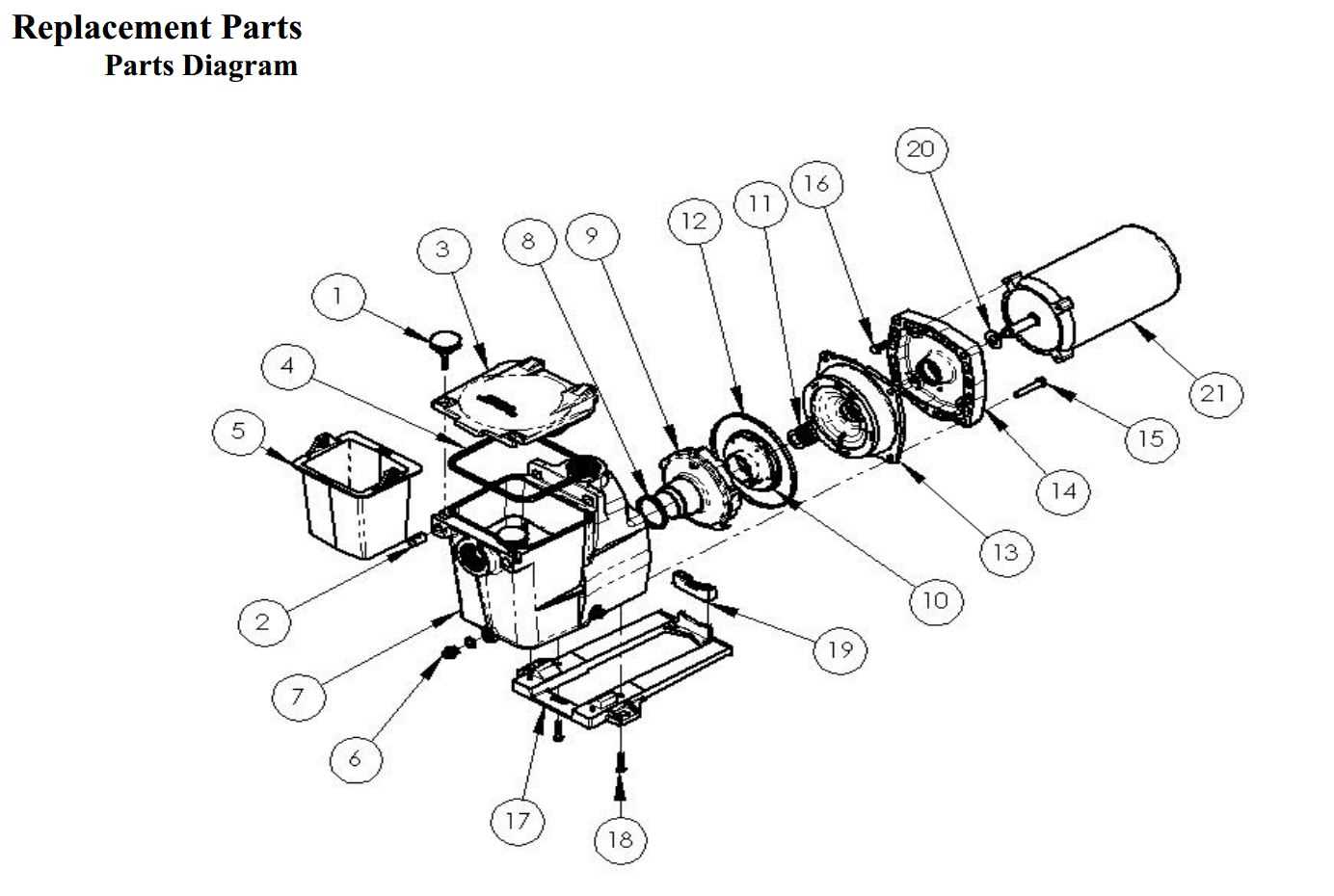
In this section, we delve into the intricate anatomy of a swimming pool pump, offering a detailed exploration of its internal mechanisms and key functional elements. Discovering the inner workings involves a visual journey through the various parts that collectively contribute to the pump’s operational efficiency.
Understanding the structure and functionality of each component enhances maintenance prowess, aiding in diagnosing and addressing potential issues effectively. This breakdown not only serves as a guide for maintenance experts but also empowers pool owners with valuable insights into their equipment.
Identifying these essential parts ensures a comprehensive grasp of the pump’s mechanical integrity, promoting optimal performance and longevity. From impellers to seals, each component plays a crucial role in the pump’s overall functionality, reinforcing the importance of regular inspection and upkeep.
Pump Components Overview

The functionality of a pool pump relies on several integral components that work together to ensure water circulation and filtration. Each element has a specific role in maintaining the system’s efficiency, ensuring that the flow of water is smooth and consistent. Understanding these key elements can help in troubleshooting and maintaining the equipment, as well as optimizing its performance.
Motor: The motor powers the system, driving the impeller to move water through the system. It is critical for ensuring the necessary pressure and flow for effective filtration.
Impeller: Positioned inside the pump housing, the impeller rotates at high speed to draw water in and push it through the system. Its design is optimized for both efficiency and durability.
Strainer Basket: This component captures debris and prevents it from entering the pump, protecting the impeller and extending the lifespan of the entire setup.
Housing: The external casing protects the internal elements and ensures that water flows through the system without leakage. It also helps with heat dissipation, keeping the system running smoothly.
Seal Plate: The seal plate ensures that the motor and pump housing are tightly connected, preventing water from leaking into the motor area, which could caus
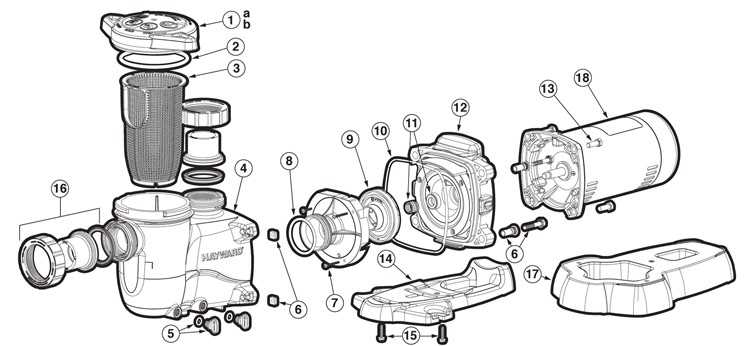
Motor Assembly Breakdown
The motor assembly consists of various interconnected components, each playing a critical role in ensuring smooth operation. Understanding the structure and placement of these elements is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
Main Components Overview
- Motor housing: The external casing that protects internal elements from external damage and contamination.
- Impeller: A rotating component responsible for creating the necessary flow by drawing in water.
- Shaft seal: Prevents water from leaking into the motor by sealing the space between the impeller and motor.
- Bearings: Reduce friction and support the rotating shaft, ensuring the motor runs efficiently.
- Capacitor: Helps the motor start by providing an initial energy boost, especially during startup.
Assembly and Disassembly
- Begin by disconnecting the power source to avoid any electrical hazards.
- Remove the motor housing screws carefully and set them aside for reassembly.
- Access the impeller by det
Impeller and Diffuser Functionality
The combined operation of the impeller and diffuser is central to the efficiency of water circulation systems. Both components work in tandem to convert mechanical energy into fluid movement, ensuring optimal flow and pressure within the system. Understanding their roles helps improve system performance and maintenance.
Component Function Impeller Responsible for moving water by creating centrifugal force, propelling the fluid through the system at increased velocity. Diffuser Helps direct and stabilize the water flow after it exits the impeller, reducing turbulence and maintaining consistent pressure. Seal Plate and Gasket Details
The seal plate and gasket serve crucial roles in maintaining the integrity of a pump system, ensuring that no fluid leaks occur. Properly installed components help to create a secure connection between different parts of the system, preventing any unwanted seepage and ensuring long-lasting operation.
Seal Plate Features

- Designed to provide a tight seal between key pump components.
- Made from durable materials to withstand constant pressure and fluid exposure.
- Includes attachment points to fit securely into the pump housing.
Gasket Functions
- Creates a barrier between two surfaces to prevent leaks.
- Typically made from rubber or flexible materials to ensure a snug fit.
- Requires periodic inspection to ensure it maintains its sealing capabilities.
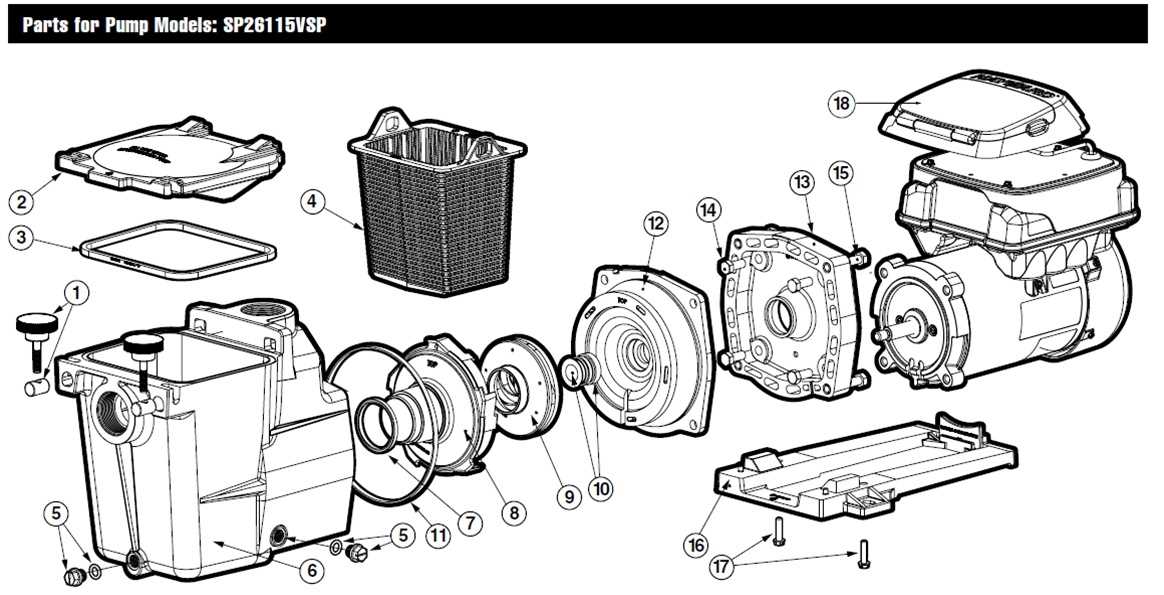
Strainer Cover and Basket Design
The strainer cover and basket are essential components for ensuring debris filtration in water systems. Their design enhances the efficiency of water flow by preventing unwanted particles from entering critical areas. The combination of these parts helps maintain smooth operation, extending the life of the system.
Component Material Function Strainer Cover Durable Plastic Seals the strainer chamber, allowing easy inspection and cleaning Basket Reinforced Mesh Catches debris while allowing water to pass through freely Both the cover and basket are
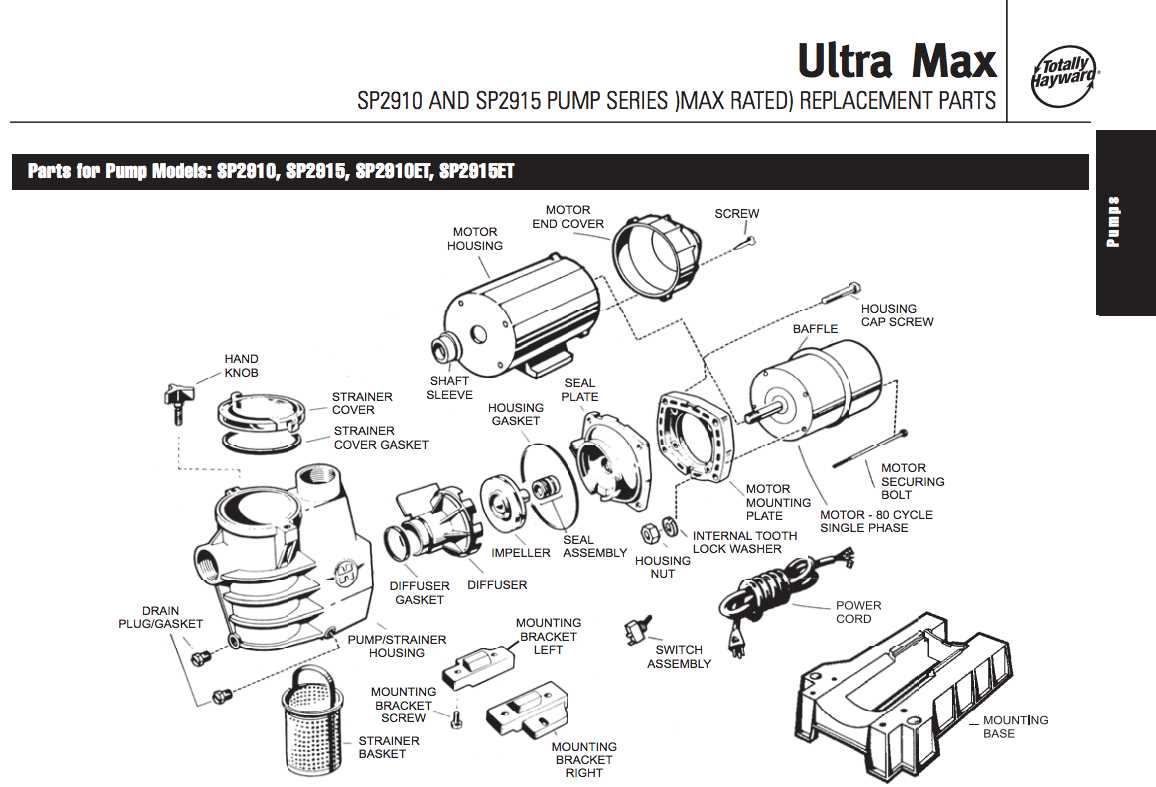
Understanding the Housing Structure
The housing structure plays a critical role in protecting and maintaining the efficiency of various components within a system. This outer casing is designed to ensure that all internal mechanisms are securely enclosed, safeguarding them from external elements such as debris, moisture, and physical damage. The integrity of the housing directly influences the system’s durability and longevity.
Main Sections of the Housing
Typically, the housing consists of multiple sections, each serving a specific function. The main body provides a sturdy enclosure, while access points or lids allow for maintenance and adjustments. Reinforced areas within the casing often support key components, ensuring they remain in proper alignment during operation.
Importance of Proper Sealing
A well-sealed housing is essential for preventing leaks and contamination. Gaskets or seals are often placed at the joints to create a tight fit, minimizing the risk of external interference.
Discharge Port Configuration
The discharge port plays a crucial role in directing the water flow out of the pump system. Proper alignment and setup of this port ensure efficient operation and prevent potential water pressure issues. Configuring the discharge port correctly contributes to overall system performance and longevity.
When setting up the discharge outlet, consider the angle and connection type to ensure compatibility with your plumbing system. A properly adjusted outlet minimizes energy loss and helps maintain optimal flow rates. Additionally, the material and sealing method used in the port connection are important for ensuring long-term durability and leak prevention.
O-ring Placement and Importance
O-rings play a crucial role in ensuring the tightness and functionality of various mechanical systems. Their correct placement prevents leaks and ensures that components work effectively under pressure. Without proper sealing, systems may experience unnecessary wear, reduced efficiency, or complete failure.
Critical Locations for O-ring Placement
O-rings are typically found in areas where two components meet and need to maintain a secure connection. These locations often involve junctions that handle liquid flow, pressure, or environmental barriers. Ensuring O-rings are seated properly in these areas helps maintain the system’s integrity and avoid costly damage.
The Role of O-rings in System Efficiency
When installed correctly, O-rings enhance the longevity and performance of a system by reducing friction and wear on moving parts. They act as a protective barrier, minimizing the risk of contamination and ensuring that fluids or gases remain contained. Proper maintenance and replacement of worn O-rings are essential to prevent malfunctions and extend the life of the system.
Volute Casing and Flow Dynamics
The volute casing is a critical component in fluid handling systems, influencing the movement and pressure of liquids within pumps. Its design is essential for optimizing the efficiency of flow dynamics, ensuring smooth transition of water or other fluids through the impeller and out of the pump system. Proper alignment of the casing with the impeller minimizes turbulence, allowing for more stable and efficient operation.
- The shape of the casing directs fluid flow smoothly around the impeller.
- Its structure converts kinetic energy into pressure energy as the fluid decelerates.
- Well-engineered casings reduce hydraulic losses, improving system efficiency.
Understanding the interaction between the volute casing and fluid dynamics can lead to significant improvements in pump performance, reducing energy consumption and wear on mechanical parts.
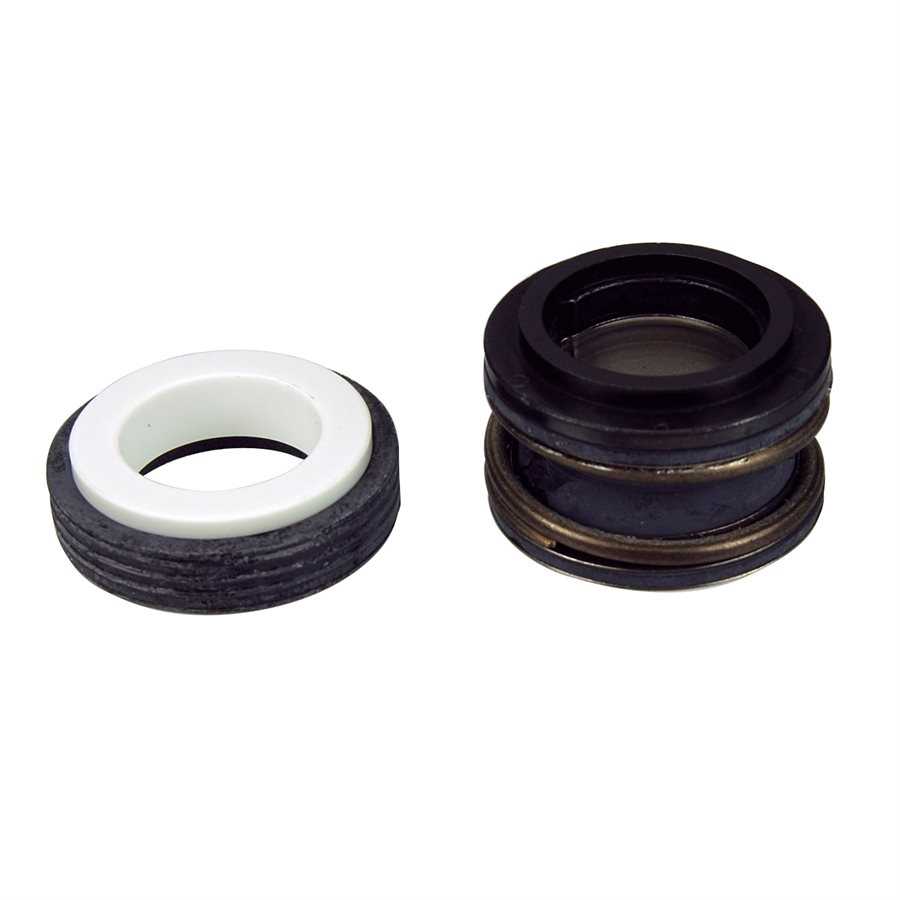
Shaft Seal Replacement Guide
Replacing the shaft seal is a crucial maintenance task to ensure proper functioning and longevity of your equipment. The shaft seal prevents water from leaking into the motor, protecting its internal components from damage. In this guide, we will walk through the steps required to replace the seal, ensuring a secure fit and reliable operation.
Tools and Materials Needed
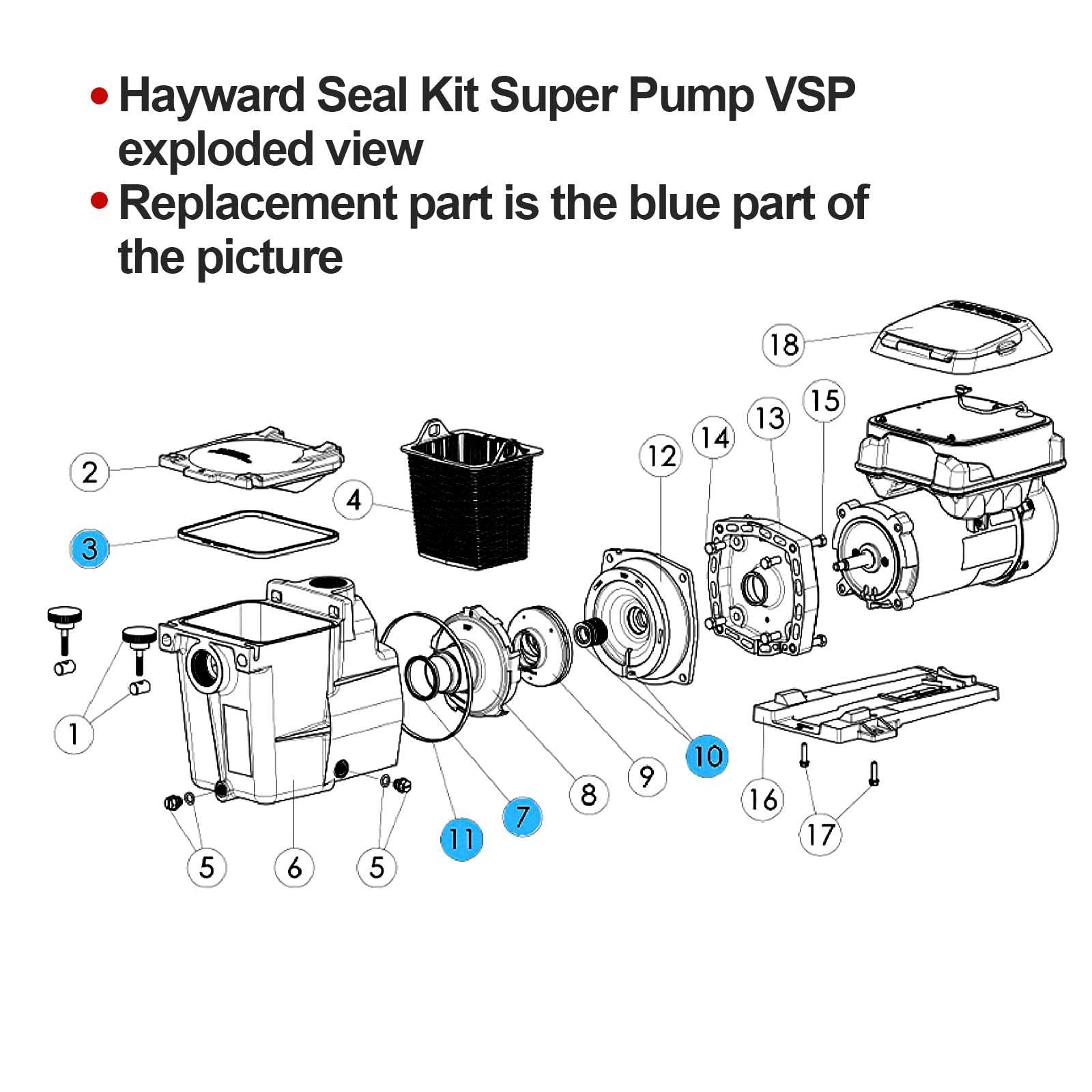
Tool Purpose Wrench To loosen and tighten bolts Screwdriver For removing screws on the casing Shaft Seal New seal to replace the old one Lubricant To ensure smooth installation Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Turn off the power supply to the equipment and disconnect it from the system to avoid accidents.
2. Begin by removing the pump
Parts Compatibility and Alternatives
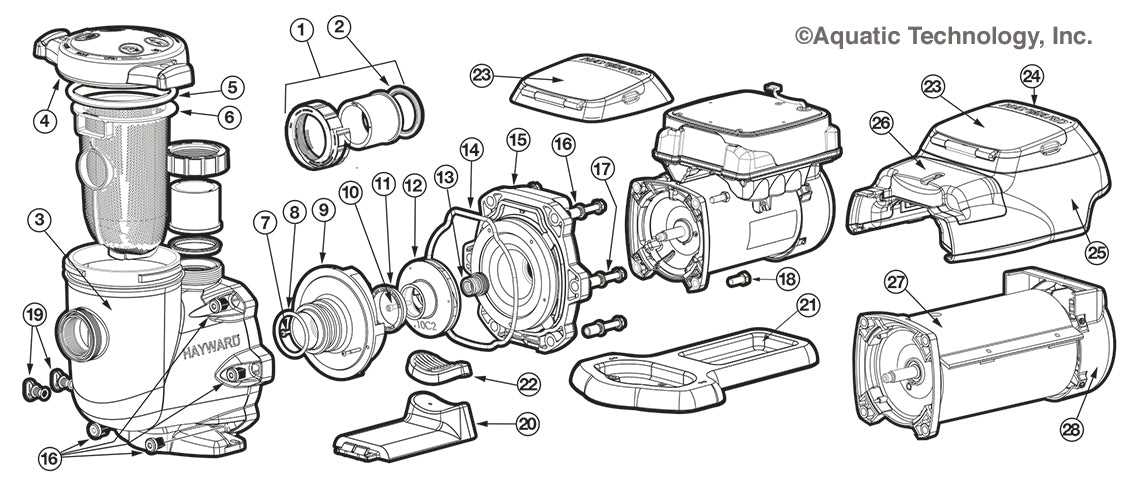
When selecting replacement components for your equipment, it is important to consider compatibility to ensure proper functionality. Understanding which models and materials work seamlessly together can prevent malfunctions and extend the life of your system. Additionally, exploring alternative components can sometimes offer more affordable or durable options.
Key Considerations for Compatibility
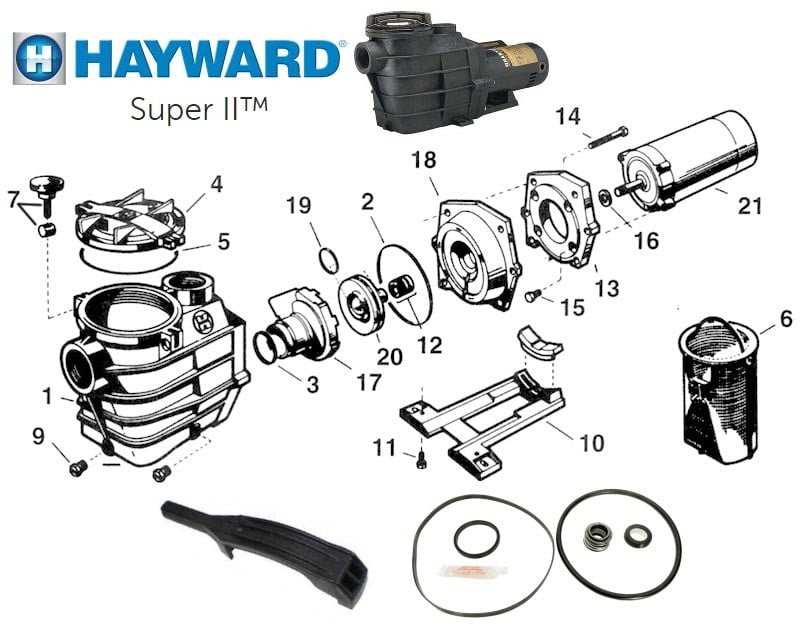
- Ensure the dimensions match your current setup.
- Check that the material is suitable for the operational environment.
- Review the manufacturer’s specifications for interchangeable components.
Alternative Options
In some cases, alternative models or aftermarket solutions can provide cost-effective replacements without sacrificing quality. These alternatives can offer enhanced features, greater durability, or ease of installation.
- Aftermarket components often come at a lower cost while maintaining similar performance.
- Upgraded materials may offer better resistance to wear and tear.
- Some alternatives are designed for easier maintenance and longer service life.