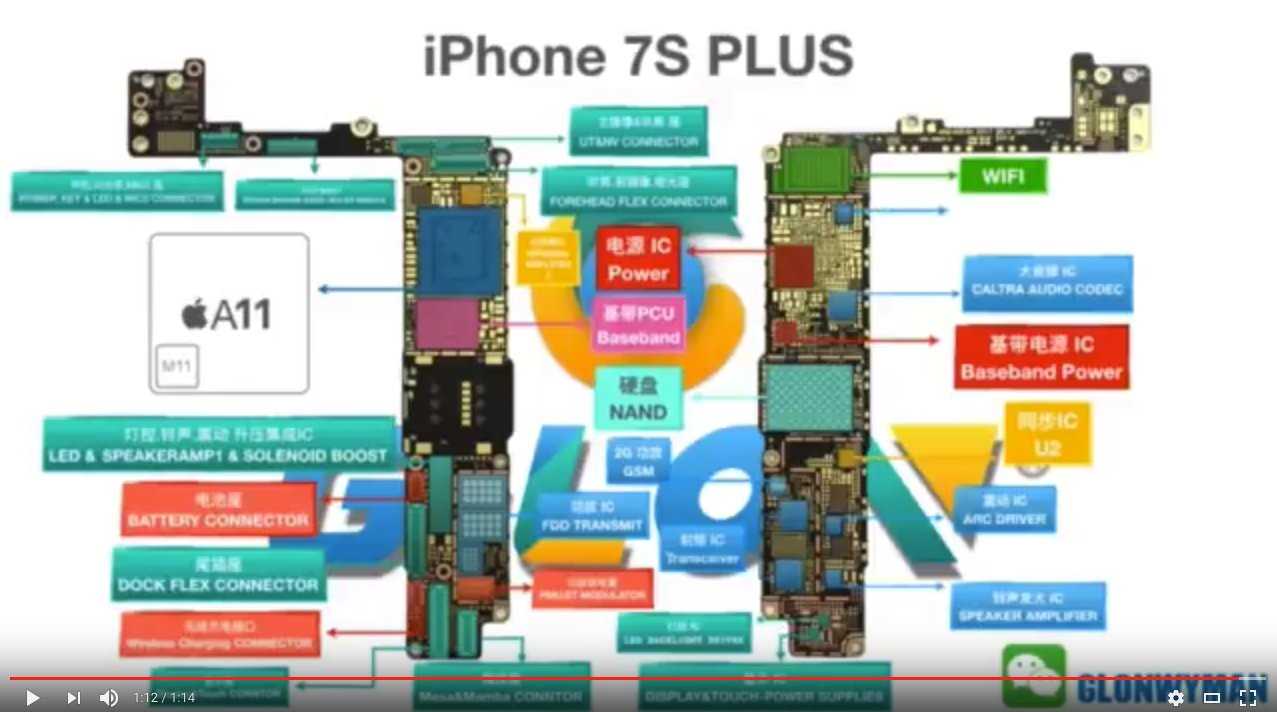
Exploring the intricate framework of the technological marvel known for its compact complexity, this segment delves into a comprehensive breakdown of its inner workings. Highlighting the structural elements and functional nodes that collectively define its operational integrity, this diagrammatic exposition elucidates the interconnected systems that empower its functionality.
An in-depth scrutiny reveals a network of specialized units, each contributing uniquely to the holistic performance. From foundational components that establish the core framework to specialized modules facilitating diverse functionalities, this portrayal illuminates the synergy of engineering precision and digital innovation at the heart of its design.
Unveiling the interplay between form and function, this schematic journey elucidates how each element harmonizes with others to ensure seamless operation. Beyond mere physicality, it encapsulates a testament to technological evolution, where precision meets innovation in a synthesis that transcends conventional boundaries.
Understanding the Layout of the Device
In this section, we explore the arrangement and structure of the device’s components and elements. Understanding how these elements are positioned and interconnected provides insight into the functional organization of the device.
Component Groupings
The device is organized into distinct groups of elements, each contributing to its overall functionality and operation. These groupings are strategically positioned to optimize performance and user interaction.
Key Structural Features
A detailed examination reveals essential structural features that support the device’s core operations. These features are integral to the seamless integration and functioning of its various components.
| Component Groupings | Key Structural Features |
|---|---|
| 1. Central Processing Elements | 1. Frame and Housing |
| 2. Input and Output Mechanisms | 2. Display Module |
| 3. Power and Connectivity Modules | 3. Button Interfaces |
Key Components of the Device
Understanding the essential elements that constitute a mobile gadget is crucial for both users and technicians. Each component plays a significant role in the functionality and performance of the device, contributing to its overall user experience. Here, we will explore the major parts that are integral to its operation.
Core Components
- Display Unit: The visual interface that allows interaction with the system, featuring touch capabilities for seamless navigation.
- Battery: The power source that ensures the device remains operational throughout the day, influencing both performance and longevity.
- Processor: The brain of the device, responsible for executing tasks and managing applications efficiently.
- Camera Modules: Essential for capturing images and videos, these components vary in quality and functionality, impacting photography experiences.
Supporting Elements
- Motherboard: The central hub that connects all components, facilitating communication and power distribution.
- Storage: A crucial element for saving data, applications, and multimedia, with options ranging from internal to external solutions.
- Audio System: This includes speakers and microphones, enabling sound output and voice communication.
- Connectivity Modules: Essential for network access, these components support Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connections.
Exploring Internal Structures and Features
Understanding the intricate layout and components within a smartphone is essential for grasping its functionality and performance. Each element plays a vital role, contributing to the device’s overall efficiency and user experience. This exploration reveals how these internal structures interact, ensuring seamless operation while providing various features that enhance daily tasks.
Component Interconnectivity
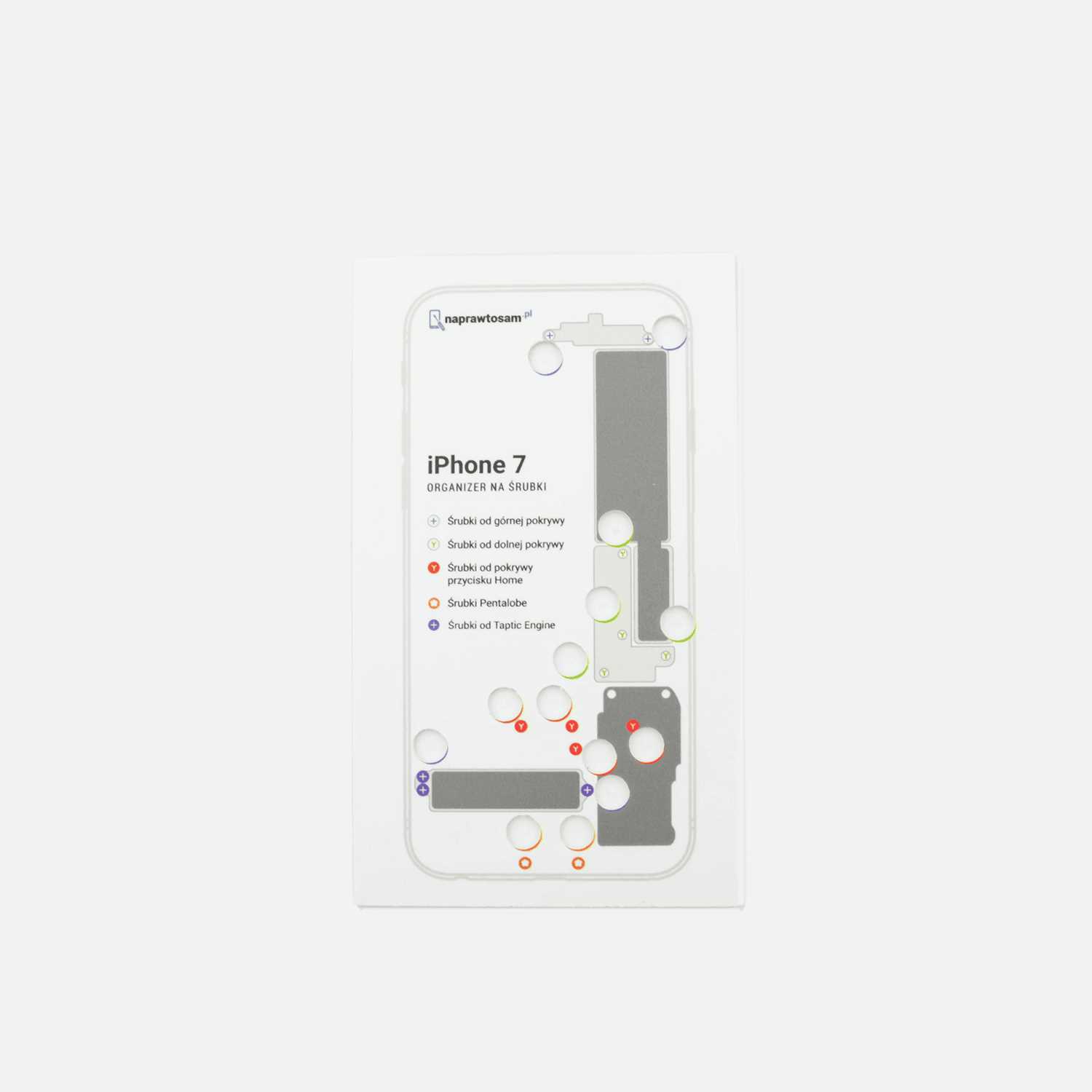
The interconnection of various elements is fundamental to the device’s architecture. From the central processing unit to memory units, each component communicates with others through meticulously designed pathways. This interconnectedness not only boosts processing speed but also allows for efficient energy management, ensuring longevity and reliability during usage.
Innovative Features and Their Impact
Advanced functionalities, such as high-resolution cameras and biometric sensors, are made possible by sophisticated internal designs. These innovations leverage cutting-edge technology to deliver enhanced user experiences. By examining how these features are integrated, one can appreciate the engineering prowess that transforms theoretical concepts into tangible capabilities.
Identifying the Main Circuit Board
The section aims to elucidate the core component responsible for orchestrating the intricate functionalities within the device. Understanding its configuration and interconnections is crucial for comprehending the operational dynamics of this central unit.
Components and Layout: Examining the arrangement and components housed within this pivotal unit provides insights into its functional capabilities. Each element plays a definitive role, contributing collectively to the overall functionality of the device.
Identification Methods: Various methodologies can be employed to discern the unique attributes and characteristics that distinguish this component from others within the assembly. These methods are pivotal for accurate assessment and troubleshooting.
Interconnectivity: The circuit board’s integration with peripheral components underscores its role as a nexus for data transmission and operational control. Understanding these connections is essential for diagnosing and rectifying operational issues.
Technological Evolution: Over time, advancements in design and integration have influenced the configuration and capabilities of this critical unit, reflecting broader trends in electronics engineering.
Conclusion: Mastery of the main circuit board’s identification is fundamental for anyone engaged in maintenance, repair, or technical exploration of modern electronic devices.
Battery Specifications and Placement
The power source of a mobile device plays a crucial role in its overall performance and usability. Understanding the technical specifications and optimal positioning of this energy reservoir is essential for effective maintenance and enhancement. In this section, we will delve into the characteristics and placement of the power unit, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of its function within the device.
Specifications Overview
The energy cell typically has a capacity measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), reflecting its ability to store and supply energy. A higher mAh rating indicates a longer potential usage time between charges. Additionally, the voltage rating is critical, as it affects the performance and efficiency of the device. Manufacturers often optimize these specifications to balance longevity and size, making it imperative to consider both aspects for a seamless user experience.
Placement Considerations
Proper positioning of the energy cell within the device is vital for efficient operation and safety. The power unit is usually located in a compartment that allows for effective heat dissipation and easy access for replacement. This placement is designed to minimize interference with other components while ensuring secure connectivity to the mainboard. Understanding these spatial dynamics can aid in troubleshooting issues related to battery performance and overall device functionality.
Camera Modules and Their Functions
In modern smartphones, the functionality of imaging components plays a crucial role in enhancing user experience. These modules are designed to capture high-quality photos and videos, each serving distinct purposes to optimize performance under various conditions. Understanding the roles of these components helps users appreciate the technology behind their devices.
| Module Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Main Camera | Captures high-resolution images and videos, providing primary photographic capabilities. |
| Front Camera | Designed for selfies and video calls, often featuring wide-angle lenses. |
| Telephoto Lens | Enables optical zoom, allowing for close-up shots without losing image quality. |
| Wide-Angle Lens | Captures broader scenes, ideal for landscapes or group photos. |
| Depth Sensor | Enhances portrait modes by providing depth information, creating a bokeh effect. |
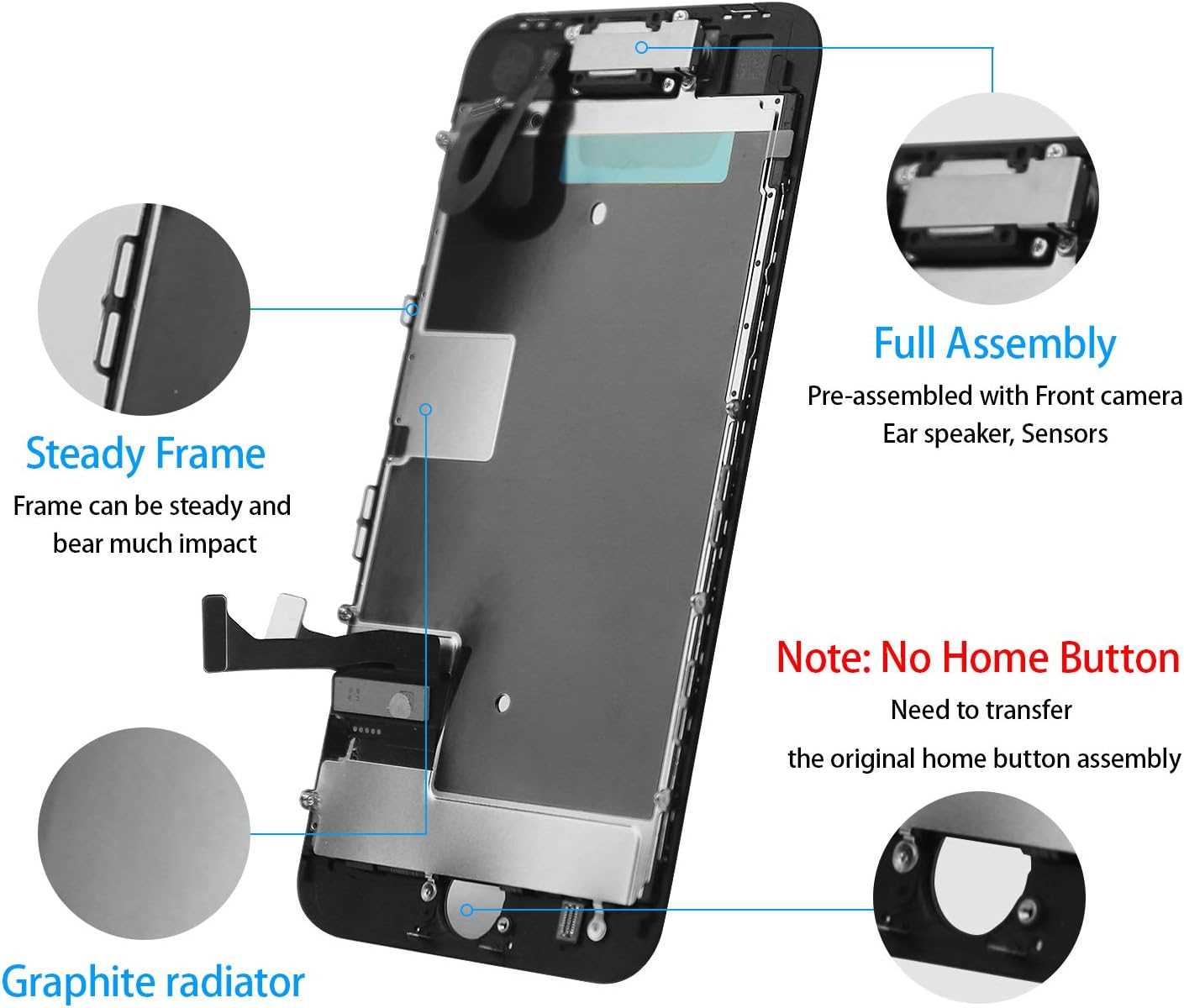
Understanding the Display Assembly
The display assembly serves as a crucial component in modern smartphones, playing a vital role in user interaction and overall functionality. It comprises several integral elements that work together to deliver high-quality visuals and responsive touch capabilities.
Key components of the display assembly include:
- Display Panel: The primary surface that presents images and content to the user.
- Touch Digitizer: A layer that detects touch input, enabling users to interact with the device.
- Frame: The structural element that houses and supports the display components.
- Backlight: A system that illuminates the display for visibility in various lighting conditions.
Each of these components plays a significant role in ensuring optimal performance:
- Visual Clarity: The display panel is designed for crisp resolution, enhancing the viewing experience.
- Touch Sensitivity: The digitizer ensures precise detection of gestures and taps, improving usability.
- Durability: The frame provides protection, ensuring that the display remains intact during daily use.
- Lighting Quality: The backlight contributes to vibrant colors and sharp contrasts, crucial for media consumption.
Understanding these elements helps in appreciating how they contribute to the overall performance of the device, enhancing user experience and functionality.
Ports and Connectors Overview
In this section, we delve into the various interfaces and linkage points that facilitate connectivity and interaction within the device. These essential conduits serve as entryways and outlets for data, power, and peripheral integration, ensuring seamless operational synergy between internal mechanisms and external peripherals.
- A primary interface that facilitates high-speed data transfer and charging capabilities.
- An audio connection point, enabling sound transmission and reception.
- A small opening designed for inserting and ejecting a storage medium.
- Several small, specialized connections that serve distinct operational functions.
Understanding these diverse channels is crucial for comprehending the device’s functional capabilities and versatility, showcasing its adaptability in accommodating various user needs and technological advancements.
Cooling Mechanisms and Heat Dissipation
Effective thermal management is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in modern electronic devices. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency, potential hardware failures, and a compromised user experience. To prevent such issues, various strategies are employed to manage heat generation and promote effective heat dissipation.
One of the primary approaches to temperature regulation involves:
- Material Selection: The use of thermally conductive materials helps to distribute heat away from critical components.
- Heat Sinks: These structures absorb and dissipate heat, increasing surface area to enhance cooling.
- Thermal Paste: Applied between components and heat sinks, it improves heat transfer efficiency.
In addition to passive methods, active cooling systems may include:
- Fans: Small fans can circulate air to lower the temperature of internal components.
- Liquid Cooling: Circulating coolant through channels can effectively remove heat from high-temperature areas.
- Heat Pipes: These utilize phase change to transfer heat efficiently from one area to another.
Moreover, software solutions play a vital role in managing heat. Adaptive performance algorithms can adjust processing loads based on temperature readings, ensuring that devices operate within safe thermal limits. By integrating these mechanisms, devices can achieve enhanced reliability and longevity, providing users with a seamless experience even under heavy usage.
Common Replacement Parts and Tools
When it comes to maintaining or repairing mobile devices, understanding the essential components and tools can significantly enhance the process. Familiarity with these elements allows users to effectively address common issues, prolong the life of their devices, and save on repair costs.
Key elements that often require attention include display assemblies, battery units, and various connectors. Each of these components plays a crucial role in device functionality and performance. Additionally, having the right tools on hand–such as precision screwdrivers, suction cups, and spudgers–can facilitate the repair process, ensuring that tasks are completed safely and efficiently.
By equipping oneself with both knowledge of essential components and the necessary tools, anyone can tackle repairs with confidence, making the most of their mobile technology investment.