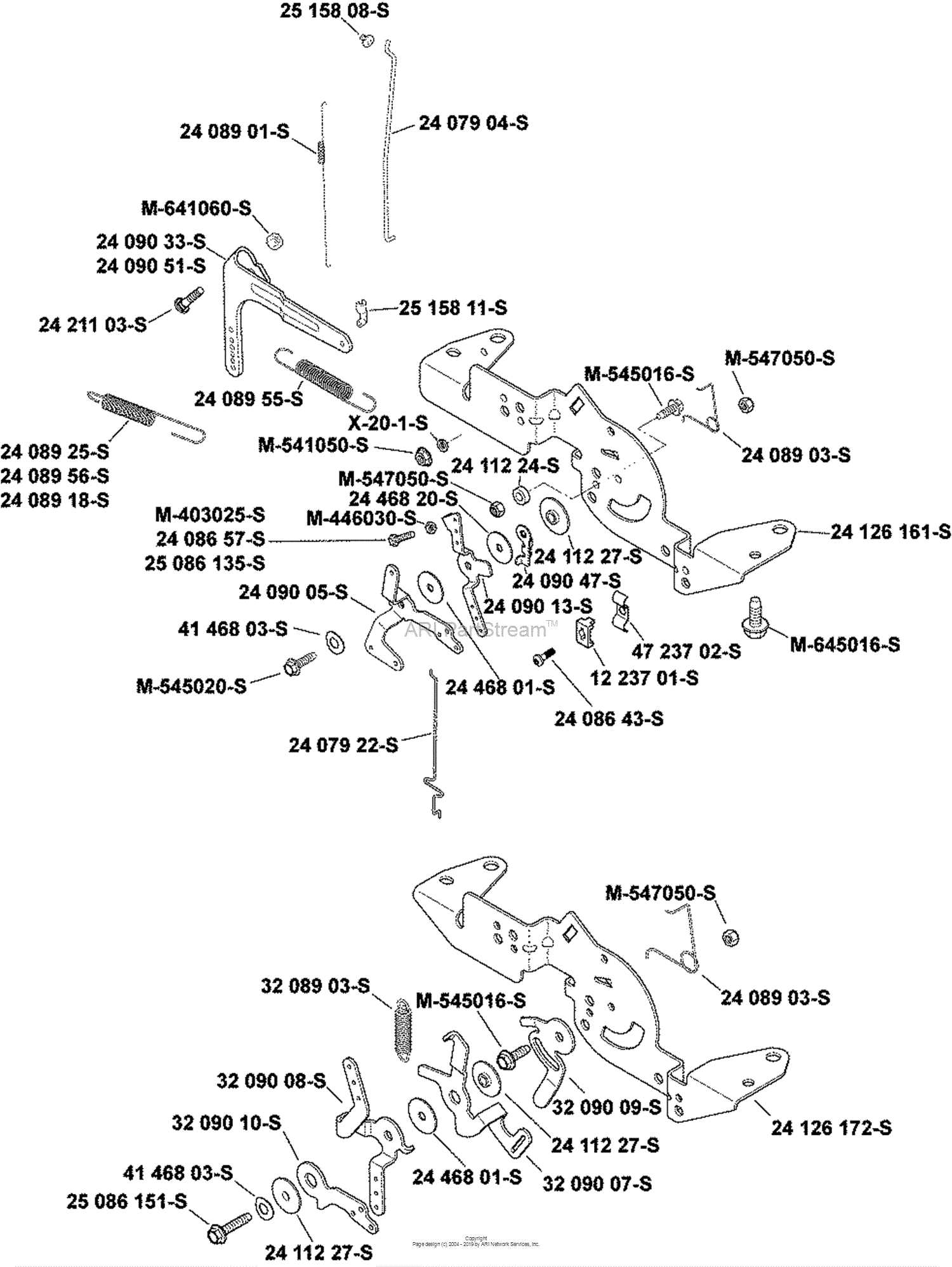
Understanding the structure and layout of engine components is essential for proper maintenance and repair. A clear and detailed schematic helps ensure that each piece fits together seamlessly, contributing to optimal performance and longevity.
In this section, we will explore the intricate design of various engine mechanisms, breaking down the elements that work together to drive efficient operation. The visual representation of these elements can greatly assist in troubleshooting and routine inspections, providing a clear guide for anyone performing technical tasks.
By familiarizing yourself with the layout, you gain a deeper understanding of the functionality behind each component. This knowledge ensures better decision-making when it comes to replacements or repairs, ultimately improving the engine’s durability and reliability.
Kohler Command 23 Parts Overview
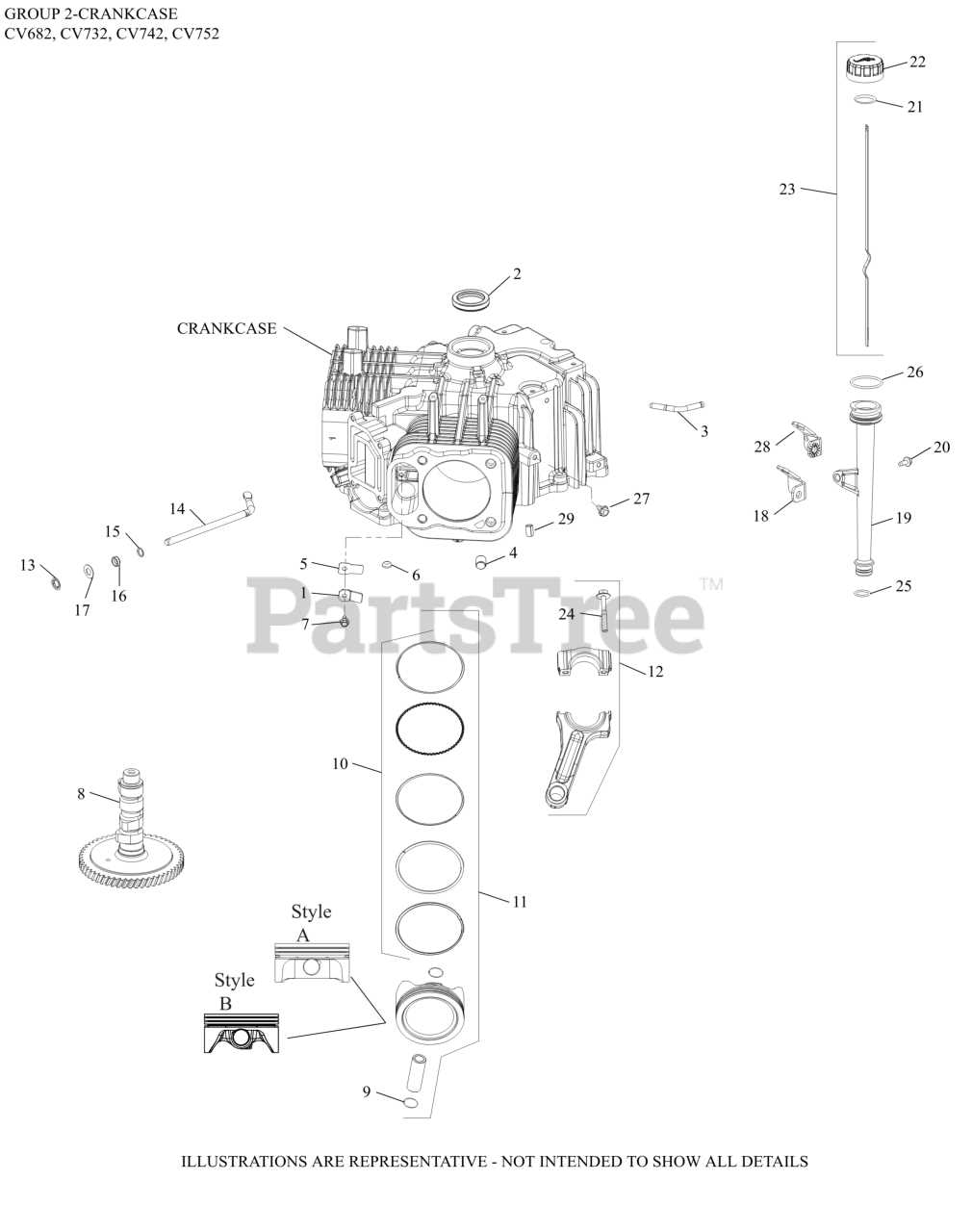
In this section, we delve into the components that comprise the intricate mechanism of the Kohler Command 23 engine. Exploring the intricate makeup of its internal mechanisms, we uncover the various elements that contribute to its functionality. Highlighting the essential components that form the core of its operation, we examine the intricate details that define its inner workings. Emphasizing the critical elements essential for optimal performance, we dissect the intricate framework that underpins its functionality.
Engine Components Breakdown
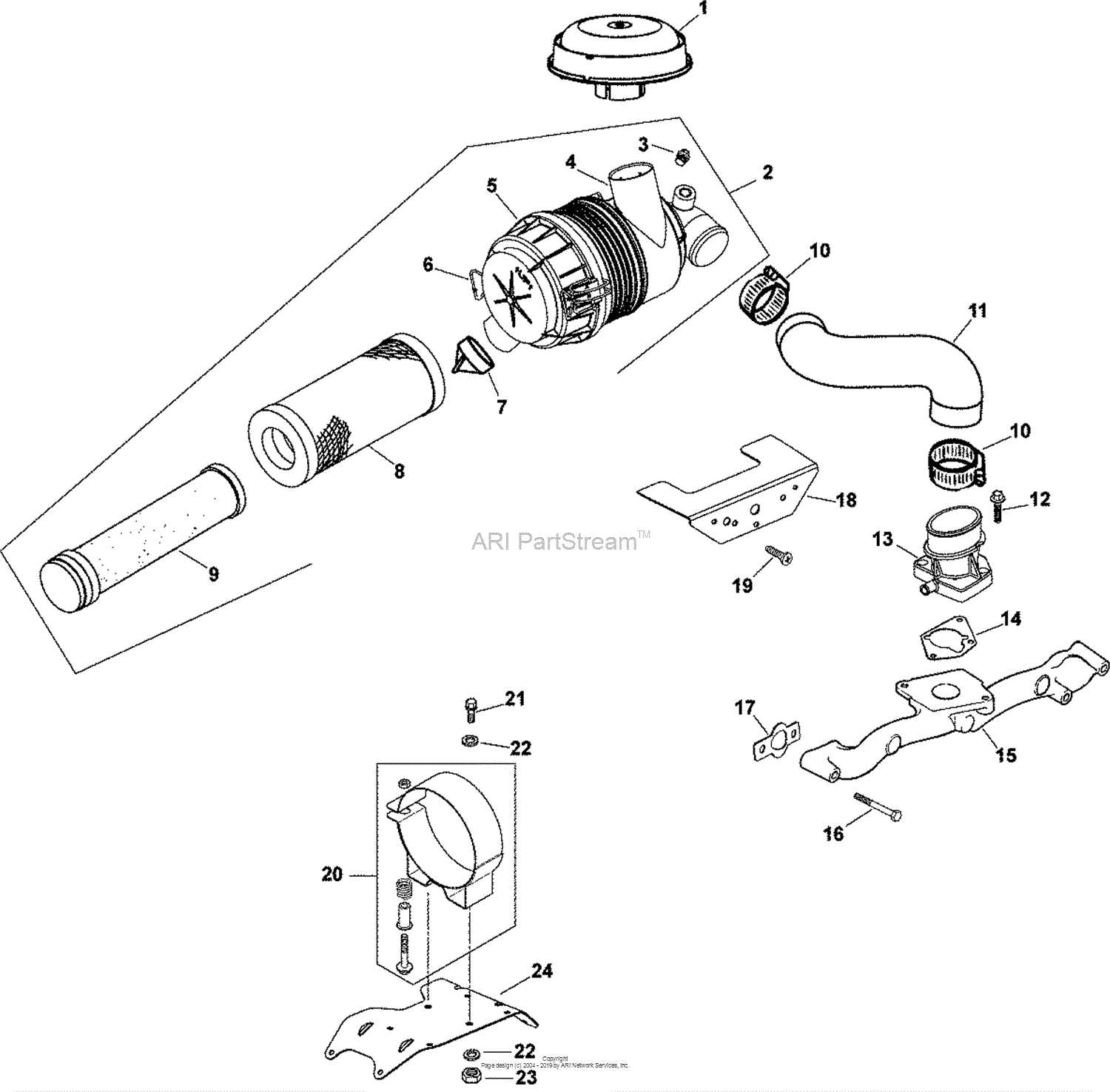
Understanding the structure and functionality of a motor involves examining its various key elements. These components work together to ensure efficient operation and power delivery, each playing a crucial role in the overall performance of the engine. This section provides an overview of these elements without delving into technical diagrams or specific labels.
Main Structural Elements
The primary components of an engine include the cylinder block, crankshaft, and pistons. These core elements are essential for converting fuel into mechanical power. The cylinder block houses the pistons, while the crankshaft converts their movement into rotational energy, driving the machine forward. Additionally, the connecting rods link the pistons to the crankshaft, transferring force between the two.
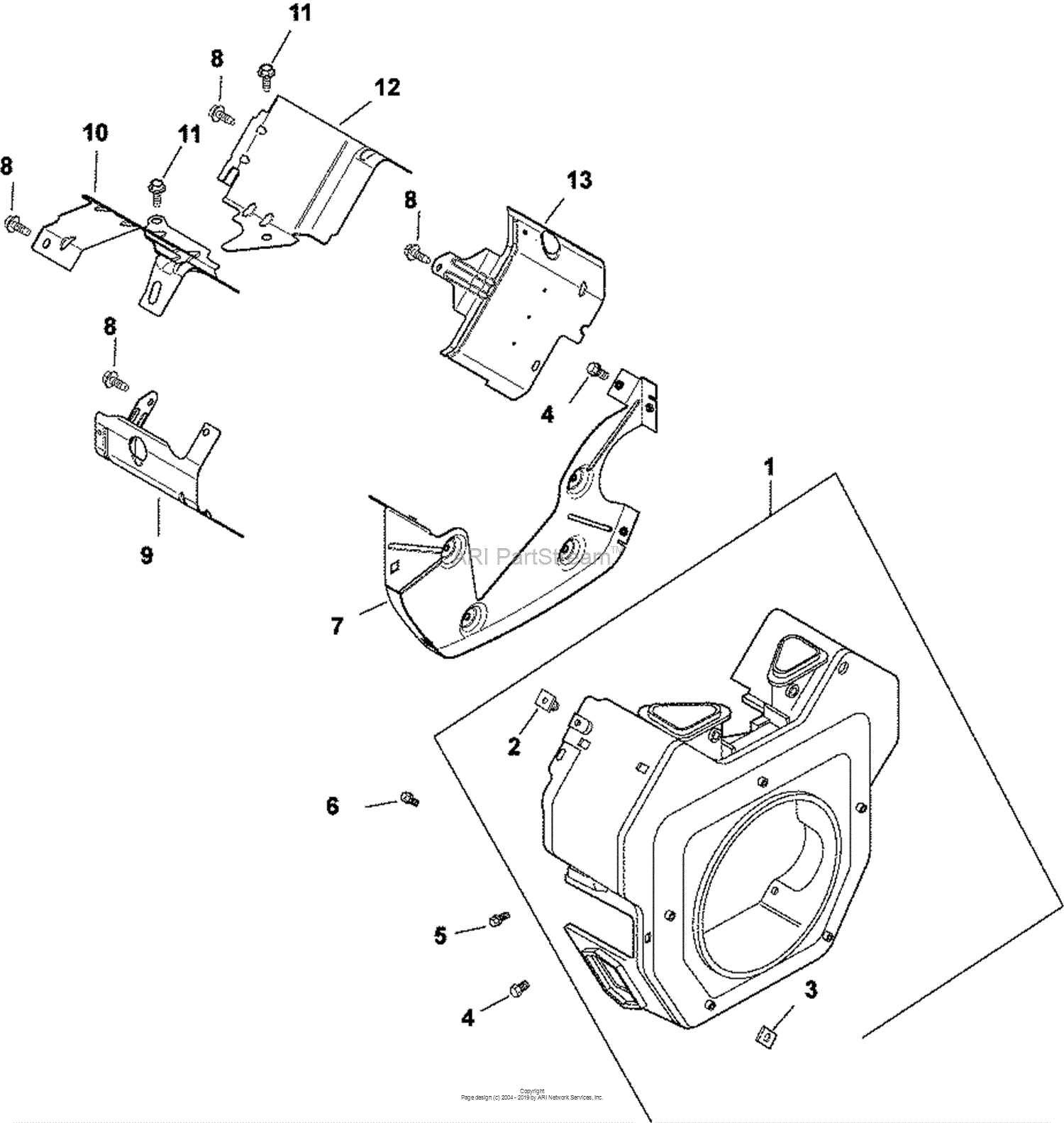
Supporting Systems
Apart from the main structural elements, supporting systems like the cooling, lubrication, and ignition systems are crucial. The cooling system ensures the engine doesn’t overheat, while lubrication reduces friction between moving parts. The ignition system is responsible for starting the combustion process, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
Ignition System and Wiring Overview
In this section, we delve into the intricate workings of the ignition setup and electrical connections of the engine. Understanding the ignition system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. It encompasses the components responsible for initiating the combustion process, along with the wiring that facilitates electrical flow throughout the system.
| Components | Description |
| Spark Plug | The spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. |
| Ignition Coil | Converts low voltage into high voltage, which is necessary for spark generation. |
| Ignition Module | Controls the timing and strength of the spark sent to the spark plug. |
| Wiring Harness | Routes electrical power and signals to the ignition components. |
The ignition system’s efficiency directly impacts engine performance and starting reliability. Proper maintenance and understanding of these components ensure smooth operation and longevity of the engine.
Fuel System Components Layout
In this section, we explore the arrangement and configuration of components within the fuel delivery system. Understanding how these elements are organized provides insight into the operational dynamics of the fuel system, emphasizing the strategic placement and interconnection of crucial parts.
The design focuses on integrating various components that collectively ensure optimal fuel supply efficiency. Each component plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the fuel system. Examining the spatial arrangement reveals a meticulous approach to component placement, enhancing accessibility for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key aspects of the layout highlight the careful consideration given to the flow dynamics and operational synergy among components. Components are strategically positioned to facilitate fluid movement and minimize operational friction, underscoring the system’s efficiency and reliability under varying conditions.
Air Intake and Filtration Setup
The air intake and filtration system plays a crucial role in maintaining engine performance by ensuring that clean air reaches the combustion chamber. This setup minimizes contaminants, improving fuel efficiency and reducing wear on internal components. Proper installation and maintenance of the system are essential for reliable operation.
Here’s an overview of the key components involved:
- Air Filter: Traps dirt, dust, and debris, allowing only clean air to flow into the engine.
- Air Intake Housing: Encases the air filter, guiding air efficiently into the engine.
- Ventilation Ducts: Channels air from the external environment to the intake system, preventing obstruction.
- Filter Seals: Ensures an airtight fit, preventing unfiltered air from entering the engine.
Regular inspection and replacement of these elements are vital to ensure optimal airflow and prevent damage caused by contaminants.
Exhaust System Parts Identification
Understanding the various components that make up the exhaust system is crucial for maintaining engine performance and efficiency. This section provides a detailed overview of the primary elements involved in the exhaust system, explaining their roles and connections within the overall engine framework.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Muffler | Reduces the noise created by exhaust gases and helps direct fumes away from the engine. |
| Exhaust Pipe | Transfers the gases from the engine to the muffler, ensuring safe emission of fumes. |
| Heat Shield | Protects nearby engine parts from the high temperatures produced by the exhaust. |
| Gaskets | Seals connections between various exhaust elements, preventing leaks and ensuring efficiency. |
| Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe. |
Cooling System Configuration
The cooling system in engines is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, ensuring performance, and preventing overheating. Proper configuration allows the engine to work efficiently under various conditions, by dissipating excess heat and regulating thermal levels throughout the system. Understanding the components and flow dynamics is key to optimizing engine longevity.
Main Components
- Cooling Fan: Drives airflow to help cool down engine parts.
- Radiator: Heat exchanger responsible for removing heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine to ensure consistent temperature control.
Coolant Circulation
Coolant flows through the engine, absorbing heat as it moves. It is then directed to the radiator, where air passing through the radiator fins dissipates this heat. The pump ensures the coolant keeps moving, preventing any localized overheating or buildup of excess thermal energy.
Valve and Cylinder Assembly
In this section, we delve into the intricate mechanisms that govern the flow and regulation of gases within the engine. The valve and cylinder assembly forms a critical nexus where precision engineering meets operational efficiency. It orchestrates the intake of air and fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases with meticulous timing and coordination.
The Valve Mechanism: Within this assembly, valves act as gatekeepers, controlling the ingress and egress of gases during the engine’s combustion cycle. They operate in harmony with the cylinder’s movements, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing energy loss.
The Cylinder’s Role:
The cylinder, a robust chamber, encapsulates the combustion process. It houses the piston’s reciprocating motion, converting thermal energy into mechanical force. This synergy between the valve mechanism and cylinder dynamics is pivotal in sustaining the engine’s power output and longevity.
Starter Motor and Electrical Parts
The ignition system and related electrical components play a critical role in ensuring the engine starts and operates efficiently. Understanding the key elements of these systems can help diagnose issues and maintain overall engine performance.
At the heart of the electrical system, the starter motor initiates the engine’s operation by turning the crankshaft. Alongside this, the alternator generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems during use. Voltage regulators manage the electrical flow, ensuring consistent and safe operation of various components.
Wiring, connectors, and switches form the communication channels between these parts, enabling smooth and reliable operation. Periodic inspection and maintenance of the electrical system can help prevent malfunctions and prolong the lifespan of the engine.
Oil and Lubrication System Parts
In this section, we delve into the components essential for ensuring proper lubrication and oil circulation within the engine system. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the mechanical components involved in the lubrication process.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lubricant | The substance that reduces friction and wear between moving parts, ensuring smooth operation. |
| Oil Pump | Device responsible for circulating lubricant throughout the engine, ensuring all parts receive adequate lubrication. |
| Oil Filter | Component that removes impurities from the lubricant, preventing contaminants from damaging engine components. |
| Oil Cooler | Device that regulates the temperature of the lubricant, ensuring it stays within optimal operating range for efficiency. |
| Oil Pan | Reservoir at the bottom of the engine that stores the lubricant before it is pumped throughout the system. |
| Oil Lines | Tubes or hoses that transport lubricant to various engine parts, ensuring consistent oil flow. |
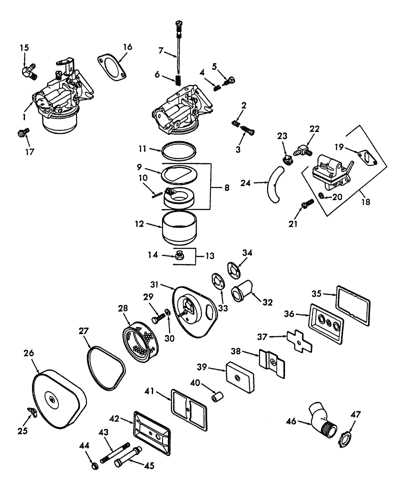
Carburetor and Throttle Control Layout
The layout of the carburetor and throttle control is essential for managing the fuel-air mixture and adjusting engine speed. Proper alignment of these components ensures smooth operation and responsive power delivery. Understanding how these parts interact can help maintain performance and address potential issues in the system.
Carburetor placement plays a key role in regulating the flow of air and fuel into the engine. Its design is optimized for efficient fuel atomization, ensuring that the mixture is properly prepared before entering the combustion chamber.
The throttle control mechanism directly affects engine speed by adjusting the opening of the carburetor. The throttle linkage connects the user-operated control to the carburetor, allowing for precise regulation of power output and overall engine performance.
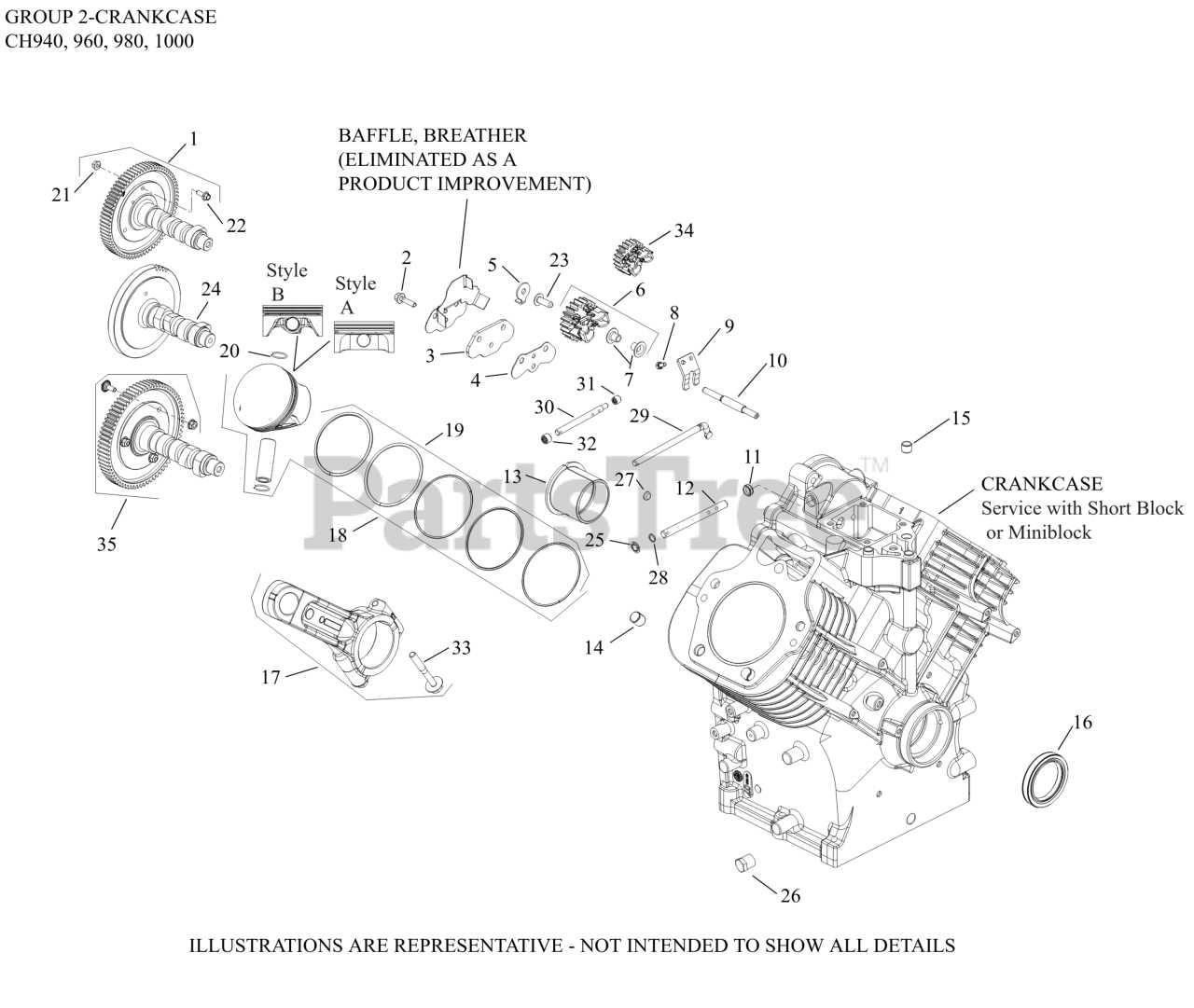
Crankshaft and Piston Assembly Diagram
The crankshaft and piston assembly is a critical component in many engine designs, playing a vital role in converting linear motion into rotational motion. Understanding this assembly is essential for anyone involved in engine maintenance or repair, as it directly impacts performance and efficiency. The connection between the crankshaft and piston is integral, as it facilitates the movement required for the engine’s operation.
In this section, we will explore the various elements that comprise this assembly, detailing their functions and relationships. Below is a simplified overview of the key components involved:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Crankshaft | The main rotating shaft that converts reciprocating motion from the piston into rotational motion. |
| Piston | A cylindrical component that moves up and down within the cylinder, creating pressure and performing work. |
| Piston Rings | Seals that prevent gas from escaping the combustion chamber and help maintain oil within the engine. |
| Connecting Rod | The link between the piston and the crankshaft, transferring force from the piston to the crankshaft. |
| Flywheel | A rotating disc that helps smooth out the power delivery and maintain momentum in the engine. |