
The transfer case plays a crucial role in distributing power between the front and rear wheels of a vehicle. It ensures that torque is transmitted efficiently, allowing for smooth transitions between different driving modes. To maintain optimal performance, it’s important to have a clear grasp of the inner structure and how its various elements interact with each other.
In this section, we’ll explore the intricate layout of the key mechanisms inside this essential system. Knowing the location and function of each component can help with identifying potential issues and ensuring proper maintenance or repairs. Whether you’re a mechanic or an enthusiast, understanding this configuration is vital for ensuring longevity and performance.
We will also delve into the function of individual elements, emphasizing their importance in the overall operation. By familiarizing yourself with this setup, you can diagnose problems more effectively and perform necessary adjustments with greater confidence.
Understanding the NP246 Transfer Case Components
The mechanism at the heart of a vehicle’s drivetrain is crucial for smooth and efficient performance. The system includes various components that work together to distribute power between the front and rear wheels. By understanding the essential elements, it’s possible to maintain optimal functionality and identify potential issues early on.
Key Components
The primary elements of the system include the clutch assembly, chain, and planetary gear set. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring proper torque distribution. The clutch assembly allows for smooth shifting between drive modes, while the chain connects the various sections of the system, enabling the transfer of power. The planetary gear set is responsible for altering gear ratios, allowing for different driving conditions.
Component Overview Table
How the NP246 Shift Mechanism Works
The shift system in this transfer case operates by utilizing a series of components that manage gear changes between different driving modes. It ensures smooth transitions between high and low ranges, as well as between two-wheel and four-wheel drive, depending on the vehicle’s needs. This functionality is crucial for handling various terrains and driving conditions.
Control of Shifting: The shifting process is guided by an electronic control module, which receives input from sensors and the driver’s commands. The module then directs the actuator to engage the desired mode, allowing the driver to switch between different driving configurations without delay.
Engagement Mechanism: At the heart of the shifting operation is the actuator motor. This motor moves a gear selector fork, which in turn engages different gears. Depending on the position of the fork, the transfer case switches between
Main Function of the Planetary Gear Set
The planetary gear system is a fundamental component used to manage torque distribution and enable different rotational speeds within mechanical systems. Its design ensures a compact and efficient means of transferring power, allowing for smooth gear shifts and optimized performance under varying load conditions.
Torque Distribution and Gear Ratios
This gear arrangement consists of multiple elements, including a central sun gear, surrounding planet gears, and an outer ring. By adjusting the interaction between these parts, the system alters gear ratios, controlling the speed and direction of rotational forces. The efficiency of this mechanism plays a key role in enhancing the overall performance of the system.
Smooth Transitions and Durability
The system’s ability to handle high loads while providing smooth transitions between different gears makes it indispensable in modern engineering applications. Its durability and compact nature contribute to longer operational lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements.
Exploring the Role of the Mode Fork
The mode fork plays a crucial function in ensuring smooth transitions within a vehicle’s transfer system. It acts as the guiding element responsible for shifting between different operational modes, enabling the drivetrain to adapt to varying road conditions and driving needs. Understanding how this component operates is key to maintaining the system’s efficiency and longevity.
How the Mode Fork Facilitates Shifting

The fork moves along a designated path to engage or disengage gears, allowing for a seamless change in the vehicle’s operating mode. Whether transitioning to a higher torque mode for off-road driving or shifting to a more fuel-efficient configuration, the fork ensures these changes happen smoothly and without excessive wear on the system.
- Aligns
Overview of the Internal Chain System

The internal chain system plays a vital role in connecting and transmitting motion between different mechanical components. Its function is crucial for maintaining proper synchronization, ensuring that torque and power are effectively distributed throughout the system. By operating in conjunction with various gears and other mechanisms, the chain system contributes to smooth operation and durability.
Functionality and Structure
The chain itself is designed to withstand significant stress while minimizing wear. It works alongside several gear assemblies, which allow for seamless transitions of movement. The chain’s robust construction enables it to handle the high demands of transferring force efficiently across rotating components, ensuring optimal system performance.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance of the chain system is essential for prolonging its lifespan. Inspection for wear and proper lubrication can prevent premature damage and ensure that the system continues to operate effectively. Taking proactive steps to maintain the chain and its associated elements will help sustain long-term reliability.
Examining the Input Shaft Operation

The input shaft plays a crucial role in transmitting power within a transfer system, linking various components together. Understanding how this mechanism operates helps in identifying potential inefficiencies or malfunctions that could disrupt the overall performance of the unit. This section explores how the input shaft engages with the surrounding gears and the process by which it converts rotational energy into effective motion.
Component Function Input Shaft Receives rotational force from the engine and passes it to the system’s internal components. Bearing Assembly Ensures smooth rotation of the input shaft, reducing friction and wear. The Function of the Encoder
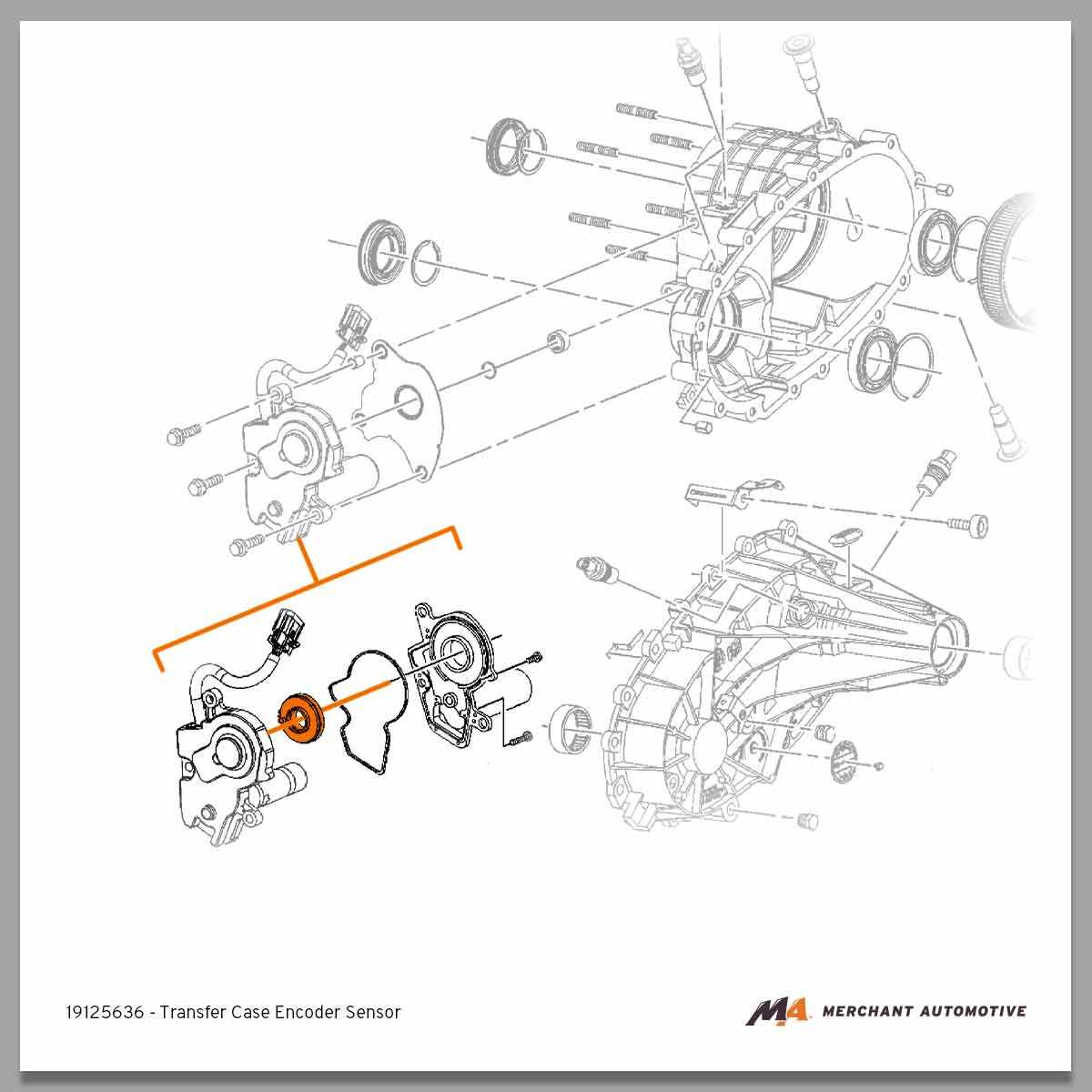
The encoder is a crucial element in ensuring proper functionality and communication within a transfer system. It helps monitor specific movements and positions, providing vital feedback to control units for smooth operation. Understanding how it operates and interacts with other components is essential for maintaining the efficiency and accuracy of the entire mechanism.
An encoder works by converting motion into a readable signal that informs the control system of the current status of the system. This signal can be used to detect the exact position or speed of rotating elements.
- Measures the angle of rotation
- Sends electrical signals based on movement
- Ensures real-time adjustments for optimal performance
- Prevents mechanical issues by providing accurate feedback
In many cases, a faulty encoder can lead to performance disruptions. Regular checks and maintenance can prevent system failures and ensure long