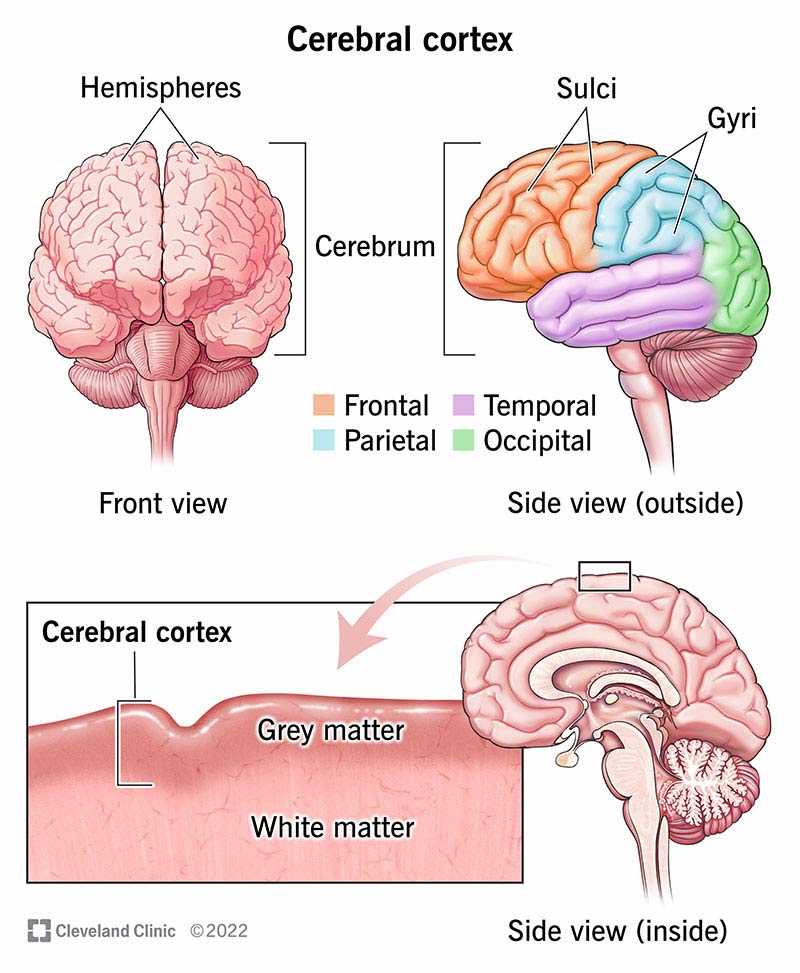
Exploring the intricate design of neural structures reveals a fascinating interplay of various regions, each contributing to overall human experience. This complex organization underlies numerous capabilities, enabling individuals to navigate daily life, engage with others, and respond to environmental stimuli.
Within this elaborate framework, every segment holds a unique position, influencing behaviors, emotions, and cognitive abilities. By delving into these specialized areas, one can appreciate how interconnected systems support processes ranging from basic survival to advanced reasoning.
As we embark on a journey through these essential elements, recognizing their unique contributions enhances our understanding of how we think, feel, and interact with the world. Unraveling these connections provides insights into the remarkable functionality of our cognitive apparatus.
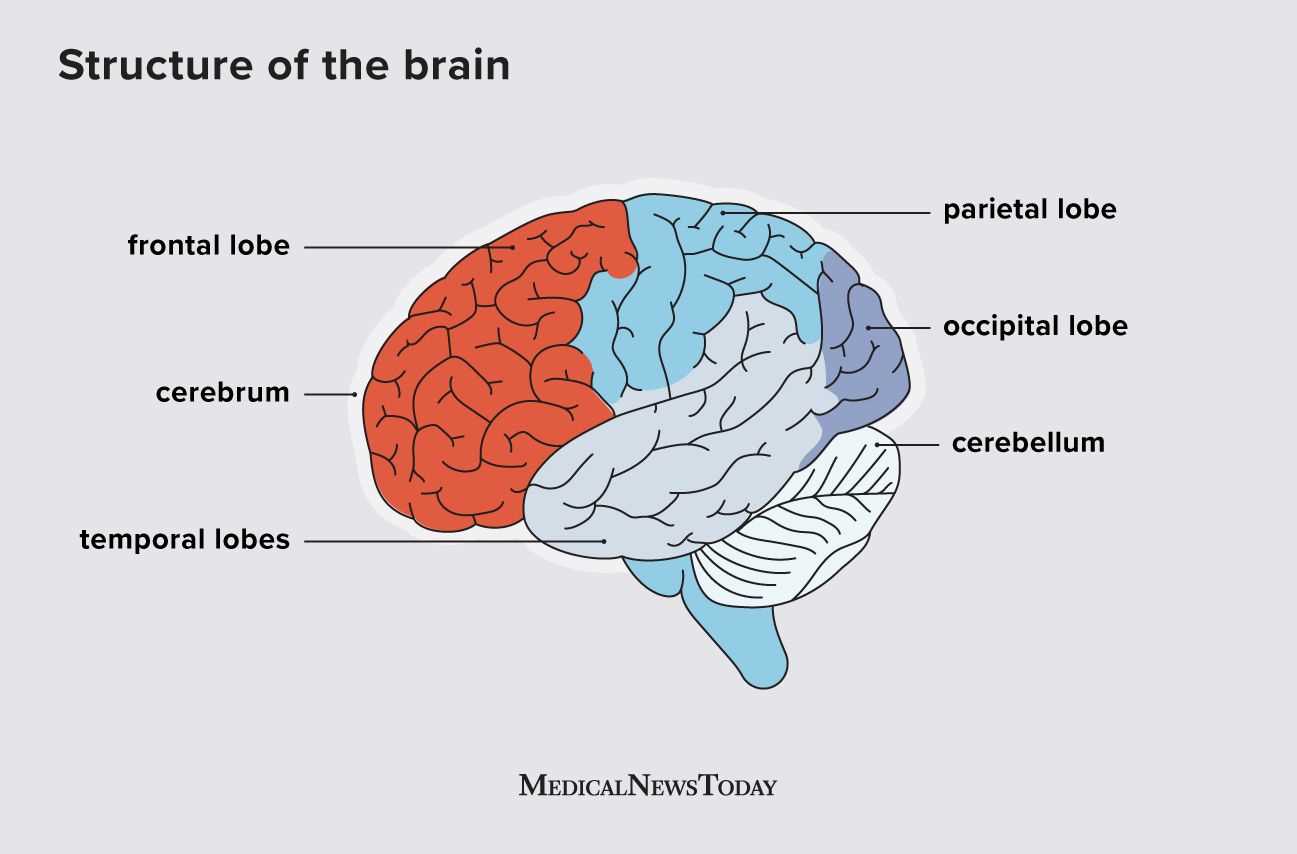
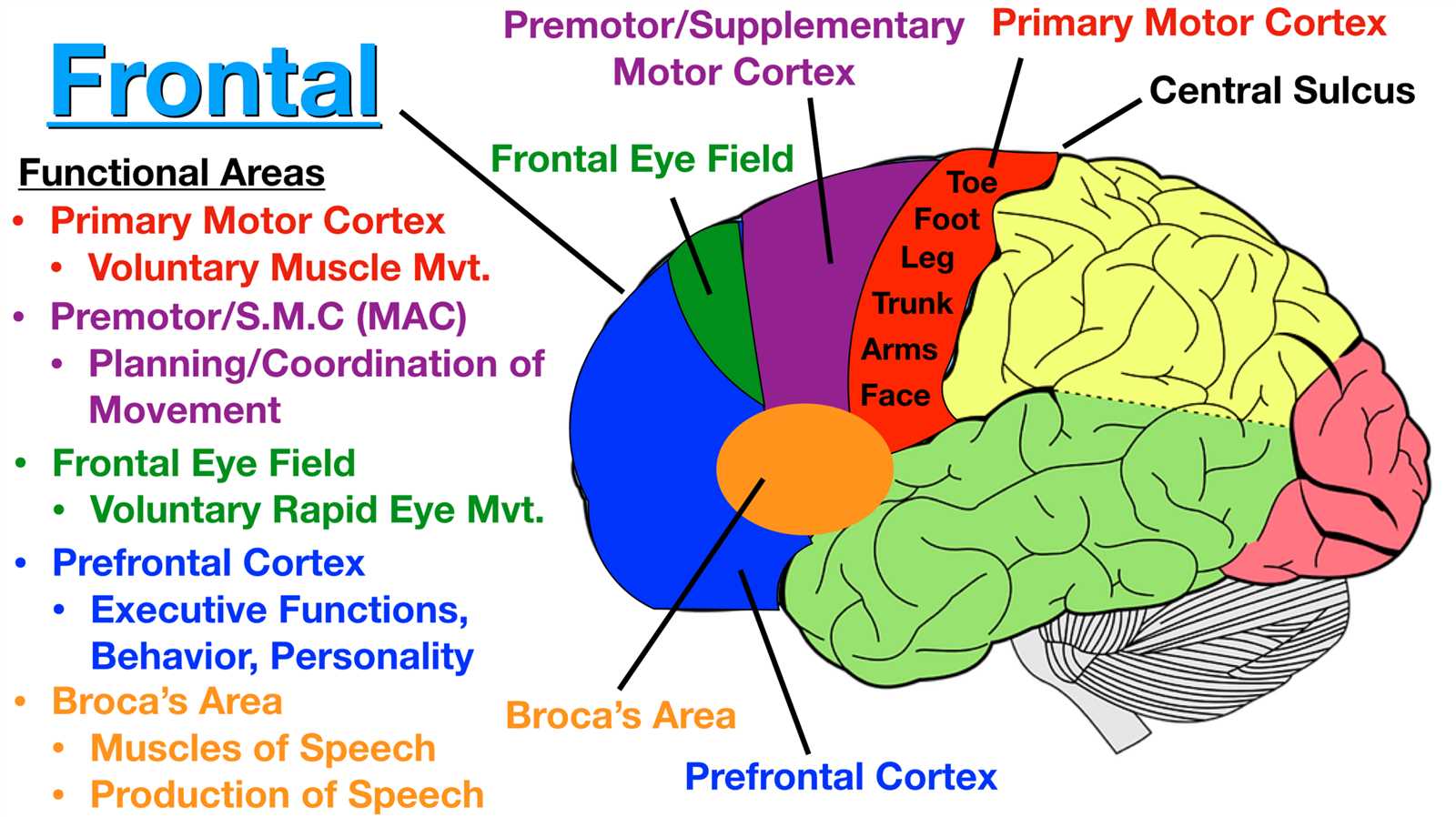
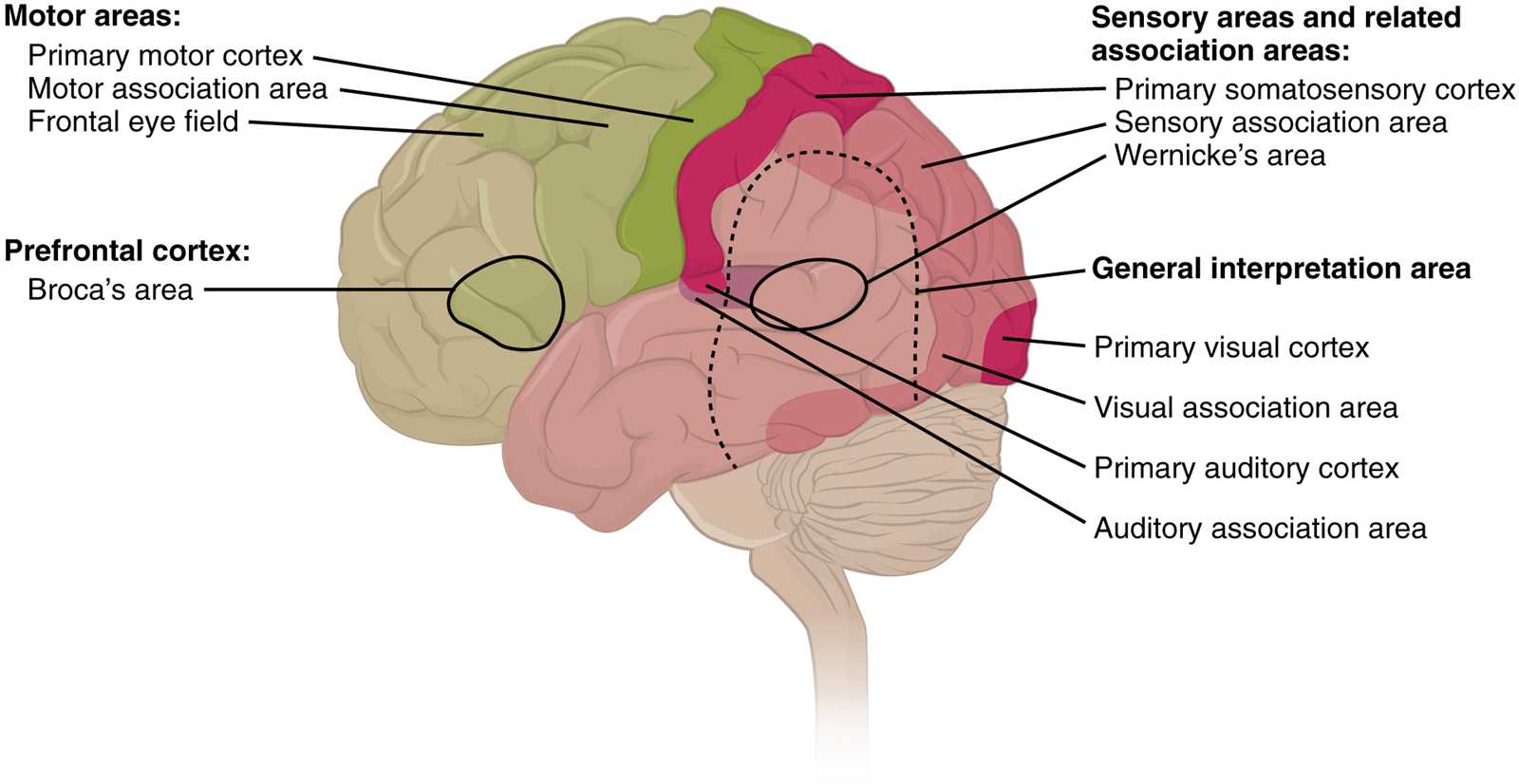
The cerebrum serves as a central hub for various cognitive activities, playing a crucial role in shaping behavior and processing sensory information. It is instrumental in enabling complex tasks and facilitating a range of capabilities.
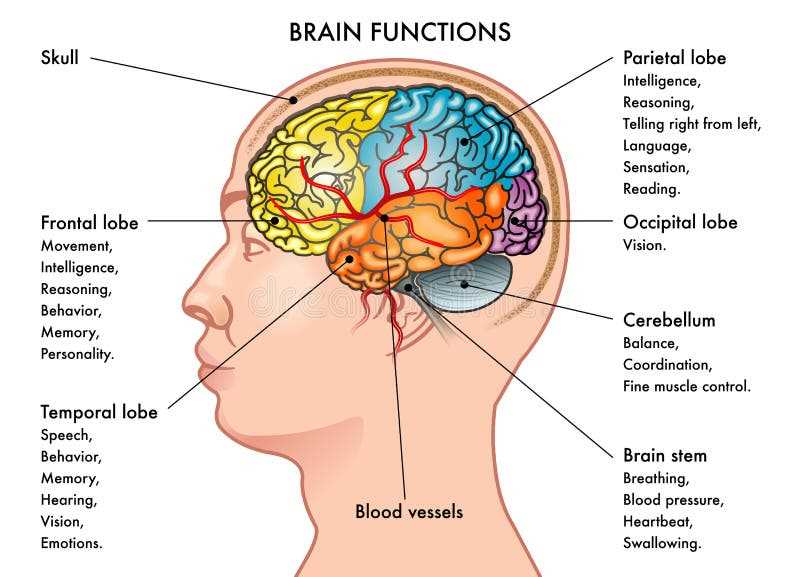
- Memory: This region is essential for storing and recalling experiences, influencing learning and decision-making.
- Language: It facilitates communication, allowing individuals to comprehend and produce verbal expressions.
- Motor Skills: It coordinates voluntary movements, ensuring fluidity and precision in actions.
- Emotion Regulation: This area is involved in processing emotions, affecting mood and social interactions.
- Sensory Processing: It interprets inputs from various senses, helping individuals understand and interact with the environment.
In summary, the cerebrum is integral to numerous higher-order activities, providing a foundation for intellectual pursuits and everyday actions.
Understanding the Cerebellum
This section delves into a crucial region responsible for coordination, balance, and motor control. It plays a vital role in ensuring smooth movements and maintaining posture. The intricate structure allows for seamless integration of sensory information, contributing to overall physical coordination.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Situated at the back of the skull, below larger hemispheres. |
| Structure | Comprised of two hemispheres with a highly folded surface, enhancing its processing capabilities. |
| Role | Facilitates balance, posture, and fine motor skills through coordination of muscle movements. |
| Connections | Interacts with various regions, including the spinal cord, to regulate movement and motor learning. |
| Dysfunction | Damage can lead to impaired coordination, dizziness, and difficulties with movement. |
Role of the Brain Stem
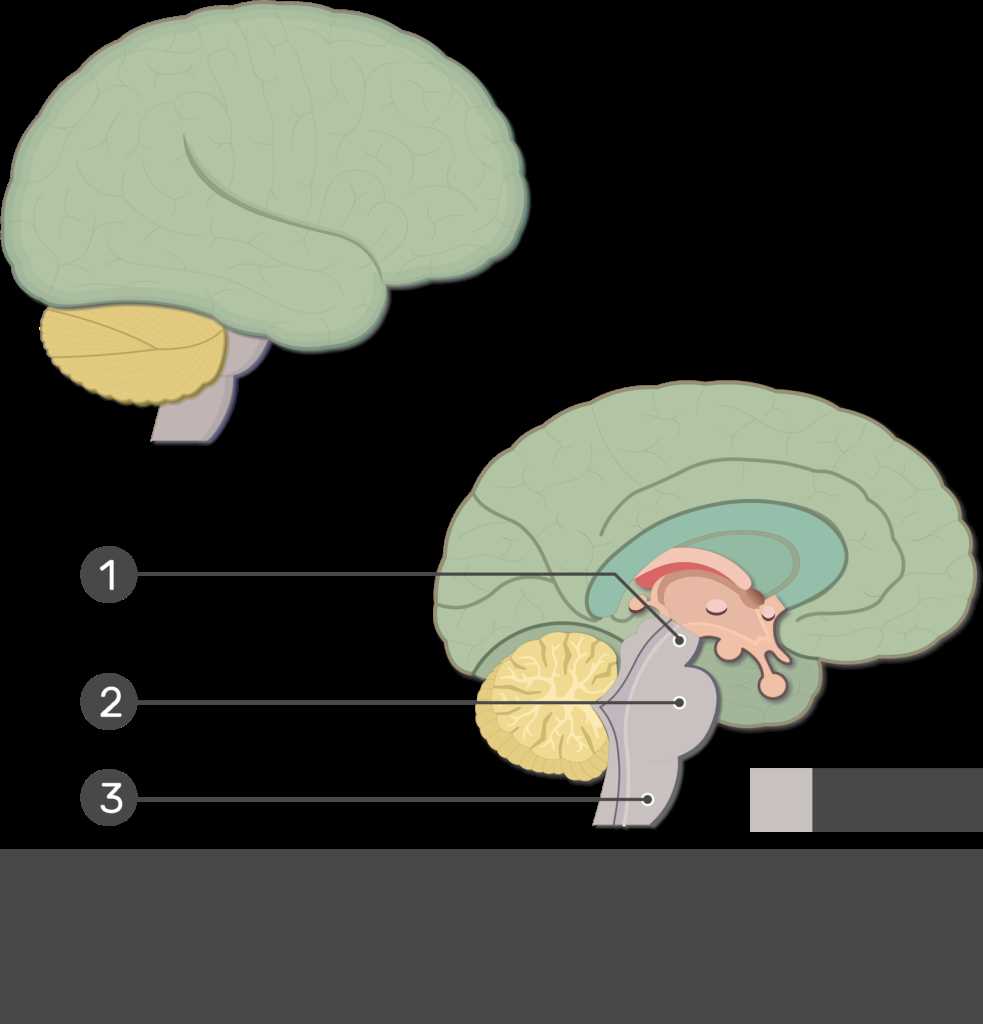
This crucial structure serves as a vital link between higher cognitive centers and basic life-sustaining functions. It coordinates essential processes that maintain overall well-being and enables communication between various regions.
Located at the base, this area is integral for regulating autonomic activities, including heart rate and respiration. Its involvement in reflex actions also highlights its importance in immediate responses to stimuli, ensuring safety and survival.
Moreover, it plays a significant role in the sleep-wake cycle, influencing alertness and overall consciousness. The interaction with neurotransmitters facilitates a balance between rest and activity, contributing to optimal functioning.
Exploring the Limbic System
This section delves into a complex network crucial for emotional experiences, behavior, and memory. It plays a significant role in regulating various psychological functions, shaping responses to stimuli, and influencing decision-making processes.
Key Components
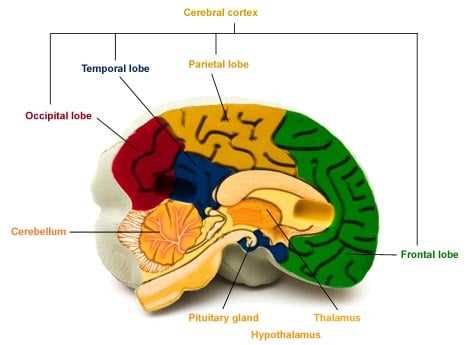
- Hippocampus: Essential for learning and memory retention.
- Amygdala: Central to emotional regulation and processing fear.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station for sensory information.
- Hypothalamus: Governs autonomic functions and emotional responses.
Significance of the Limbic System
This network is vital for navigating social interactions, forming memories, and managing emotional responses. Its influence extends to various psychological conditions, highlighting its importance in understanding mental health.
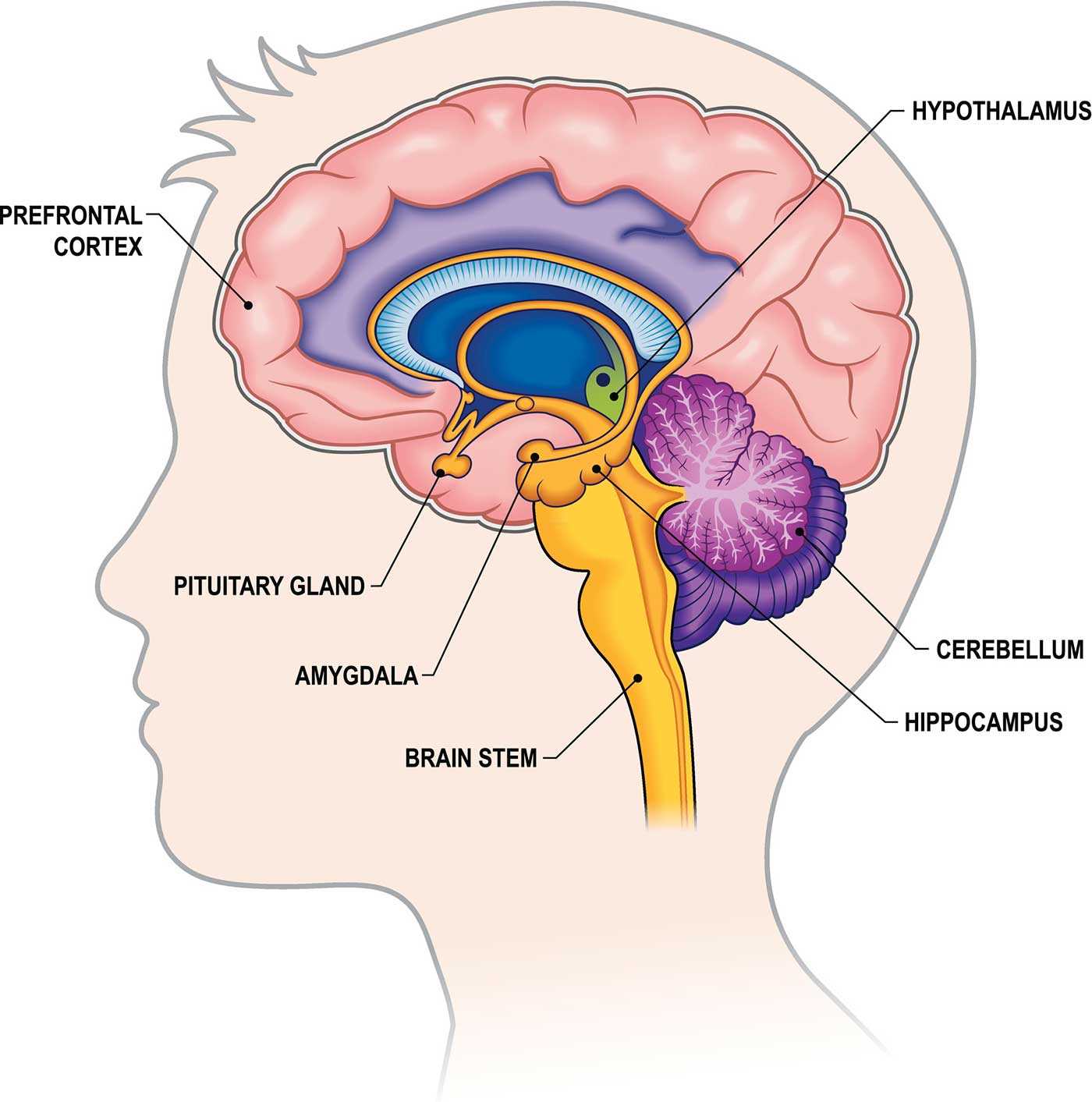
Importance of the Thalamus
The thalamus serves as a crucial hub for information relay, playing a pivotal role in sensory perception and motor signal transmission. Its strategic position allows it to process various types of data before sending it to appropriate areas, thus ensuring efficient communication within the central nervous system.
This structure acts as a filter, regulating the flow of sensory information. It determines which signals reach the cortex, helping prioritize crucial inputs while filtering out less significant stimuli. This selective process is vital for maintaining focus and attention in daily activities.
Additionally, the thalamus contributes significantly to cognitive functions, such as learning and memory. By facilitating connections between different regions, it enhances our ability to process complex information and respond effectively to various situations.
Moreover, dysfunction in this area can lead to a range of neurological disorders, emphasizing its importance in overall well-being. Understanding its role aids in comprehending numerous conditions that impact sensory processing and cognitive abilities.
Functionality of the Hypothalamus
This crucial structure plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. It acts as a command center, regulating various physiological processes essential for survival. Its involvement in different systems ensures that the organism can respond effectively to internal and external changes.
Key responsibilities include:
- Regulation of body temperature
- Control of hunger and thirst
- Management of sleep-wake cycles
- Influence on emotional responses
Additionally, this structure interacts closely with the endocrine system, influencing hormone release and coordination of metabolic activities. Its functions extend to:
- Secretion of hormones that control pituitary gland
- Regulation of stress responses through cortisol release
- Coordination of reproductive functions and behaviors
By overseeing these diverse processes, it ensures a balanced internal environment, crucial for optimal functioning.
Neural Pathways and Connections
In the intricate web of neural networks, communication occurs through a complex interplay of signals. These connections play a crucial role in transmitting information, enabling various activities, sensations, and cognitive processes. Understanding this connectivity unveils the remarkable efficiency of the nervous system in orchestrating responses to internal and external stimuli.
Structure of Neural Networks
Neural networks consist of interconnected cells that facilitate signal transmission. Each connection, or synapse, allows for the exchange of chemical signals, influencing the behavior of adjacent neurons. This arrangement enables rapid communication and adaptability, essential for learning and memory.
Impact on Behavior
The architecture of these networks significantly affects behavior and emotional responses. Different pathways are activated during specific tasks, shaping experiences and influencing decisions. By mapping these connections, researchers can gain insights into disorders, paving the way for innovative therapeutic approaches.
How Brain Parts Communicate
Information exchange between different regions occurs through intricate networks, ensuring seamless interaction within the neural system. These connections facilitate coordination, allowing various areas to work in harmony, ultimately influencing behavior, emotions, and cognitive abilities.
Neural Pathways and Connections
Connections between diverse regions are established through specialized structures known as neural pathways. These conduits enable signals to traverse from one area to another, permitting efficient communication. Various neurotransmitters play a crucial role in transmitting messages along these routes, influencing the overall processing of information.
Significance of Communication in Functionality
Effective interaction among different areas is essential for maintaining balance and overall performance. Disruptions in these pathways can lead to various cognitive and emotional challenges, underscoring the importance of harmonious communication for optimal functioning.
| Type of Connection | Description |
|---|---|
| Excitatory | Stimulates activity in the receiving neuron, enhancing communication. |
| Inhibitory | Reduces activity in the receiving neuron, regulating signals and responses. |
| Modulatory | Alters the strength of signals, influencing overall responsiveness. |