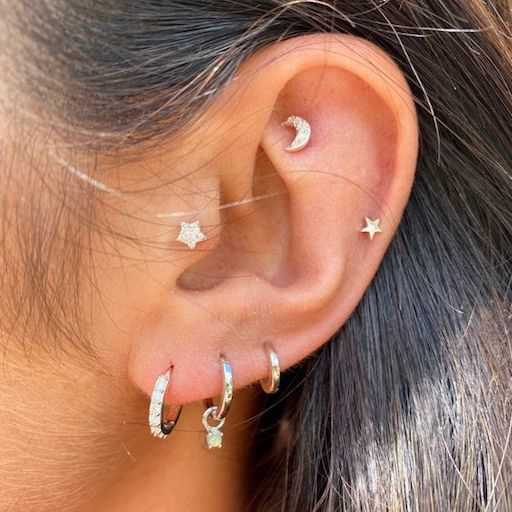
Exploring the intricate world of body modifications reveals a fascinating interplay of structure and artistry. Each modification involves various components that work harmoniously to create a unique aesthetic. Recognizing these elements enhances appreciation and knowledge of this form of self-expression.
In this section, we will delve into the specific regions involved in such transformations, highlighting their significance and role. Understanding these areas not only informs individuals about safety and care but also uncovers the cultural importance associated with body art.
By examining these foundational aspects, one can gain insights into best practices and considerations that ensure a positive experience. This knowledge ultimately empowers enthusiasts to make informed decisions in their journey of self-discovery.
Understanding Ear Piercing Anatomy
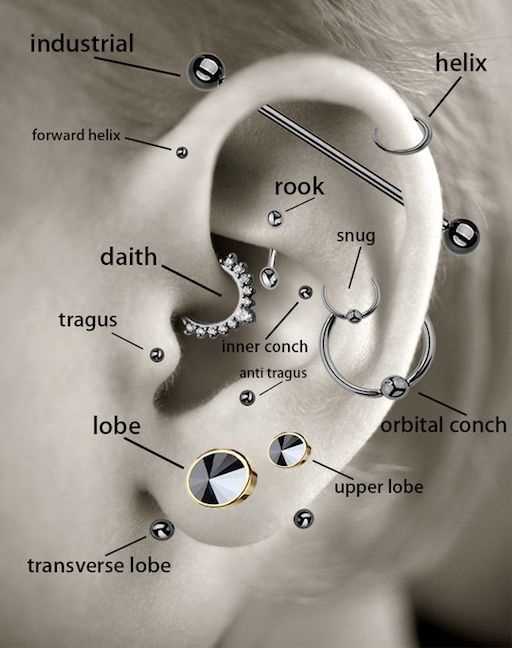
This section explores essential components involved in body modifications, focusing on their structure and significance. By grasping these elements, one can make informed choices and appreciate the artistry behind this form of self-expression.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Outer Layer | The visible part that serves as a canvas for adornment. |
| Cartilage | A flexible tissue providing shape and support, often used for specific styles. |
| Skin | Protective covering that requires care and attention during modifications. |
| Vascular Network | A complex system of blood vessels that plays a role in healing processes. |
Types of Ear Piercings Explained
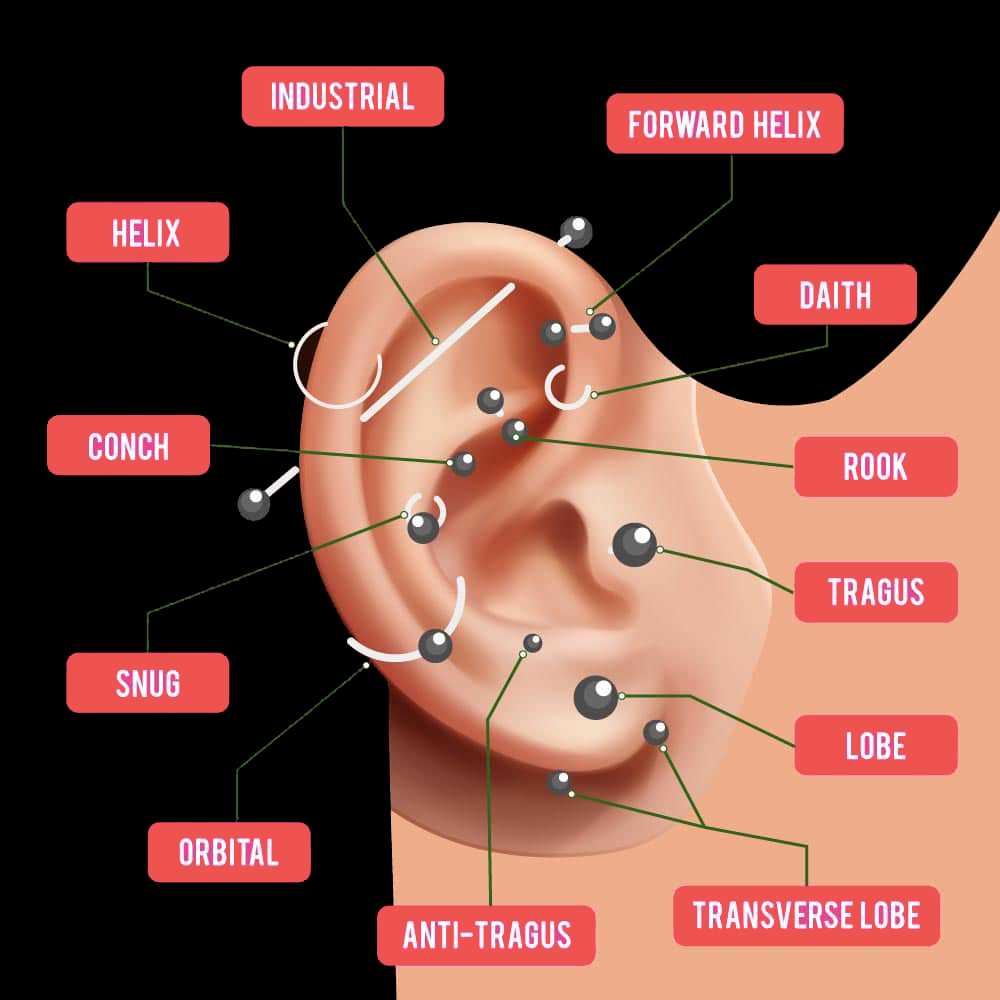
This section explores various styles of body modifications that adorn the lobes and cartilage. Each method offers a unique aesthetic and cultural significance, reflecting individual expression and personal taste.
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Lobe | The most common choice, usually located on soft tissue at the bottom. |
| Helix | Placed along the upper rim, offering a stylish and subtle look. |
| Tragus | Located on the small flap of cartilage that covers the ear canal. |
| Conch | Situated in the center of the outer ear, creating a bold statement. |
| Daith | Done through the innermost cartilage fold, often linked with alternative therapies. |
Key Components of Ear Structure
Understanding intricate elements within auditory anatomy is essential for grasping how sound perception occurs. Each component plays a pivotal role in collecting, amplifying, and transmitting auditory signals, ultimately facilitating communication and environmental awareness.
Outer portion functions as a funnel, capturing sound waves and directing them inward. This section is vital for initial sound detection.
Middle section contains delicate bones that amplify vibrations. These ossicles enhance sound transmission to the inner region.
Inner area houses sensory organs responsible for converting vibrations into neural signals, crucial for interpreting sounds. Within this complex, cochlea plays a significant role, housing specialized cells that respond to varying frequencies.
Comprehending these essential elements not only enriches knowledge about sound processing but also highlights their importance in overall auditory health.
Illustrating the Piercing Process
This section aims to provide a clear representation of how body modifications are executed safely and effectively. Understanding each phase can enhance appreciation for the artistry and precision involved in such procedures.
- Preparation: Ensuring a clean environment and gathering necessary tools.
- Marking: Identifying desired locations with careful attention to symmetry and aesthetics.
- Disinfection: Applying antiseptics to prevent infection and ensure a safe experience.
- Procedure: Using specialized instruments to create openings, executed with skill and care.
- Aftercare: Providing guidance on how to maintain hygiene and promote healing.
Each stage plays a crucial role in achieving a successful outcome while minimizing risks. Following recommended practices can lead to a satisfying experience and lasting results.
Safety Measures for Ear Piercing
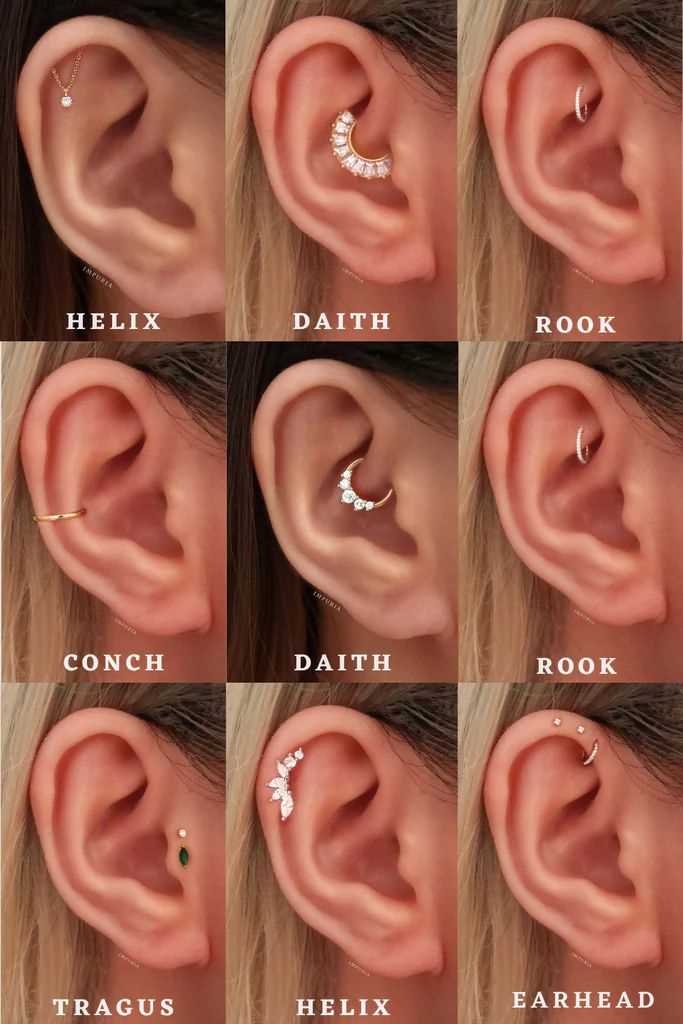
Ensuring a safe experience during a body modification procedure is essential. Proper precautions can minimize risks and promote healing. Below are some key guidelines to follow.
- Choose a reputable establishment with certified professionals.
- Verify that all tools are sterilized and single-use where possible.
- Ask about the types of jewelry being used; opt for hypoallergenic materials.
Preparation is also vital for a successful outcome. Here are some tips:
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you have any medical conditions.
- Avoid alcohol and blood thinners prior to the procedure.
- Ensure you are well-hydrated and have eaten something light before.
Post-procedure care plays a significant role in recovery. Consider the following practices:
- Follow aftercare instructions provided by the professional.
- Avoid touching or twisting the jewelry unnecessarily.
- Keep the area clean and avoid swimming in pools or oceans during the healing period.
By adhering to these safety measures, individuals can enjoy their experience with greater confidence and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Common Materials for Piercing Jewelry
Choosing suitable materials for body adornments is essential for both safety and aesthetics. Different substances offer unique benefits, making them popular among enthusiasts.
- Stainless Steel: Known for durability and resistance to tarnish.
- Titanium: Lightweight, hypoallergenic, and ideal for sensitive skin.
- Gold: Classic choice, but ensure it’s high-quality to avoid irritation.
- Bioplast: Flexible and safe for healing piercings.
- Silver: Attractive but can tarnish; best for healed adornments.
Considerations include personal sensitivity, maintenance requirements, and aesthetic preferences when selecting materials for your body jewelry.
Aftercare Tips for New Piercings
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring a smooth healing process and preventing complications. Following specific guidelines can significantly enhance recovery and comfort during this time. Consistent care will help to avoid infections and promote optimal results.
Keep it Clean: Use a saline solution or a gentle cleanser to clean the area twice daily. Avoid harsh soaps or alcohol-based products, as they can irritate the skin and hinder healing.
Avoid Touching: Minimize touching or twisting the jewelry. This practice helps to prevent irritation and reduces the risk of introducing bacteria.
Be Mindful of Activities: Steer clear of swimming pools, hot tubs, and saunas until fully healed. These environments can expose the area to bacteria, increasing the likelihood of infection.
Watch for Signs: Pay attention to any unusual symptoms such as excessive redness, swelling, or discharge. If these occur, consult a professional for advice.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports overall health and can assist in the healing process. A well-hydrated body promotes skin elasticity and recovery.
Follow Professional Advice: Adhere to any specific instructions provided by your piercer. Each individual’s healing journey may vary, so tailored recommendations are vital for a successful outcome.
Pain Levels: What to Expect
When considering body modifications, understanding discomfort is essential for informed decision-making. Each individual may experience varying sensations during the process, influenced by factors such as location and technique. This section aims to provide insight into anticipated feelings during the procedure.
General Sensation: Most individuals report a brief moment of sharpness followed by a dull ache. This initial feeling is typically fleeting, lasting only a few seconds.
Location Matters: Certain areas are more sensitive than others, resulting in differing levels of discomfort. For instance, regions with thicker skin might yield a less intense experience compared to those rich in nerve endings.
Aftermath: Post-procedure sensations often include tenderness or mild soreness, which can vary in intensity. It’s crucial to recognize that these feelings usually diminish within a few days as healing progresses.
Ultimately, preparing for varying levels of discomfort can help ease anxiety and lead to a more positive experience.
Healing Times for Different Piercings
Understanding recovery durations for various placements is essential for anyone considering modifications. Each location on the anatomy has unique healing characteristics influenced by factors like blood flow, tissue type, and aftercare practices.
Generally, healing times can vary significantly. For instance, standard placements may take around 6 to 8 weeks to fully mend, while more intricate areas might require 3 to 6 months. Certain regions, especially those with thicker cartilage, could demand up to 1 year for optimal recovery.
Aftercare plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth healing process. Following professional guidelines and maintaining cleanliness will help minimize complications and enhance recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
Engaging in body modification procedures can lead to various health concerns. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone considering this enhancement, as awareness can significantly mitigate adverse effects.
Infection Risks
One of the primary dangers involves infections, which may arise from improper aftercare or unsanitary conditions. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and discharge, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Allergic Reactions

Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to materials used in jewelry. This can manifest as irritation or inflammation, emphasizing the importance of selecting hypoallergenic options.
Choosing the Right Piercing Location
Selecting an appropriate spot for an adornment can significantly impact both aesthetic appeal and comfort. Various factors influence this decision, including personal style, lifestyle, and pain tolerance. It’s essential to consider how each placement may interact with daily activities and body movements.
Individual anatomy plays a crucial role in determining suitable options. Different regions vary in sensitivity and healing time, making it vital to research each choice. Furthermore, societal norms and trends might sway preferences, but personal significance should take precedence.
Consultation with experienced professionals can provide valuable insights. They can suggest placements that align with individual features while ensuring safety and proper technique. Ultimately, the ideal location should resonate personally, complementing overall expression and enhancing confidence.
Trends in Ear Piercing Styles
In recent years, body modifications have evolved, showcasing diverse expressions of individuality. Various techniques and placements have emerged, reflecting personal tastes and cultural influences.
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimalist | Simple and elegant choices, focusing on subtlety. |
| Stacked | Multiple adornments on one lobe, creating a layered effect. |
| Cartilage | High placements offering a bolder statement. |
| Hoops | Circular designs gaining popularity for their versatility. |
| Colorful | Bright gems and unique materials adding flair to choices. |