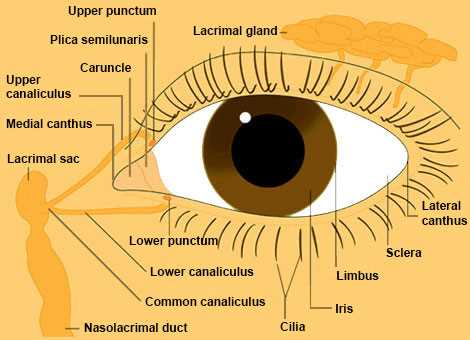
Understanding human vision involves delving into various components responsible for sight. This interactive exploration provides an engaging way to familiarize oneself with these crucial elements. Participants will enhance their knowledge while having fun, making learning enjoyable and memorable.
Through this challenge, individuals will have the opportunity to test their familiarity with different structures and their functions. Recognizing these features plays a significant role in comprehending how vision operates, offering insights into both health and anatomy.
Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply curious about visual mechanisms, this activity promises to broaden your understanding. Engage in this stimulating experience and discover how much you really know about the intricacies of visual anatomy.
Understanding the Anatomy of Eyes
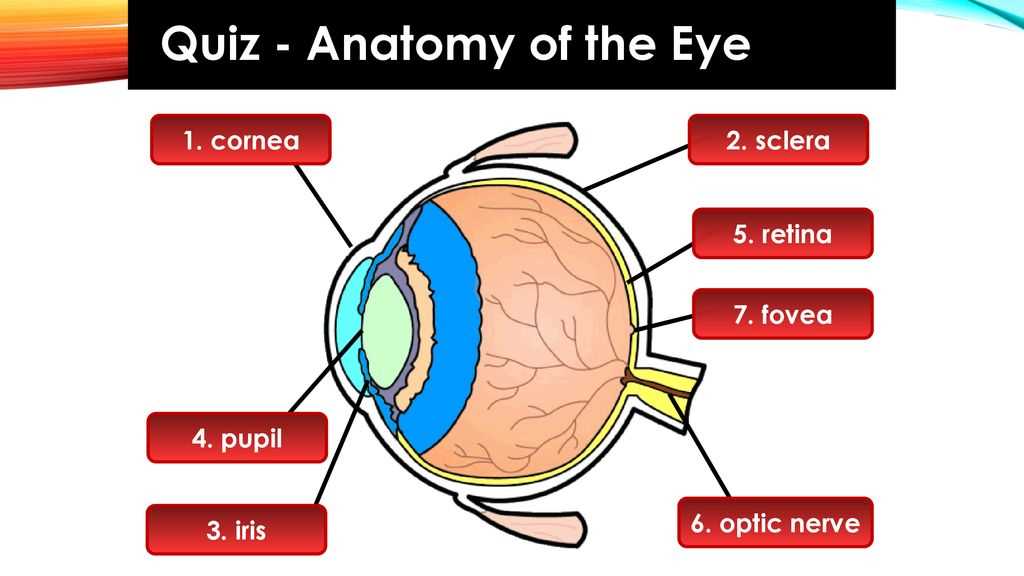
The structure responsible for vision is intricate and fascinating, encompassing various components that work together to create the experience of sight. Each element plays a critical role in processing visual information, enabling individuals to perceive the surrounding world.
Key Components
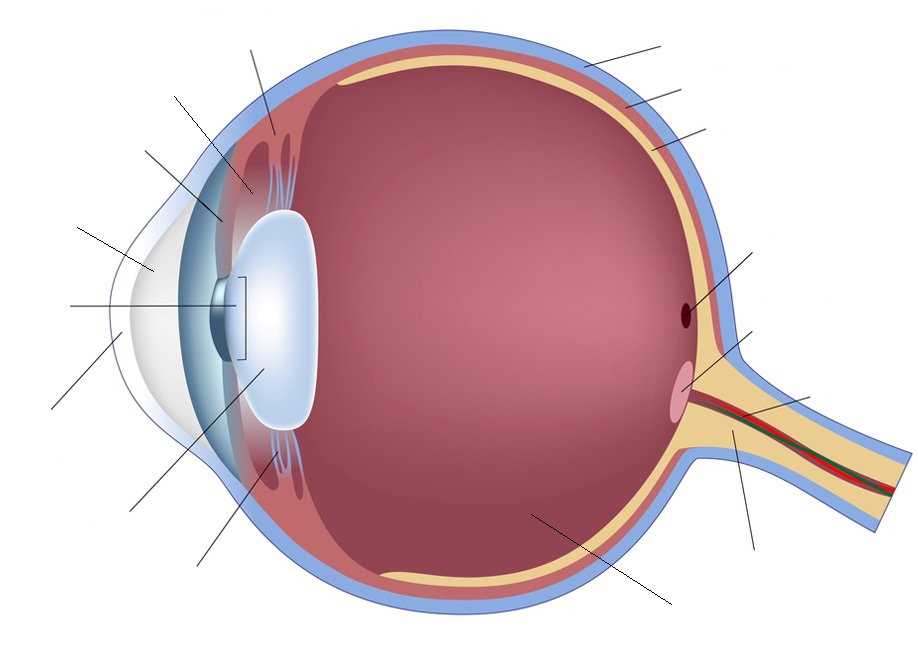
- Cornea: The transparent layer that covers the front of the globe.
- Iris: The colored portion that regulates the amount of light entering.
- Pupil: The opening that adjusts in size depending on light conditions.
- Lens: A flexible structure that focuses light onto the retina.
- Retina: The layer containing photoreceptors that convert light into neural signals.
- Optic Nerve: The pathway that transmits visual information to the brain.
Functions of Each Element
- Cornea: Acts as the primary lens, providing most of the optical power.
- Iris: Controls light exposure and contributes to depth of field.
- Pupil: Adjusts size to optimize light intake for varying environments.
- Lens: Changes shape to focus on objects at different distances.
- Retina: Processes visual stimuli and initiates the signal transmission.
- Optic Nerve: Facilitates communication between the visual system and the brain.
Understanding these elements enhances appreciation for how vision operates and emphasizes the complexity involved in perceiving one’s surroundings.
Key Functions of Eye Structures
This section explores essential roles played by various components in visual perception, highlighting their importance in processing and transmitting light to create images. Understanding these functions helps to appreciate the complexity of vision and the intricacies involved in seeing.
Primary Components and Their Roles
- Cornea: Serves as a protective layer and refracts incoming light.
- Pupil: Regulates light entry by adjusting size according to brightness.
- Iris: Controls pupil size and contributes to color perception.
- Lens: Focuses light onto the retina, adjusting shape for clarity.
- Retina: Converts light into neural signals for brain processing.
Additional Supporting Structures
- Conjunctiva: Keeps the surface moist and protects against infections.
- Vitreous Humor: Maintains shape and provides a medium for light transmission.
- Optic Nerve: Transmits visual information to the brain.
- Ciliary Body: Adjusts lens shape and produces aqueous humor.
Common Eye Disorders Explained
Various conditions affecting vision can significantly impact daily life. Understanding these ailments is essential for early detection and effective treatment. Here, we explore several prevalent issues that individuals may encounter.
Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, occurs when distant objects appear blurry while close ones remain clear. This condition is often due to an elongation of the eyeball or excessive curvature of the cornea.
Hyperopia, or farsightedness, is the opposite of myopia. It leads to difficulty focusing on nearby objects, making reading or detailed tasks challenging. This disorder may arise from a shorter-than-normal eyeball or a cornea that is too flat.
Astigmatism results from an irregular shape of the cornea or lens, causing blurred or distorted vision at any distance. Individuals with this condition often experience discomfort and eye strain.
Cataracts involve the clouding of the lens, leading to gradual vision loss. This condition is typically age-related and may require surgical intervention to restore clarity.
Glaucoma is characterized by increased pressure within the eyeball, potentially damaging the optic nerve. If untreated, this disorder can result in permanent vision loss, making regular eye examinations crucial.
Macular degeneration affects the central part of the retina, leading to a decline in sharpness of vision. It is more common in older adults and can significantly impact daily activities such as reading and driving.
Awareness of these conditions is vital for maintaining good vision. Regular check-ups and prompt attention to any changes can greatly enhance overall eye health.
Importance of Vision Health
Maintaining optimal visual wellness is crucial for overall quality of life. Regular eye examinations and appropriate care can prevent numerous issues, ensuring clarity and comfort in daily activities. Awareness of various factors affecting vision allows individuals to take proactive measures.
Incorporating healthy habits and routine screenings fosters long-term well-being. Key components influencing visual health include nutrition, protection from harmful rays, and managing screen time effectively.
| Factor | Impact on Vision |
|---|---|
| Nutrition | Supports retinal function and overall sight quality |
| UV Protection | Reduces risk of cataracts and other damages |
| Screen Time Management | Prevents digital strain and discomfort |
Prioritizing vision wellness not only enhances individual experiences but also contributes to sustained independence and productivity.
Interactive Eye Diagram Features
This section explores engaging elements designed to enhance understanding of ocular structures. These features offer an immersive experience, allowing users to explore various components while testing their knowledge.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Hover Interaction | Users can hover over different areas to reveal detailed information about specific components. |
| Clickable Sections | Each segment can be clicked for a deeper dive into its functions and importance. |
| Feedback System | Immediate responses guide users in assessing their understanding and retention of information. |
| Progress Tracking | Participants can monitor their advancement through various activities, enhancing motivation. |
Visual Aids for Learning Anatomy
Utilizing visual resources can significantly enhance understanding of biological structures. These tools not only facilitate memorization but also foster a deeper grasp of complex systems. Engaging with various formats, such as illustrations, models, and interactive software, enriches the educational experience.
Types of Visual Resources
Different formats cater to diverse learning styles, ensuring a comprehensive approach to studying anatomical features. Some popular types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Illustrations | Detailed drawings that highlight specific characteristics, providing a clear representation of structures. |
| 3D Models | Physical or digital models that allow manipulation and exploration from various angles, enhancing spatial understanding. |
| Interactive Software | Programs that enable users to explore anatomical features through simulations and virtual dissections. |
Benefits of Using Visual Aids
Incorporating these resources into study routines promotes active engagement and retention. Visuals can simplify complex information, making it more accessible and memorable. Furthermore, they encourage critical thinking and the ability to visualize relationships between different structures.
Engaging Quizzes for Eye Education
Interactive assessments serve as an excellent tool for enhancing knowledge about vision. These activities can make learning about ocular functions enjoyable and informative, allowing individuals to test their understanding and retention in a fun environment.
Benefits of Interactive Assessments
Enhancing Retention: Engaging challenges encourage better memory retention by allowing participants to actively apply what they’ve learned. Repetition and interaction can solidify concepts effectively.
Types of Interactive Activities
Multiple Choice Challenges: These formats provide a range of options, promoting critical thinking as individuals decide on the correct answer. True or false statements can also offer quick insights into one’s understanding.
How Light Affects Vision
Light plays a crucial role in how we perceive our surroundings, influencing clarity and color recognition. When light interacts with various surfaces, it creates signals that are transmitted to our brain, allowing us to interpret visual information.
Brightness is one of the key factors that impact visibility. Different intensities can enhance or hinder our ability to see objects clearly. In dim environments, our vision adjusts, but this adaptation can sometimes lead to reduced detail recognition.
Color perception is equally vital. Various wavelengths of light correspond to different colors, enriching our visual experiences. The brain processes these wavelengths, enabling us to distinguish a wide spectrum of hues, which can evoke emotions and affect our mood.
Moreover, contrast significantly enhances visibility. High contrast between objects and their backgrounds allows for easier identification, while low contrast can obscure details. Understanding how light influences these aspects is essential for optimizing environments where visual clarity is necessary.
Identifying Eye Parts Easily
Understanding components of vision is essential for both education and daily life. Familiarity with various structures helps in recognizing their functions and importance. Here, we explore effective methods for easily identifying these crucial elements.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Protects and refracts light |
| Iris | Regulates pupil size |
| Pupil | Controls light entry |
| Lens | Focuses light onto retina |
| Retina | Receives and converts light |
Utilizing visual aids and engaging methods can enhance retention and recognition of these vital components.
Fun Facts About Human Eyes
Exploring the fascinating world of vision reveals many intriguing insights about these remarkable organs. From their complexity to their unique capabilities, there is much to learn and appreciate.
Unique Features
Did you know that each individual possesses distinct characteristics? Just like fingerprints, no two sets of irises are identical. This uniqueness contributes to the personalization of vision and enhances our ability to recognize one another.
Color Perception
The capacity to perceive colors varies widely among individuals. Some people can see a broader spectrum of hues due to a condition known as tetrachromacy. These individuals possess an extra type of photoreceptor, allowing them to distinguish shades that others might miss. Vision truly is an extraordinary aspect of human experience!
Resources for Further Eye Studies
This section aims to provide valuable materials for those interested in deepening their understanding of visual organs and their functions. A variety of references can enhance knowledge and support exploration in this fascinating field.
- Books:
- “Anatomy of Vision” by Author Name
- “Understanding Optical Systems” by Author Name
- “Fundamentals of Visual Science” by Author Name
- Online Courses:
- Coursera: Visual Science Fundamentals
- edX: Advanced Topics in Vision
- Udemy: Introduction to Optical Structures
- Research Articles:
- Journal of Vision Research
- International Journal of Ophthalmology
- Visual Neuroscience Reviews
- Web Resources:
- American Academy of Ophthalmology
- Vision Science Society
- National Eye Institute