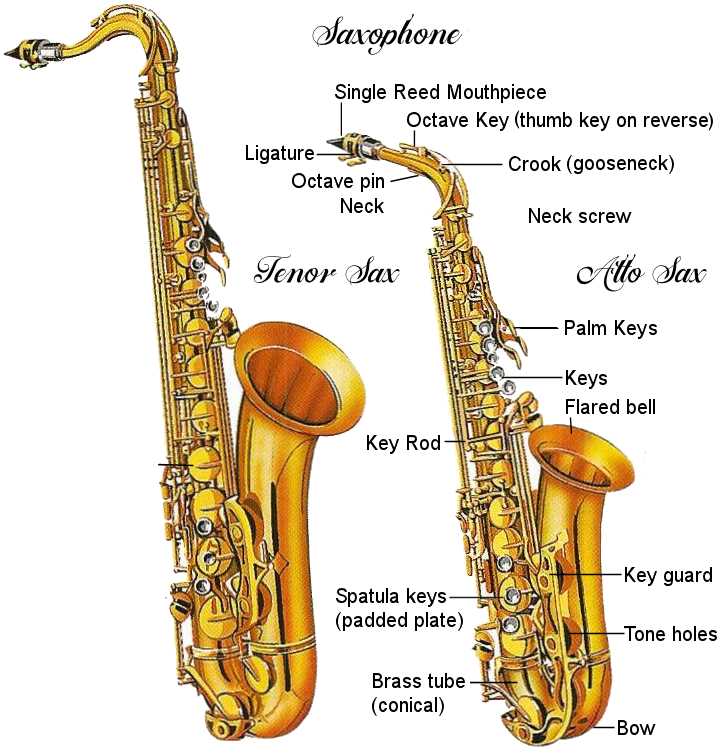
In the world of music, mastering a particular woodwind instrument requires a deep comprehension of its construction and functionality. Each component plays a vital role in producing the rich, vibrant sounds that enthusiasts and professionals alike strive to create. By exploring the intricacies of its design, players can enhance their technique and overall performance.
Delving into the essential elements reveals how they interact to facilitate sound production and modulation. From the mouthpiece to the bell, each section contributes uniquely to the instrument’s tonal quality. Recognizing the significance of these sections allows musicians to troubleshoot issues, maintain their equipment, and even customize their setup for optimal playability.
As we break down the various components, it becomes clear that knowledge of this intricate structure is not merely academic; it is a practical necessity for anyone looking to elevate their musical journey. A thorough understanding empowers players to make informed decisions, whether they are purchasing a new instrument or performing maintenance on an existing one.
Understanding the Saxophone Anatomy
The intricate design of this woodwind instrument plays a crucial role in producing its distinctive sound. Each component contributes to the overall functionality, allowing for a wide range of tones and expressions. By exploring the various sections, one can appreciate how they work together to create music that resonates with audiences.
Main Sections of the Instrument
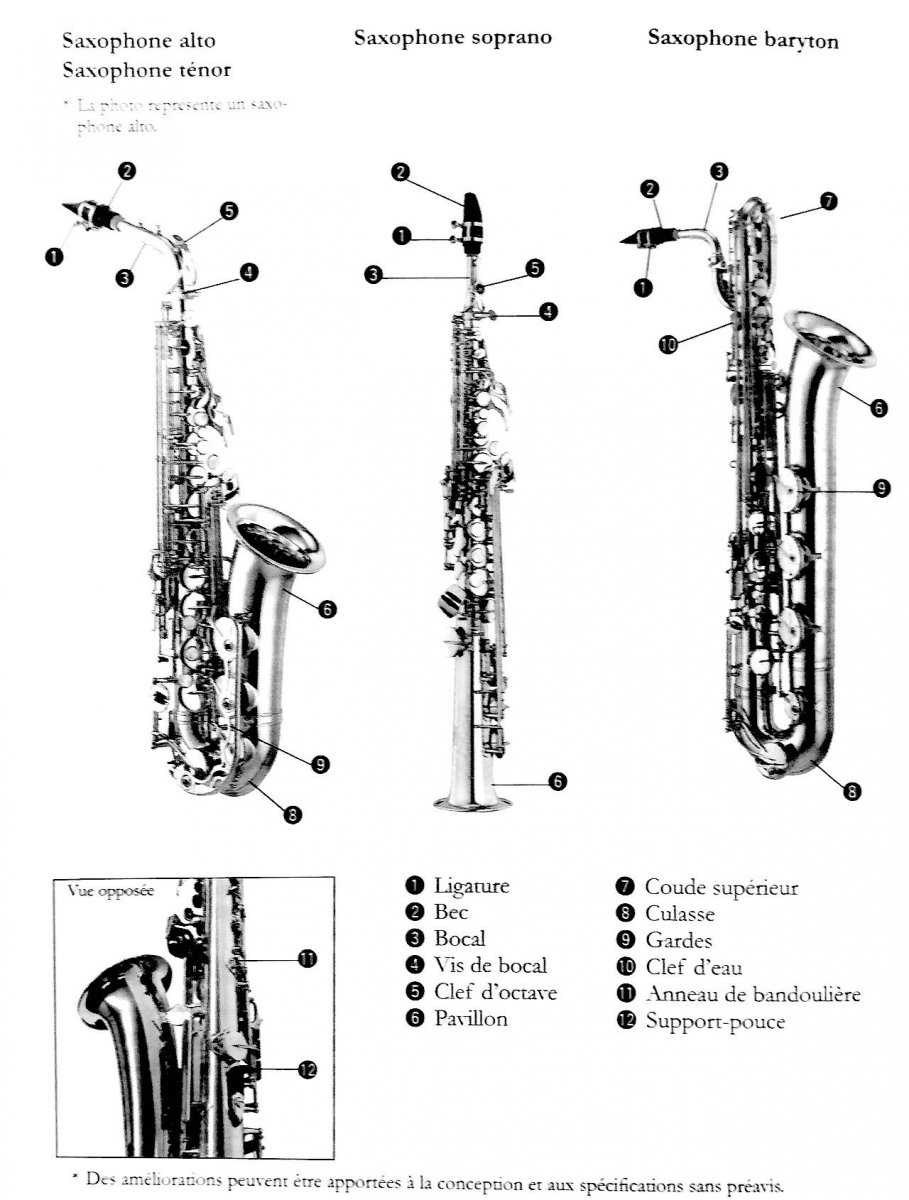
The structure can be divided into several key areas, including the body, neck, and mouthpiece. The body houses the tone holes and keys, which are essential for altering pitch and dynamics. The neck connects the body to the mouthpiece, influencing intonation and overall playability. Each section is meticulously crafted to ensure optimal performance and ease of use.
The mouthpiece, often made of hard rubber or metal, is where the musician’s breath meets the instrument. It is crucial for sound production and can greatly affect timbre. Attached to the mouthpiece is the reed, a thin piece of material that vibrates to create sound. The choice of reed and mouthpiece significantly influences the player’s tone, making them vital elements in achieving the desired musical expression.
Essential Components of a Saxophone
The construction of a certain woodwind instrument encompasses a variety of critical elements that work in harmony to produce its distinctive sound. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall functionality and tonal quality of the instrument.
Body: The main structure is crafted from brass and serves as the resonating chamber. Its shape influences the tonal characteristics significantly.
Neck: This elongated section connects the main body to the mouthpiece, aiding in the modulation of pitch and tone.
Mouthpiece: Positioned at the top, this part is where the musician blows air, and its design directly affects the airflow and sound production.
Reed: Attached to the mouthpiece, this thin strip of cane vibrates when air passes over it, generating sound waves.
Keys: These mechanical levers allow for the opening and closing of tone holes, enabling the player to produce various notes.
Bell: The flared end of the instrument, which enhances projection and tonal richness, plays a crucial role in sound dispersion.
How the Mouthpiece Functions
The mouthpiece serves as a crucial interface between the musician and the instrument, playing a vital role in sound production and control. It is designed to facilitate the flow of air, allowing for the creation of various tonal qualities and dynamics. The interaction between the player’s embouchure and the structure of the mouthpiece significantly influences the overall performance experience.
Adjustments to the positioning and pressure applied by the player can lead to a wide range of expressive capabilities. Subtle changes in technique can yield varying results, allowing for nuanced performances that reflect individual artistry. Thus, the mouthpiece is not merely a component; it is an essential element that shapes the musician’s voice and style.
Exploring the Neck’s Role
The neck of a wind instrument plays a crucial role in shaping the overall sound and functionality. This component serves as a vital link between the body and the mouthpiece, influencing both tonal quality and ease of playability.
Understanding its significance involves examining various aspects:
- Sound Production: The neck impacts resonance and projection, affecting how notes are articulated.
- Tuning: This section is essential for achieving accurate pitch, allowing musicians to adjust their instrument for optimal performance.
- Articulation: The design of the neck affects the responsiveness, enabling players to execute techniques like slurs and staccatos.
- Materials: Different materials used in crafting the neck can alter timbre and character, providing unique tonal qualities.
Ultimately, the neck is not merely a connecting element; it is integral to the expressive capabilities of the instrument, allowing musicians to convey emotion and artistry through their performance.
The Body: Structure and Design
The design and framework of this musical instrument play a crucial role in its sound production and overall functionality. This central component is not only a vessel for air but also a vital element that influences tonal quality and resonance.
Material Choices
Various materials are utilized in crafting this section, each contributing unique acoustic properties. Brass is the most common choice, providing durability and a warm sound, while bronze offers a richer tonal palette. The choice of material can greatly affect the timbre and projection of notes.
Shape and Ergonomics
The curvature and dimensions are carefully engineered to enhance playability and comfort for musicians. An ergonomic design ensures that players can perform for extended periods without strain, ultimately allowing for greater expression and nuance in their music.
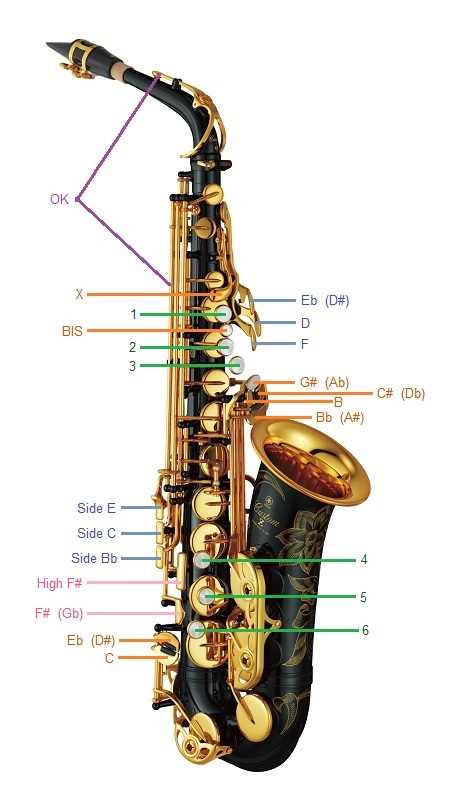
Mechanics of the Key System
The intricate framework that enables sound production through a woodwind instrument is a marvel of engineering and design. Each component plays a crucial role in the functionality and performance of the instrument, allowing for a diverse range of notes and tonal expressions.
At the heart of this mechanism lies the interaction between various elements, which can be categorized as follows:
- Keys: These are the levers that the musician presses to open or close tone holes, affecting pitch and volume.
- Posts: Metal rods that provide support for the keys and ensure proper alignment and movement.
- Springs: These components return the keys to their original position after being pressed, facilitating rapid playability.
The coordination of these elements is vital for achieving a smooth playing experience. When a musician applies pressure to a key, it engages the associated mechanisms, which in turn manipulate the airflow through the instrument. The following steps outline this process:
- The musician depresses a key.
- This action causes a corresponding post to pivot.
- As the post moves, it opens or closes the designated tone hole.
- Airflow is altered, resulting in a change in pitch.
Understanding the mechanics behind these interactions enhances a musician’s ability to maintain and troubleshoot their instrument, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Importance of the Reed
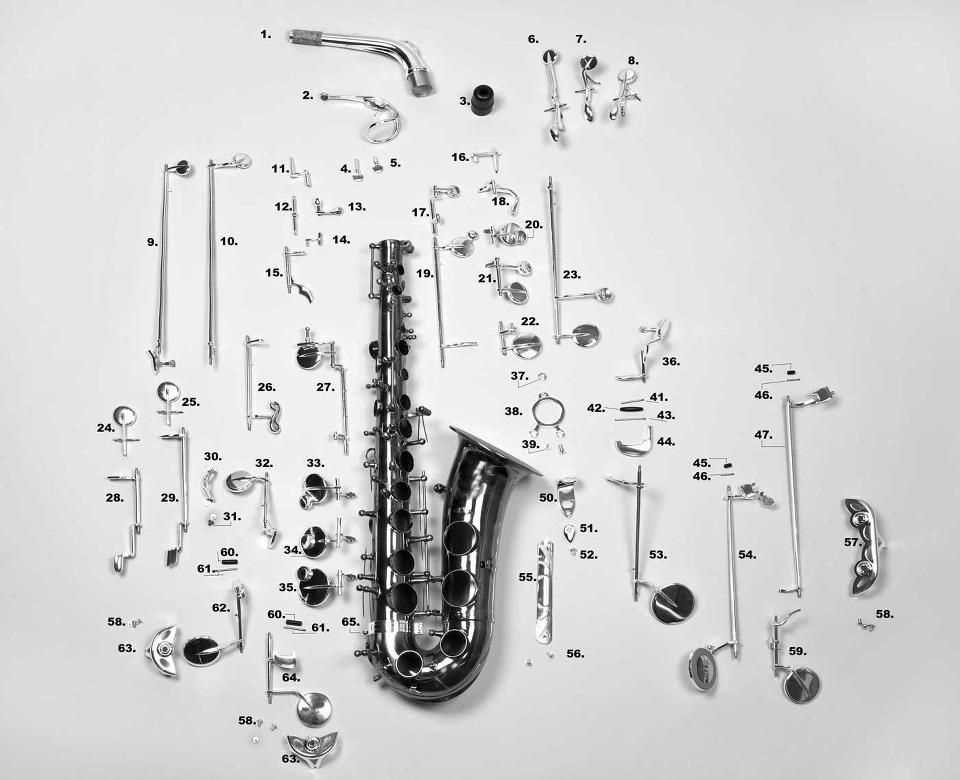

The functionality and overall sound quality of woodwind instruments heavily rely on a small yet crucial component. This element plays a vital role in producing sound, influencing the instrument’s timbre and responsiveness. Understanding its significance is essential for musicians seeking to enhance their performance.
Several factors contribute to the importance of this component:
- Sound Production: It acts as the primary source for sound creation, vibrating when air passes through it.
- Tone Quality: The characteristics of this element directly affect the richness and clarity of the sound.
- Control and Flexibility: A well-selected piece allows for greater expressive capabilities and dynamic range.
- Maintenance: Regular care and timely replacement can prevent deterioration and maintain optimal performance.
Choosing the right option can greatly influence a musician’s ability to convey emotion and technical skill, making it an indispensable aspect of their instrument. In essence, the small piece serves as the bridge between the player and the audience, translating breath into musical expression.
Types of Pads and Their Uses

In the realm of woodwind instruments, various cushioning materials play a crucial role in sound production and overall performance. These components ensure airtight seals, enabling optimal resonance and playability. Understanding the different varieties and their specific applications can significantly enhance the instrument’s functionality and longevity.
Felt Pads
Felt pads are commonly utilized for their excellent compressibility and ability to create a snug fit. Typically made from wool or synthetic fibers, these pads are ideal for key mechanisms that require a balance between sound quality and responsiveness. They are especially favored for their durability, making them suitable for both beginner and professional instruments.
Leather Pads
Leather pads offer a more traditional approach, often preferred for their rich tonal qualities. They provide a firm, stable surface that can enhance sound projection. While they may require more maintenance and careful handling to prevent moisture damage, leather pads are renowned for their longevity and superior performance in professional settings.
Role of the Bell in Sound
The bell of a wind instrument plays a crucial role in shaping the overall tone and projection of the sound produced. Its design and dimensions significantly influence the instrument’s acoustic characteristics, affecting how the sound resonates and is perceived by listeners. This component acts as a resonating chamber, amplifying the vibrations generated by the musician and enhancing the richness of the sound.
Acoustic Properties
The bell’s shape and size determine the way sound waves interact within the instrument. A larger bell can create a broader, more expansive sound, while a narrower one may produce a focused, concentrated tone. This variability allows musicians to select instruments that best suit their style and desired sound quality. Additionally, the material of the bell contributes to the timbre, offering a range of tonal colors that can be explored during performance.
Impact on Projection
Another essential function of the bell is its influence on sound projection. A well-designed bell enhances the instrument’s ability to project sound over distances, making it essential for performance in larger venues. The way sound waves exit through the bell can affect not only the volume but also the clarity and definition of each note, enabling musicians to convey their expressions more effectively. Understanding the importance of this component allows players to appreciate its role in their overall sound production.
Common Repairs and Maintenance Tips
Maintaining your musical instrument is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular check-ups and simple repairs can significantly enhance the playing experience and prevent more significant issues down the line.
Routine Maintenance
- Clean the exterior regularly to remove dust and fingerprints.
- Inspect pads and corks for wear and replace them as needed.
- Oil moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Check for leaks by conducting a “suction test” on the keys.
Common Repairs
- Replacing pads: If you notice air leaks or sound issues, it may be time to change the pads.
- Fixing springs: Weak or broken springs can hinder performance; consider replacing them.
- Adjusting key height: If keys stick or are misaligned, adjustments may be necessary.
Upgrading Saxophone Parts for Performance
Enhancing the components of your instrument can lead to significant improvements in sound quality and playability. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned player, investing in better materials and craftsmanship can transform your experience.
- Consider replacing the mouthpiece for improved tone and flexibility.
- Upgrade the ligature to enhance the responsiveness of your reed.
- Evaluate the pads and springs; better quality can enhance sealing and action.
- Invest in quality reeds tailored to your style for optimal sound production.
Each upgrade can ultimately contribute to a richer, more resonant sound, allowing for greater artistic expression.
Visual Guide to Saxophone Parts
This section provides an informative overview of the various components that contribute to the creation of sound in a specific woodwind instrument. Each element plays a crucial role in defining the instrument’s unique characteristics and functionality.
Key Components
- Body: The main structure that houses the internal mechanisms.
- Neck: The section connecting the body to the mouthpiece.
- Mouthpiece: Where sound production begins, housing the reed.
- Reed: A thin piece of material that vibrates to create sound.
Additional Elements
- Pads: Sealing elements that close the tone holes when keys are pressed.
- Keys: Mechanisms used to open and close tone holes for pitch control.
- Bell: The flared end that amplifies the sound produced.
Understanding these components enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship and design behind the instrument, ultimately enriching the playing experience.