
Proper maintenance and repair of any tool require a clear understanding of its internal components and how they interact. Knowing the layout and function of each element is key to ensuring smooth operation and longevity. This section will help you get familiar with the detailed structure of your device, offering insights into how to keep it in optimal condition.
We’ll guide you through a breakdown of essential elements, explaining their purpose and role within the larger system. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a much clearer picture of the internal mechanics and how each piece fits into the overall design, allowing you to handle both routine checks and more complex adjustments with ease.
Understanding Essential Components
Each device designed for fluid application relies on a variety of critical elements to ensure smooth and effective operation. Familiarizing yourself with these components can help with maintenance, efficient use, and troubleshooting. Below is an overview of the key elements you will encounter in these systems.
- Pump Mechanism: Responsible for generating the necessary pressure to disperse liquids. A well-functioning pump ensures consistent flow and reach.
- Nozzle: This part controls the spray pattern and coverage. Different types of nozzles allow for fine or wide dispersion, depending on the task at hand.
- Tank: The main reservoir where the liquid is stored. Tanks come in various sizes and materials, ensuring durability and the right capacity for different jobs.
- Trigger or Valve: A control mechanism that releases the liquid when needed. Proper care and regular checks ensure precise control during operation.
Main Functions of Sprayer Parts
Each component of the equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation. The elements work together to distribute liquids evenly, allowing users to cover areas with precision. Understanding how these parts interact helps in maintaining the device’s functionality and prolonging its lifespan.
Pumping mechanism: The primary task of this part is to generate pressure, enabling fluid movement through the system. Proper maintenance of this feature ensures consistent flow and optimal performance.
Control valve: This part regulates the flow of liquid, allowing the user to adjust the output according to the task at hand. It provides flexibility, making it easier to manage different spraying needs.
The nozzle determines the spray pattern, playing a key role in how the liquid is dispersed. A well-maintained nozzle ensures that the liquid is applied evenly, reducing waste and improving coverage.
Hose: Serving as the passage for the
Identifying Key Components of the Sprayer
The structure of a handheld device for dispersing liquids relies on several interconnected elements. Each piece plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation and smooth distribution of the liquid. Understanding how these parts work together is essential for maintaining the functionality and extending the equipment’s lifespan.
Handle and Trigger: These provide control over the release of liquid, allowing the user to manage flow with precision. The ergonomic design ensures comfort during prolonged use.
Tank: The reservoir stores the liquid that will be sprayed. It is typically made from durable materials to resist wear and corrosion over time. A secure lid prevents spills while ensuring easy access for refilling.
Nozzle: This component is responsible for the dispersion pattern of the liquid. Adjustable
Overview of the Pump Mechanism
The pump mechanism is a key component responsible for generating the necessary pressure to ensure fluid movement. Its efficient functioning is crucial for the proper operation of the system, as it allows for smooth and controlled distribution of liquids. Understanding how this mechanism works can help with maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Pump
The pump assembly consists of several parts working in unison. These include a piston, a cylinder, and various seals that maintain the integrity of the system by preventing leaks and ensuring pressure retention.
Operation Process
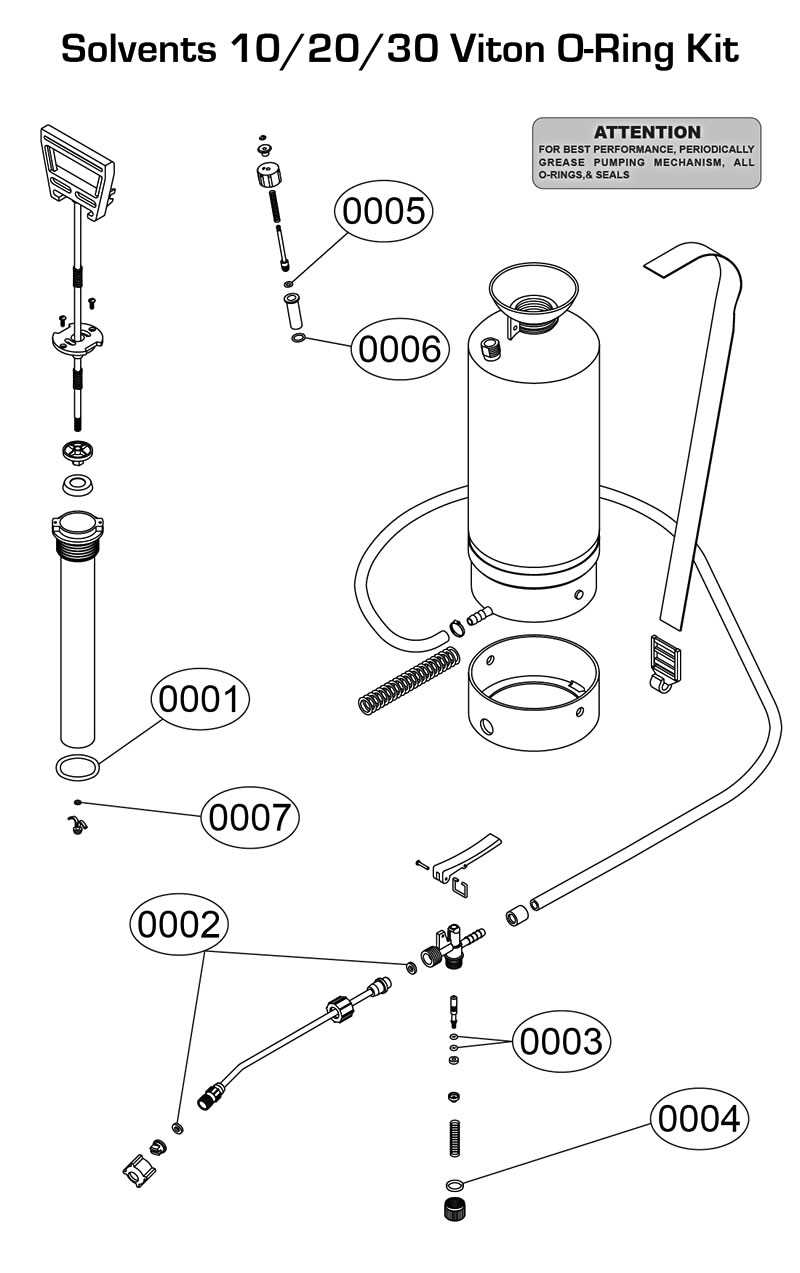
As the piston moves within the cylinder, it creates pressure, which forces liquid through the system. The movement of the piston is often manually controlled, but it is designed to be efficient and effective for consistent output.
Nozzle Types and Their Applications
Nozzles play a critical role in determining the efficiency and precision of liquid distribution. Different designs cater to specific tasks, making it essential to understand the variety of options available and their optimal uses. Choosing the right type can significantly improve performance, ensuring accurate coverage and reducing waste.
Flat Fan Nozzles
Flat fan nozzles are known for producing a wide, even spray pattern, ideal for covering large surfaces. They are commonly used in scenarios where uniform application is necessary, providing consistent distribution over broad areas.
Cone Nozzles
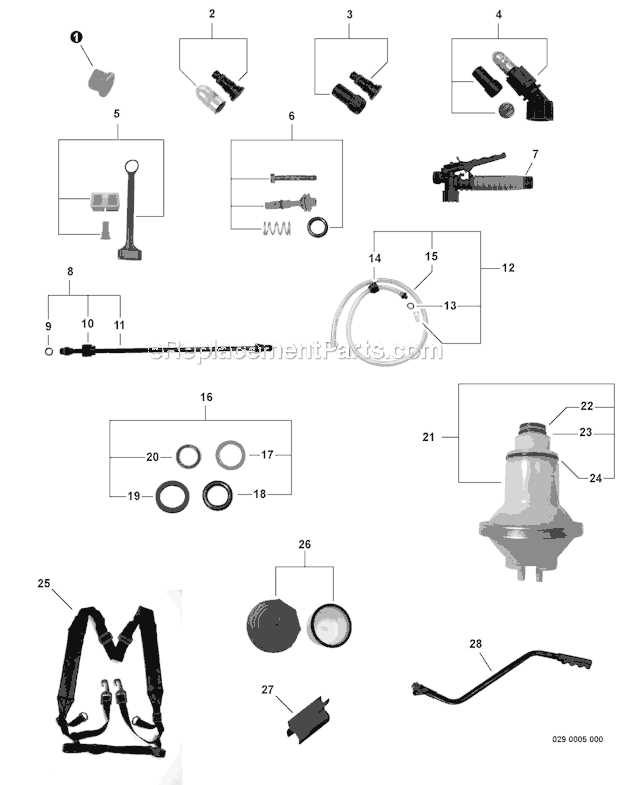
Cone nozzles create a circular spray pattern and are effective for more targeted applications. They are often used when precise control is required, allowing for focused delivery of liquid to specific areas or objects.
Handle and Trigger Assembly Breakdown
This section provides a detailed overview of the components involved in the handle and trigger mechanism, essential for effective operation. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal functionality.
Key Components
- Handle: The primary grip used to control the device.
- Trigger: The mechanism that activates the dispensing function.
- Spring: A vital component that returns the trigger to its original position.
- Safety Lock: Ensures the trigger cannot be inadvertently activated.
Functionality Overview
The handle and trigger assembly plays a significant role in the usability of the equipment. Proper engagement of the trigger allows for precise control of the output, while the handle ensures a comfortable grip during operation.
- Pressing the trigger activates the dispensing mechanism.
- The spring returns the trigger to its resting position once released.
- The safety lock prevents accidental activation when not in use.
Tank Construction and Materials
The design and composition of containers used for fluid storage are critical to their overall functionality and durability. Various materials are employed to ensure that the vessel can withstand the pressures and conditions of its intended use, while also providing resistance to corrosion and other forms of degradation.
Material Types
Commonly, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is favored due to its robust nature and lightweight properties. This material is known for its chemical resistance and ability to endure temperature fluctuations. Additionally, metal options, such as aluminum or stainless steel, are utilized for their strength and longevity, offering excellent resistance to physical wear and environmental factors.
Design Features
Tank design often incorporates features that enhance usability and safety. For instance, many tanks include reinforced areas to prevent damage during handling or transport. Furthermore, transparent sections or integrated level indicators may be present to allow for easy monitoring of fluid levels, ensuring optimal performance during operation.
Seals and Gaskets: Importance and Maintenance
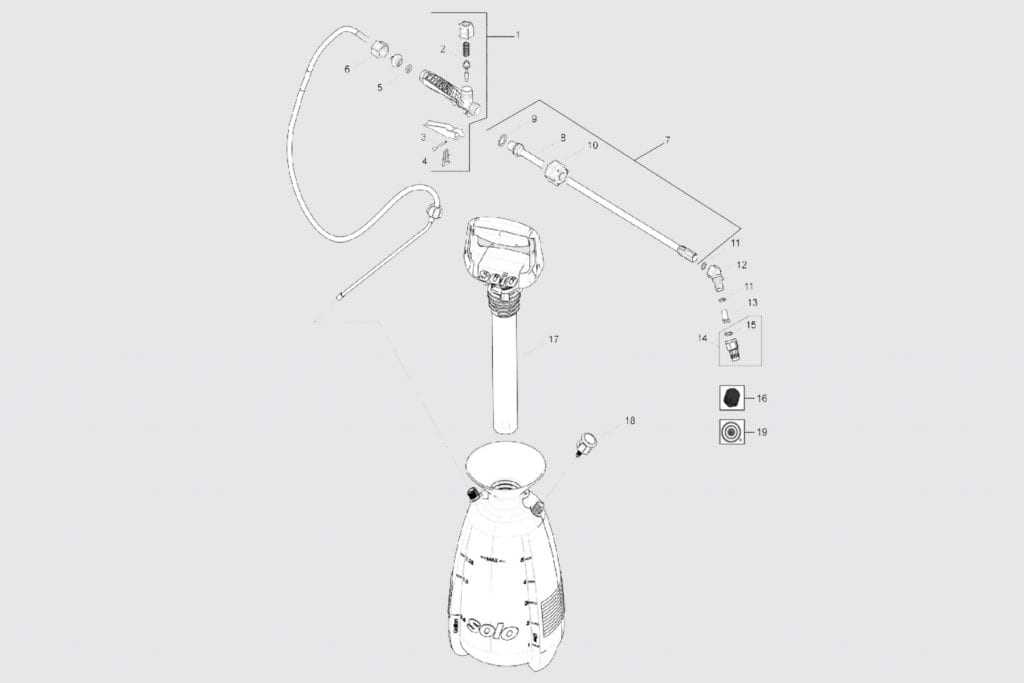
In any equipment that relies on fluid dynamics, the integrity of sealing components is crucial for optimal performance. These elements play a vital role in preventing leaks and ensuring that systems operate efficiently. Regular maintenance of these components is essential to prolong the lifespan of the machinery and to avoid costly repairs.
Proper upkeep includes routine inspections and timely replacements, as wear and tear can lead to diminished efficiency and functionality. Understanding the types of seals and gaskets in use can help in making informed decisions regarding their maintenance and replacement.
Type Function Maintenance Tips O-rings Prevent leakage at joints Check for cracks; replace if damaged Flat gaskets Seal flat surfaces Inspect regularly; ensure proper torque during installation V-rings Provide a tight seal against rotating shafts Lubricate to avoid friction damage Sealant Fill gaps and create a barrier against leakage Reapply as needed; check for hardening Filtration System and Its Role
The filtration mechanism is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of any application involving liquid transfer. This system works to remove impurities and particulates that could potentially disrupt the flow or damage components, ensuring a smooth operation.
Importance of Filtration
- Prevents clogging of nozzles and hoses.
- Enhances the quality of the output by ensuring clean delivery.
- Reduces wear and tear on pumps and other integral components.
Types of Filtration Systems
- Mechanical Filtration: Utilizes screens or mesh to trap larger particles.
- Chemical Filtration: Involves the use of substances that can absorb or neutralize contaminants.
- Biological Filtration: Often employed in scenarios where biological agents are used, promoting a healthy balance in the system.
Common Wear and Tear Parts
In any equipment designed for spraying liquids, certain components are prone to wear over time due to constant use and exposure to various substances. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring longevity.
Component Signs of Wear Recommended Action Seals Leaking fluids, reduced pressure Replace if damaged Nozzles Inefficient spray pattern, clogging Clean or replace as needed Filters Restricted flow, poor performance Clean or replace regularly Pumps Noisy operation, loss of pressure Inspect and replace if necessary Hose Connections and Compatibility
Ensuring proper connections between hoses is crucial for optimal functionality and efficiency. Understanding the different types of connections available and their compatibility with various systems can help prevent leaks and operational issues.
Compatibility is key when selecting hoses and fittings. Various models may have distinct connection types, and using the right combination ensures a secure fit. It is advisable to check the specifications of each component to confirm their suitability.
When replacing hoses or fittings, consider the material and diameter of the connections. These factors significantly impact performance and longevity. Additionally, regular inspection of connections can help identify wear and potential problems before they escalate.
Ultimately, paying attention to hose connections and their compatibility not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment, making maintenance simpler and more effective.
Replacement Tips for Worn Components
Maintaining optimal performance in equipment requires regular attention to its essential elements. Over time, various components may become less effective, necessitating timely replacements to ensure continued functionality.
When considering the replacement of these crucial elements, keep the following tips in mind:
- Identify Signs of Wear: Regularly inspect components for any visible damage, cracks, or signs of fatigue.
- Consult Documentation: Reference manufacturer guides for specifications on compatible replacements and installation instructions.
- Use Quality Replacements: Opt for high-quality substitutes to ensure longevity and reliability.
- Keep a Spare Inventory: Maintain a small stock of essential parts to minimize downtime during repairs.
- Follow Proper Installation Procedures: Adhere to recommended installation practices to avoid future issues and ensure correct functionality.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage replacements and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
How to Assemble and Disassemble a Sprayer
Proper assembly and disassembly of your equipment are crucial for its optimal performance and longevity. This process involves a systematic approach to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly and can be taken apart without damage. Understanding each segment’s role will enhance your ability to manage maintenance tasks efficiently.
Steps for Assembly
To begin the assembly, gather all necessary components and tools. Start with the base and progressively attach additional elements following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Ensure that each part is securely fitted and check for any signs of wear before proceeding to the next step. This will help prevent potential malfunctions during operation.
Disassembly Procedure
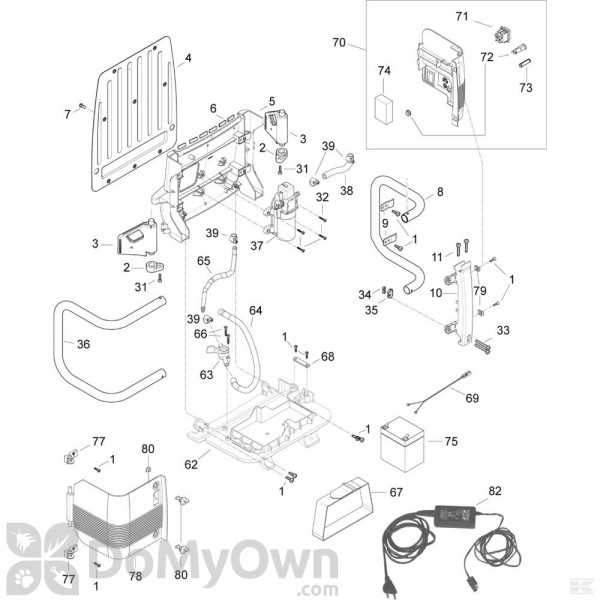
When it’s time to disassemble, follow a reverse order of the assembly steps. Carefully remove each part, ensuring not to force any components, as this could lead to damage. It’s advisable to keep track of all pieces by organizing them systematically, which will simplify reassembly later.
Component Assembly Step Disassembly Step Base Unit Attach to the platform Unscrew from the platform Handle Insert and secure Remove bolts Tank Connect to the base Detach from the base Nozzle Fit into the hose Unclip from the hose