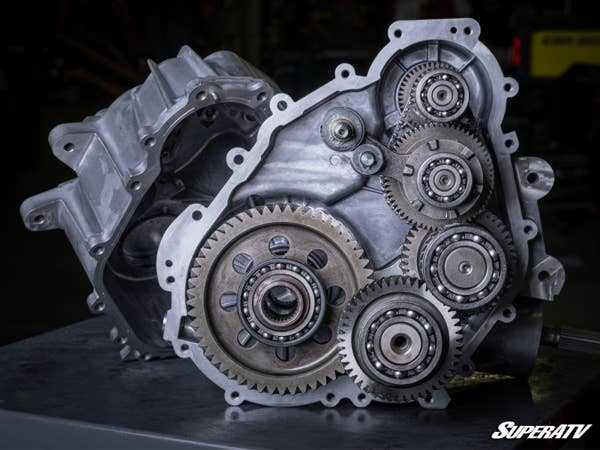

In mechanical systems, every element has a specific place and function. Understanding how various units and structures interact is key to ensuring smooth operation and timely maintenance. Visual representations of these elements offer a clear roadmap for anyone looking to familiarize themselves with how intricate mechanisms are organized.
A detailed layout of components can help users identify connections between different sections, aiding both troubleshooting and upgrades. Whether you’re dealing with complex machinery or simple tools, knowing the internal structure is essential for effective handling and upkeep.
This guide will walk you through the intricacies of a popular model’s internal arrangement, offering insights into the organization of its mechanical and electrical components. With this knowledge
Polaris Ranger 800: Key Components Overview
The vehicle’s core mechanical structure consists of several essential systems that work together to provide functionality and performance. These systems include power generation, steering, suspension, and braking mechanisms, each contributing to the vehicle’s capability in various terrains and conditions. Understanding these components helps ensure the longevity and efficiency of the machine, enabling smoother operation and easier maintenance.
Powertrain and Engine System
- Engine: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for generating the power needed to drive.
- Transmission: Manages power distribution between the engine and wheels, allowing for controlled movement and speed adjustment.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating by regulating the engine temperature through
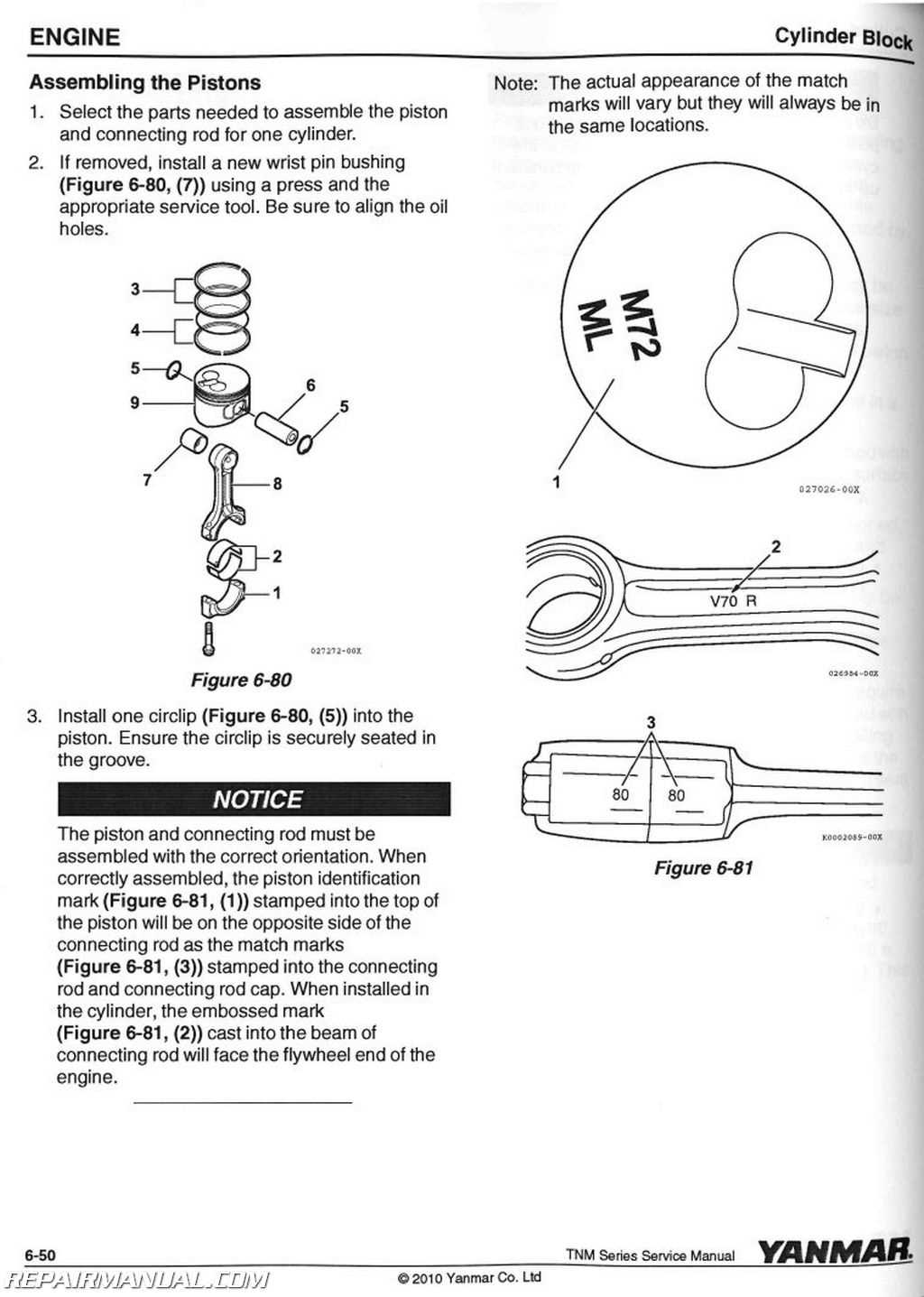
Engine Parts and Their Function
The internal components of an engine are critical for its overall performance and efficiency. Each element plays a specific role in converting fuel into the power needed to operate a vehicle. Understanding the basic components and their interactions helps to grasp how the engine operates smoothly under different conditions.
Cylinders and Pistons
Cylinders are the chambers where fuel combustion occurs, and pistons move within these cylinders to transfer energy. The pistons compress the air-fuel mixture, leading to combustion, which generates the power that drives the vehicle’s motion. Their movement is crucial for turning the mechanical energy into forward momentum.
Crankshaft and Connecting Rods
The crankshaft is the rotating part that converts
Suspension System: Main Elements
The suspension system plays a critical role in providing a smooth and controlled ride, ensuring stability and comfort over varying terrains. It consists of several key components that work together to absorb impacts, maintain tire contact with the ground, and support the overall weight of the vehicle. Understanding the main elements of this system is essential for maintaining performance and ensuring durability.
One of the primary elements is the shock absorber, which helps dampen the force from bumps and uneven surfaces. Closely tied to this are the springs, which bear the load of the vehicle and provide flexibility in movement. Additionally, control arms are vital for connecting the wheels to the frame while allowing vertical motion, and bushings help reduce friction at pivot points, ensuring smoother operation. Together,
Brake Mechanism Breakdown
The brake system plays a crucial role in ensuring safe vehicle operation by converting kinetic energy into heat, allowing for controlled deceleration and stopping. Understanding the components and functionality of the braking system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
The system typically consists of several interconnected parts, each responsible for different stages of the braking process. The main components include brake discs or drums, which provide the surface for friction, and pads or shoes, which press against these surfaces to generate the required stopping force.
Another key element is the hydraulic system, responsible for transmitting the force applied to the brake pedal to the braking components. It relies on fluid pressure to amplify the input and ensure even pressure distribution. Regular inspection of this system can prevent performance issues and ensure reliable stopping power.
Electrical Components of the Ranger 800
The vehicle’s electrical system is a crucial part of its operation, ensuring that all the power-dependent features function correctly. This section focuses on the essential elements of the wiring and electronic equipment, which contribute to both performance and safety. Understanding these components is key to maintaining reliability and efficiency.
Main Electrical Units
- Battery: Provides the necessary power to start the engine and supports various electrical systems.
- Alternator: Recharges the battery while the engine is running, ensuring all systems have sufficient power.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect circuits from overloads and ensure proper electrical distribution.
Lighting and Controls
The lighting system and control
Transmission System: Critical Parts
The transmission system is a vital component of any vehicle, playing a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its key elements can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of the machine. This section will explore the essential components that ensure smooth operation and effective power delivery.
Key Components Overview
At the heart of the transmission system lies the gearbox, responsible for adjusting the torque and speed transmitted to the drivetrain. Additionally, the clutch assembly enables the driver to engage and disengage the engine from the wheels, facilitating smooth gear shifts. The proper functioning of these elements is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency.
Supporting Mechanisms
Other significant elements include the drive shafts, which connect the gearbox to the wheels, ensuring that power is transmitted effectively. Moreover, transmission fluid plays a crucial role in lubrication and cooling, preventing overheating and ensuring seamless operation. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are vital for the longevity of the transmission system.
Cooling System Elements and Diagram

The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures within a vehicle’s engine. By effectively dissipating heat, it prevents overheating and ensures efficient performance. This section explores the key components of the cooling system and provides a visual representation to aid in understanding their arrangement and functionality.
Main Components
- Radiator: This component is responsible for transferring heat from the coolant to the outside air, allowing the engine to maintain a stable temperature.
- Water Pump: This pump circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that it flows efficiently to absorb and dissipate heat.
- Thermostat: This device regulates coolant flow based on temperature, allowing the engine to warm up quickly while preventing overheating.
- Coolant Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between various components of the cooling system.
- Expansion Tank: A reservoir that accommodates coolant expansion and contraction, helping to maintain proper pressure within the system.
System Overview
The cooling system operates through a closed-loop mechanism. The water pump circulates coolant, which absorbs heat from the engine. This heated coolant flows to the radiator, where it releases heat to the air. As the coolant cools, it returns to the engine to repeat the cycle. The thermostat plays a pivotal role in this process, ensuring that the system operates efficiently under varying conditions.
Fuel System: Core Parts Explained

The fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of a vehicle, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for efficient operation. Understanding the key components of this system can help in maintaining and troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
At the heart of the fuel delivery mechanism are several essential elements that work together to facilitate proper fuel flow. Below is a summary of these components and their functions:
Component Description Fuel Tank The reservoir that holds the fuel before it is delivered to the engine. Fuel Pump Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, maintaining adequate pressure. Fuel Filter Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Fuel Injectors Spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold for optimal mixing with air. Fuel Pressure Regulator Maintains consistent fuel pressure within the system, ensuring efficient engine performance. By familiarizing yourself with these core components, you can better understand the functionality of the fuel system and address any potential maintenance needs effectively.
Drive System Overview for Polaris 800

The drive system of a utility vehicle is a crucial component that facilitates the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This system not only enhances performance but also contributes to the vehicle’s overall functionality and maneuverability. Understanding the key elements of the drive mechanism can help operators maintain and optimize their vehicle’s efficiency.
Key Components
- Transmission: The transmission plays a vital role in adjusting engine power to suit different driving conditions. It ensures smooth gear shifts and optimal power delivery.
- Driveline: The driveline includes various shafts and joints that transmit power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for efficient movement across diverse terrains.
- Differential: The differential enables the wheels to rotate at different speeds, particularly important when turning, enhancing stability and control.
- Axles: Axles connect the wheels to the vehicle, supporting the weight and facilitating movement by transmitting torque from the differential.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect all components for wear and tear.
- Ensure proper lubrication of the transmission and differential to prevent overheating and damage.
- Check for any leaks in the driveline system and address them promptly.
- Maintain correct tire pressure to enhance handling and drive efficiency.
Steering Components and Their Role
The steering system is a vital part of any vehicle, facilitating precise control and maneuverability. It consists of various elements that work together to ensure that the driver can easily guide the machine in the desired direction. Understanding the functions of these components can enhance maintenance efforts and improve overall performance.
Steering Wheel: This is the primary interface between the driver and the steering system. It allows the operator to communicate directional intentions to the vehicle.
Steering Column: This component connects the steering wheel to the rest of the steering mechanism. It houses essential wiring for controls, ensuring that all functions are easily accessible.
Steering Gear: The steering gear translates the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement. It plays a crucial role in determining the responsiveness of the steering system.
Linkage System: This assembly connects the steering gear to the wheels. It transmits the motion generated by the steering wheel, enabling the wheels to turn accurately and effectively.
Power Steering Pump: This hydraulic system enhances the driver’s ability to steer, reducing the effort needed to turn the wheel. It plays a significant role in improving comfort and control.
Each component in the steering assembly has a specific role that contributes to the smooth operation of the vehicle. Proper maintenance and awareness of these elements can significantly improve safety and performance during use.
Lighting and Signal Parts Breakdown
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the components related to illumination and signaling systems within utility vehicles. Understanding these elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety on the road. Each component plays a significant role in visibility and communication with other drivers, which is essential for any off-road or utility vehicle.
Key Lighting Components
- Headlights: Essential for visibility during low-light conditions, these fixtures are designed to illuminate the path ahead.
- Taillights: Located at the rear, these lights indicate the vehicle’s presence and movements to others on the road.
- Turn Signal Lights: Critical for communicating directional intentions to other drivers, these lights blink to indicate turns or lane changes.
- Fog Lights: These are specifically designed to cut through fog or heavy rain, providing better visibility in adverse weather conditions.
Signaling Components
- Emergency Flashers: Used to alert other drivers to a temporary hazard, these lights flash in a specific pattern to ensure attention.
- Reverse Lights: Activating when the vehicle is in reverse, these lights help to illuminate the area behind the vehicle and signal that it is backing up.
- License Plate Light: Illuminates the license plate for visibility at night, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Marker Lights: These small lights enhance visibility from all angles and are often found on larger vehicles for added safety.
Body and Frame Parts Layout
The structure and exterior components of a utility vehicle are essential for its durability and functionality. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. This section outlines the various segments that make up the vehicle’s body and frame, providing insights into their roles and interconnections.
Frame: The frame serves as the foundation of the vehicle, supporting all other components. It is typically constructed from robust materials to withstand stress and impacts while ensuring stability during operation.
Body Panels: These elements form the exterior shell, protecting the internal components from environmental factors. They also contribute to the overall aesthetics of the vehicle. Each panel is designed to fit seamlessly with others, enhancing both functionality and appearance.
Fenders: Positioned over the wheels, fenders shield the vehicle from mud and debris. They play a significant role in maintaining the cleanliness of the body and preventing damage to other parts from flying objects.
Doors: Access to the cabin is facilitated by doors, which provide safety and security. Their design often includes features that enhance user convenience and comfort.
Bumpers: These components are crucial for impact absorption. They protect the vehicle’s frame and body during minor collisions, minimizing potential damage and ensuring safety for occupants.
Mounting Points: Various attachment points are integrated into the frame and body layout, allowing for secure installation of accessories and additional equipment. These points are strategically placed to optimize balance and performance.
In summary, the configuration of the body and frame elements is fundamental to the vehicle’s integrity and performance. Familiarity with these components aids in effective maintenance and ensures longevity in various operational environments.