
The efficient operation of a heating system relies on a well-structured arrangement of various elements. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the system functions smoothly, providing reliable warmth to residential and commercial spaces. Understanding how these components work together can enhance maintenance practices and improve overall performance.
In this section, we will explore the intricate layout of a typical heating unit, shedding light on the essential components and their respective functions. By breaking down the configuration, readers can gain insights into the operational intricacies and identify potential issues that may arise over time.
Whether you are a homeowner seeking to comprehend your system better or a technician aiming to refine your diagnostic skills, familiarizing yourself with these critical elements will prove invaluable. Knowledge of the arrangement and interaction of these components can lead to more effective troubleshooting and maintenance strategies.
Understanding Burnham Series 2 Components
To maintain efficient operation and ensure long-lasting performance, it is essential to be familiar with the critical elements that make up the heating system. Each part has a specific role in regulating temperature, pressure, and overall function, contributing to both safety and efficiency.
Below is a list of key components you’ll typically encounter:
- Control Unit: Manages temperature settings and activates various system functions based on user input.
- Circulator Pump: Moves heated water through the piping system, ensuring even distribution to radiators or other connected systems.
- Pressure Relief Valve: Protects the system by releasing exces
Overview of Boiler Functionality
In this section, we will explore the core principles behind how heating systems work. These systems are designed to convert energy into heat, which is then distributed throughout a building to maintain a comfortable indoor climate. Through a combination of different components, heat is produced and transferred to the necessary locations efficiently.
The process relies on several key elements working together to ensure a consistent and reliable flow of warmth. Below is a simplified outline of the main functions and their roles within the system:
Component Function Heat Exchanger Transfers energy from the source to the water or air, distributing warmth efficiently. Key Elements of Gas Boilers
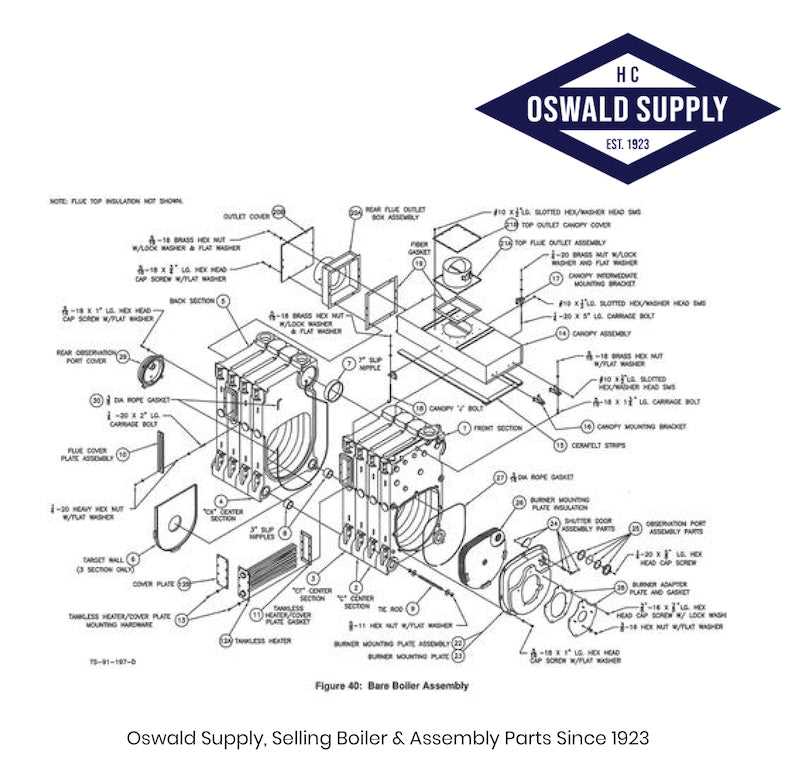
Efficient heating systems rely on a variety of components working together to provide warmth and comfort. Understanding the main elements involved helps in maintaining and troubleshooting these systems, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity.
Main Components of Heating Systems
- Heat Exchanger – This component transfers thermal energy to the surrounding medium, providing the necessary warmth for your environment.
- Burner – Responsible for initiating the combustion process, this part generates the energy required to heat the system.
- Circulator – This motor-driven mechanism ensures the flow of the heated medium through the network of pipes or radiators.
- Ignition System – Modern systems often feature automatic ignition
Identifying Major Assembly Parts
The central heating system relies on several key components that work together to provide effective heat distribution. Understanding the individual elements within the overall mechanism can help in diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, and ensuring proper functionality. In this section, we will explore the essential structural elements that contribute to the operation of the system.
Main Operational Elements

Among the most significant parts are those responsible for igniting the heating process and circulating warmth. These elements manage the flow of energy and ensure safety during operation. Recognizing these components is crucial for troubleshooting and regular upkeep.
Supporting Components

In addition to the core operational units, several auxiliary elements contribute to the overall performance. These include regulators, monitoring devices, and various connectors that
Common Replacement Components
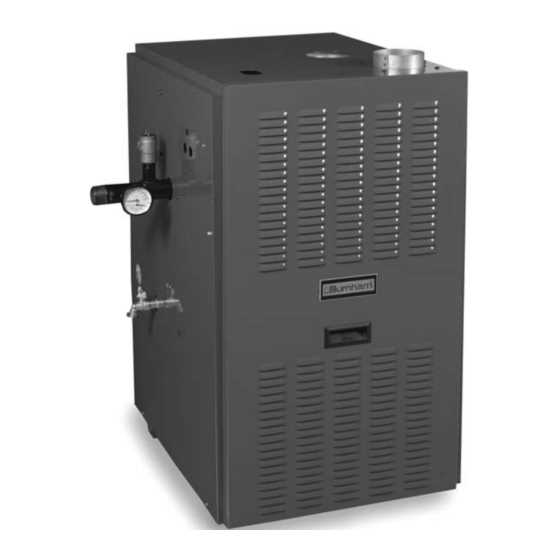

In heating systems, certain elements are more prone to wear and tear due to regular usage. Recognizing these frequently replaced components can help ensure timely maintenance and reduce downtime. This section will highlight some of the most commonly needed replacements that keep the system operating efficiently.
Control Mechanisms
The control units are essential for regulating various functions within the system. These include components that manage temperature, pressure, and the overall operation of the heating unit. Replacing malfunctioning control elements is a key aspect of maintaining the system’s reliability.
Heat Exchanger and Valves
The heat exchanger plays a critical role in
Maintenance Considerations for Longevity

To ensure optimal performance and an extended lifespan of your heating system, regular upkeep is essential. Proper care can prevent common issues and minimize the need for costly repairs. This section outlines key aspects of maintenance that contribute to the durability of your unit.
Inspection and Cleaning
Routine inspections and cleaning are vital for keeping your equipment running smoothly. Accumulated debris or dirt can reduce efficiency and cause components to wear out prematurely. By scheduling regular check-ups, you can identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
Monitoring Key Components
Certain parts of the system require particular attention due to their critical role in daily operation. Monitoring their condition helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensures a reliable heating experience. The following table highlights several components that should be regularly checked and maintained:
Component Maintenance Frequency Action Required Heat Fuel System Components Explained
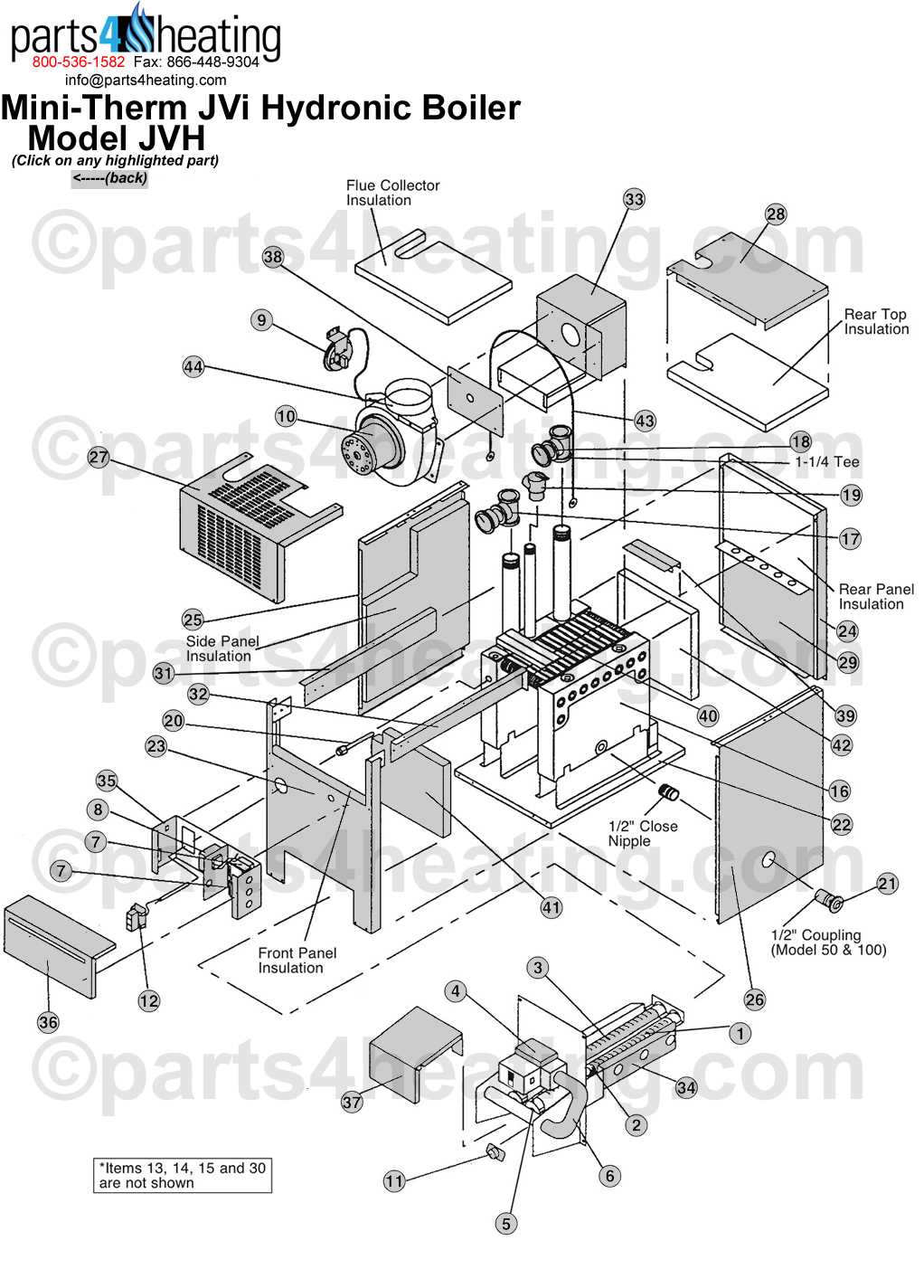
The fuel system serves as the backbone of efficient operation, ensuring proper delivery and control of energy flow within the heating unit. Understanding each component’s role is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring long-term reliability.
Fuel Valve: This essential component regulates the entry of energy into the unit, providing the precise amount required for ignition and operation. It acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring that fuel reaches the necessary areas only when needed.
Ignition System: Responsible for initiating the combustion process, the ignition system works in harmony with the control board to start the process at the right time. Without it, the entire system would be unable to function.
Burner Assembly: The burner is where the actual combustion happens, turning the fuel into heat. It requires consistent and precise regulation to ensure that the heating process is both safe and efficient.
Safety Sensors: Various sensors monitor the performance of the fuel delivery and combustion, ensuring that the system runs within safe parameters. If any issues are detected, these sensors trigger a shutdown to prevent accidents.
Each of these components works together to ensure smooth operation and efficient energy use, making regular inspection and
Understanding Electrical Connections
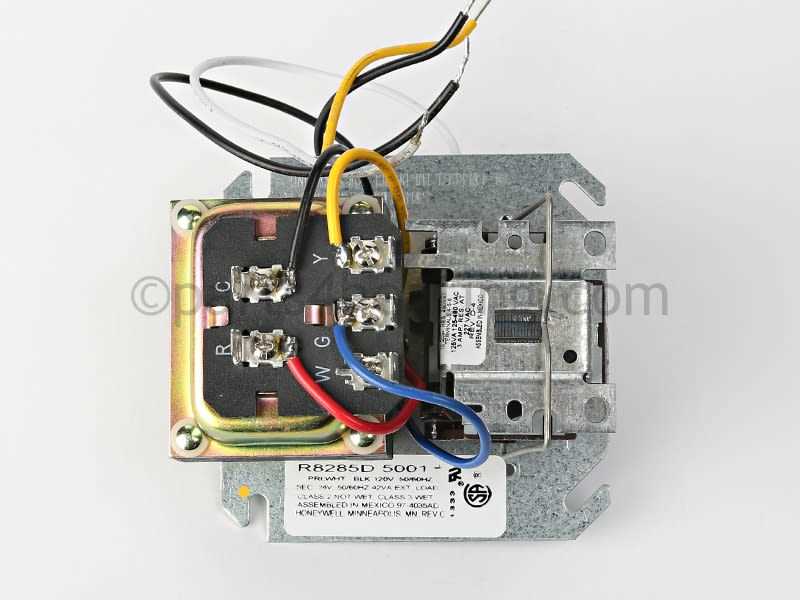

Proper comprehension of the wiring layout is essential for ensuring efficient performance and safe operation of heating systems. By accurately identifying and working with the various terminals and pathways, technicians can guarantee that the electrical components are well-integrated, leading to consistent and reliable functionality.
Key Wiring Elements
Each electrical connection plays a critical role in regulating temperature controls, powering ignition systems, and managing sensors. Understanding how these elements communicate is crucial for diagnosing issues or enhancing the system’s efficiency. Recognizing the color codes, wire functions, and control mechanisms simplifies maintenance and repair tasks.
Safety Considerations
Before making any adjustments to electrical circuits, it’s important to cut off the power supply. Failure to do so can result in electrical hazards. Always double-check that connections are
Safety Features in the Design
Ensuring user protection is a critical element in the development of modern heating systems. Several mechanisms are integrated to prevent potential hazards and enhance overall reliability. These design elements serve to monitor, control, and safeguard the operation of the unit, minimizing risks and ensuring longevity.
Automatic Shutoff Mechanisms
A primary safeguard is the inclusion of automatic shutoff functions. These systems continuously monitor temperature, pressure, and flame stability, deactivating the unit when abnormal conditions arise. This prevents overheating and potential malfunctions, keeping the environment secure.
Pressure Regulation
Another vital safety component is the control of internal pressure. Integrated relief valves
Typical Issues and Solutions

Heating systems, especially those with intricate components, can experience a variety of challenges over time. Understanding these common problems and their resolutions is essential for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of the unit. By identifying recurring patterns in malfunctions, users can better anticipate maintenance needs and avoid prolonged downtimes.
Inconsistent Heat Distribution: A frequent concern is uneven warmth throughout the space. This can often be traced back to blocked air passages or inefficient flow, requiring the cleaning or replacement of specific elements to restore balance.
Frequent Cycling: Another issue arises when the system switches on and off too frequently. This
Parts Diagram Interpretation Guide
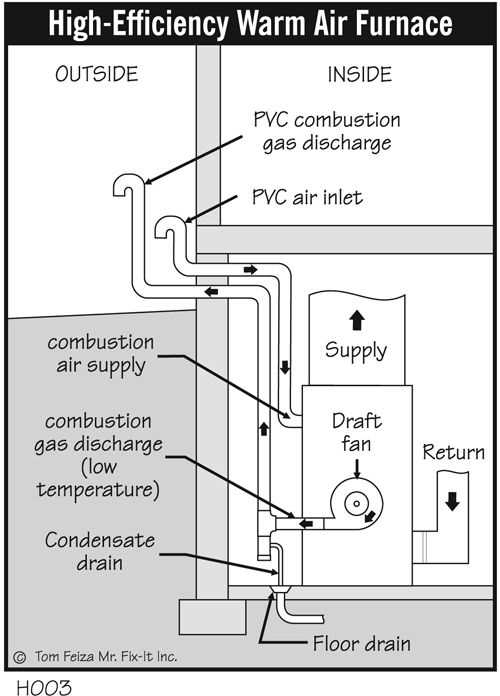
Understanding the intricacies of a heating appliance’s structure is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This guide aims to provide insights into interpreting the schematic representations that illustrate the various components and their interconnections. By familiarizing yourself with these visual aids, you can enhance your ability to diagnose issues and perform repairs with confidence.
Key Components Explained

Each element depicted in the schematic serves a distinct purpose and contributes to the overall functionality of the system. Familiarity with these components will enable you to quickly identify potential problem areas during inspections.
Component Description Heat Exchanger Transfers heat from the combustion process to the water. Burner Assembly Responsible for igniting the fuel and generating heat. Control Module Regulates the operation and ensures safe functioning of the appliance. Circulator Pump Facilitates the movement of heated water throughout the system. Interpreting the Visual Representation
When examining the schematic, pay attention to the symbols and lines that represent each component’s relationship. Lines typically indicate connections, while various shapes signify different types of elements, such as valves, sensors, and switches. A clear understanding of these symbols is vital for accurate analysis a
Finding OEM Replacement Parts
Locating original equipment manufacturer (OEM) replacements can significantly enhance the efficiency and longevity of your heating system. Ensuring compatibility with your unit is crucial, as using non-genuine components may lead to performance issues and void warranties.
Researching Trusted Sources is the first step in securing authentic components. Reputable suppliers often provide detailed catalogs that include part numbers, specifications, and compatibility details. Check online platforms and local dealers known for their reliability.
Consulting Technical Manuals can be invaluable in identifying the exact specifications needed for replacements. These resources often contain diagrams and lists that make it easier to locate the required items.
Online Communities and forums can also serve as helpful resources. Engaging with other users may lead to recommendations for reliable suppliers and shared experiences regarding specific components.
Lastly, consider contacting Customer Support for the manufacturer. They can provide guidance on obtaining the right components and might even assist in placing orders for authentic replacements.
Installation Best Practices
Effective installation is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of heating systems. By adhering to industry standards and employing proper techniques, one can significantly reduce the likelihood of future issues. This section outlines key recommendations to facilitate a successful setup.
Prior to commencing the installation, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications. Conduct a thorough assessment of the installation site, ensuring that all necessary tools and materials are readily available. Adequate preparation will streamline the process and minimize potential delays.
When positioning the unit, ensure it is placed on a stable surface, allowing for adequate ventilation and access for maintenance. Avoid obstructions that could impede airflow or cause overheating. Additionally, ensure that all connections are securely fastened to prevent leaks and ensure efficient operation.
Following the initial setup, perform a comprehensive inspection of all components. Check for any signs of wear or damage and address them promptly. After installation, test the system thoroughly to confirm that it operates as intended, making adjustments as needed to optimize performance.
Lastly, it is advisable to provide users with clear instructions on operating the system and maintaining it properly. Educating users on best practices can enhance the overall experience and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.