
Understanding the core elements involved in crafting tools allows users to enhance their skills and perform tasks with greater precision. Each section of such equipment plays a unique role, contributing to seamless operation and ensuring efficiency during use.
These devices are composed of multiple interconnected segments, each carefully designed for specific functions. From mechanisms responsible for movement to features that support material handling, every element has an essential purpose.
Knowing how individual components collaborate helps operators troubleshoot potential issues and maintain the tool effectively over time. By familiarizing oneself with these structures, users can unlock the full potential of their creative process.
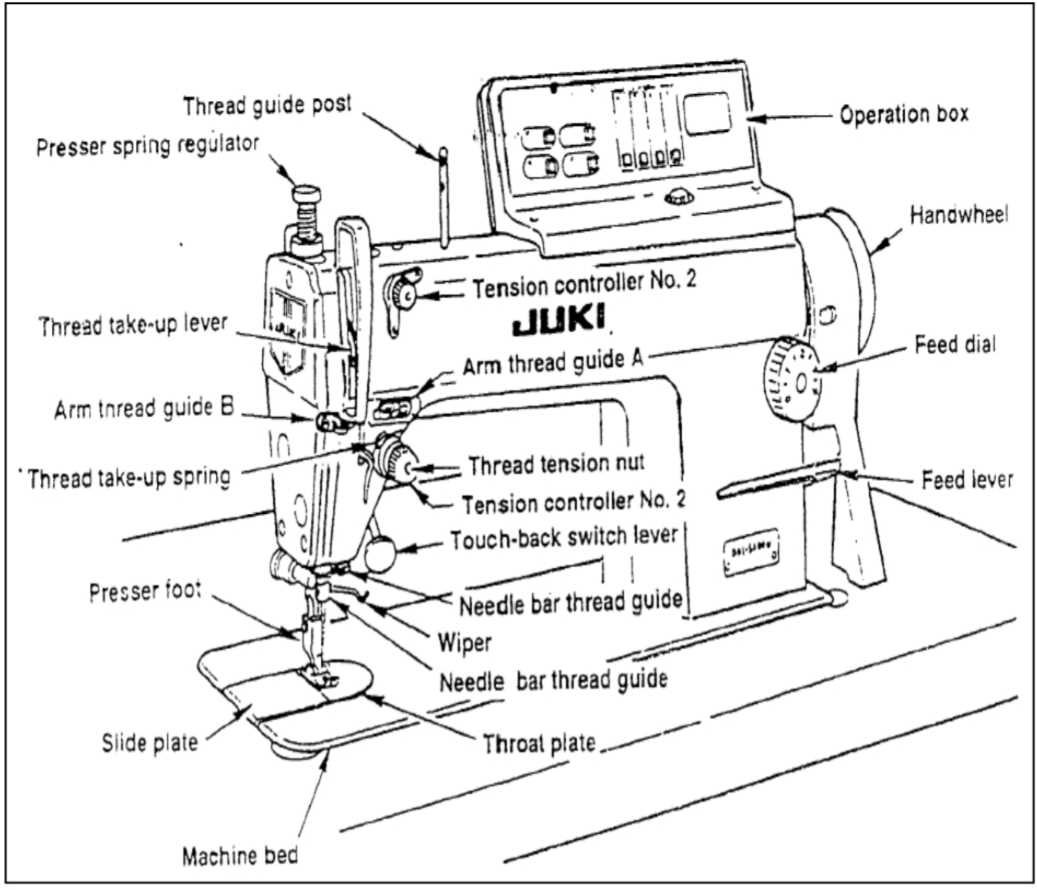
Diagram of a Sewing Machine and Its Parts
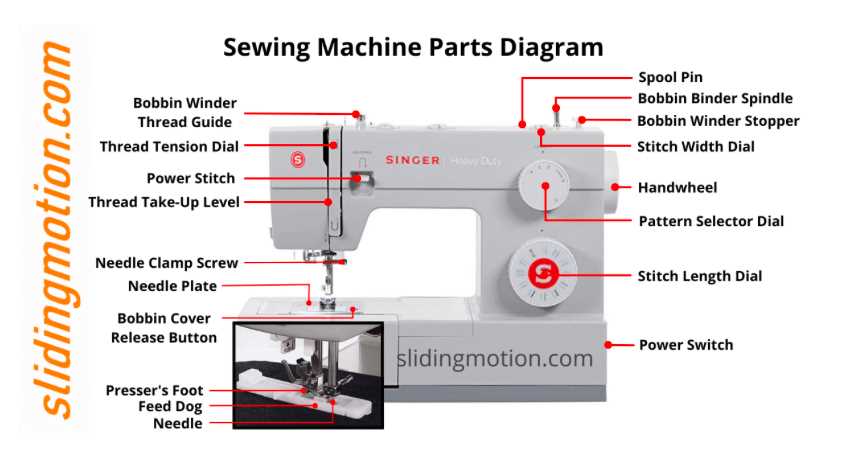
A technical overview of a fabric-stitching device reveals how individual components interact to create precise patterns on various materials. Understanding the structure helps users maintain the equipment and optimize their work process, ensuring smooth operation over time.
The upper section houses elements responsible for guiding thread and controlling tension, ensuring consistent stitches. Meanwhile, the lower part contains mechanisms that manage fabric movement and secure thread loops. Each segment plays a vital role in transforming raw materials into finished textiles efficiently and accurately.
Clear knowledge of these elements allows for troubleshooting common issues, enhancing performance, and extending the lifespan of the tool. Mastering the interaction between these sections enables seamless workflow and reduces potential disruptions.
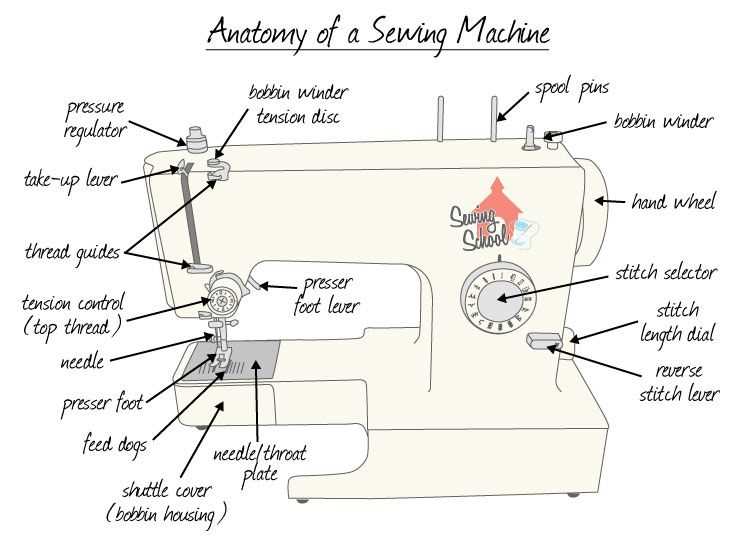
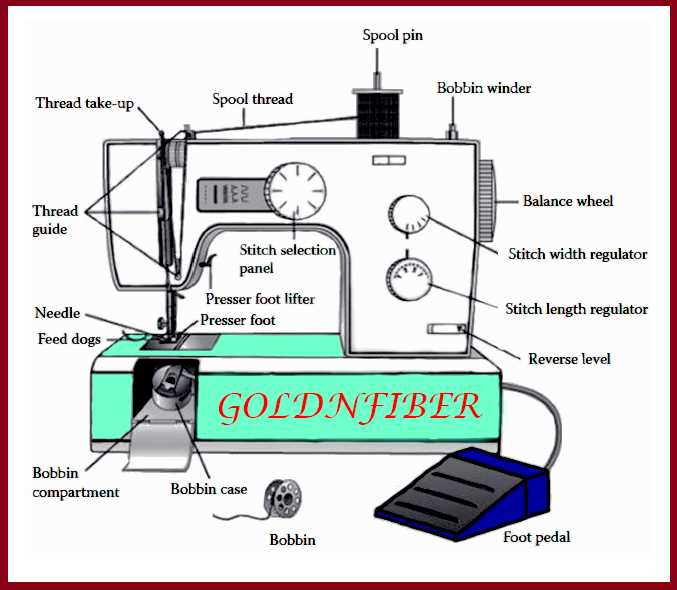
Overview of Sewing Machine Components

The functionality of textile crafting devices relies on a collection of interconnected elements. Each component serves a specific role, contributing to the overall efficiency and precision of the operation. Understanding these elements can enhance one’s ability to utilize these tools effectively and maintain them properly.
Key Elements
Central to the operation is the needle, responsible for creating stitches by penetrating the fabric. The bobbin plays a vital role as well, storing thread that interlocks with the upper thread, forming the stitch. Other significant components include the feed dogs, which move the material through the mechanism, and the presser foot, which holds the fabric in place during stitching.
Additional Features
Advanced models may include various attachments and settings that allow for different types of stitching techniques. These enhancements provide greater versatility, enabling users to execute a wide range of creative tasks. Understanding these additional features can greatly improve the crafting experience and outcomes.
Key Functions of Internal Mechanisms
The internal components of textile apparatus play a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and high-quality output. Each mechanism is designed to perform specific tasks that collectively contribute to the overall functionality of the device. Understanding these functions provides insights into the intricate workings of this essential tool.
Essential Mechanisms and Their Roles
- Stitch Formation: This process is vital for creating strong and durable seams. It involves the interaction of various elements that work together to produce consistent stitches.
- Tension Regulation: Proper tension is necessary for optimal performance. This mechanism adjusts the tightness of the thread to prevent issues such as puckering or thread breakage.
- Feed System: The feeding mechanism advances the fabric through the device, ensuring smooth movement and precise stitching at consistent intervals.
Additional Functions
- Needle Movement: The needle’s vertical and horizontal movements are essential for accurate stitch placement and pattern execution.
- Bobbin Mechanism: This component stores the lower thread and interacts with the needle to form stitches effectively.
- Presser Foot Action: The presser foot maintains fabric contact with the feed dogs, enhancing stability during the stitching process.
Types of Needles and Their Use
Understanding the different varieties of needles is essential for achieving optimal results in textile projects. Each type serves a specific function, making it crucial to select the right one based on the fabric and the intended technique.
Common Types of Needles
- Universal Needles: Suitable for a variety of fabrics, these are versatile and ideal for general stitching tasks.
- Ballpoint Needles: Designed for knits and stretch fabrics, they have a rounded tip that prevents damage to the material.
- Sharps Needles: Perfect for lightweight or delicate fabrics, these needles have a slender shaft and a sharp point.
- Quilting Needles: Specifically made for quilting projects, they feature a tapered point that allows for easy penetration through multiple layers.
- Zipper Needles: These have a narrow, sharp point, making them suitable for sewing zippers and other close-fitting applications.
Choosing the Right Needle
When selecting a needle, consider the following factors:
- Fabric Type: Different materials require different needle types to prevent damage.
- Thread Thickness: The needle’s size should match the thread to ensure smooth stitching.
- Sewing Technique: Certain techniques may require specialized needles for optimal results.
By carefully selecting the appropriate needle, you can enhance the quality of your work and achieve the desired finish in your projects.
Role of the Bobbin in Stitching
The bobbin serves a vital function in the overall process of creating stitches, playing a crucial role in the interplay between upper and lower threads. This component ensures that the threads are securely locked together, allowing for consistent and reliable seams. Understanding its significance enhances one’s appreciation of the intricacies involved in fabric manipulation.
Positioned beneath the needle, the bobbin provides the lower thread that works in conjunction with the upper thread to form a cohesive stitch. The tension applied to this thread affects the quality of the final output, influencing not just durability but also the aesthetic appeal of the sewn item.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Thread Supply | Holds the lower thread required for stitching. |
| Tension Control | Affects the stitch’s tightness and overall quality. |
| Stitch Consistency | Ensures even distribution of threads during the sewing process. |
| Variety of Threads | Accommodates different types of threads for various applications. |
Threading the Machine: Step-by-Step Guide
Properly preparing your equipment is essential for achieving optimal results in your crafting endeavors. This segment provides a comprehensive walkthrough to assist you in the precise setup of the threading process, ensuring smooth operation and beautiful outcomes.
Gathering Necessary Tools
Before you begin, make sure you have all required supplies at hand. This includes your preferred type of filament, a pair of scissors, and any instructional manual that may come with your device. Having everything ready will facilitate a smoother setup experience.
Executing the Threading Procedure
Start by raising the needle to its highest position. Next, place the filament on the designated spool pin, ensuring it is secured properly. Follow the guide on the side of your apparatus to loop the thread through the tension mechanism and across any guides. Once the filament is in place, thread it through the needle’s eye, making sure it is correctly positioned for operation. After completing these steps, you can perform a test run to verify that everything is functioning seamlessly.
Adjusting Tension for Smooth Sewing
Proper adjustment of the pressure exerted on the thread is essential for achieving flawless results in any textile project. This process ensures that the fabric layers are held securely together, preventing puckering and ensuring even stitching. Understanding how to fine-tune this aspect can significantly enhance the quality of your creations.
Why Tension Matters
Maintaining the correct pressure on the thread offers several advantages:
- Prevents fabric distortion
- Ensures even stitch formation
- Reduces the likelihood of thread breakage
- Enhances the overall appearance of the final product
How to Adjust Tension
Follow these steps to achieve the right pressure:
- Identify the tension control mechanism on your device.
- Start with a neutral setting, usually indicated by a specific number.
- Test with a sample piece of fabric to assess the stitch quality.
- If the thread appears loose or too tight, adjust the tension gradually.
- Repeat the testing process until optimal results are achieved.
Regular checks and adjustments will ensure consistent performance and high-quality outcomes for all your textile endeavors.
Presser Foot: Variations and Applications

The presser foot is a crucial accessory in textile crafting, offering various functionalities that cater to different techniques and fabrics. Understanding the diverse types of presser feet can significantly enhance the quality and efficiency of projects. Each variation serves a specific purpose, making it essential for crafters to choose the right one for their needs.
Types of Presser Feet
There are numerous types of presser feet, each designed for unique tasks. Standard presser feet are versatile and suitable for basic stitching, while zigzag presser feet allow for decorative stitching and finishing edges. Walking feet are particularly beneficial for handling multiple layers or slippery materials, ensuring even feeding during the sewing process.
Applications in Textile Crafting
The selection of a presser foot can influence the final outcome of a project. For instance, a quilt guide foot is ideal for quilters seeking precise stitch lines, while a buttonhole foot simplifies the creation of professional-looking openings. Understanding the capabilities of each type empowers crafters to experiment and achieve remarkable results in their textile endeavors.
Importance of the Feed Dogs in Fabric Movement
The functionality of any textile manipulation system relies heavily on specific components that facilitate the transportation of materials. Among these essential elements, the feed dogs play a crucial role in ensuring that fabrics are advanced smoothly and consistently through the mechanism, allowing for accurate stitching and a polished finish.
Key Functions of Feed Dogs
- Movement Control: Feed dogs grip the fabric and propel it forward, maintaining a steady pace for uniform results.
- Stitch Length Regulation: By adjusting the height and movement of the feed dogs, users can influence the length of each stitch, impacting the overall appearance of the finished project.
- Fabric Handling: They accommodate various types of textiles, enabling seamless transitions between lightweight and heavy materials.
Benefits of Properly Functioning Feed Dogs
- Enhanced Precision: Reliable feed dogs contribute to precise stitching patterns, which are essential for quality craftsmanship.
- Reduced Fraying: Consistent fabric movement minimizes the risk of fraying edges, ensuring durability and longevity.
- Increased Efficiency: With effective advancement, users can work more swiftly, improving overall productivity during textile projects.
Controls and Settings for Stitch Patterns
This section delves into the various controls and configurations that influence the appearance and functionality of stitch designs. Understanding these elements is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes in fabric manipulation and textile artistry.
Adjusting Stitch Length and Width
The first aspect to consider is the adjustment of stitch length and width. These settings determine how closely or widely the stitches are placed, impacting both the durability and aesthetic of the finished product. A longer stitch length is typically used for basting or gathering, while shorter lengths are ideal for decorative effects.
Selecting Stitch Types
Another vital component involves selecting different stitch types available on the device. Various styles, such as straight, zigzag, or decorative options, can be chosen based on the project requirements. Each type serves a specific purpose, enhancing the overall quality and appeal of the fabric work.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Machine Parts
Regular upkeep of various components is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Proper care not only enhances functionality but also minimizes wear and tear, leading to fewer repairs and a more enjoyable experience. This section outlines essential practices for maintaining cleanliness and efficiency in the equipment.
Routine Cleaning Procedures
It is essential to establish a consistent cleaning schedule. Dust, lint, and debris can accumulate, potentially affecting operation. Use a soft brush or a lint roller to gently remove particles from surfaces. For a deeper cleanse, a damp cloth with mild soap can be employed, ensuring that no moisture seeps into sensitive areas. After cleaning, allow the components to dry thoroughly before reassembly.
Periodic Maintenance Tasks
In addition to routine cleaning, certain maintenance tasks should be performed at regular intervals. Lubrication of moving elements is vital for smooth operation; appropriate oils should be applied according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Furthermore, inspecting for signs of wear or damage can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs. Taking these proactive steps will enhance the overall performance and reliability of the equipment.
Troubleshooting Common Sewing Issues
When working with fabric creation tools, encountering problems is a frequent occurrence. Understanding how to identify and resolve these challenges is crucial for achieving optimal results. This section provides insights into common difficulties and effective solutions to enhance your crafting experience.
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Skipped Stitches | Incorrect needle type, dull needle, or improper threading | Replace needle with the correct type, ensure it’s sharp, and re-thread the tool |
| Fabric Jamming | Improper feed, tangled threads, or incorrect tension | Clean the area, check the feed dogs, and adjust the tension settings |
| Puckering | Poor fabric choice, incorrect stitch length, or high tension | Use appropriate fabric, adjust the stitch length, and lower the tension |
| Uneven Stitching | Worn feed dogs or incorrect presser foot pressure | Inspect and replace feed dogs if necessary, adjust presser foot pressure |