
The structure and function of various elements in this renowned cutting device play a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and maintenance. By examining the connections and configurations within this tool, users can achieve a better grasp of how each element contributes to overall performance. Knowing the layout and relationship between different mechanisms can aid in quicker troubleshooting and replacement when necessary.
From internal mechanisms that manage power output to external features designed for user control, each segment has a specific role in maintaining efficiency. Recognizing how these various sections interact is essential for those aiming to keep their equipment in optimal working condition. A detailed look into these arrangements can save time and effort when handling repairs or modifications.
For anyone seeking to extend the longevity of their equipment, understanding the arrangement of each functional element can make a significant difference. A close inspection of these designs reveals insights into the precise engineering that supports effective performance, making upkeep easier and more intuitive.
The Function and Layout of the Engine Components
The inner mechanism relies on a combination of precisely engineered elements, each playing a crucial role in delivering power and efficiency. Understanding the arrangement and purpose of these components helps in maintaining peak performance and resolving potential issues.
- Cylinder and Piston: This duo forms the core of the combustion process, where fuel is ignited to create the necessary energy. The cylinder guides the piston’s movement, while the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture, allowing for efficient combustion.
- Carburetor: It ensures the optimal mix of air and fuel before entering the combustion chamber. Proper calibration of this component is vital for smooth operation, affecting acceleration and fuel efficiency.
- Ignition System: Responsible for generating the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture. This system includes a spark plug, which must be in good condition to maintain reliable starts and consistent power output.
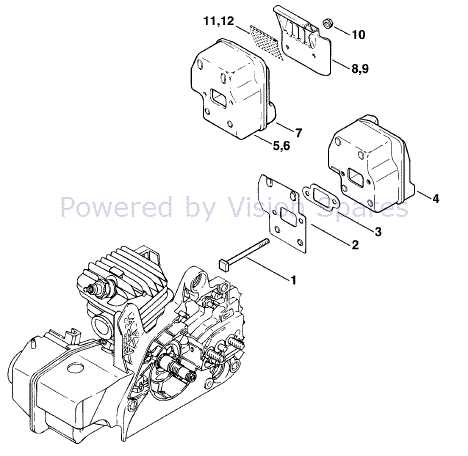
- Muffler: This part minimizes noise produced during exhaust release and helps direct gases away from the operator. It is designed to enhance performance by maintaining back pressure and controlling emissions.
- Air Filter: Keeps debris and dust from entering the engine, ensuring a clean air supply. A well-maintained filter prevents clogs and protects internal components from wear.
Each element is strategically placed to balance power, weight, and efficiency, ensuring the engine operates smoothly under various conditions. Proper upkeep and timely adjustments can significantly extend the lifespan of these integral parts.
Understanding the Chain Brake Mechanism
The chain brake mechanism is a crucial safety feature in power cutting tools, designed to prevent accidents during operation. It functions by quickly stopping the movement of the cutting element when engaged, providing an essential layer of protection for the user.
This mechanism typically operates through a lever that can be activated manually or automatically. When triggered, it effectively halts the rotation of the cutting chain, minimizing the risk of injury from unexpected kickback or loss of control. Understanding how this system works not only enhances safety but also ensures optimal performance and longevity of the tool.
Key Components:
- Brake Band: Wraps around the clutch drum, applying friction to stop the chain.
- Brake Handle: Allows the user to engage or disengage the brake swiftly.
- Spring Mechanism: Ensures that the brake returns to its original position after activation.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the brake system are vital for safe operation. Users should familiarize themselves with its functionality to enhance both efficiency and security while using power cutting devices.
Identifying Parts of the Handle Assembly
The handle assembly is a crucial component of any cutting tool, providing both functionality and comfort during operation. Understanding its various elements helps in maintenance and enhances user safety.
Key Components
Several integral parts make up the handle assembly, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Grip: The area where the operator holds the tool, designed for comfort and control.
- Trigger: Controls the activation of the tool, allowing for precise operation.
- Safety Switch: A critical feature that prevents accidental activation, ensuring safe use.
Assembly Features
Familiarity with the handle’s layout can improve efficiency in repairs and replacements:
- Locking Mechanism: Secures the handle in place, preventing unwanted movement.
- Support Brackets: Provide stability and support for the entire assembly, enhancing durability.
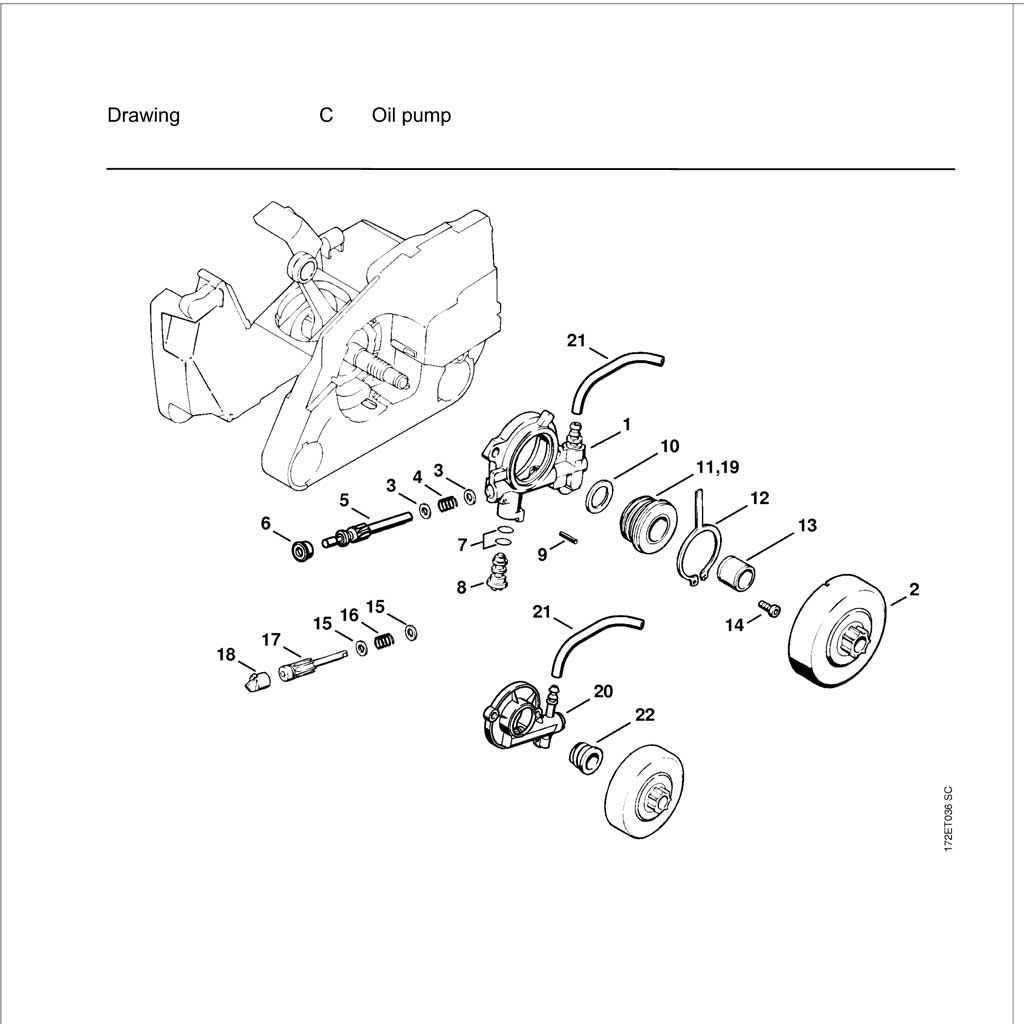
An Overview of the Oil Pump and Lubrication System
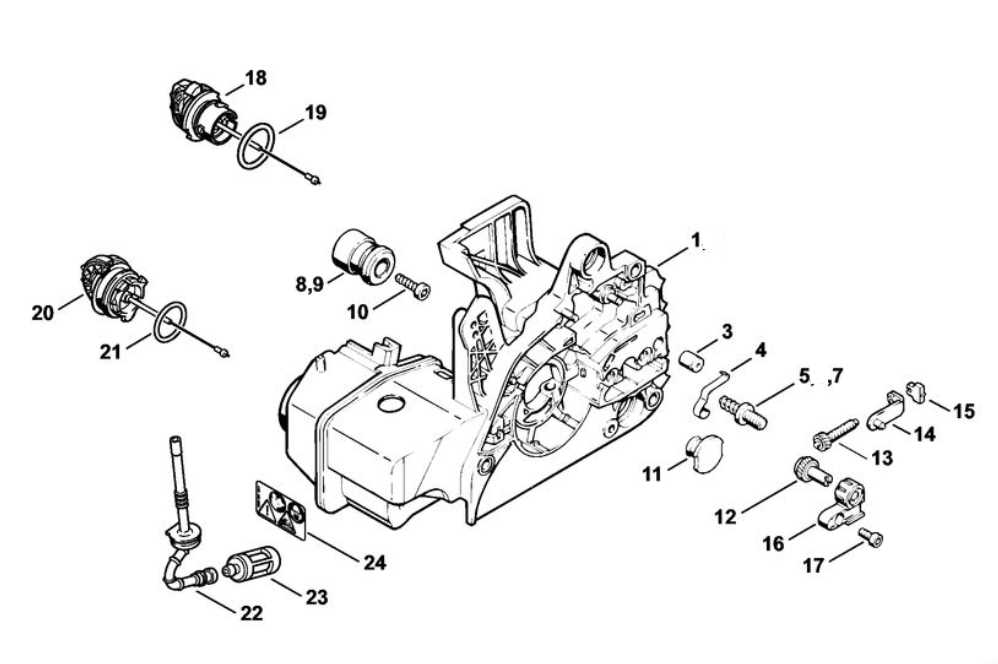
The lubrication mechanism is crucial for the efficient operation of mechanical devices that require continuous movement. This system ensures that vital components receive the necessary oil to reduce friction, prevent wear, and enhance overall performance.
Functionality of the Oil Pump
The oil pump plays a vital role in maintaining the proper flow of lubrication fluid throughout the system. Its key functions include:
- Delivering oil to critical areas to minimize wear.
- Maintaining consistent oil pressure for optimal performance.
- Regulating the amount of oil distributed based on operational demands.
Importance of Lubrication
Effective lubrication is essential for prolonging the life of moving parts and ensuring reliable operation. The benefits include:
- Reduction of heat generated by friction.
- Protection against rust and corrosion.
- Enhanced efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Examining the Clutch and Sprocket Components
This section focuses on understanding the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of a cutting tool. The clutch and sprocket play crucial roles in the transmission of power, ensuring efficient operation and performance during use.
Overview of the Clutch System
The clutch is a vital component that connects and disconnects the engine’s power to the cutting mechanism. Its primary function is to manage the engagement, allowing the user to control the tool effectively. Key features of the clutch system include:
- Engagement Mechanism: Enables smooth transition between idle and active states.
- Spring Tension: Maintains the balance between engagement and disengagement.
- Durability: Designed to withstand high torque and temperature fluctuations.
Sprocket Functionality and Importance
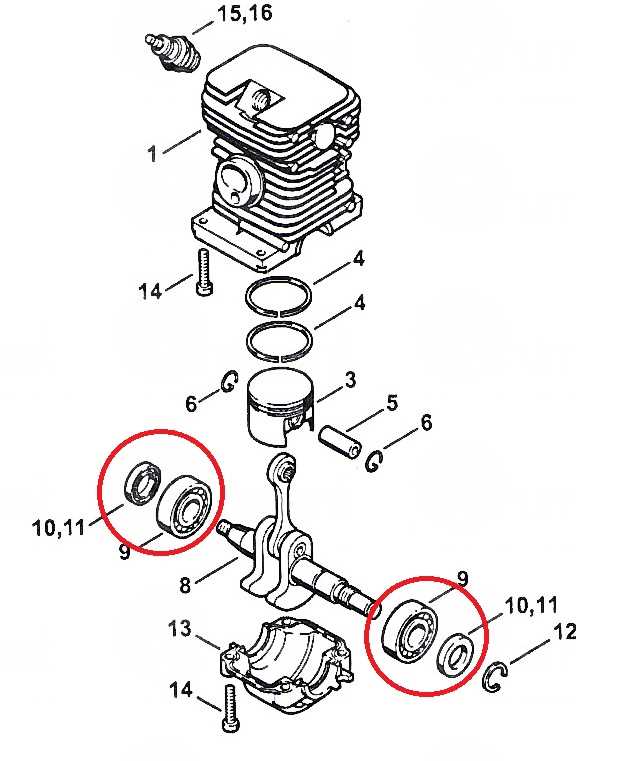
The sprocket is responsible for transferring motion from the clutch to the cutting element. Its design is critical for ensuring optimal chain movement and performance. Important aspects of the sprocket include:
- Teeth Design: Engineered for efficient grip and movement of the cutting chain.
- Material Quality: Constructed from robust materials to resist wear and tear.
- Alignment: Proper positioning is essential for smooth operation and reduced friction.
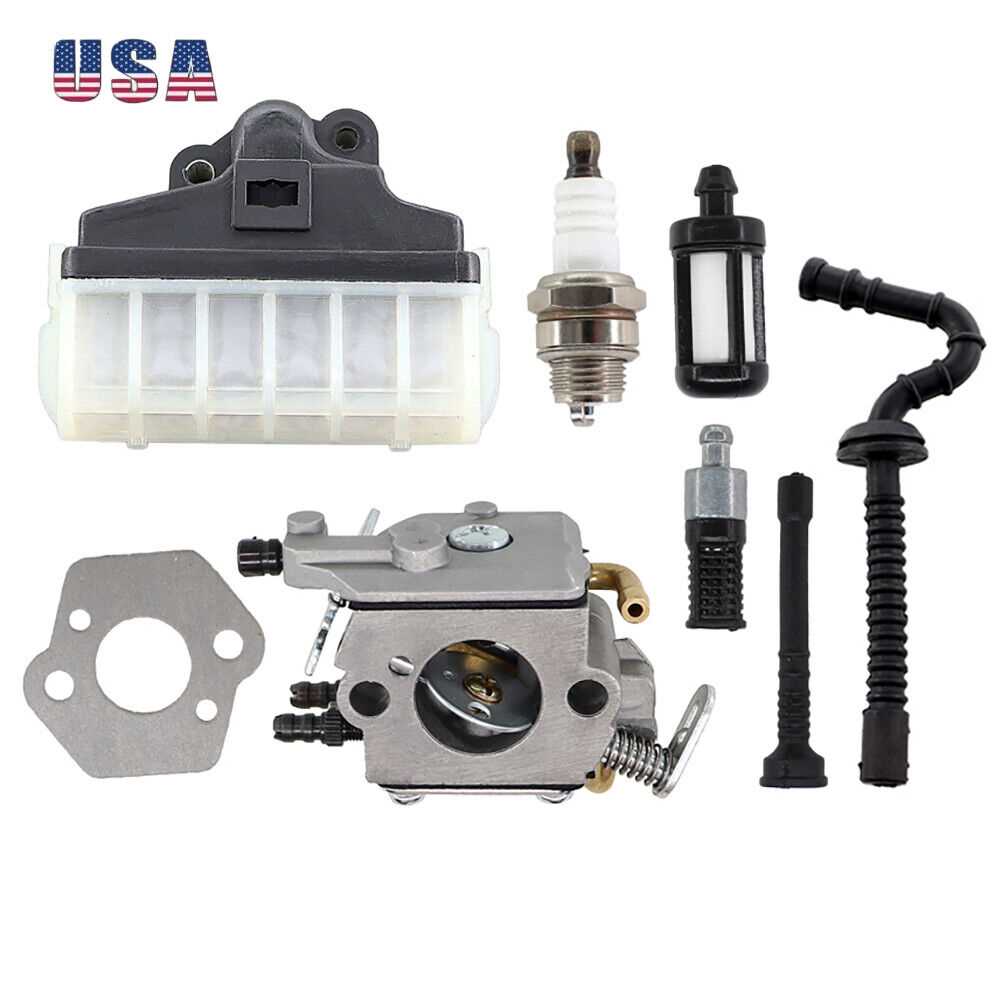
Detailing the Carburetor and Fuel System Parts
The efficiency of any cutting tool relies heavily on its fuel delivery mechanism. Understanding the components that regulate fuel flow and mixture is essential for optimal performance. This section will explore the critical elements involved in ensuring that the engine receives the right amount of fuel for smooth operation.
The carburetor plays a vital role in this system, as it mixes air and fuel in precise proportions. Its design features various elements such as jets and adjustment screws that allow for tuning the mixture to match specific operating conditions. Regular maintenance of the carburetor ensures it functions effectively, minimizing the risk of engine issues.
Additionally, the fuel lines are crucial for transporting fuel from the tank to the carburetor. Any leaks or blockages in these lines can lead to performance issues, making it important to inspect them frequently. Proper sealing and secure connections are necessary to maintain fuel integrity.
Analyzing the Ignition System and Spark Plug
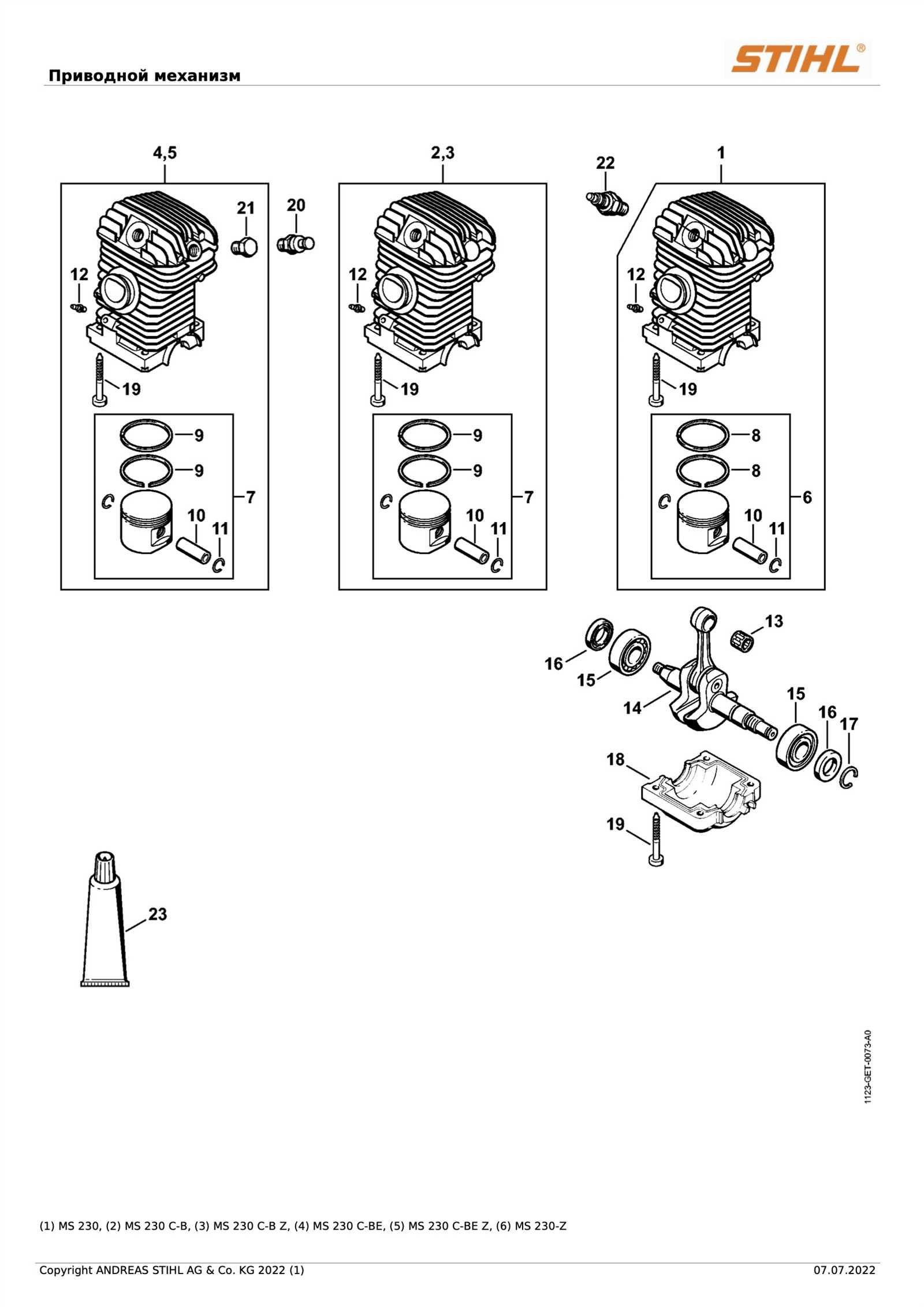
The ignition mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance of outdoor power equipment. This section delves into the components involved in ignition, particularly focusing on the spark plug and its significance in engine functionality.
Understanding the Ignition Mechanism
The ignition system is responsible for generating a spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture within the combustion chamber. Key elements of this system include:
- Coil: Converts low voltage to high voltage for ignition
- Flywheel: Generates magnetic field to trigger the spark
- Wiring: Connects components and transmits electrical signals
The Role of the Spark Plug
The spark plug serves as the bridge between the ignition system and the engine’s combustion chamber. Its functions include:
- Creating a reliable spark to initiate combustion
- Regulating engine temperature by dissipating heat
- Ensuring efficient fuel consumption and performance
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to prevent performance issues and ensure longevity.
Inspecting the Chain Tensioner and Adjuster Mechanism
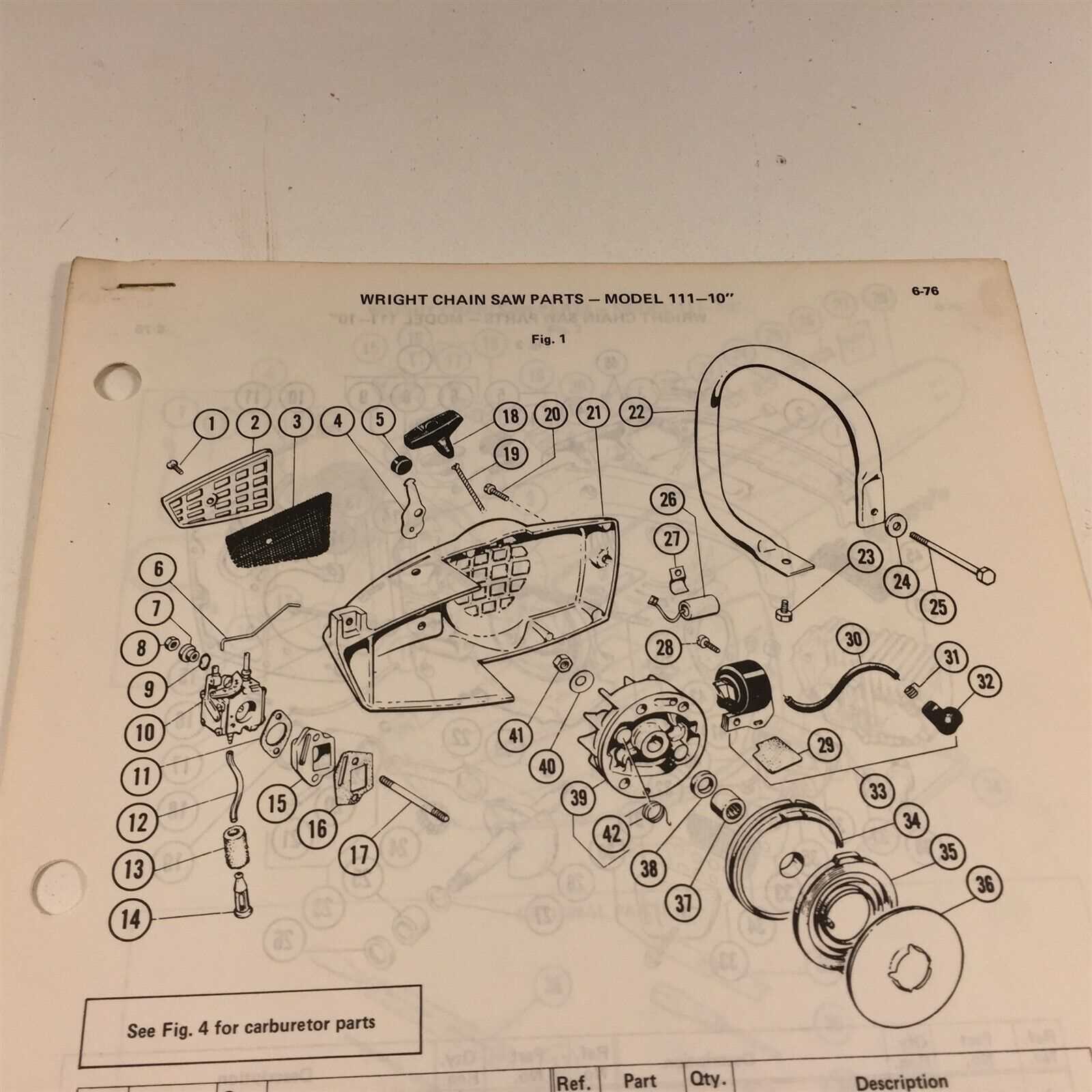
The chain tensioning system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety of the cutting tool. Regular inspection of this mechanism is essential for maintaining the tool’s efficiency and prolonging its lifespan. By examining the tensioner and adjuster, users can identify any wear or malfunction that could affect operation.
First, ensure that the device is turned off and disconnected from any power source before beginning the inspection. This precaution guarantees safety during maintenance. Next, locate the tensioner assembly and observe its condition for any signs of damage, such as cracks or excessive wear. It is important to verify that the adjuster moves smoothly and does not exhibit any resistance.
After visual inspection, check the tension of the chain itself. An adequately tensioned chain should not sag excessively or be overly tight. If adjustments are needed, utilize the adjuster mechanism to achieve the appropriate tension. Regular monitoring of this component can prevent future complications and enhance overall performance.
Explaining the Air Filter and Intake System

The air filtration and intake mechanism plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of any motorized tool. This system is responsible for ensuring that clean air enters the engine, allowing for optimal combustion and performance. Proper maintenance of these components is essential to prolong the life of the equipment and enhance its functionality.
Functionality of the Air Filter
The air filter’s primary purpose is to trap dust, debris, and other contaminants from the incoming air. By doing so, it prevents these particles from entering the engine, which can lead to wear and damage over time. Regular inspection and replacement of the air filter are vital to maintain airflow and ensure the engine operates smoothly.
Intake System Dynamics
The intake system channels air from the environment into the engine. It consists of various components that work together to regulate airflow and optimize performance. Understanding how this system functions helps in diagnosing issues related to airflow restrictions, which can significantly impact the efficiency and power of the tool.
Overview of Safety Features and Accessories
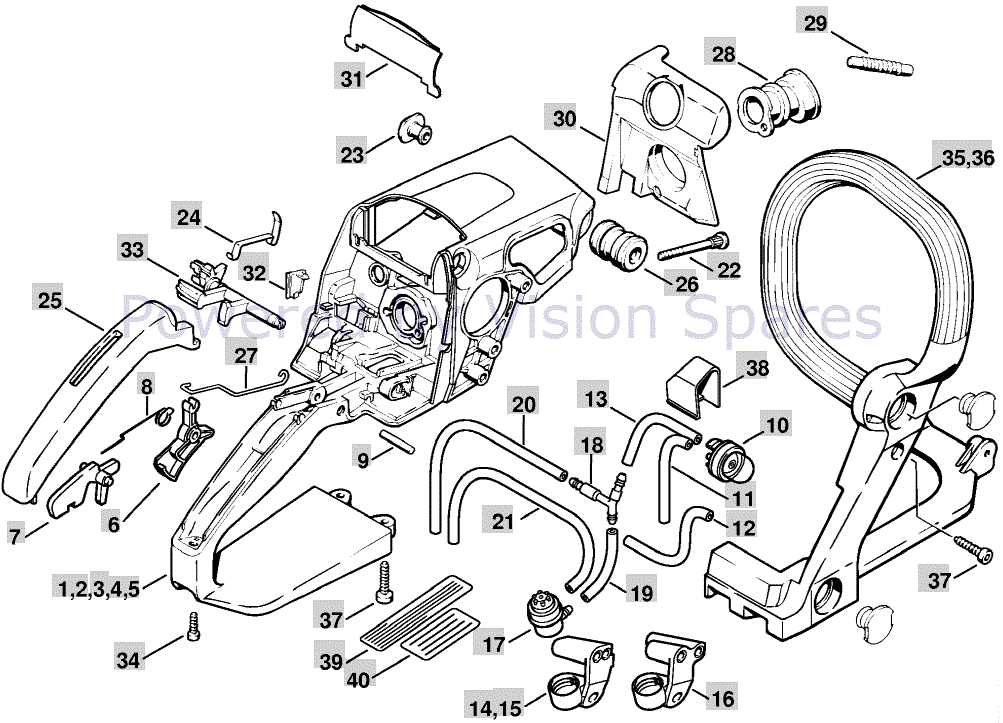
This section explores the essential safety attributes and supplementary components designed to enhance user protection while operating equipment. Understanding these features is crucial for ensuring a safe and efficient experience.
Key Safety Features
- Chain Brake: Instantly stops the cutting chain to prevent injury during kickback incidents.
- Throttle Lock: Prevents accidental activation, ensuring control during operation.
- Hand Guard: Shields the user’s hands from debris and accidental contact with the cutting area.
Recommended Accessories
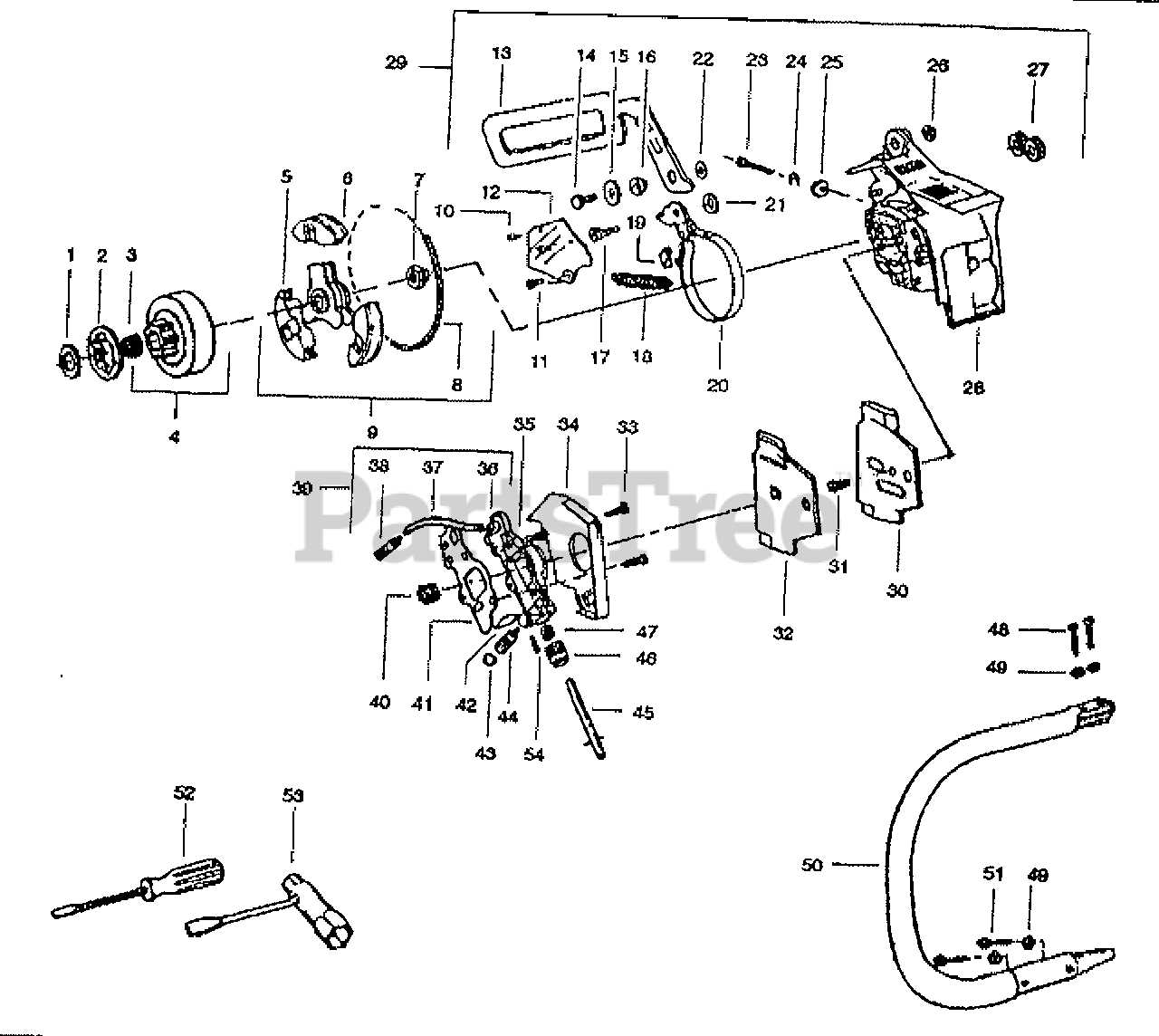
- Protective Gear: Includes helmets, gloves, and goggles for comprehensive safety.
- Maintenance Tools: Essential for regular upkeep, helping to keep the equipment in optimal condition.
- Carrying Cases: Provides safe storage and transport, reducing the risk of accidents.