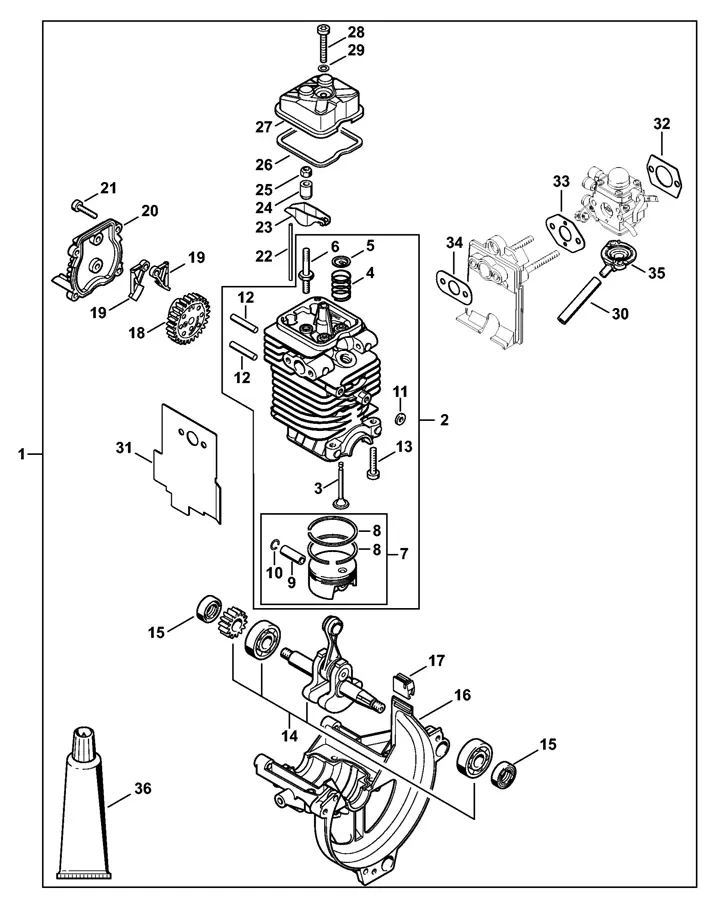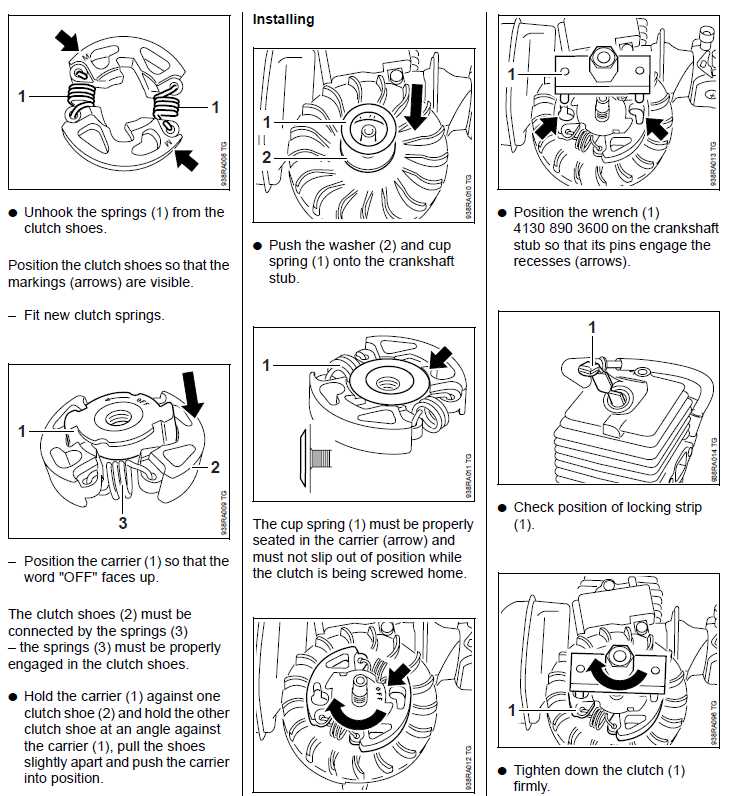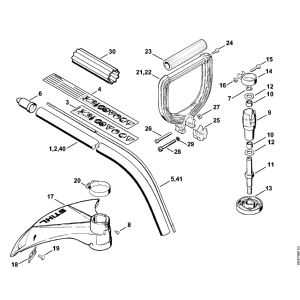
Delving into the inner workings of the FS 40 unveils a complex interplay of components and mechanisms designed to deliver reliable performance. Understanding the intricacies beneath the surface involves deciphering the assembly of essential parts that contribute to its functionality.
This examination goes beyond mere structure; it involves uncovering the integration of elements that drive the tool’s operational capabilities. Each segment plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and durability, reflecting meticulous engineering principles.
Peering into this intricate framework reveals the synergy between different parts, highlighting their collective contribution to the tool’s overall reliability and longevity.
Understanding Key Components of Stihl FS 40
In this section, we delve into the fundamental elements that make up the functionality of the Stihl FS 40, focusing on its essential components and their roles within the system. Exploring the integral parts that contribute to its operation, we uncover the intricacies of how each element interacts to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Engine Assembly Breakdown and Functions
The internal structure of the engine comprises several interconnected components that work in harmony to deliver power efficiently. Each element has its own role, contributing to the overall operation and ensuring smooth functionality. Understanding the layout and purpose of these components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing issues during use.
Main Mechanical Components
At the heart of the system, the cylinder and piston form the core, converting fuel energy into mechanical motion. The crankshaft transfers this motion, driving other elements responsible for operation. Together, these parts ensure consistent energy output for extended operation. Regular inspection of these key elements helps in maintaining their efficiency over time.
Supporting Elements
The system also includes supporting components like gaskets, seals, and valves, which ensure that pressure is maintained, and no leaks affect performance. These parts play a vital role in balancing pressure and enabling the engine to function seamlessly. Ensuring that these smaller components are intact prevents unnecessary wear and tear on the larger elements.
Fuel System Overview and Maintenance Tips
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and long-term reliability. It involves several components working together to deliver the necessary mixture for optimal engine performance. Keeping this system in good condition is essential for smooth functionality and minimizing potential issues.
Regular inspection of the fuel lines, filters, and connections can help prevent blockages or leaks, which could lead to reduced efficiency. Checking for cracks or wear in the tubing is important, as even small damage can disrupt fuel flow.
Maintaining a clean fuel filter ensures that contaminants don’t enter the engine, preserving its life and performance. Replacing the filter periodically according to manufacturer recommendations can prevent dirt buildup. Additionally, keeping the fuel tank free of sediment will contribute to a more stable fuel flow.
It’s essential to use the correct fuel mixture, as improper blending can cause issues such as engine stalling or poor combustion. Ensuring proper fuel storage, away from extreme temperatures, helps maintain its quality over time.
Fuel Line and Carburetor Parts Explained
The operation of small engines relies heavily on the correct flow and mixing of fuel and air. Key components ensure that fuel is efficiently delivered and that the right balance is achieved to maintain performance and reliability. In this section, we explore the vital elements responsible for managing this process, with a focus on the connectors and mechanisms involved in ensuring smooth engine operation.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Line | Transfers liquid from the reservoir to the central mixing area, ensuring a consistent supply during operation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carburetor | Mixes liquid and air in precise proportions, regulating the engine’s power output and fuel efficiency. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primer Bulb | Facilitates starting by manually pumping fuel into the lines, bypassing potential air blockages in the system. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gaskets and Seals | Prevent leaks by ensuring a tight connection
Ignition System Parts and Their Roles
The ignition mechanism in a power tool is a critical component that ensures smooth operation by creating the necessary spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture. Understanding the various elements involved in this process allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring the machine remains reliable over time. Spark plug: This small yet essential element is responsible for creating the initial spark needed for combustion. It transforms the electrical signal into a high-voltage arc that ignites the mixture in the combustion chamber. Ignition coil: Acting as a transformer, the ignition coil boosts the low voltage from the tool’s electrical system into the high voltage required by the spark plug. Without this component, the spark wouldn’t be strong enough to start the engine. Flywheel: The flywheel generates the magnetic field necessary to induce current in the ignition coil. Its proper functioning is essential to keep the spark consistent and timed correctly for the engine to run smoothly. Maintaining these components and ensuring they function correctly is key to the overall performance of the machine’s ignition system. Spark Plug and Ignition Module InsightsThe ignition system in small outdoor equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable operation. Understanding the relationship between key components like the spark generator and the electronic ignition unit is vital for maintaining peak performance. These elements work together to create the initial burst of energy required to start and run an engine efficiently. Below is a summary of the core functions of the ignition components:
|