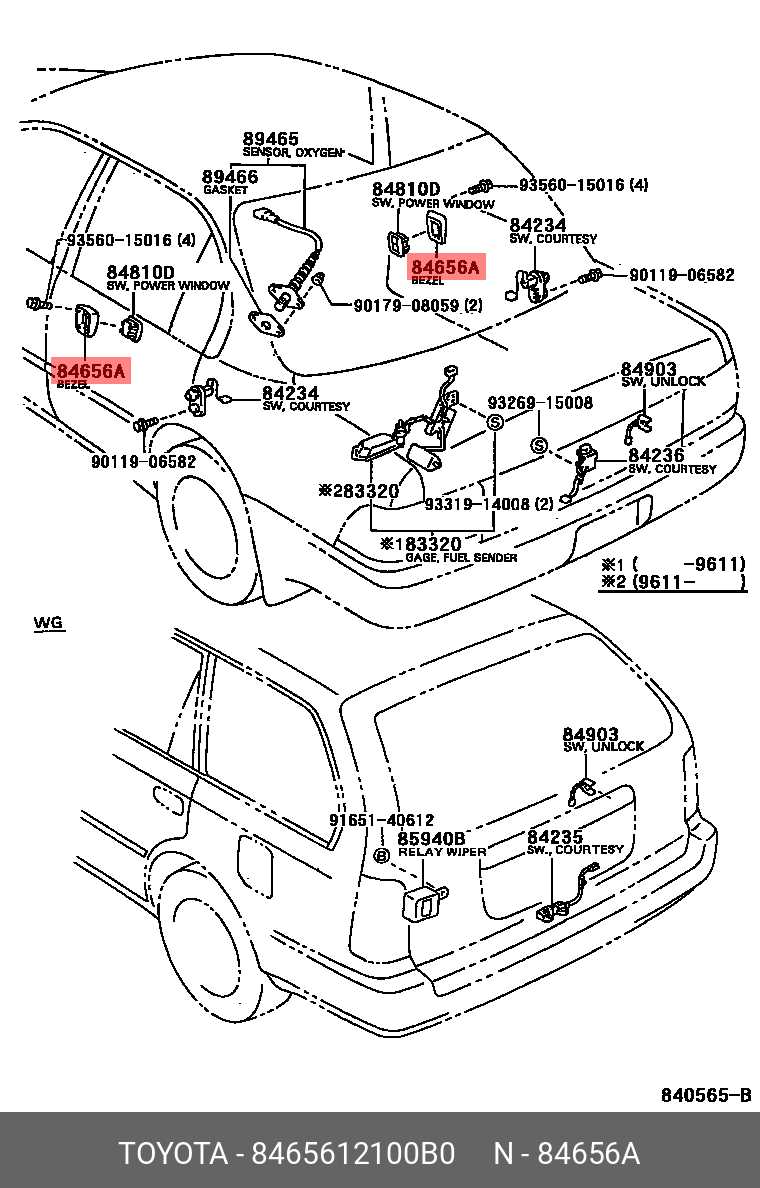
The transparent sections of the vehicle play a crucial role in ensuring visibility and comfort for both the driver and passengers. These components, made from various glass materials, are designed to protect against external elements while maintaining a clear view of the surroundings. Additionally, the window mechanisms are built to provide smooth operation, allowing for easy adjustment and control as needed.
By incorporating various glass technologies, these elements enhance not only the vehicle
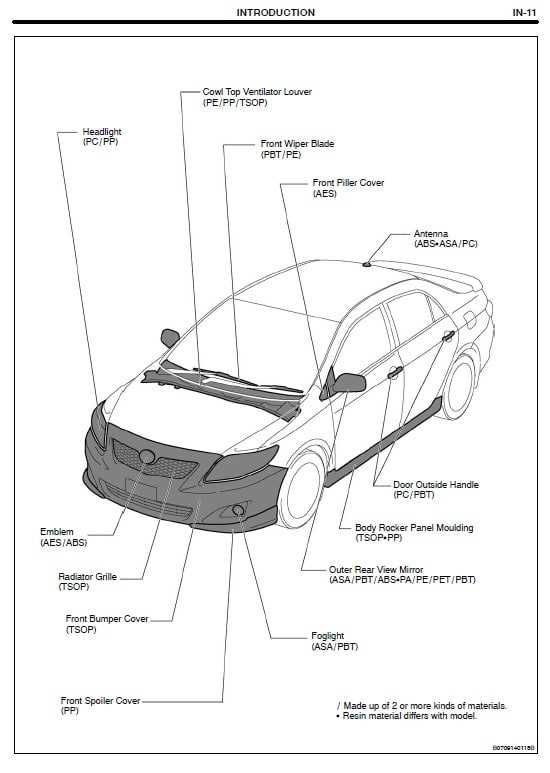
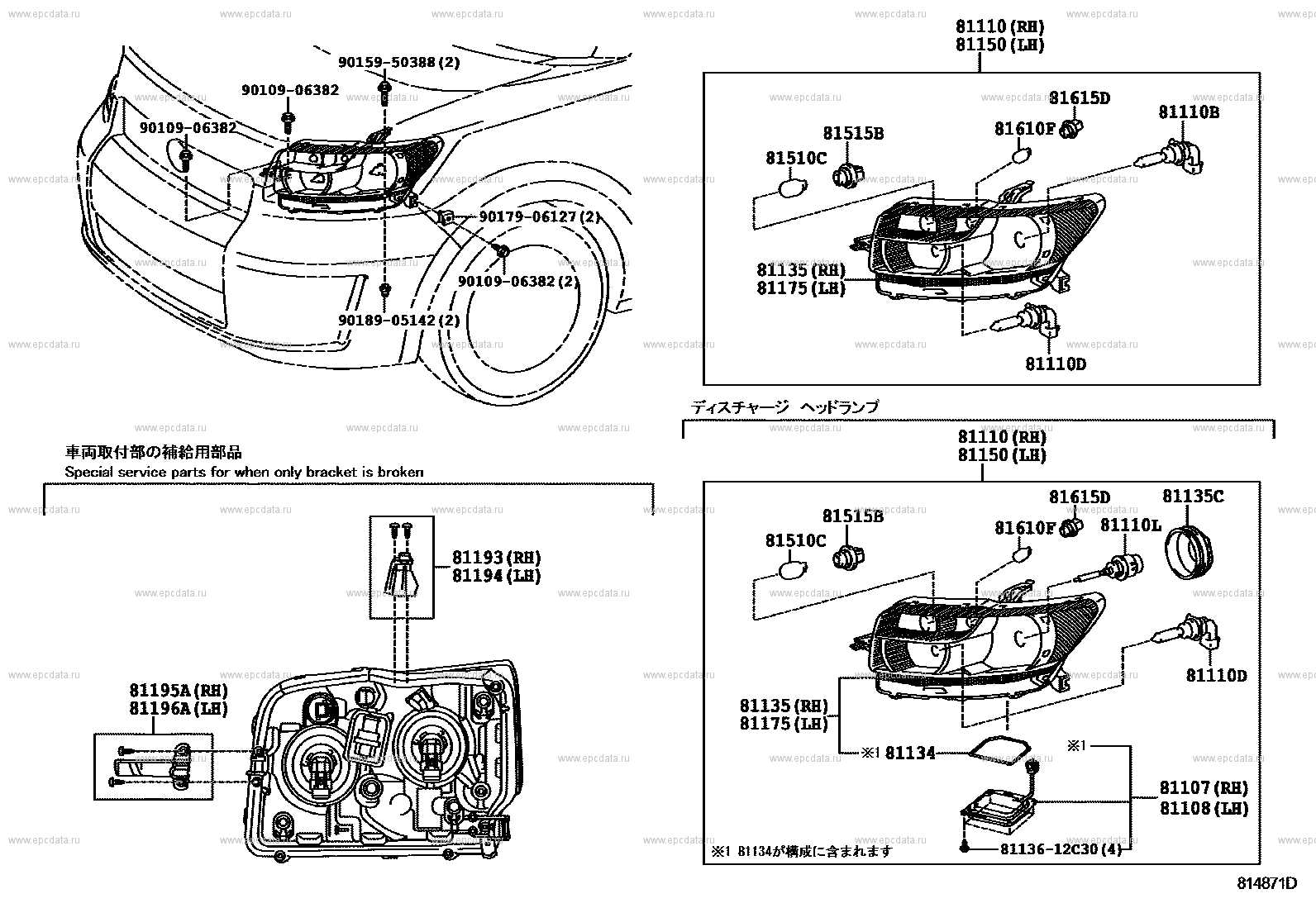
The illumination mechanisms in vehicles play a crucial role in ensuring visibility and safety during operation. These systems encompass various light sources, each serving distinct functions, ranging from headlights to signal indicators. Proper arrangement and functionality of these components are essential for optimal performance, contributing to both aesthetics and practicality.
Front-facing lights are vital for nighttime travel and adverse weather conditions. Positioned at strategic angles, they enhance the driver’s visibility while also signaling the vehicle’s presence to other road users.
Located at the rear, these lights are essential for communication with other drivers. Tail lights ensure visibility from behind, while turn indicators signal intended maneuvers, promoting road safety.
| Light Type |
Location |
Function |
| Headlights |
Front |
Illuminates the road ahead |
| Fog Lights |
Front |
Improves visibility in foggy conditions |
| Tail Lights |
Rear |
Indicates the presence of the vehicle |
| Turn Signals |
Front and Rear |
Indicates turning intentions |
| Brake Lights |
Rear |
Signals slowing down or stopping |
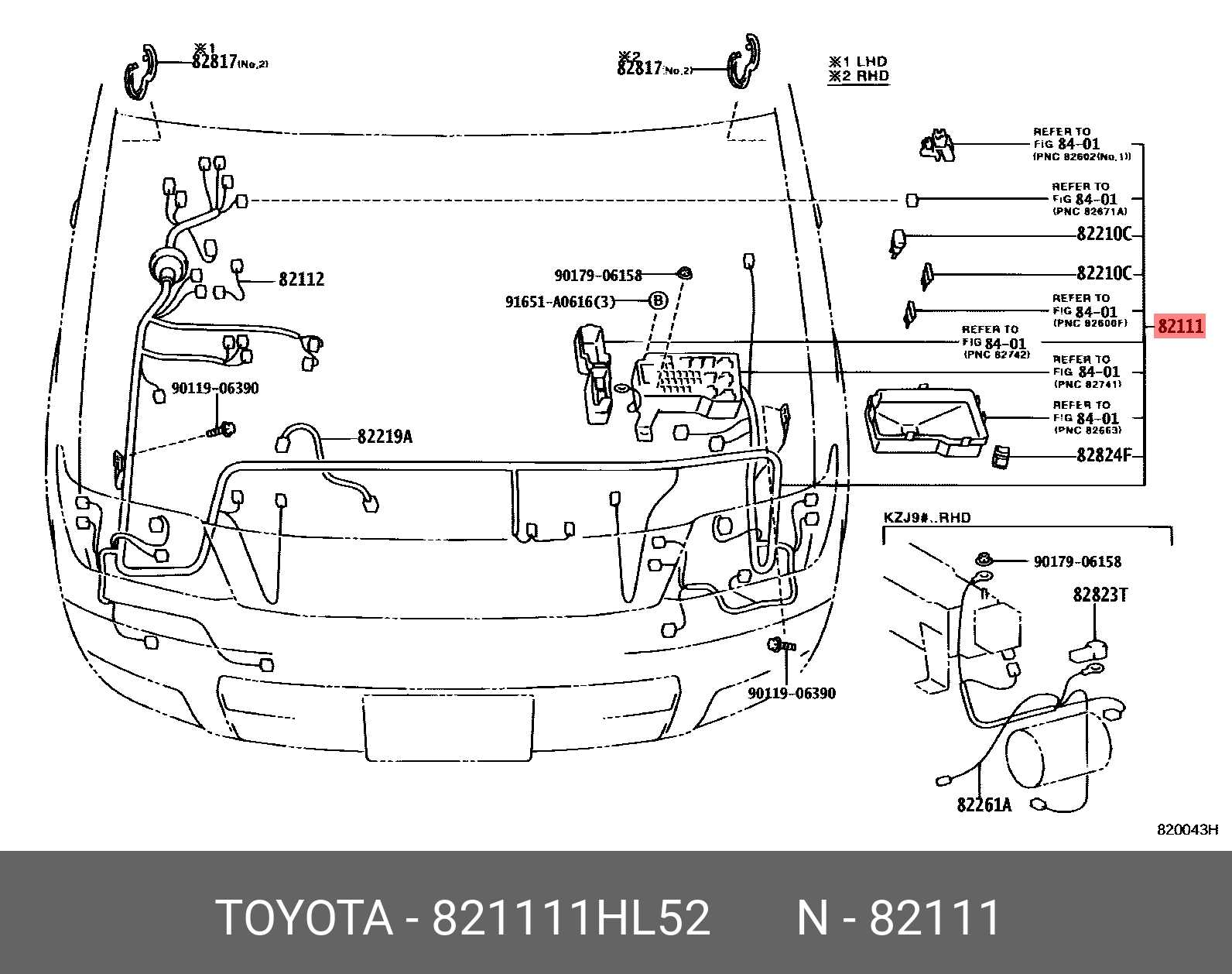
Hood and Engine Cover Assembly
The assembly that shields the engine compartment plays a crucial role in both functionality and aesthetics. This structure not only provides access to vital components but also enhances the vehicle’s overall appearance. Understanding its features and arrangement is essential for maintenance and repair tasks.
Components of the Assembly
- Hood: The primary exterior element that covers the engine.
- Insulation Material: Used to reduce noise and heat transfer.
- Struts: Mechanisms that support the hood when opened.
- Latches and Catches: Devices that secure the hood in a closed position.
- Seals: Rubber components that prevent water and debris from entering the engine bay.
Functionality and Maintenance
- Regularly inspect the hood for signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure latches are functioning correctly to maintain security.
- Check insulation for deterioration, as it affects soundproofing and heat retention.
- Examine seals to prevent leaks that could harm engine components.
- Lubricate struts periodically for smooth operation.
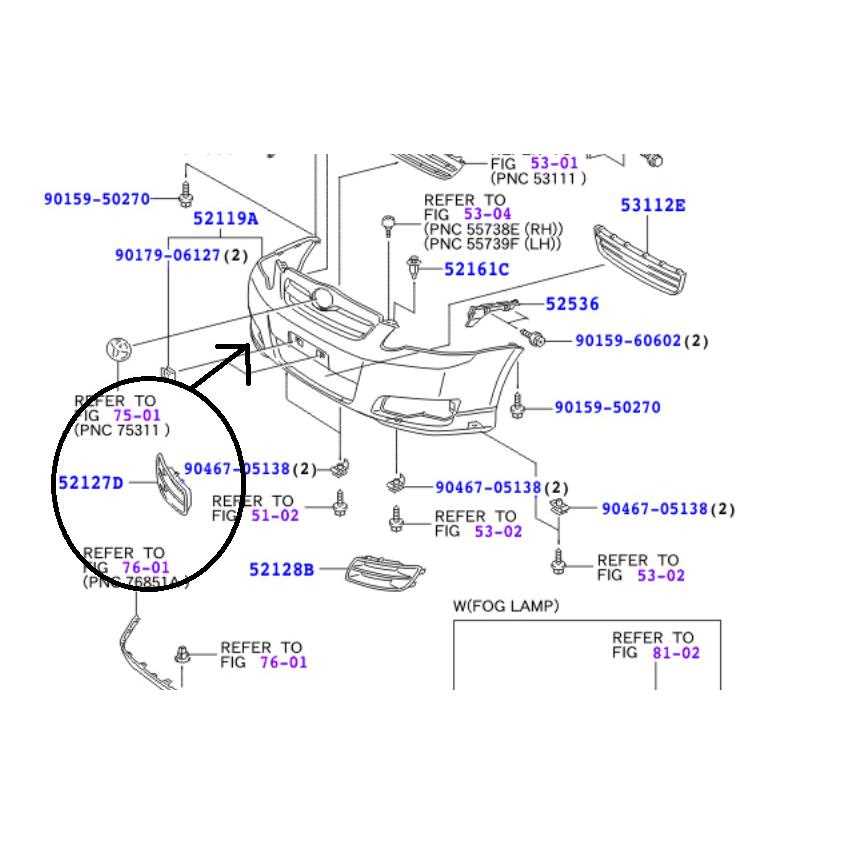
Bumper and Grille Components
The front assembly of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This section delves into the various elements that contribute to the structure and appearance of the frontal area, particularly focusing on the protective covering and the supporting mesh, which are vital for both safety and airflow management.
Bumper Structure
The protective covering serves as the first line of defense against minor collisions and impacts. It is designed to absorb energy and minimize damage to the underlying framework. Typically made from durable materials, its design can vary significantly, accommodating different styles and preferences.
Grille Functionality
The mesh component not only enhances the visual appeal of the frontal area but also allows air to flow into the engine compartment. This airflow is essential for cooling and engine performance. Additionally, the grille often incorporates features such as logos or decorative trims that reflect the identity of the vehicle.
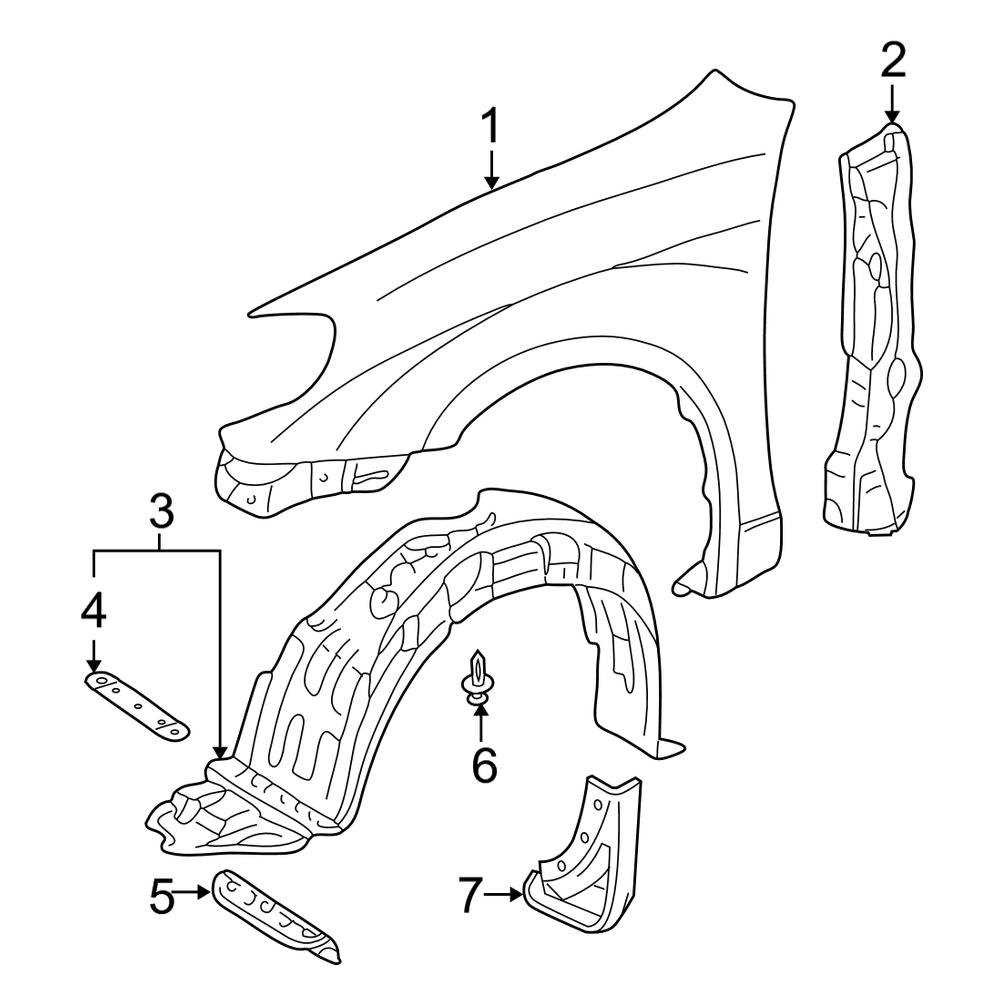
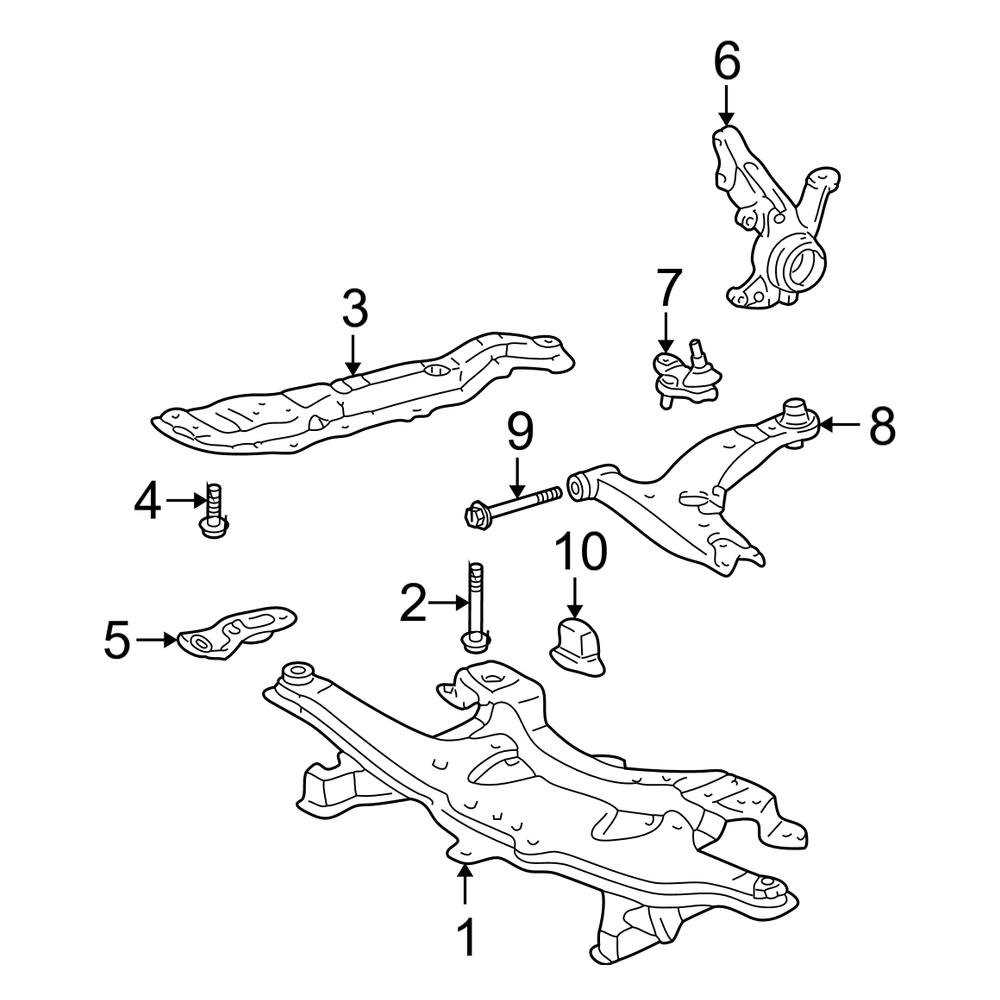
Wheel Arch and Fender Details
The wheel arch and fender assembly play a crucial role in the overall aesthetics and functionality of a vehicle. These components not only contribute to the design but also provide protection to the wheels and the underlying structure. Proper alignment and fitment are essential to ensure that the wheels can operate effectively while safeguarding against debris and road hazards.
Design Considerations
When examining the design of the wheel arch and fender, it is important to note the contours and curvature that enhance the vehicle’s appearance. These elements are often engineered to minimize aerodynamic drag while maximizing visual appeal. Additionally, materials used in their construction must be durable enough to withstand the elements and physical impacts.
Maintenance and Replacement
Routine inspections of the wheel arch and fender area can prevent larger issues from developing over time. Signs of wear, such as rust or dents, may indicate the need for repair or replacement. Timely intervention is crucial to maintaining the vehicle’s integrity and ensuring optimal performance on the road.
Roof and Sunroof Construction
The upper section of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. It serves as a protective barrier against environmental elements while contributing to the overall structural integrity. Within this area, features such as sunroofs enhance user experience by allowing natural light and fresh air into the cabin. Understanding the construction and components of these features provides insight into their importance in automotive design.
Structural Composition
The construction of the upper section typically involves a combination of materials designed to balance weight, strength, and insulation. Common materials include high-strength steel, aluminum, and composite elements. The integration of these materials not only ensures durability but also aids in reducing noise and improving energy efficiency.
Sunroof Mechanism
The sunroof system is an intricate assembly that allows for various configurations, including tilt and slide functions. This mechanism includes tracks, motors, and seals that work together to ensure smooth operation and effective weatherproofing. Regular maintenance of the sunroof is essential to prevent leaks and ensure optimal functionality.
| Component |
Material |
Function |
| Roof Panel |
High-strength Steel |
Structural Support |
| Sunroof Glass |
Tinted Laminated Glass |
Light Entry and UV Protection |
| Sunroof Frame |
Aluminum |
Lightweight Support |
| Weather Seal |
Rubber |
Leak Prevention |
| Motor Assembly |
Plastic and Metal |
Operation of Sunroof |
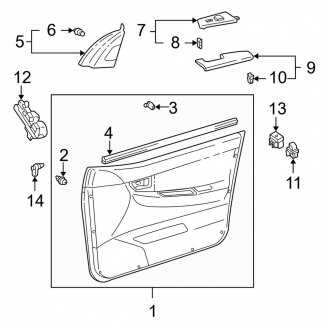
Mirror and Handle Placement
The arrangement of reflective surfaces and gripping mechanisms on a vehicle is essential for both functionality and aesthetics. These components not only enhance the overall appearance but also play a critical role in safety and ease of use. Understanding their positioning can greatly aid in maintenance and customization efforts.
Reflective surfaces are typically mounted on the outer edges of the vehicle’s doors, providing optimal visibility for the driver. Their placement is designed to minimize blind spots while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. In contrast, gripping mechanisms are strategically located near the entrance points, facilitating smooth access to the interior. Their ergonomic design is intended to enhance user comfort and efficiency during entry and exit.
It is crucial to consider the alignment and angles of these elements. Improper positioning can lead to visibility issues or hinder the ease of access. Therefore, when making adjustments or replacements, it is advisable to refer to manufacturer specifications to ensure proper fit and function.
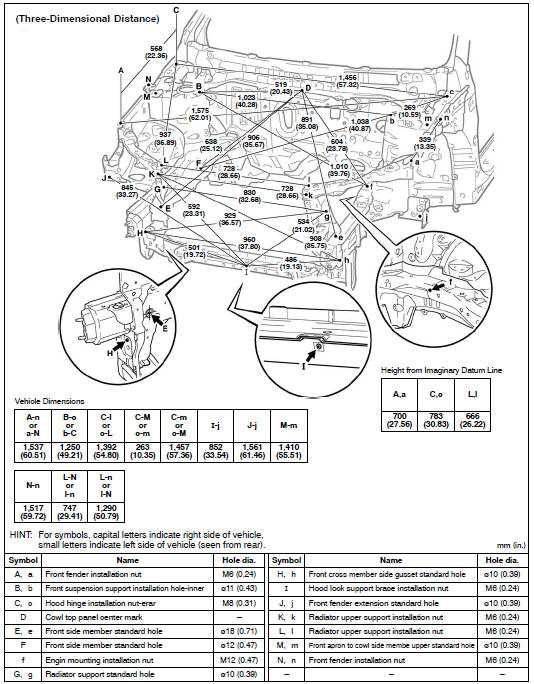
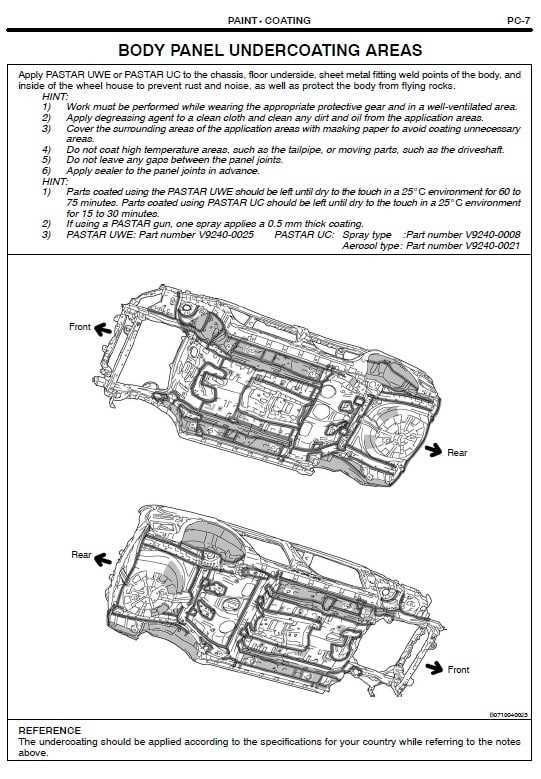
Chassis Integration with Exterior Panels
The harmonious connection between the structural framework and the outer coverings of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This integration ensures not only the vehicle’s visual appeal but also its overall performance and safety. A well-designed interaction between these components contributes to the vehicle’s rigidity and enhances its resistance to external forces.
Structural Support and Aesthetics
The framework serves as the backbone, providing essential support for the outer panels. These external layers are designed to fit seamlessly onto the chassis, ensuring a cohesive appearance. Effective integration minimizes gaps and misalignments, which can lead to increased wind noise and reduced aerodynamic efficiency. Furthermore, the design of the outer elements must account for factors such as impact resistance and weatherproofing to enhance the longevity of the vehicle.
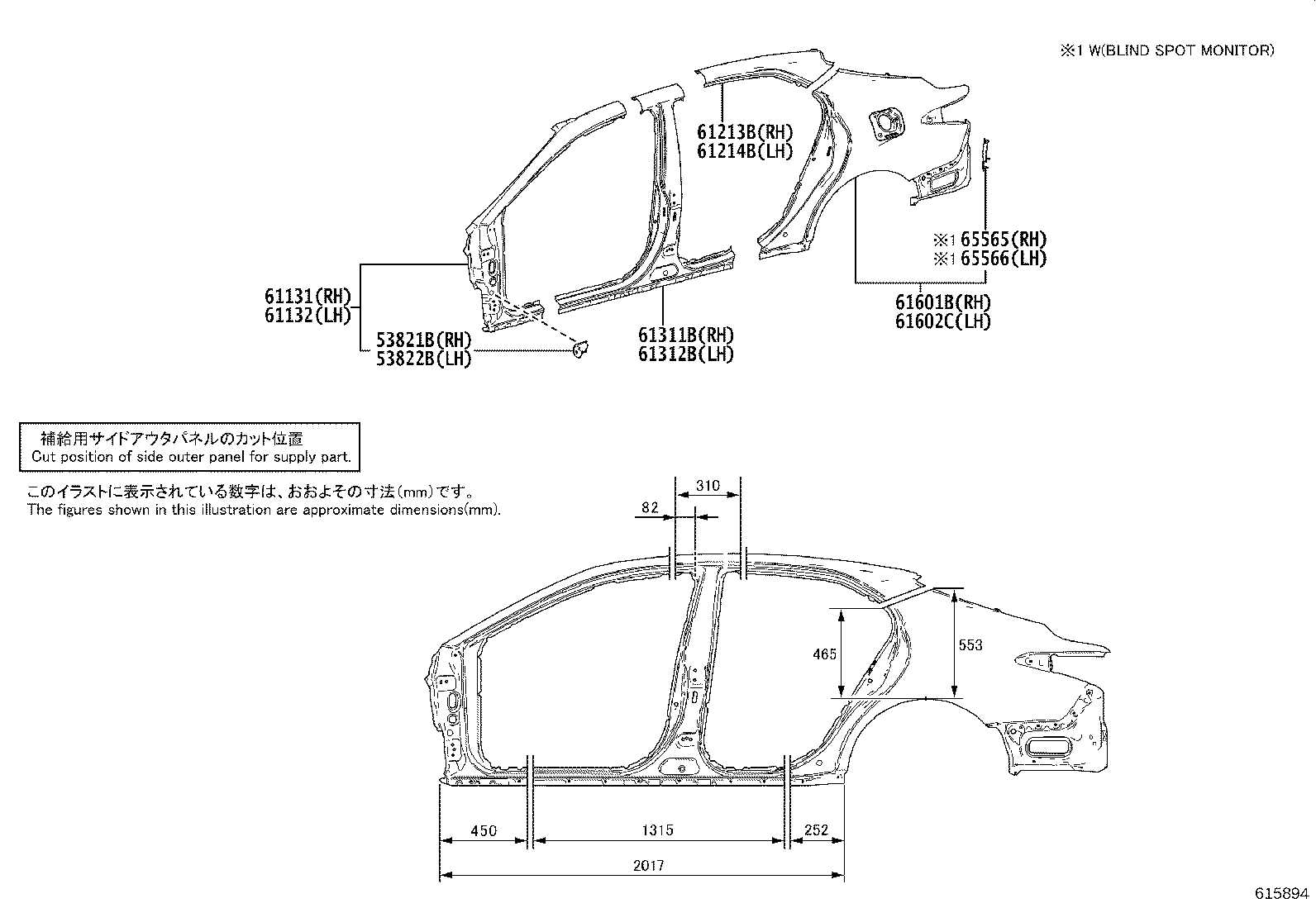
Impact on Performance
The synergy between the structural components and the external coverings significantly affects the vehicle’s performance. A well-integrated assembly can improve the car’s overall handling and stability. Additionally, this connection helps distribute forces encountered during driving, which is essential for maintaining integrity during collisions. Robust engineering ensures that the integration supports not just visual cohesion but also the safety and efficiency of the vehicle.