
The structure of modern heavy-duty machinery involves numerous interconnected elements working together to ensure optimal performance. These machines are designed to tackle demanding tasks in various environments, relying on robust mechanisms that function seamlessly in tandem. Understanding how these components interact is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance.
Each segment of the machine contributes to its overall functionality, with certain key sections bearing the majority of the mechanical load. By examining these essential areas, one can gain insights into the machine’s capabilities and how its core systems are designed to handle diverse operations.
Whether focusing on the energy source, propulsion system, or control mechanisms, every part plays a vital role in the machine’s long-term reliability. Ensuring that these components remain in good condition is critical for avoiding breakdowns and ensuring consistent performance over time.
Key Components of a Tractor’s Engine
The core of any heavy-duty machine lies in its engine, responsible for delivering the power necessary for various operations. Understanding the essential elements that make up the heart of these machines helps in both maintaining and optimizing their performance. By focusing on the primary components, it becomes easier to grasp how the entire system functions together.
At the forefront is the cylinder block, the main structure housing key moving parts like pistons. Pistons move within cylinders, transferring force from expanding gas to crankshafts. The crankshaft, in turn, converts this motion into rotational energy. Fuel and air mixture enters the combustion chamber, where spark plugs ignite it, generating the required power.
Another significant element is the cooling system, which regulates temperature and prevents overheating. Alongside this is the lubrication system, ensuring all moving pieces operate smoothly without friction damage. These components work together seamlessly, providing the necessary power output and longevity.
Understanding the Engine’s Main Parts
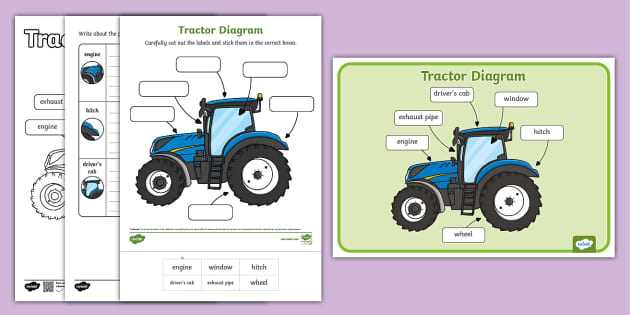
The heart of any machine responsible for propulsion lies in its power source. This core component converts energy into motion, driving various systems essential for performance. Each section plays a vital role, working together to maintain smooth operation and reliability over time.
The central unit consists of a block housing crucial elements such as cylinders, pistons, and valves. The movement within the cylinders creates the force needed to generate power. Other important components include the crankshaft and camshaft, which regulate the timing and movement of these internal mechanisms.
To ensure efficiency, systems for cooling and lubrication are integrated, preventing overheating and reducing friction between moving parts. These auxiliary systems support long-term functionality and enhance the performance of the overall unit.
The Role of the Hydraulic System
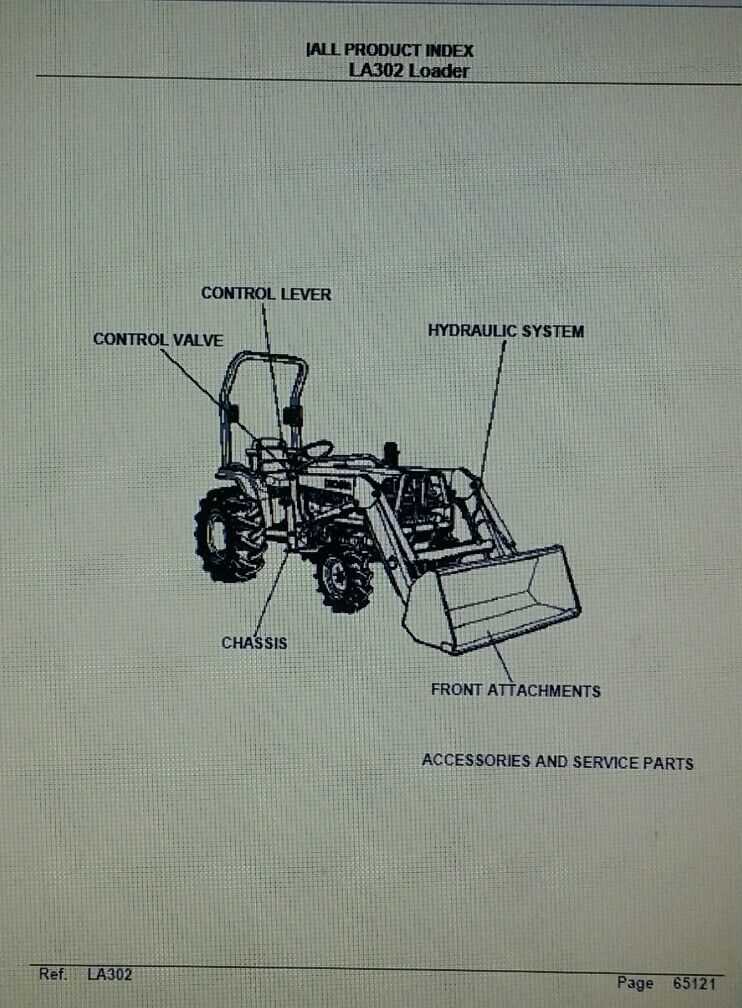
The hydraulic system plays a vital function in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of various machinery. It is designed to transfer power through fluid movement, enabling controlled actions across different components and mechanisms.
Key benefits of this system include:
- Efficient power transmission over distances
- Precision control of lifting, lowering, and steering mechanisms
- Enhanced responsiveness during operation
Hydraulics are widely appreciated for their ability to manage heavy loads with minimal effort, making them a cornerstone in many mechanical applications.
Functions of Hydraulic Parts in a Tractor
Hydraulic systems play a vital role in modern machinery, enabling various components to work efficiently. They provide the necessary force to perform key operations and allow for precise control in different tasks. These systems utilize fluid pressure to transfer energy and are essential in managing multiple operations that involve lifting, lowering, and moving heavy loads.
Main Components of Hydraulic Systems
The hydraulic system typically consists of several critical elements that ensure proper function. These include pumps, which generate fluid flow, and cylinders that convert this flow into mechanical movement. Valves control the direction and pressure of the fluid, allowing the operator to manage the power needed for different tasks.
How Hydraulic Systems Enhance Performance
Through efficient distribution of energy, hydraulic systems ensure smooth and precise operations. Whether controlling implements or providing power for attachments, the system’s ability to generate substantial force with minimal input is crucial to optimizing performance and reducing strain on the equipment.
Transmission System in Modern Tractors
The transmission system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and functionality of machinery used for heavy-duty tasks. This system is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing smooth and controlled movement. Without a well-designed transmission, vehicles would struggle to perform effectively across various terrains and under different loads.
Main Components of the Transmission
A typical transmission setup consists of several key elements, including gears, clutches, and shafts. These components work in unison to manage speed and torque, optimizing the performance. Gears help control the output power, while clutches assist in the smooth engagement of different gear sets during operation.
Advanced Features of Modern Transmission Systems
Modern systems have evolved to include advanced features such as automatic gear shifting and hydrostatic control. These innovations not only enhance operational ease but also improve fuel efficiency and reduce the wear on components over time. With technology continually advancing, these systems are becoming more adaptive to varying work conditions, ensuring reliability and longevity.
Key Transmission Components and Their Purpose
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the functionality of machinery by facilitating the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels or implements. Understanding the essential components involved in this system helps in recognizing their specific functions and importance in overall performance.
Primary Components

Key elements of the transmission system include the gearbox, drive shafts, clutches, and differentials. Each of these components contributes uniquely to the movement and control of the machine, ensuring that power is effectively managed and utilized.
Component Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Gearbox | Changes the torque and speed of the output power to suit various working conditions. |
| Drive Shaft | Transmits power from the engine to the gearbox and from the gearbox to the wheels. |
| Clutch | Allows for the engagement and disengagement of power transmission for smooth operation. |
| Differential | Enables the wheels to rotate at different speeds, especially during turns, improving maneuverability. |
Importance of the Tractor’s PTO
The power take-off (PTO) mechanism plays a vital role in transferring energy from the engine to various implements, enabling them to perform a range of tasks efficiently. This system is crucial for optimizing productivity in various field operations, ensuring that machinery operates smoothly and effectively.
Key Functions of the PTO
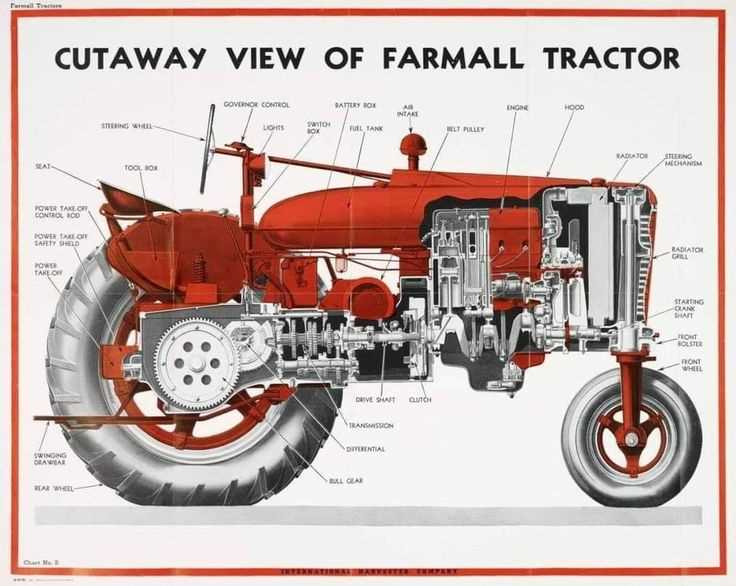
- Facilitates the operation of attachments such as mowers, balers, and tillers.
- Allows for the use of hydraulic systems to enhance functionality.
- Enables quick changes between different tools, increasing operational flexibility.
Benefits of Using a PTO
- Improved efficiency in executing agricultural tasks.
- Reduction in manual labor, leading to time savings.
- Enhancement of overall machinery performance and longevity.
Power Take-Off Mechanism Explained
The power take-off mechanism is a crucial component in various machinery, enabling the transfer of power from the main engine to auxiliary devices. This system is designed to facilitate efficient operation by harnessing the engine’s output and directing it to power different implements or tools. Understanding its functionality is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring seamless integration with various equipment.
This mechanism typically involves a series of gears and shafts that engage and disengage as needed. Its design allows for a versatile approach to power management, making it suitable for a range of applications. Below is a summary of the key elements and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Gearbox | Modulates power output and speed |
| Drive Shaft | Transmits power from the engine to implements |
| Clutch | Enables engagement and disengagement of power transfer |
| PTO Shaft | Connects the mechanism to external devices |
In conclusion, the power take-off mechanism plays a vital role in enhancing the versatility and efficiency of equipment, allowing for the use of various attachments to perform different tasks effectively.
How a Tractor’s Cooling System Works
The cooling mechanism of heavy machinery is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing overheating. This system regulates the temperature of the engine by dissipating excess heat generated during operation. Understanding how this process functions can help ensure efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism
- Radiator: This component plays a vital role in transferring heat away from the engine. It allows coolant to circulate through its fins, where air flow cools the fluid before it returns to the engine.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator. It maintains a constant flow, ensuring that the engine remains at a stable temperature.
- Thermostat: This device regulates the temperature of the engine by controlling the flow of coolant. It opens and closes based on the engine’s temperature, allowing for efficient heat exchange.
- Coolant: A mixture of water and antifreeze that absorbs heat from the engine and carries it to the radiator for dissipation.
Operation Process
The cooling system operates through a continuous cycle. Initially, the coolant absorbs heat from the engine, raising its temperature. The heated fluid then flows to the radiator, where air passing through the fins cools it down. As the coolant temperature drops, it returns to the engine, maintaining a balanced temperature.
- The engine generates heat during operation.
- Coolant absorbs the heat and becomes warmer.
- The water pump circulates the heated coolant to the radiator.
- Airflow cools the coolant in the radiator.
- The cooled coolant returns to the engine, repeating the cycle.
Regular maintenance of the cooling system is essential to prevent overheating and ensure the machinery operates efficiently. Checking coolant levels, inspecting hoses, and cleaning the radiator are simple steps that can significantly extend the life of the equipment.
Cooling System Parts and Their Functions
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in machinery, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance. This section outlines the essential components that contribute to the cooling process, along with their respective roles.
Key Components

- Radiator: This device dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool down before returning to the engine.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that all areas receive adequate cooling.
- Thermostat: This valve regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, opening and closing to maintain optimal heat levels.
- Coolant: A mixture of water and antifreeze that absorbs and transfers heat away from the engine.
- Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between the various components, maintaining a closed-loop system.
Functions of Each Component
- The radiator cools the heated coolant before it re-enters the engine.
- The water pump ensures continuous circulation of coolant, preventing localized overheating.
- The thermostat maintains a consistent operating temperature by controlling coolant flow.
- Coolant absorbs heat and prevents freezing, providing protection in extreme conditions.
- Hoses connect all elements of the cooling system, enabling efficient coolant movement.
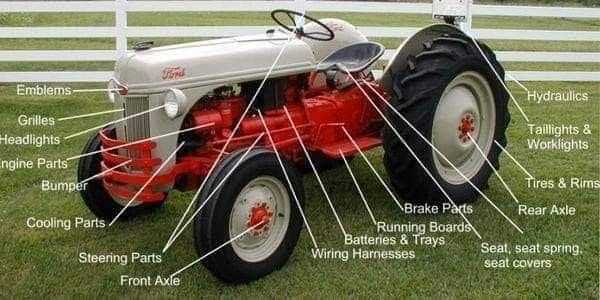
Braking System Components of a Tractor

The braking mechanism is a crucial aspect of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. It consists of various elements that work together to reduce speed and bring the machine to a complete stop. Understanding these components is essential for maintaining efficiency and reliability in performance.
Main Elements of the Braking System
- Brake Pedal: The primary control for the operator, allowing them to initiate braking action.
- Master Cylinder: Converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Lines: Carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brakes.
- Brake Calipers: Clamp down on the brake pads against the rotating discs to create friction.
- Brake Pads: Friction material that presses against the discs to slow down the vehicle.
- Brake Discs: Rotating components that work with the calipers to facilitate stopping.
Types of Braking Mechanisms
- Hydraulic Brakes: Utilize fluid pressure to apply force to the braking components.
- Air Brakes: Operate using compressed air to engage the braking system.
- Mechanical Brakes: Use mechanical linkages to apply pressure directly to the braking elements.
Proper maintenance and understanding of these components enhance safety and operational efficiency, preventing potential hazards and ensuring optimal performance.
Brake Mechanism and Safety Features
The braking system is a crucial component in any heavy machinery, ensuring that operators can stop safely and effectively during operation. This system not only enhances control but also significantly contributes to overall safety, especially in challenging working environments.
Brake mechanisms typically employ hydraulic or pneumatic principles, allowing for efficient force application. These systems are designed to provide reliable stopping power, even under varying loads and conditions. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential failures that could lead to hazardous situations.
Safety features integrated into the braking system play a vital role in minimizing accidents. These may include automatic engagement systems, warning indicators, and redundant systems that activate if the primary brake fails. Such features are essential for maintaining high safety standards and protecting both the operator and surrounding personnel.
Electrical System Parts in a Tractor

The electrical network in machinery is vital for its overall functionality and efficiency. It encompasses various components that work together to ensure smooth operation and reliable performance. Understanding the elements within this system is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
Among the significant elements are the battery, which stores energy and provides the necessary power to start the engine. Additionally, the alternator plays a critical role by generating electricity while the engine runs, replenishing the battery and powering other electrical systems. Wiring harnesses connect these components, facilitating the flow of electricity throughout the machine.
Control and Monitoring
Furthermore, switches and relays are essential for controlling electrical circuits, enabling operators to manage different functions with ease. Instrument clusters provide crucial information regarding system status, helping users monitor performance efficiently. Regular checks and maintenance of these components can prevent potential issues, ensuring longevity and reliability.