The intricate mechanisms that enable a vehicle’s drivetrain to function efficiently rely on a variety of essential elements. These components work together to facilitate the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth and reliable performance under diverse driving conditions. A thorough examination of these components reveals their unique roles and the way they interact to deliver optimal functionality.
In this section, we delve into the specific elements that constitute this crucial assembly. By exploring their arrangement and functionality, we can appreciate the complexity involved in their design and engineering. Each element contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system, playing a vital part in the vehicle’s operation.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a curious enthusiast, understanding the arrangement and roles of these components is fundamental. This knowledge not only aids in maintenance and repair but also enhances the overall driving experience, ensuring vehicles operate as intended for years to come.
Understanding Transfer Case Functionality
The mechanism responsible for distributing power from the engine to the wheels plays a crucial role in vehicle dynamics. This system enables a vehicle to adapt to various terrains, enhancing performance and control. Its design facilitates the seamless transfer of torque, allowing for smooth operation across different driving conditions.
Key Components and Their Roles
Several critical elements contribute to the effective operation of this mechanism. The primary unit is responsible for engaging and disengaging different drive modes. Additionally, components such as gears and clutches work in tandem to manage power distribution, ensuring optimal traction and stability. The interaction between these elements is vital for maintaining vehicle performance.
Operating Mechanisms
This system employs various operating principles to achieve its functions. For instance, electronic sensors monitor wheel speed and traction levels, enabling real-time adjustments to power delivery. Moreover, hydraulic actuators play a significant role in engaging different drive settings, allowing drivers to select the most suitable mode for their current conditions. Such versatility underscores the importance of this assembly in modern vehicles.
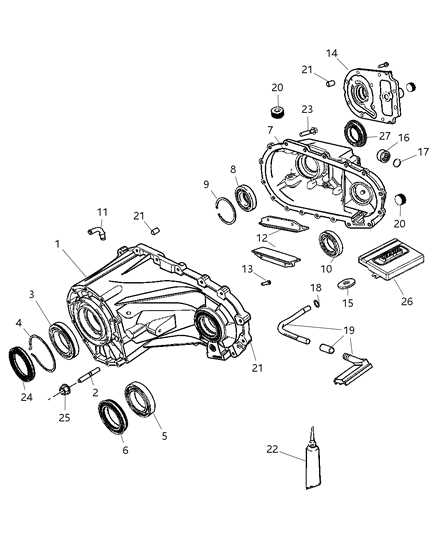
Essential Components of Transfer Cases
Understanding the crucial elements within a drivetrain mechanism is vital for the optimal functioning of all-wheel and four-wheel vehicles. These components work together to distribute power effectively, ensuring smooth operation and enhanced traction across diverse terrains.
Main Elements
The primary components responsible for the functionality of the drivetrain assembly include various gears, shafts, and housing structures. Each part plays a significant role in facilitating power transfer from the engine to the wheels, allowing for dynamic performance in different driving conditions.
Overview of Key Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | The outer shell that protects internal mechanisms and contains lubrication. |
| Input Shaft | Connects the system to the engine and transfers rotational motion. |
| Output Shaft | Delivers power to the axles, enabling wheel movement. |
| Gear Set | Adjusts the speed and torque delivered to the wheels based on driving conditions. |
| Chain/Belt | Transfers power between gears, ensuring smooth operation. |
| Selector Mechanism | Allows the driver to switch between different operational modes. |
Common Transfer Case Types Explained
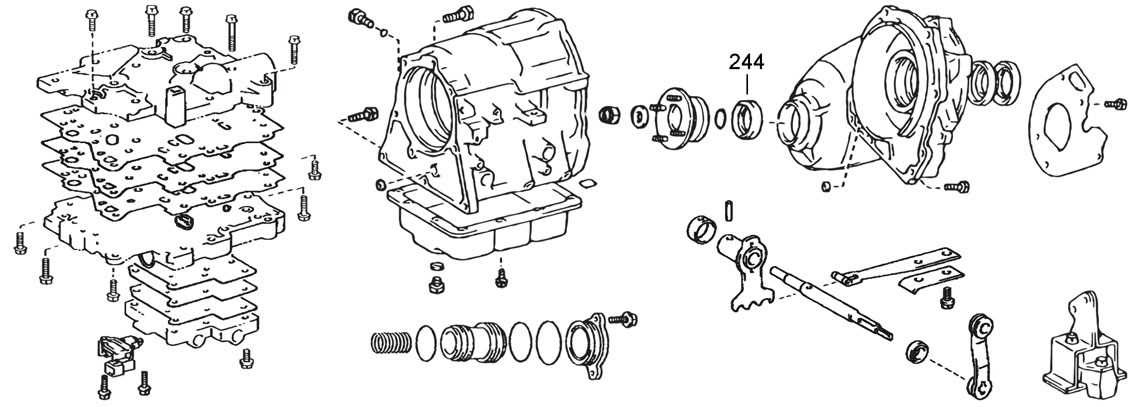
Understanding the various designs of drive components is essential for both enthusiasts and professionals. Each configuration offers unique benefits and drawbacks, influencing performance, capability, and adaptability in different driving conditions. This section provides an overview of the most prevalent types of these essential mechanisms.
Full-Time Systems
Full-time mechanisms are engineered to provide power to all wheels at all times. This design enhances traction and stability, particularly in adverse weather. Vehicles equipped with these systems typically do not require driver intervention to engage different modes, as they automatically adjust based on conditions.
Part-Time Systems
Part-time variants allow the operator to switch between two-wheel and all-wheel drive. This flexibility can lead to improved fuel efficiency when four-wheel traction is unnecessary. Operators can engage the full power distribution as needed, making these systems popular for off-road enthusiasts who require versatility.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Time | Enhanced traction, automatic engagement | Reduced fuel efficiency, increased wear |
| Part-Time | Fuel efficiency, versatility | Requires manual engagement, may affect stability |
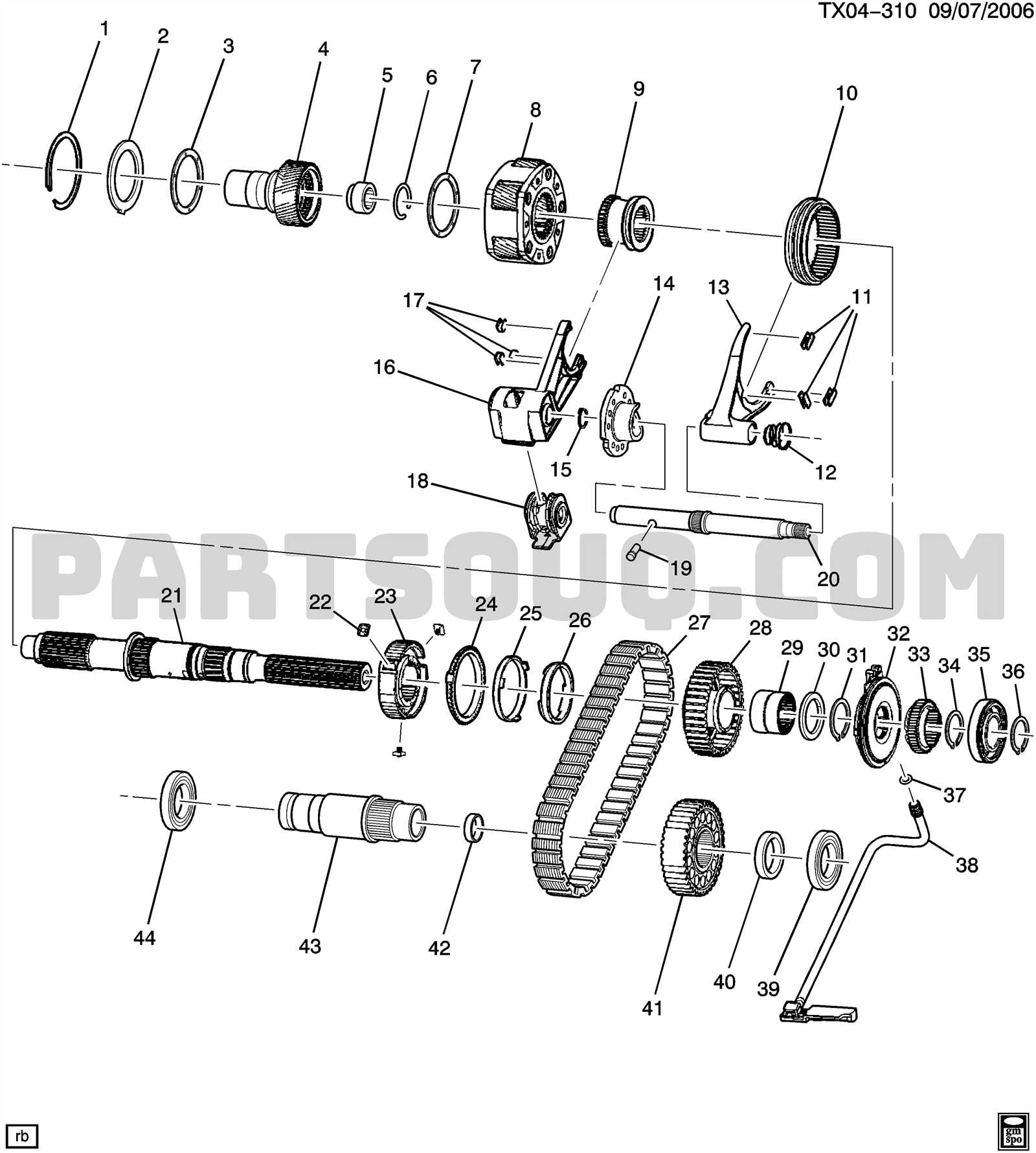
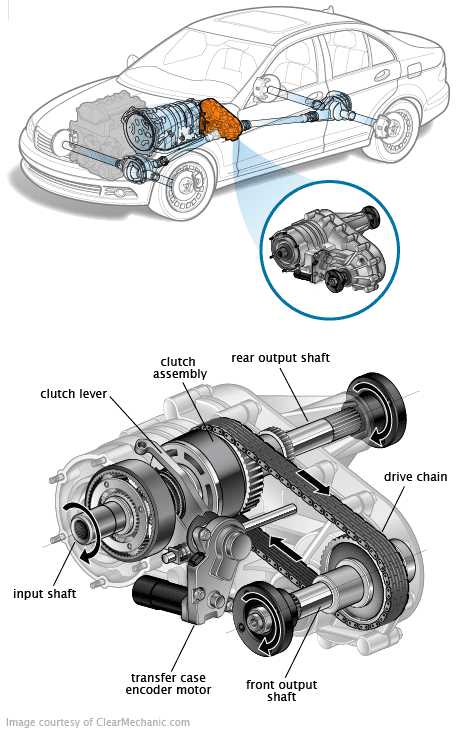
Diagram of a Typical Transfer Case
This section provides an overview of the essential components commonly found within a system designed to manage power distribution between axles. Understanding the layout of these elements is crucial for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components

- Housing: The outer structure that encloses the mechanism.
- Input Shaft: Responsible for receiving power from the transmission.
- Output Shafts: These distribute power to the front and rear axles.
- Chain or Gear Drive: Facilitates the transfer of torque to the output shafts.
- Shift Mechanism: Allows the driver to select between different operational modes.
- Differential: Balances the rotational speed between the output shafts.
Operational Functions
- Power Distribution: Ensures torque is adequately shared between the front and rear axles.
- Mode Selection: Enables various driving configurations for different terrains.
- Torque Management: Maintains optimal performance during various driving conditions.
Transfer Case Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep of essential components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding proper care techniques helps prevent costly repairs and ensures seamless operation. Following some fundamental guidelines can significantly enhance durability and reliability.
Routine Inspection
Frequent checks are necessary to identify wear and tear early. Look for leaks, unusual noises, or vibrations while operating. Addressing issues promptly can prevent further damage and prolong functionality.
Fluid Changes
Maintaining the right fluid levels is vital for optimal operation. It is recommended to replace fluids at regular intervals as specified by the manufacturer. This practice helps maintain lubrication and cooling, reducing friction and wear.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Inspection | Every 3,000 miles | Check for color and consistency. |
| Fluid Replacement | Every 30,000 miles | Follow manufacturer recommendations. |
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Look for leaks and damage. |
| Noise Check | During operation | Listen for unusual sounds. |
Identifying Transfer Case Issues
Understanding the signs of malfunction in a vehicle’s drivetrain component is crucial for maintaining performance and safety. This section delves into common indicators that suggest the need for attention to this specific assembly.
Common Symptoms of Malfunction
- Strange Noises: Unusual sounds such as grinding, clunking, or whining can indicate internal wear or damage.
- Fluid Leaks: Puddles or stains beneath the vehicle may suggest a leak from seals or gaskets.
- Difficulty Engaging Gears: Trouble shifting between modes can signify issues with the internal mechanisms.
- Warning Lights: Dashboard alerts related to drivetrain components should not be ignored.
Inspection and Diagnosis
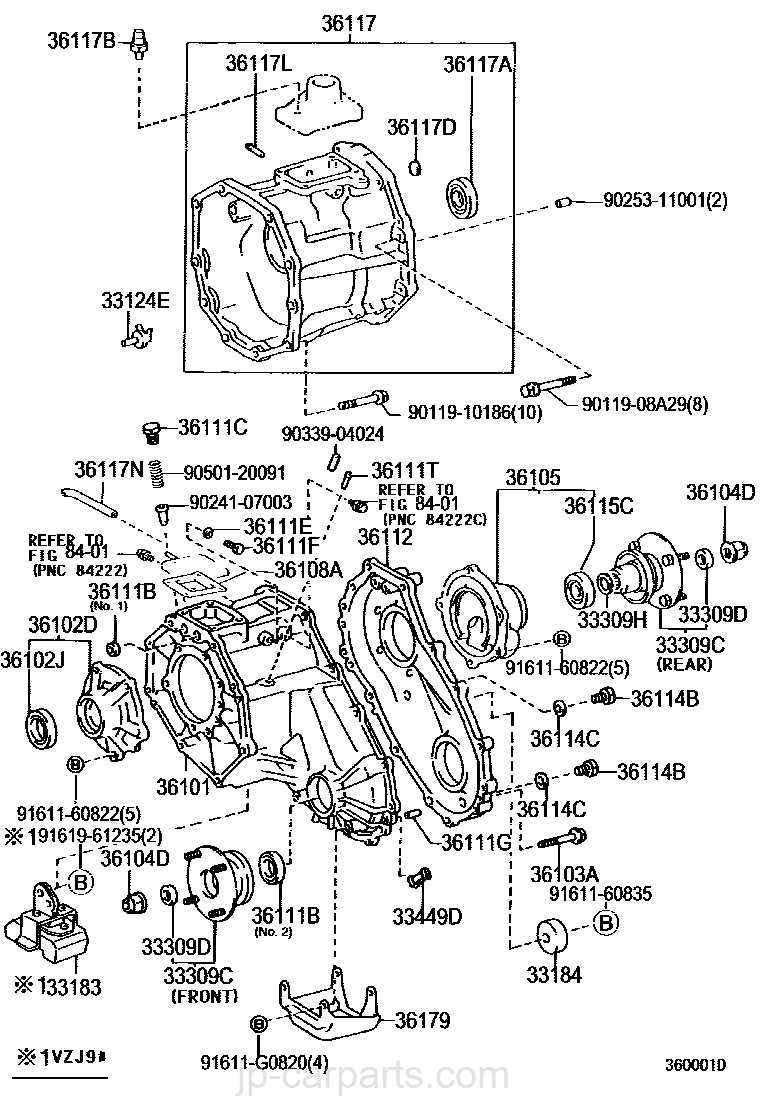
Regular inspections can help in early detection of problems. Consider the following steps:
- Check for visible leaks around the assembly.
- Listen for abnormal sounds during operation.
- Assess the fluid level and condition; dark or burnt fluid is a warning sign.
- Test the functionality of gear engagement under various conditions.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more significant damage and costly repairs, ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly.
Role of Gears in Transfer Cases
Gears serve a critical function in the operation of a power distribution system within vehicles, particularly those designed for off-road and varying terrain conditions. Their primary purpose involves managing the allocation of power from the engine to the wheels, enabling optimal performance across different driving scenarios.
Transmission Efficiency: The arrangement of these components is essential for maintaining efficiency. By adjusting the torque and speed, they ensure that the vehicle can navigate both challenging and standard terrains without losing power or traction.
Adaptive Performance: Furthermore, these mechanical elements contribute to the adaptability of the vehicle. They allow for the selection of different drive modes, which enhances the vehicle’s capabilities, whether it’s climbing steep inclines or traversing slippery surfaces.
Durability and Maintenance: The construction and materials used for these components also play a significant role in the overall reliability of the system. High-quality gears are designed to withstand heavy loads and prolonged usage, minimizing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
Understanding Transfer Case Fluid Types
Choosing the right liquid for a specific gearbox is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Various formulations are available, each designed to meet the demands of different mechanical systems. Understanding these formulations helps ensure that the mechanism operates smoothly and efficiently.
Here are the primary types of fluids commonly used in these systems:
- Conventional Oil: Traditional lubricant that provides adequate protection and functionality for standard applications.
- Synthetic Oil: Engineered liquid that offers superior protection against wear, improved thermal stability, and enhanced performance in extreme conditions.
- All-Weather Fluid: Formulation designed to perform well across a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various driving conditions.
- Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF): Specifically designed for automatic systems, providing excellent lubrication and protection for internal components.
- Heavy-Duty Oil: Formulated for high-stress applications, offering added protection and durability for demanding environments.
Factors influencing the selection of an appropriate liquid include:
- Operating Conditions: Temperature, load, and driving style affect the choice of fluid.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Following guidelines provided by the vehicle manufacturer ensures compatibility and effectiveness.
- Performance Requirements: Depending on the specific demands of the system, certain formulations may be more suitable than others.
Maintaining the correct lubricant not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the entire mechanism, reducing the likelihood of costly repairs.
Transfer Case Shift Mechanisms Overview
This section delves into the various components and systems responsible for altering the drive settings in four-wheel-drive vehicles. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for comprehending how vehicles adapt to different terrains and driving conditions.
Typically, these systems operate through a combination of levers, cables, and electronic controls. Below are the primary types of shifting mechanisms:
- Manual Shifters: Often found in older models, these require the driver to engage the desired mode physically.
- Electronic Shifters: Utilizing sensors and electronic actuators, these systems offer precision and ease of use, enabling automatic adjustments based on driving conditions.
- Pneumatic Systems: Some advanced vehicles employ air pressure to control the engagement of different modes, providing a responsive driving experience.
- Hydraulic Mechanisms: Leveraging fluid pressure, these systems can facilitate smooth transitions between modes, often found in heavier-duty vehicles.
Each of these systems comes with its unique advantages and drawbacks, influencing vehicle performance and driver control. Regular maintenance and understanding of these mechanisms can significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of the drivetrain.
Benefits of Upgrading Your Transfer Case
Enhancing your vehicle’s ability to handle various terrains and driving conditions can significantly improve overall performance. Upgrading components associated with the system responsible for power distribution can lead to a more robust and efficient operation. This not only enhances driving experience but also increases the longevity of your vehicle.
Improved Performance
One of the most notable advantages of enhancing your system is the noticeable boost in performance. Upgraded components can handle higher torque and improve acceleration, making your vehicle more responsive in challenging situations. Whether navigating rocky trails or managing inclement weather, improved functionality ensures a smoother ride.
Enhanced Durability
Investing in superior components often results in increased durability. Enhanced materials and designs can withstand greater stresses, reducing the likelihood of failures. This means fewer repairs and lower long-term costs, allowing for peace of mind during your adventures.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Performance Boost | Improves responsiveness and acceleration in various conditions. |
| Durability | Enhanced materials increase resistance to wear and tear. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimized components can lead to better fuel consumption. |
| Off-Road Capability | Improves handling and stability on rough terrains. |
Transfer Case Repair vs. Replacement
When it comes to addressing issues with vehicle drivetrain components, one often faces the dilemma of whether to fix or substitute the damaged assembly. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, which can significantly impact performance and longevity.
Repairing involves fixing the specific issues within the existing unit, potentially restoring its functionality at a lower initial cost. However, it may not address underlying problems that could arise later. Conversely, opting for a full replacement can ensure enhanced reliability and performance, but typically requires a larger financial investment.
| Aspect | Repair | Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront expense |
| Time | Often quicker turnaround | May require more time for installation |
| Reliability | Potential for recurring issues | Typically more dependable long-term |
| Warranty | Limited warranty on repairs | Usually comes with a new warranty |
Ultimately, the choice between fixing and substituting depends on various factors, including the extent of the damage, budget constraints, and long-term vehicle goals. Consulting a professional can provide valuable insights to make an informed decision.
Aftermarket Parts for Transfer Cases
In the world of automotive repair and enhancement, the availability of additional components offers enthusiasts and professionals a chance to optimize performance and durability. These supplementary items can significantly improve the functionality and longevity of the drivetrain, catering to diverse driving conditions and personal preferences.
Benefits of Upgraded Components
Utilizing enhanced components can lead to better efficiency, increased strength, and improved handling. Many enthusiasts seek out these modifications to tailor their vehicles for specific applications, whether for off-road adventures or daily commuting. Quality aftermarket solutions often provide a cost-effective alternative to original equipment manufacturer (OEM) items, allowing for customization without breaking the bank.
Popular Options to Consider
When exploring aftermarket solutions, options such as high-performance bearings, gaskets, and seals are among the most sought after. Additionally, enthusiasts might opt for gear ratios that better match their driving style or intended use, enhancing acceleration or towing capacity. This wide range of choices ensures that vehicle owners can find the perfect fit for their specific needs.