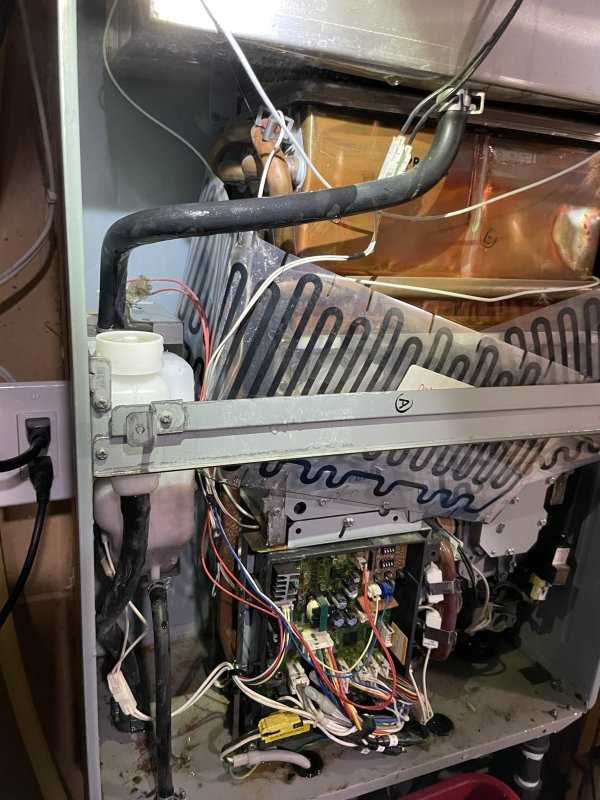
In today’s world, efficiency and convenience in home appliances have become crucial. One of the most important systems that bring comfort to our daily lives is the unit responsible for providing warm liquid flow on demand. This system is designed to deliver heated fluid without the need for large reservoirs, ensuring energy savings and consistent output whenever required.
Each element of such a setup plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and reliable operation. From the mechanism that controls temperature to the smaller elements that ensure proper flow, understanding how these components work together is essential for both maintenance and repair. Knowing how the various parts fit together will help in troubleshooting issues and optimizing performance.
This section will explore the various essential pieces of the system, offering insights into their functions and how they interact to create a seamless and efficient process. Understanding this structure can greatly enhance your ability to diagnose and maintain the system for years of trouble-free service.
Rheem Tankless Water Heater Overview
Modern heating systems have transformed the way we manage household energy consumption. These devices offer efficiency and convenience, ensuring continuous warm water flow without the need for large storage units. The compact design saves space while the advanced technology optimizes energy use.
One of the key advantages is the immediate availability of heated water, which is maintained by an intelligent system that only activates when necessary. This reduces waste and increases longevity, making it a practical solution for both small and large homes.
Additionally, maintenance is simplified thanks to modular components, allowing for easy replacement or upgrades over time. Users can enjoy a balance of performance and energy savings, tailored to suit their specific needs.
Main Components of Rheem Heaters
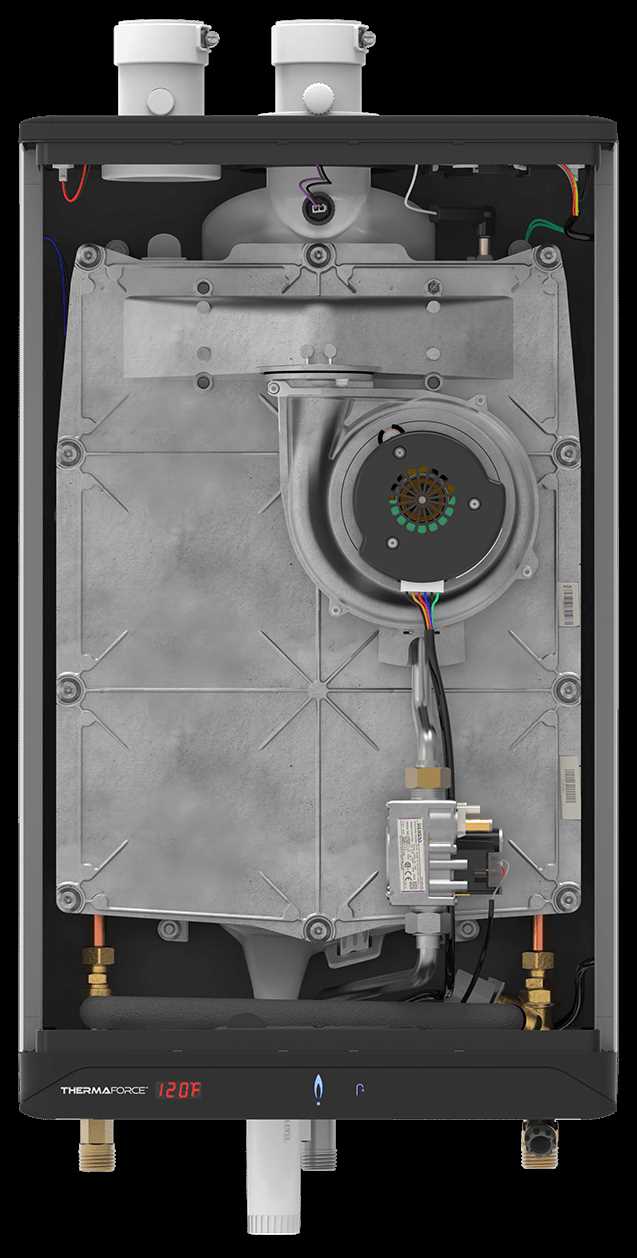
The internal structure of these modern systems consists of several key elements that work together to provide efficient performance and consistent output. Each component is specifically designed to handle a critical function, contributing to the overall operation and longevity of the device.
Core Mechanism
At the heart of the system lies the main control unit, which regulates the flow of energy and adjusts temperatures according to user preferences. This component is equipped with safety features to prevent overheating and ensure smooth functionality over time.
Flow Control and Monitoring
The flow management system monitors the intake and output, ensuring the right amount of resource is used. Sensors integrated into this part provide real-time data, allowing for precise adjustments and energy savings. This helps to maintain optimal conditions and avoid unnecessary consumption.
Control Board and Its Function
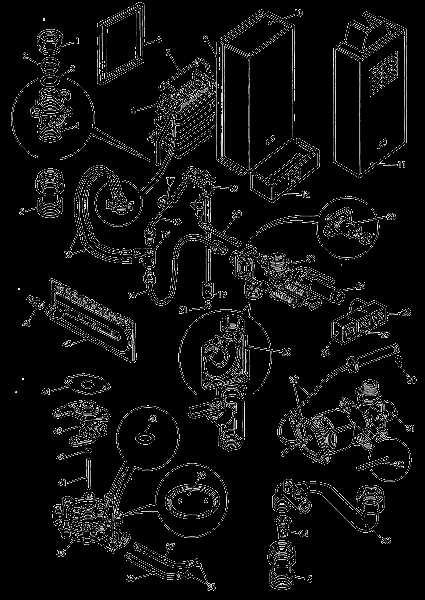
The control board serves as the central hub responsible for managing the entire system’s operations. This critical component ensures that all elements work in harmony, allowing for precise monitoring and control of various functions. Its advanced circuitry enables real-time adjustments, enhancing efficiency and maintaining safe performance levels.
Below is a table outlining key features and functions of the control board:
| Feature | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Regulation | Monitors and adjusts temperature settings to maintain optimal performance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| System Diagnostics | Provides real-time feedback and alerts on system status, identifying potential issues. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy Efficiency Control | Ensures the system operates at peak efficiency, adjusting power use as needed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Safety Mechanisms | Includes built-in safety features to prevent
Burner Assembly Structure
The burner assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient fuel combustion within the heating system. It is designed to evenly distribute the flame, optimizing energy transfer while maintaining safety standards. The arrangement and components of this assembly work together to regulate airflow and fuel mixture, essential for stable operation and performance. Main ComponentsKey elements include the burner head, which directs the flame, and the manifold, responsible for supplying gas to the burner. These components must be precisely aligned to ensure consistent combustion. The assembly also incorporates various safety mechanisms that monitor the flame and gas pressure, preventing potential hazards. Airflow and Fuel ControlProper airflow is critical for combustion. The burner assembly integrates air shutters or dampers to control the amount of oxygen mixed with fuel, ensuring efficient burning. Any imbalance can lead to inefficient operation or even system failure, making the calibration of these components vital. Heat Exchanger Role in EfficiencyThe heat exchanger plays a pivotal role in the overall performance of modern energy systems. By transferring thermal energy between fluids without direct contact, it significantly influences how effectively the system operates. Its design and materials are critical to ensuring minimal energy loss during the process, directly impacting efficiency levels. Optimized Thermal TransferEfficiency largely depends on how well the heat exchanger transfers heat from one medium to another. By optimizing the surface area and flow dynamics, energy transfer can be maximized, reducing the need for additional fuel or power. The better the heat transfer, the more energy is conserved. Minimizing Energy Loss
Another key aspect is minimizing heat loss during operation. Advanced technologies in heat exchanger construction help contain and direct thermal energy, ensuring that the majority of it is used for its intended purpose. This reduces overall consumption and contributes to a more energy-efficient system. Water Flow Sensor Operation
The flow detection mechanism plays a crucial role in the functionality of modern heating systems. By accurately measuring the movement of fluid, it ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency. Understanding its operation is essential for both users and technicians alike. Functionality OverviewThis mechanism is designed to monitor the flow of liquid through the system. When the fluid starts moving, the sensor activates various processes, ensuring the unit responds accordingly. Here are the main aspects of its operation:
Importance in Efficiency
Accurate flow sensing contributes significantly to energy savings and performance. When the system can gauge the flow accurately, it minimizes waste and enhances overall user experience. Key benefits include:
Importance of the Gas ValveThe gas valve plays a crucial role in the functionality and safety of heating appliances that rely on gas as their fuel source. Its primary purpose is to control the flow of gas, ensuring that the unit operates efficiently while minimizing the risk of leaks or other hazards. Understanding the significance of this component is essential for both users and technicians alike. Functionality and Efficiency
The gas valve regulates the amount of fuel entering the system, directly affecting its performance. A properly functioning valve ensures that the correct gas pressure is maintained, which is vital for optimal heating. If the valve malfunctions, it can lead to inefficient operation, increased energy consumption, and elevated operational costs. Thus, regular maintenance and timely replacement of the gas valve are essential for maintaining the efficiency of the appliance. Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when dealing with gas appliances. The gas valve serves as a critical safety mechanism, preventing gas leaks that could lead to dangerous situations. In the event of an emergency, such as a malfunction or excessive pressure, the valve can automatically shut off the gas supply, safeguarding users and property. Therefore, ensuring the gas valve is in good working order is not only important for performance but also for the overall safety of the environment. Ignition System Breakdown
The ignition system plays a crucial role in initiating the heating process. Understanding its components and functionality can help users troubleshoot and maintain the unit effectively. This section delves into the intricacies of the ignition mechanism, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Key Components of the Ignition Mechanism
Understanding the Functionality
The ignition system operates by following a specific sequence:
Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to ensure a safe and efficient operation. Temperature Sensors and Their LocationsTemperature sensors play a crucial role in monitoring and regulating the heat levels within a system. These components ensure that the desired temperature is achieved and maintained, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the operation. Their accurate placement is essential for optimal performance, allowing for precise readings and timely adjustments. Common Types of Temperature SensorsVarious types of temperature sensors are utilized in modern systems, including thermocouples, thermistors, and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs). Each type has unique characteristics suited for different applications, providing reliable temperature data to the control unit. Location of Temperature SensorsIn a typical configuration, temperature sensors are strategically positioned at key points to capture critical data. Often, they can be found near the inlet and outlet connections, ensuring that the temperature at these junctions is accurately monitored. Additionally, sensors may be placed within the heating elements themselves, providing direct feedback on the heating process. Maintenance of Air Intake FiltersRegular upkeep of air intake filters is essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of your system. These components play a crucial role in maintaining clean airflow, which directly affects the overall functionality and longevity of the appliance. Neglecting their maintenance can lead to various issues, including reduced efficiency and potential system failures. To keep air intake filters in top condition, follow these key maintenance steps:
By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can enhance the performance of your equipment and extend its service life, ensuring it operates efficiently for years to come. Pressure Relief Valve DetailsThe pressure relief valve is a crucial safety component in any heating system, designed to prevent excessive pressure buildup. This device ensures that the system operates within safe limits, automatically releasing pressure when it exceeds the designated threshold. Understanding its functionality and maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and safety of the entire system. Functionality of the Pressure Relief ValveThis valve primarily serves to protect the system from pressure surges. When the internal pressure reaches a certain level, the valve opens, allowing excess pressure to escape. This not only safeguards the heating apparatus but also prevents potential hazards such as leaks or explosions. Regular checks on this valve are necessary to ensure it functions correctly and efficiently. Maintenance TipsTo maintain optimal performance, it is advisable to inspect the pressure relief valve periodically. Look for any signs of leakage or corrosion, which may indicate a need for replacement. Additionally, testing the valve by lifting the lever can help confirm its operational integrity. Implementing these maintenance practices can greatly enhance the safety and efficiency of the entire heating system. Electrical Connections in the Unit
Understanding the electrical links within the system is crucial for its efficient operation. Proper connections ensure that the unit functions safely and reliably, allowing for optimal performance. This section will explore the various electrical components and their interconnections, highlighting the importance of each element in the overall setup. Every component plays a significant role in the functionality of the system. Below is a breakdown of the key electrical components typically found in such units, along with their respective functions:
|








