
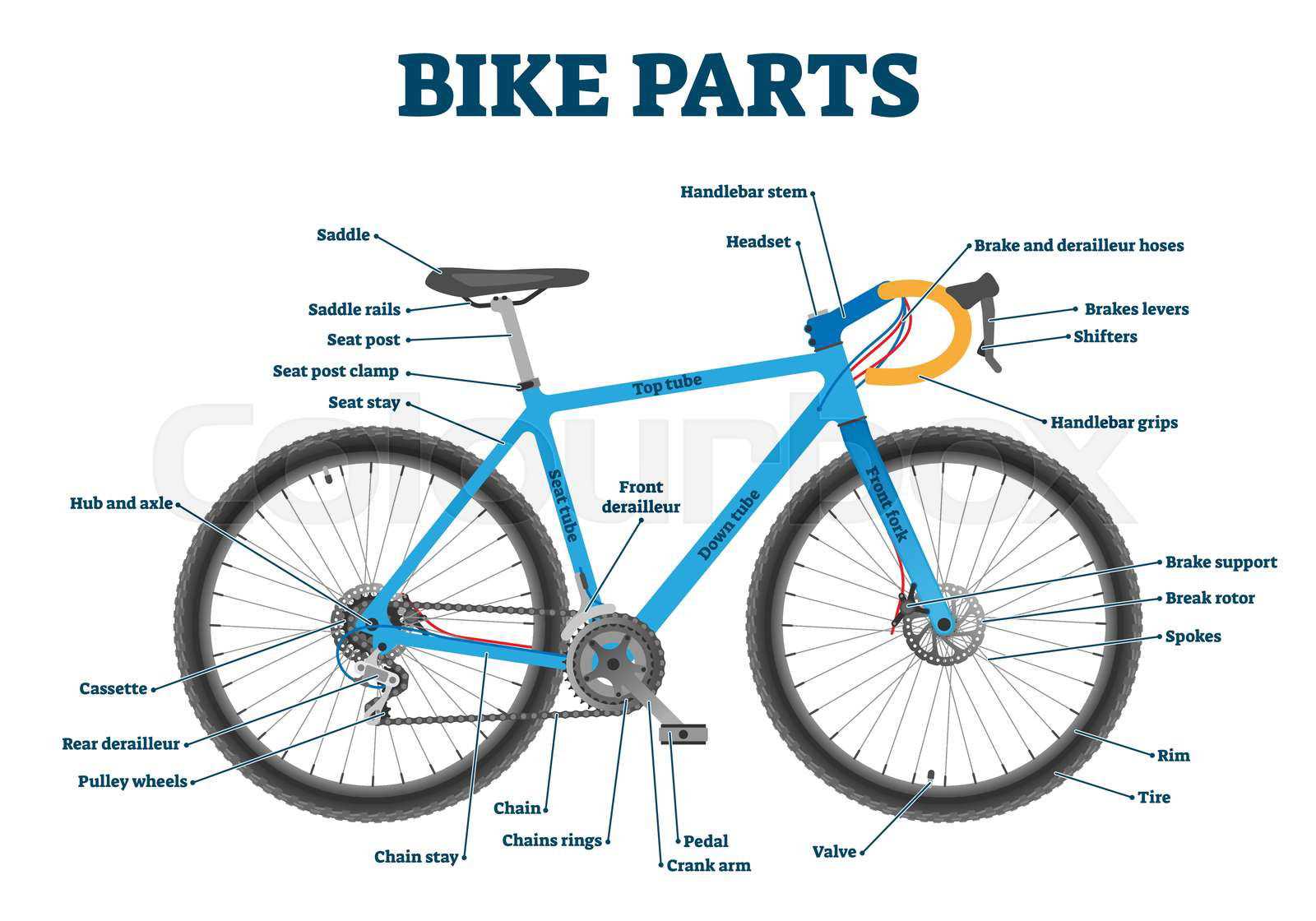
When it comes to the mechanics of two-wheeled transportation, the rotating component plays a critical role in both stability and motion. Comprising various elements that work in harmony, this system is fundamental to ensuring smooth travel and control. Each element contributes to performance, making it essential to understand how these components interact.
From the circular frame to the supporting spokes, every aspect is meticulously designed for both function and efficiency. The interplay between these elements ensures a balance of strength, flexibility, and durability, allowing for a reliable and comfortable ride. Recognizing the importance of each piece will help in both maintenance and potential upgrades.
By examining this essential mechanism in detail, you can gain a better appreciation of how modern engineering has refined the design to achieve maximum efficiency and reliability. W
Understanding Bicycle Wheel Components
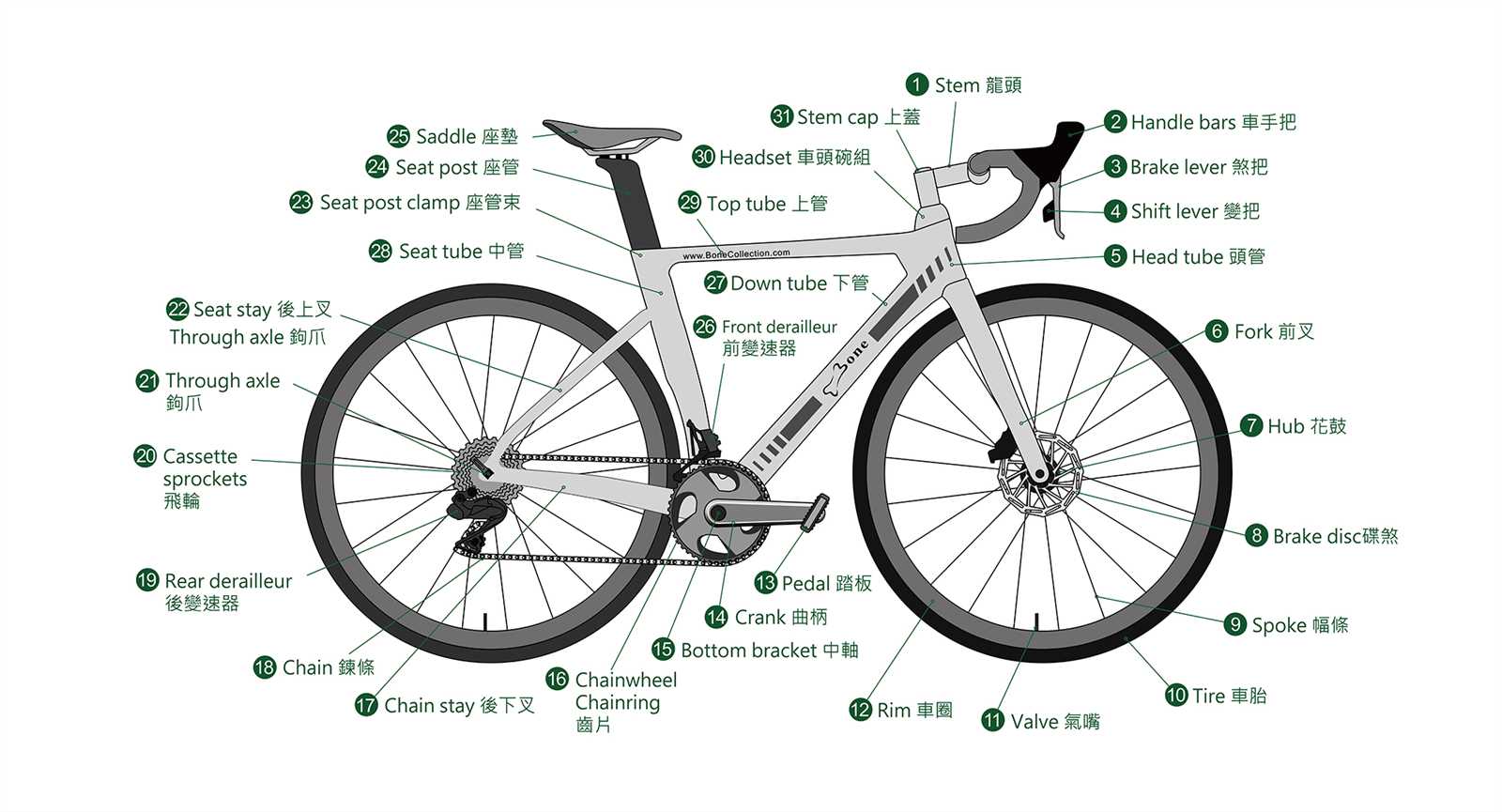
When exploring the structure of a two-wheeler’s key mechanisms, it’s essential to grasp the various elements that work together to ensure smooth movement and stability. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining balance, supporting weight, and enabling efficient propulsion. The interaction between these elements is what allows for fluid motion, providing both strength and flexibility.
Central hub serves as the core, anchoring the entire setup and ensuring even distribution of force. Surrounding this, a network of tensioned connectors, often referred to as spokes, stretches outward, contributing to the structural integrity and resilience of the assembly. These connectors are vital for absorbing shocks and maintaining form.
Lastly, the outer ring, often seen as the contact point with the ground, ensures proper grip and traction, completing the design by providing the necessary friction to facilitate movement. Together, these elements form a cohesive system, designed
Main Elements of a Bicycle Wheel
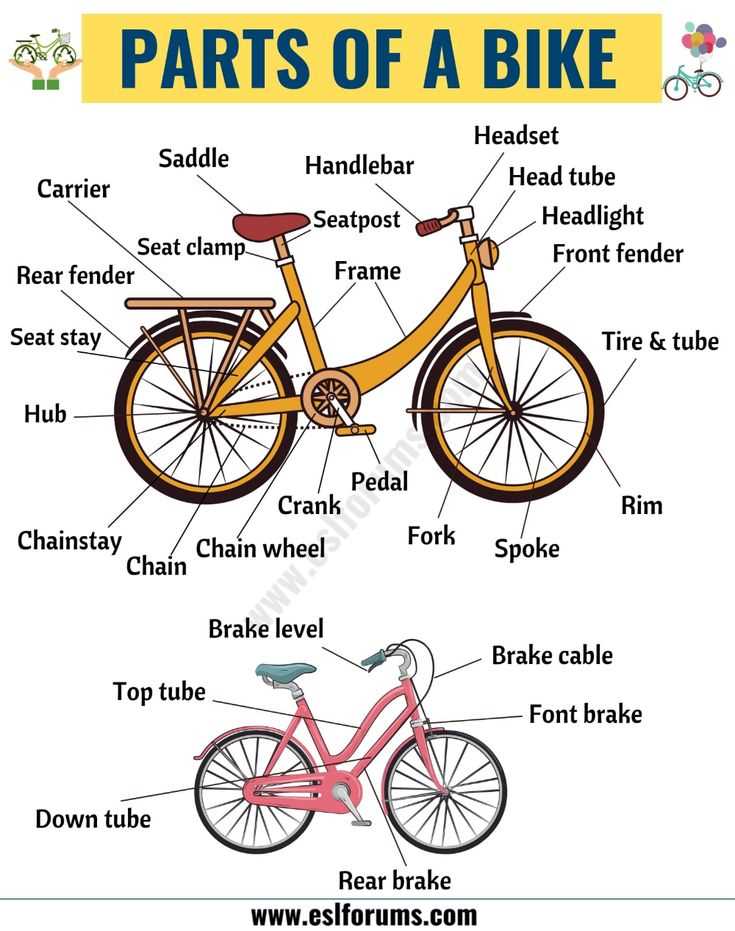
The structure that supports movement and balance is composed of several interconnected components, each contributing to its overall functionality. These elements work together to ensure smooth motion, distribute force evenly, and maintain stability during rides. Understanding how these parts interact can help improve performance and extend the lifespan of the mechanism.
Hub
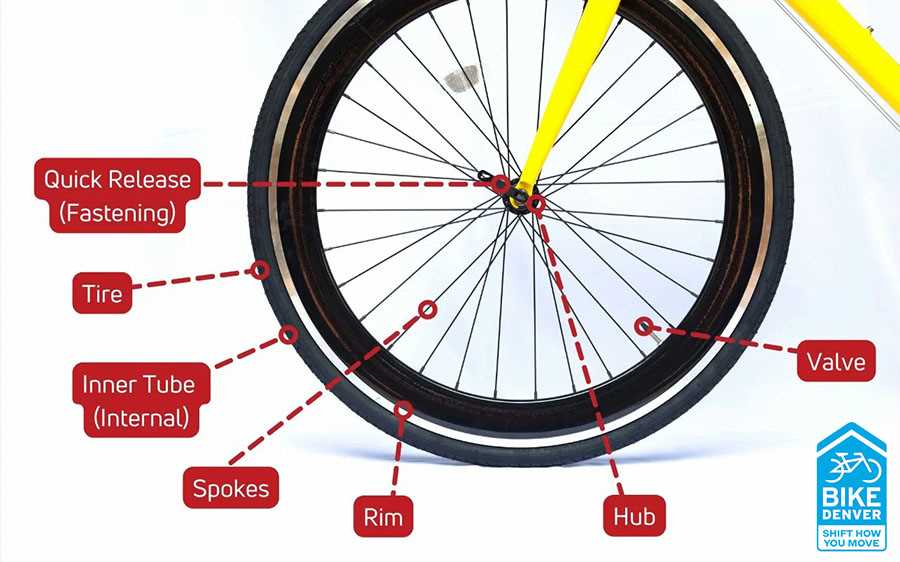
At the center lies the hub, a crucial component that connects the entire framework. It serves as the anchor point for other parts, allowing rotation and ensuring the smooth transition of energy. A well-maintained hub helps in achieving a seamless and efficient ride.
Rim
The rim forms the outer edge, providing the necessary foundation for movement. It supports the weight and ensures even pressure distribution across all surfaces. A strong and properly aligned rim is essential for both comfort and safety.
Spokes and Their Role in Stability
Spokes are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of a circular framework. They distribute force evenly across the rim, allowing the structure to handle significant pressure without deforming. By doing so, they ensure balance and durability during use, making the entire construction more resilient to external impacts.
When properly tensioned, these slender components work in harmony to absorb shocks and vibrations, preventing sudden damage. The tension in each spoke directly influences how well the entire system stays aligned, which is crucial for smooth, consistent performance.
Without properly functioning spokes, the framework would lose its shape, becoming vulnerable to collapse. Their role is crucial in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the whole mechanism, especially when subjected to rough conditions or prolonged use.
Rims: Structure and Importance
The rim plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall strength and integrity of a rotating system. Its design ensures stability and durability while supporting the tension required for proper performance. Understanding its composition and function is key to appreciating its impact on the performance of the entire setup.
- Material: Rims are often crafted from lightweight yet strong materials, which helps balance durability and efficiency.
- Shape: The contour and profile influence aerodynamics and how smoothly the system functions, making this an essential feature.
- Strength: Proper tension and structure provide stability, preventing distortion under pressure and heavy use.
The importance of rims cannot be overstated, as their design and condition directly affect not only performance but also safety during operation. Regular maintenance and understanding their role can significantly enhance longevity and functionality.
Hub Mechanism and Functionality
The hub serves as a crucial element in the overall assembly, enabling smooth rotational motion and supporting the structure’s efficiency. This component acts as a central point where various elements come together, allowing movement to be transferred seamlessly. Its internal workings are essential to ensuring consistent and stable performance, with each part playing a specific role in maintaining balance and control.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Axle | Provides a stable axis for rotation, maintaining alignment. |
| Bearings | Reduce friction during movement, enabling smoother operation. |
| Shell | Encases the internal parts, offering protection and structural support. |
| Spoke Flanges | Connect to other components, ensuring even distribution of tension. |
Types of Wheel Bearings
Understanding the various types of bearings is essential for ensuring optimal performance and durability in any rolling mechanism. These components play a critical role in reducing friction and supporting rotational movement, which enhances efficiency and responsiveness. Different designs cater to specific requirements and conditions, offering distinct advantages depending on the application.
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are among the most common types used in various applications. They consist of balls that are held in place between two races, allowing for smooth rotation. These bearings are well-suited for high-speed operations and are often preferred for their simplicity and reliability.
Roller Bearings

Roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers instead of balls to support loads. This design enables them to handle greater loads and provide better stability under pressure. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications and are often found in equipment where robustness is crucial.
| Type | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | High speed, low friction | Electric motors, fans |
| Roller Bearings | High load capacity, stability | Heavy machinery, automotive |
Axle Construction and Its Purpose
The axle is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the overall functionality of a vehicle’s movement system. This structural element connects two wheels, allowing them to rotate simultaneously while providing stability and support.
Design and Materials
Typically, axles are crafted from durable materials to withstand various stresses and strains during operation. The design may vary based on the specific requirements of the vehicle, but common characteristics include:
- Robust construction for enhanced strength
- Precision engineering to ensure smooth rotation
- Corrosion resistance to prolong lifespan
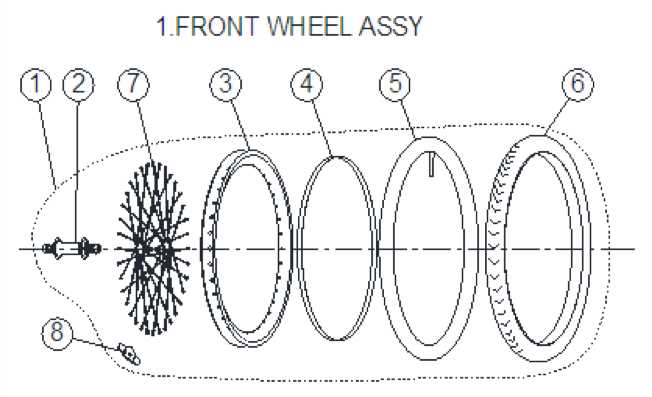
Functions of the Axle
The axle serves multiple essential functions, contributing to the overall performance and safety of the vehicle. Key purposes include:
- Supporting the weight of the vehicle and its load
- Facilitating the transfer of power from the drivetrain to the wheels
- Ensuring proper alignment and balance for effective handling
Understanding the construction and role of the axle can help in recognizing its importance in the efficiency and reliability of the overall system.
Valve Stem and Tire Inflation
The valve stem plays a crucial role in the maintenance of air pressure within a tire. It acts as a conduit for inflating and deflating the inner tube, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Proper understanding and handling of this component can significantly enhance the longevity and functionality of the entire system.
To maintain the desired air pressure, it is essential to regularly check and inflate the tire as needed. The valve stem allows for easy access to the air chamber, making the inflation process straightforward. Utilizing a reliable pump or compressor, one can achieve the correct pressure, which is vital for achieving stability and control during use.
Key points to consider:
- Ensure the valve stem is clean and free from debris before inflating.
- Check the pressure regularly to prevent under or over-inflation.
- Replace damaged or worn valve stems promptly to avoid leaks.
By paying attention to the valve stem and the inflation process, one can ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience, reducing the likelihood of issues that can arise from improper air pressure.
Exploring Different Tire Types

When it comes to choosing the right rubber for your ride, understanding the various options available can greatly enhance your experience on the road or trail. Each variety offers unique characteristics that cater to different preferences and conditions, making it essential to explore the distinctions among them.
Standard Tires are the most common type, designed for general use. They provide a balanced performance, offering decent traction and comfort on various surfaces. These are ideal for everyday activities, making them a popular choice among casual riders.
Performance Tires focus on speed and agility, featuring a smoother surface that reduces rolling resistance. They are typically lighter and may sacrifice some durability for enhanced efficiency, making them suitable for competitive environments.
All-Terrain Tires are engineered to handle diverse conditions, from paved roads to rugged trails. Their robust construction and tread patterns provide better grip and stability, ensuring a reliable performance regardless of the environment.
Studded Tires come equipped with metal spikes that enhance traction on icy or snowy surfaces. These are particularly beneficial during winter months, allowing for safer navigation in harsh weather conditions.
Understanding these variations allows individuals to select the most appropriate type for their riding style and the terrain they plan to traverse, ultimately improving overall performance and enjoyment.
Wheel Truing and Maintenance Tips

Maintaining optimal performance and safety is essential for any rider. Regular adjustments and upkeep of the circular components contribute significantly to a smoother and safer experience. This section provides valuable insights into achieving the perfect alignment and ensuring longevity through effective care techniques.
To keep your circular structure in excellent condition, consider the following recommendations:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Check for any visible damage or wear regularly. Look for bends, cracks, or loose fittings that could affect performance. |
| Proper Tension | Ensure that the tension of the spokes is consistent. Uneven tension can lead to misalignment and instability. |
| Use a Truing Stand | A dedicated tool can help accurately align the circular assembly. It allows for precise adjustments and can significantly improve performance. |
| Lubricate Components | Regularly applying appropriate lubricants to the moving parts helps reduce friction and wear, enhancing overall functionality. |
| Professional Assistance | Seek help from a qualified technician if unsure about adjustments or repairs. Professional servicing ensures safety and optimal performance. |
Common Issues with Wheel Components
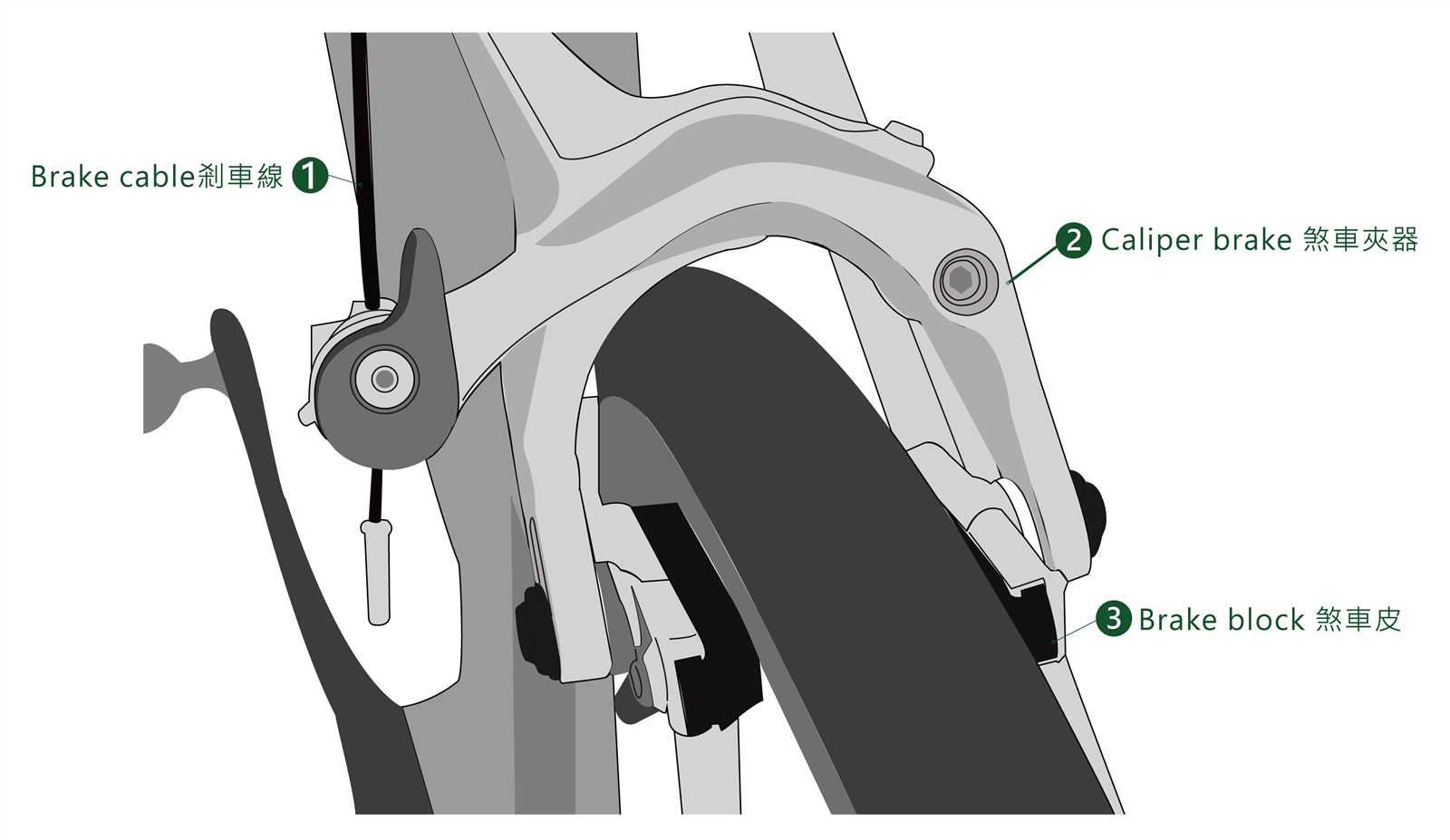
Various challenges can arise with the essential elements of a rolling mechanism, impacting its performance and safety. Understanding these issues is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and longevity.
- Improper Tension: Uneven or incorrect tension in spokes can lead to deformation or failure of the structure.
- Misalignment: Misalignment of the rim or hub may cause wobbling, affecting stability and ride quality.
- Brake Problems: Inadequate brake response due to worn pads or misadjusted calipers can compromise safety.
- Wear and Tear: Regular usage may lead to degradation of bearings and other critical components, requiring timely replacement.
- Inflation Issues: Incorrect air pressure can result in poor handling and increased risk of punctures.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to these challenges can help enhance the functionality and reliability of rolling mechanisms.