When it comes to maintaining a reliable off-road vehicle, knowing the various elements that make up its structure is essential. Every mechanical part has a role in ensuring the smooth performance and longevity of your vehicle. From the suspension to the engine, each piece is interconnected, forming a complex system that requires proper understanding.
In this article, we will explore the intricate setup of an all-terrain vehicle, detailing the connections and systems that contribute to its functionality. By breaking down the individual mechanisms, we aim to provide a clearer understanding of how everything works together to deliver both power and stability during off-road adventures.
Whether you’re looking to perform routine maintenance or replace specific elements, understanding how the different sections fit together will make the process more efficient. Let’s dive into the essentials of keeping your off-road machine in top shape.
2002 Yamaha Kodiak 400 Parts Overview
Understanding the key elements of this all-terrain vehicle is essential for maintaining its functionality and performance. Each mechanical piece plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle, contributing to both its durability and reliability on various terrains.
Key Components
The vehicle’s engine, transmission, and suspension are integral parts that provide the necessary power and control. Internal mechanisms such as the fuel system and braking assembly ensure efficient energy usage and safety. Maintaining these components in good condition is important for overall performance.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular attention to the drive system, exhaust, and electrical connections is essential to prolong the lifespan of the machine. Preventative care can prevent breakdowns and ensure the vehicle is always ready for rugged adventures.
Engine Components Breakdown
The internal structure of an engine consists of various interconnected elements that work in harmony to generate power. Understanding how these elements function together can help in maintaining and troubleshooting the system effectively.
Key Internal Elements
- Pistons and cylinders – central to the combustion process, converting fuel into mechanical movement.
- Crankshaft – transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational force.
- Camshaft – controls the opening and closing of valves, synchronizing the engine’s operation.
Other Essential Components
- Valves – regulate the flow of fuel and air into the engine and the expulsion of exhaust gases.
- Spark plug – initiates combustion by igniting the air-fuel mixture within the cylinder.
- Connecting rods – link the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting force to generate motion.
Understanding the Suspension System
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride over uneven terrain. It helps absorb shocks and vibrations, providing both comfort and control. Understanding its components and how they interact can help in maintaining or improving the vehicle’s performance.
Several key elements make up this system, each contributing to the overall handling and stability:
- Shock absorbers: These dampen the impact of bumps and dips, reducing the force transmitted to the frame.
- Springs: Responsible for supporting the vehicle’s weight and helping return it to its normal position after compression.
- Control arms: These maintain the proper alignment of the wheels and manage the range of motion.
- Bushings: They reduce friction between moving parts and help isolate vibrations.
Proper maintenance of the suspension system is vital to ensure the vehicle operates effectively on various types of terrain, offering both safety and comfort to the rider.
Electrical Parts and Wiring Diagram
Understanding the electrical components and the overall wiring system is crucial for maintaining the functionality of any all-terrain vehicle. The electrical system includes various elements responsible for powering different functions and ensuring smooth operation. By analyzing the layout of the wiring, one can troubleshoot issues, perform repairs, or even upgrade existing systems.
Main Electrical Components
Several key elements form the foundation of the electrical network. These include ignition systems, fuses, and switches that control the vehicle’s power flow. Each component plays a role in delivering energy from the battery to the engine and other critical areas. Identifying these parts is essential for diagnosing problems.
Wiring Structure and Connections
The wiring structure involves a complex network of cables and connectors that link the electrical components. A well-organized wiring system ensures efficient power distribution and minimizes potential failures. Understanding the connections between different systems helps in maintaining reliable operation.
Brake System Structure
The brake system in off-road vehicles plays a critical role in ensuring safety by providing reliable stopping power under various conditions. Understanding the basic components and how they work together helps maintain the vehicle’s performance. This section will cover the general layout of the braking system and its primary functions.
Main Components of the Brake System
At the core of the brake system are key parts that ensure proper deceleration. These include the master cylinder, calipers, brake pads, and rotors. Each component works in harmony to generate the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. The hydraulic pressure produced by the master cylinder is transferred to the calipers, which squeeze the brake pads against the rotors.
Hydraulic Operation and Maintenance
The brake system operates using hydraulic fluid, which amplifies the force applied to the brake pedal. Regular maintenance of the fluid levels and the inspection of the brake lines are essential for ensuring smooth and responsive braking. Leaks or air in the lines can significantly reduce efficiency and compromise safety.
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Master
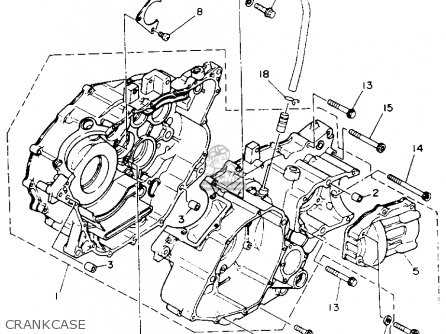
Chassis and Frame Parts Layout
The arrangement of structural components plays a crucial role in the overall performance and stability of an off-road vehicle. Understanding how these elements interact can enhance maintenance and repair efforts, ensuring longevity and optimal functionality.
Fuel System ConfigurationThe fuel system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of an all-terrain vehicle. It is designed to deliver the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal combustion and power output. Understanding the components and layout of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This configuration typically includes a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and injectors or carburetors, depending on the specific setup. Each part works together to ensure a steady flow of fuel, which is vital for the engine’s operation. Below is a simplified representation of the components involved in the fuel delivery process:
By regularly checking and maintaining these components, owners can ensure their vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Transmission Assembly and GearsThe transmission assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of any off-road vehicle, enabling smooth gear shifts and optimal power delivery. Understanding its components and their arrangement can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. Within the transmission, several key elements work together to ensure efficient operation:
Regular inspection of the transmission components can help identify wear or damage, ensuring reliable performance over time. Proper lubrication and timely replacements of worn parts are also vital for maintaining the integrity of the assembly. Exhaust System DiagramThe exhaust system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of any engine. Understanding its layout and components can help in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal functionality. Key elements of the exhaust assembly include:
Proper maintenance and inspection of these components can lead to improved engine performance and reduced emissions. Regular checks ensure that the system remains free from blockages and leaks, ultimately extending the lifespan of the vehicle. Steering Mechanism ComponentsThe steering mechanism is a crucial part of any vehicle, enabling precise control and navigation. Understanding its components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety. Various elements work together to create a responsive and effective steering system. Main Components
Additional Elements
Cooling System Parts ExplanationThe efficiency of an engine largely depends on its cooling mechanism, which ensures optimal operating temperatures and prevents overheating. This section will delve into the components responsible for maintaining the thermal balance, highlighting their functions and significance within the overall system. Key ComponentsAt the heart of the cooling assembly lies the radiator, a crucial element that dissipates heat generated by the engine. Coolant circulates through the engine, absorbing heat before flowing to the radiator, where it cools down. Hoses connect various components, ensuring the smooth transfer of coolant throughout the system. Cooling Fan and ThermostatThe cooling fan plays a vital role in enhancing airflow through the radiator, particularly during low-speed operations. Additionally, the thermostat regulates coolant flow based on temperature, opening and closing as needed to maintain an ideal thermal environment for the engine. |