
When it comes to maintaining a reliable and efficient vehicle, a clear understanding of its internal systems is crucial. Detailed breakdowns of the various elements can provide valuable insights for repairs, upgrades, or routine checks. These overviews help drivers and technicians identify key connections and configurations within the structure, ensuring that every element functions in harmony.
In this article, we will explore the intricate arrangement of essential mechanisms, highlighting how each section is interconnected. By focusing on the overall setup, we aim to simplify the navigation through the complex network of mechanical and electrical components, helping to facilitate repairs and maintenance tasks.
Whether you’re an enthusiast or a professional, gaining a deeper comprehension of these systems allows for a more informed approach when addressing specific challenges. By examining each key structure, you will be able to approach troubleshooting with confidence and accuracy.
Overview of Essential Components
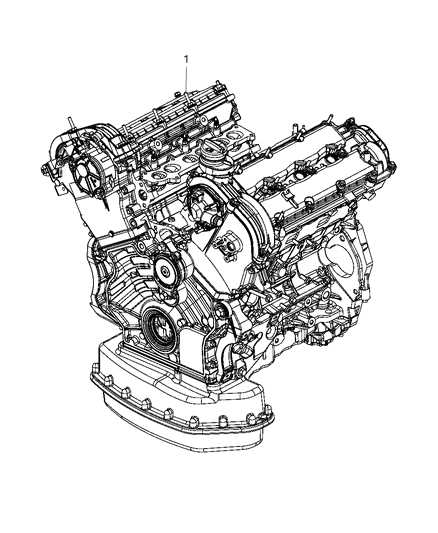
In any complex system, the efficiency and reliability largely depend on the proper functioning of several key elements. These vital components are designed to work together seamlessly, ensuring optimal performance across various operations. Understanding the role of each piece can help in diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, and improving overall functionality.
- Engine Assembly: The core of the system, responsible for generating power and ensuring smooth operation under different conditions.
- Transmission Unit: Manages the distribution of power, ensuring that the system adapts to varying speeds and loads efficiently.
- Electrical System: Controls various electronic functions, ensuring proper communication between different subsystems.
- Cooling Mechanism: Keeps temperatures regulated, preventing overheating and ensuring longevity.
- Steering and Suspension: These parts ensure stability, control, and a comfortable experience during operation.
- Braking System: Ensures safety by providing reliable stopping power in different environments.
Each of
Electrical System Layout Explanation
The electrical framework of a vehicle is a complex network that ensures the seamless functioning of various components. This system coordinates the distribution of power to all essential modules, ensuring that everything from lighting to control units operates efficiently. It connects key parts, distributing energy and enabling communication between different systems.
Main Components and Connections
- Power Distribution Center – Manages and allocates energy to crucial elements.
- Battery – Stores and supplies the initial power required to start and run various subsystems.
- Alternator – Continuously charges the battery while the engine is running, maintaining energy levels.
- Ground Connections – Ensures stability in electrical circuits, preventing overload or malfunction.
Communication and Control
Communication between the systems is facilitated by a series of control units that process and relay signals. These control modules are interconnected through a network, allowing real-time monitoring and adjustments to enhance performance. For instance, sensors feed information to the control units, which then send commands to adjust various functions.
- Sensors – Provide data from various systems for processing.
- Control Modules – Act as the brain of the electrical network, processing signals and adjusting components.
- Wiring Harness – The physical pathway for electrical signals and power, connecting
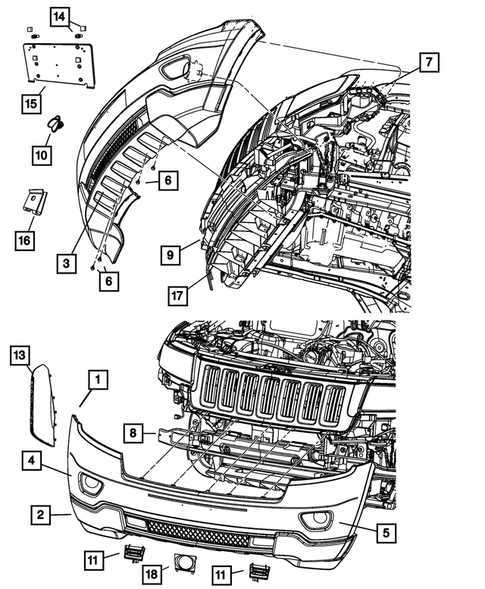
Engine Bay Structure and Key Parts
The layout under the hood is designed for efficient performance and accessibility. It encompasses various essential components that work together to ensure the smooth operation of the vehicle. Understanding the configuration can help with maintenance and troubleshooting, making it easier to locate specific elements when necessary.
- Power Unit: The central piece of the system, responsible for generating the necessary force to drive the vehicle.
- Cooling System: This section helps regulate the temperature of the main machinery, preventing overheating during extended use.
- Airflow Components: Elements responsible for delivering fresh air to the power system, ensuring optimal combustion and performance.
- Electrical Modules: Various units in charge of supplying energy and maintaining electronic functions.
- Fluid Reservoirs: Tanks that store necessary liquids, such as oil and coolant, for proper system lubrication and cooling.
The engine bay’s structure is a carefully organized system, allowing for easy access to each component for repair or replacement when needed.
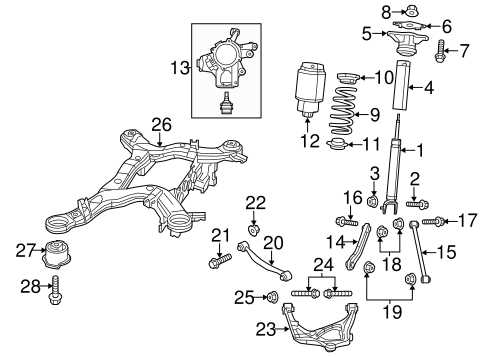
Suspension Elements and Their Placement
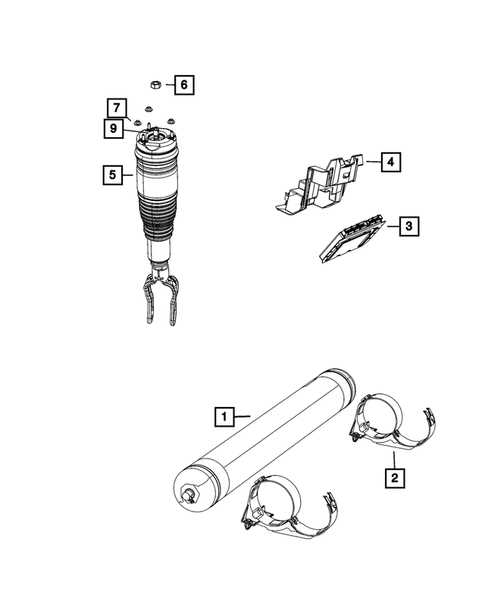
The system of components responsible for vehicle stability and comfort is a crucial part of its overall functionality. These elements work together to absorb shocks from the road surface, maintain tire contact, and ensure smooth operation. Understanding where each of these components is located helps to better grasp their role in providing a safe and controlled ride.
Control arms are integral for managing the movement of the wheels. Typically connected to both the wheels and the frame, they allow controlled vertical movement while minimizing side-to-side motion.
Shocks and struts serve as the primary means of absorbing impact. Positioned near each wheel, they reduce the force from road irregularities, providing a comfortable ride.
Another essential component, the sway bar, connects both sides of the suspension. Its function is to limit body roll during turns, enhancing stability and cornering performance.
Springs, either coil or leaf types, are strategically placed to bear the vehicle’s weight while allowing for controlled motion. These springs compress and expand as the vehicle moves, assisting in shock absorption.
All of these elements are strategically located to ensure maximum efficiency and balance, contributing to both the performance and safety of the vehicle.
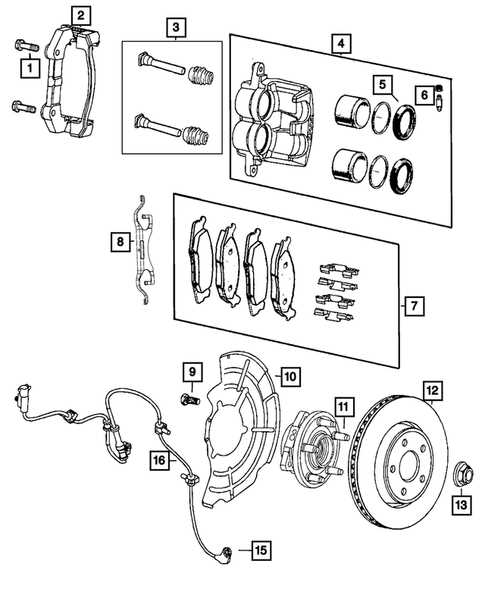
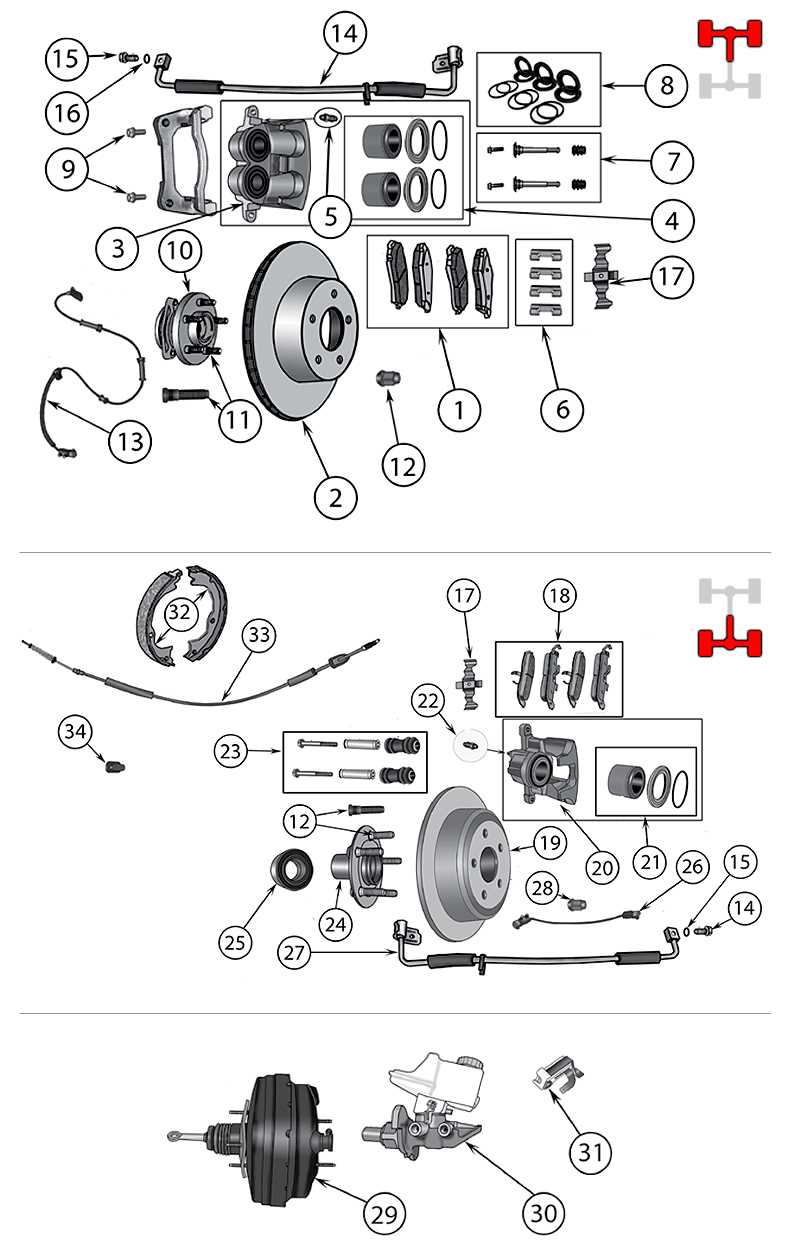
Brake System Components and Locations
The brake system plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle safety by providing the necessary control during various driving conditions. Understanding the key elements involved in this system and their positions within the vehicle helps to maintain optimal functionality and avoid potential failures.
Primary Components
The essential parts include the hydraulic unit, calipers, pads, and rotors. The hydraulic unit distributes force to the wheels, ensuring effective stopping power. Calipers, which house the pads, engage the rotors to slow down the movement when the brake pedal is pressed. These components work together to reduce speed and bring the vehicle to a halt.
Locations and Functionality
The hydraulic unit is typically positioned near the engine bay, while calipers and rotors are attached directly to each wheel. Brake lines run throughout the vehicle, transmitting pressure from the master cylinder to each wheel, activating the calipers. Regular maintenance and inspection of these elements are essential to ensure their proper operation and prevent wear-related issues.
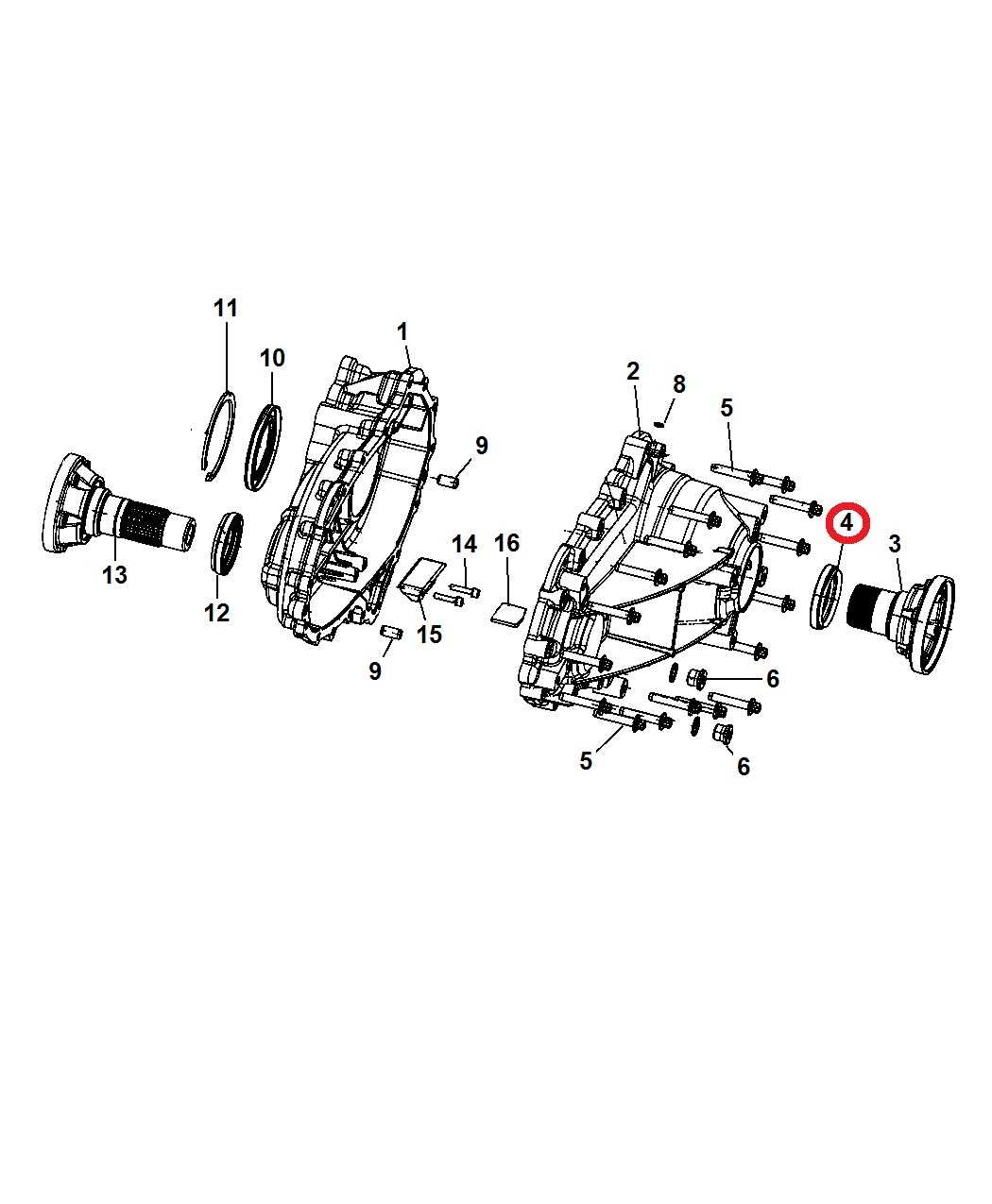
Transmission System Parts Overview

The transmission system is a vital component of any vehicle, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. It consists of various elements that work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding the key components of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Transmission Assembly: This is the main unit that houses all the gears and components necessary for changing the vehicle’s speed and torque. It operates by engaging different gears based on the driver’s input and the vehicle’s speed.
Torque Converter: Located between the engine and the transmission, this component allows for a smooth transition of power by multiplying engine torque. It plays a crucial role in enabling the vehicle to come to a stop without stalling.
Gear Sets: These are responsible for changing the gear ratios, allowing the vehicle to accelerate and decelerate efficiently. Different gear sets are engaged based on the driving conditions and speed requirements.
Control Module: This electronic unit manages the operation of the transmission, ensuring that the right gears are engaged at the appropriate times. It utilizes various sensors to monitor performance and adjust settings for optimal efficiency.
Fluid Pump: Essential for lubricating and cooling the transmission components, the fluid pump circulates transmission fluid throughout the system. Proper fluid levels and quality are crucial for maintaining transmission health.
Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can significantly extend the lifespan of the transmission system and enhance overall vehicle performance.
Fuel System Components Arrangement

The layout of the components within the fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. A well-organized configuration allows for smooth fuel flow, precise pressure regulation, and effective filtration, contributing to the overall functionality of the vehicle. Understanding this arrangement is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components Overview
Key elements of the fuel system include the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel lines, fuel filter, and injectors. Each component has a specific function and is strategically placed to maximize efficiency. The fuel tank serves as the reservoir, while the pump transports the fuel to the engine. Filters are integrated to remove impurities, ensuring only clean fuel reaches the injectors, which deliver the precise amount of fuel to the combustion chamber.
When analyzing the arrangement, it is important to consider the proximity of components to reduce the risk of fuel pressure loss and vapor lock. The layout should also allow for easy access during servicing. Proper insulation and routing of fuel lines are essential to prevent leaks and maintain safety standards. Understanding these aspects can aid in diagnosing issues and implementing effective solutions.
Cooling System Layout and Key Parts
The efficiency of a vehicle’s thermal management is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the arrangement of the cooling system components is essential for maintaining engine temperature and preventing overheating. This section delves into the fundamental elements that make up this vital system.
The cooling mechanism typically comprises several core components, each playing a significant role. The radiator is responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant throughout the engine. Additionally, hoses connect these parts, ensuring the fluid flows smoothly. Thermostats regulate the coolant temperature, opening and closing as needed to maintain an ideal operating range. Lastly, fans assist in airflow, enhancing the cooling process, especially during low-speed operations or when the engine is under heavy load.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to prevent potential failures. Identifying leaks in hoses, checking the condition of the radiator, and ensuring the proper functioning of the water pump can save considerable time and resources. Understanding the layout and function of the cooling system components empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs.
Steering Mechanism Parts Breakdown
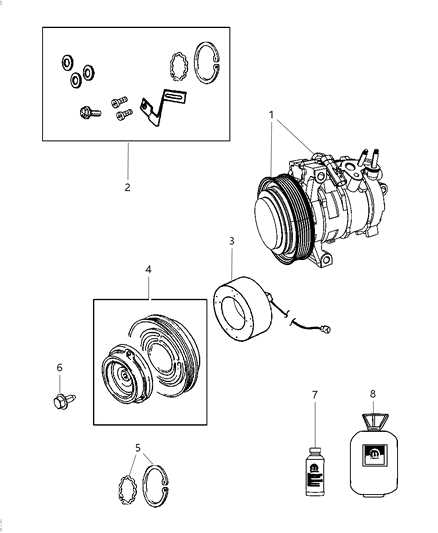
The steering system plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle control and handling. Understanding the various components involved in this mechanism can significantly enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the essential elements that contribute to the effective functioning of the steering assembly.
Key Components of the Steering System
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface through which the driver directs the vehicle.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the gear mechanism, transmitting driver input.
- Steering Gearbox: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels.
- Linkage System: Comprises various rods and joints that facilitate movement from the gearbox to the wheels.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic assistance, reducing the effort needed to turn the wheel.
Additional Components
- Steering Rack: A key element in rack-and-pinion systems, responsible for converting rotational motion into linear motion.
- Ball Joints: Allow for smooth movement and articulation between different parts of the steering linkage.
- Control Arms: Connect the steering components to the vehicle’s chassis, aiding in stability and handling.
- Tie Rods: Transmit force from the steering gear to the wheels, ensuring precise control.
Awareness of these components not only aids in effective repairs but also ensures optimal performance and longevity of the steering mechanism.
Interior Parts and Their Locations
Understanding the layout and arrangement of various components within the cabin is essential for both maintenance and enhancement of functionality. Each element plays a significant role in providing comfort, convenience, and safety to occupants. This section will explore the different fixtures found inside the vehicle and their specific placements, making it easier to identify and access them when needed.
The central console is typically positioned between the front seats, housing controls for the entertainment system and climate management. The dashboard, located directly in front of the driver, displays crucial information through gauges and screens. Door panels, situated on both sides, contain storage compartments and controls for windows and locks.
Seats, strategically placed throughout the interior, provide comfort and support. The front seats often come with adjustable features, while the rear seats may include folding mechanisms to optimize cargo space. The headliner, which forms the upper surface of the cabin, helps with insulation and aesthetic appeal. Lastly, various trim pieces and accent elements enhance the overall look, contributing to the vehicle’s interior design.
Exhaust System Components Overview
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of any vehicle. It is designed to direct harmful gases away from the engine and cabin while minimizing noise. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for maintenance and optimization of engine function.
Main Elements of the Exhaust System
At its core, the exhaust system consists of several key components, each contributing to the effective expulsion of exhaust gases. The manifold is the starting point, collecting gases from the engine’s cylinders. From there, these gases flow through the catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions before they exit the system.
Additional Components and Their Functions
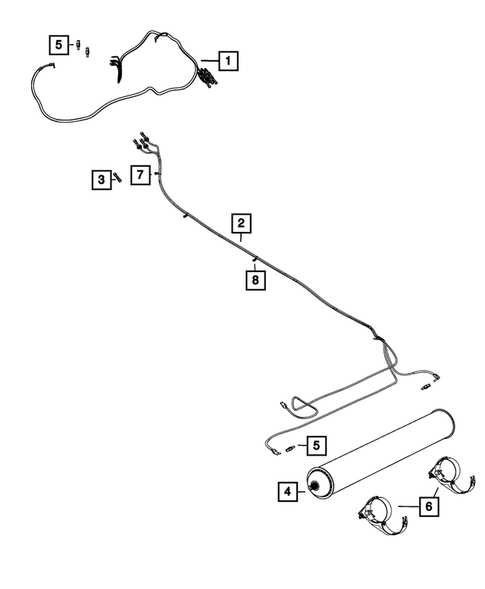
Following the catalytic converter, the exhaust gases travel through the muffler, which helps to dampen noise. Finally, the gases are expelled through the tailpipe, completing the journey. Each component is engineered to work in harmony, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with environmental regulations.
Drivetrain and Axles Layout
The arrangement of the power transmission system and axle components plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and stability of the vehicle. This section delves into the intricate layout that connects the engine’s output to the wheels, facilitating smooth movement and control.
Understanding the Configuration is essential for those interested in automotive mechanics. The drivetrain encompasses various elements, including the transmission, driveshafts, differentials, and axles, which collectively work to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. The configuration may vary based on design choices, impacting handling characteristics and overall efficiency.
Typically, a four-wheel drive system incorporates a transfer case that divides power between the front and rear axles. This setup enhances traction, especially on challenging terrains. Additionally, the axle assemblies can be categorized into front and rear components, each designed to handle specific load distributions and torque requirements.
Moreover, the choice of differential type–whether open, limited-slip, or locking–affects how power is distributed among the wheels during acceleration and cornering. A thorough comprehension of these elements is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting, as each component contributes to the vehicle’s overall functionality.