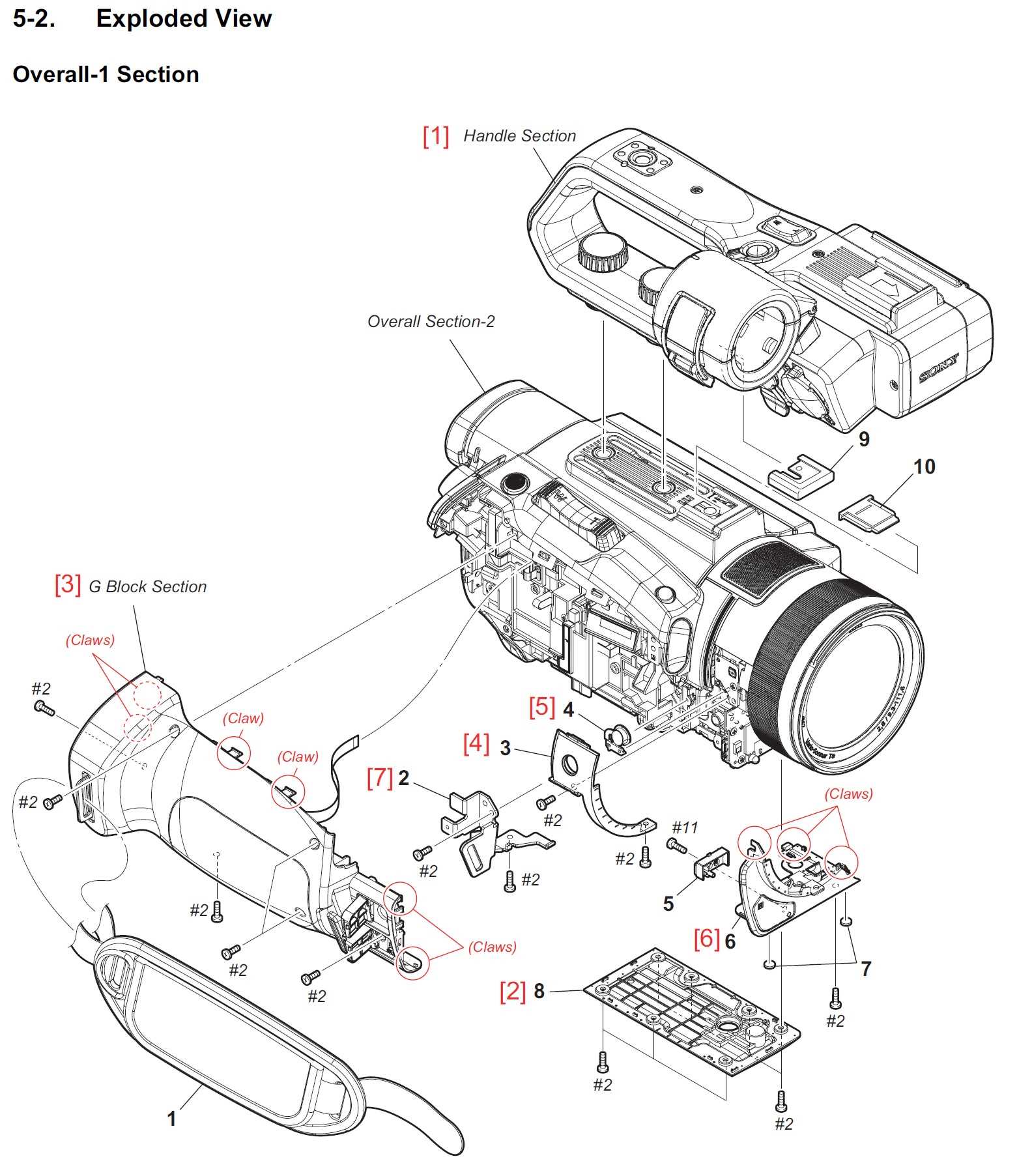
In the world of visual technology, the intricate mechanisms that contribute to capturing stunning imagery play a crucial role. Each element is designed to function harmoniously, ensuring that moments are immortalized with clarity and precision.
From the initial light entry to the final capture, every segment serves a unique purpose. This exploration aims to unveil the significance of these elements, highlighting their contributions to the overall functionality and quality of the resulting images.
As we delve deeper into this fascinating realm, we will uncover the ultimate interplay between various components, providing insights into how they work together to achieve outstanding photographic results.
Understanding Camera Components
To fully appreciate the art of photography, it is essential to grasp the various elements that contribute to the creation of stunning visuals. Each component plays a pivotal role in capturing light and transforming it into beautiful images. This section will explore the fundamental elements that make up this intricate device.
Key Elements
- Lens: Responsible for focusing light onto the sensor.
- Shutter: Controls the duration of light exposure.
- Sensor: Converts light into electronic signals.
- Viewfinder: Allows the user to frame the shot.
- Body: Houses and protects the internal components.
Functionality
Each element works harmoniously to produce an image. Understanding how they interact can enhance the creative process:
- Light enters through the lens.
- The shutter opens and closes to manage exposure.
- The sensor captures the light and creates an image.
Essential Parts of a Camera
Understanding the fundamental components of a photographic device is crucial for mastering the art of capturing images. Each element plays a specific role in the overall functionality and performance of the equipment.
- Lens: The optical system that focuses light onto the sensor.
- Sensor: Converts light into electronic signals for image processing.
- Shutter: Controls the duration of light exposure to the sensor.
- Viewfinder: Allows the user to frame and compose the shot.
- Body: The main structure housing all the essential components.
Each of these elements works in harmony to create the ultimate photographic experience, ensuring that every image captures the intended moment with clarity and precision.
The Role of the Lens
The lens serves as a critical component in optical devices, significantly influencing how images are captured and represented. It determines clarity, focus, and the overall quality of the visual output, making its design and function essential for effective imaging.
Functions of the Lens
- Focusing Light: It directs and concentrates light onto the sensor, ensuring sharp images.
- Controlling Exposure: It helps manage the amount of light entering, affecting brightness and detail.
- Creating Depth of Field: It enables the distinction between foreground and background, adding artistic depth.
Types of Lenses
- Prime Lenses: Fixed focal lengths offering superior image quality.
- Zoom Lenses: Variable focal lengths providing versatility in framing.
- Wide-Angle Lenses: Allowing for expansive scenes and greater context.
- Telephoto Lenses: Ideal for capturing distant subjects with detail.
Image Sensor Explained
The image sensor is a critical component that plays a vital role in the process of capturing visual information. It acts as the medium through which light is transformed into electronic signals, enabling the creation of digital representations of the surrounding world. Understanding its functionality helps to appreciate the intricacies of modern photography and videography.
How It Works
At its core, the sensor is composed of millions of tiny light-sensitive elements known as pixels. When light hits these pixels, it generates an electrical charge proportional to the intensity of the incoming light. This charge is then converted into digital data, allowing for the formation of an image. The sensitivity of the sensor, which influences its performance in varying lighting conditions, is a key aspect that determines overall image quality.
Types of Sensors
There are primarily two types of sensors used in imaging devices: CMOS and CCD. CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors are known for their low power consumption and faster processing speeds, making them popular in many consumer devices. On the other hand, CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensors are renowned for their superior image quality, especially in professional settings, due to their ability to capture finer details and colors accurately. Each type has its advantages, catering to different needs and preferences in the field of imaging.
Shutter Mechanism Overview
The shutter mechanism plays a crucial role in regulating light exposure, impacting the final image captured. It functions as a gate, controlling the duration and timing of light entering the sensor. Understanding this element is essential for grasping the intricacies of photographic technology.
Types of shutters vary, with some offering rapid response while others allow for gradual openings. Each type brings unique advantages, influencing not only the image quality but also the overall experience of capturing a moment.
The mechanism typically consists of several components working in harmony. When triggered, these parts operate to create a seamless flow of light, ensuring that the sensor receives the intended amount at the right moment.
In essence, the effectiveness of this mechanism can ultimately enhance the creative possibilities for photographers, enabling them to delve deeper into their craft.
Importance of the Viewfinder
The viewfinder serves as a crucial element in the process of capturing images, providing a direct connection between the photographer and the scene being framed. It enhances the overall shooting experience by allowing users to compose shots with precision and focus on key details, ensuring the final output aligns with their creative vision.
Enhanced Composition
Utilizing the viewfinder allows for better composition techniques, helping photographers achieve balanced and aesthetically pleasing shots. Key advantages include:
- Framing: It aids in framing subjects effectively, ensuring that all elements are appropriately positioned.
- Perspective: Photographers can assess depth and angle, which are essential for dynamic imagery.
- Distraction Minimization: By blocking out distractions in the surrounding environment, it allows for better concentration on the subject.
Focus and Precision
In addition to composition, the viewfinder is vital for achieving sharp focus. Its importance can be highlighted through several factors:
- Manual Focus: It offers a clearer view when adjusting focus manually, crucial for detailed shots.
- Real-Time Feedback: Users can see the effect of adjustments instantly, leading to quicker corrections.
- Low-Light Performance: In dim conditions, the viewfinder often provides a more accurate representation than screens.
In conclusion, the viewfinder not only enhances the technical aspects of image capture but also enriches the creative process, making it an indispensable tool for photographers of all skill levels.
Function of the Flash Unit
The flash unit plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of images by providing additional illumination in low-light conditions. Its primary purpose is to produce a brief burst of light, allowing the sensor to capture clearer and more vibrant visuals. This enhancement can transform a scene, ensuring that details are visible even in challenging lighting situations.
When activated, the unit emits a powerful flash that synchronizes with the shutter mechanism, illuminating the subject at the moment of exposure. This synchronization is vital for preventing overexposure or underexposure, creating a balanced and well-lit photograph. Furthermore, the flash can be adjusted in intensity, enabling photographers to control the amount of light based on the environment and desired effect.
In addition to basic illumination, the flash unit can also serve creative purposes. Techniques such as fill flash can soften shadows, while bouncing the light off surfaces can create a more natural appearance. Advanced models may offer features like multiple flash modes, allowing for versatility in various shooting scenarios.
Ultimately, the flash unit is an essential tool for achieving professional-quality images, ensuring that photographers can work effectively in diverse lighting conditions and capture moments with clarity and detail.
Battery and Power Supply Basics
The functionality of any imaging device relies heavily on its energy source. Understanding the essentials of power systems enhances the overall performance and longevity of the equipment. This section explores key components that contribute to efficient energy management.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery Type | Different chemistries affect energy density, weight, and recharge cycles. |
| Voltage Rating | Determines compatibility with various devices and overall performance. |
| Capacity | Measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), indicating how long the device can operate. |
| Charger | Essential for replenishing energy, with specifications affecting charge speed and efficiency. |
| Power Management | Systems that optimize energy consumption to prolong usage time. |
Body Structure and Design
The construction and aesthetics of photographic devices play a crucial role in their functionality and user experience. This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the overall structure, emphasizing how design influences performance and usability.
Key Features of the Body
- Material selection for durability and weight
- Ergonomic design for comfortable handling
- Placement of controls for accessibility
Aesthetic Considerations
- Color and finish options
- Shape variations to cater to different styles
- Integration of visual elements for brand identity
Ultimately, the design and structure are fundamental in enhancing both the appeal and functionality of these devices, allowing users to capture moments with ease and creativity.
Connecting Accessories to Cameras
Integrating additional components into your photography setup can greatly enhance functionality and creativity. By connecting various tools, users can tailor their devices to suit specific shooting conditions, allowing for more versatility in capturing images.
Types of Accessories
Numerous enhancements can be added, ranging from external flashes and microphones to filters and tripods. Each accessory serves a unique purpose, enhancing the overall experience and the quality of the results. Understanding the intended use of each item is essential for maximizing effectiveness.
How to Connect Accessories
Typically, external items can be attached via designated ports or mounts. It’s crucial to ensure compatibility before making connections. Proper installation not only ensures optimal performance but also safeguards the primary device from potential damage. Regularly checking connections and settings can help maintain seamless operation during shoots.
By exploring and incorporating various tools, photographers can unlock new creative possibilities and improve their skill set significantly.
Innovations in Camera Technology
Recent advancements have transformed the world of imaging, enhancing how we capture moments and express creativity. These breakthroughs not only improve image quality but also expand possibilities for users across various fields.
Key Developments
- Enhanced sensor technology for better low-light performance.
- Integration of artificial intelligence for intelligent scene recognition.
- Improved autofocus systems for precision in fast-moving scenarios.
Emerging Trends
- Compact designs that maintain high performance.
- Wireless connectivity for seamless sharing and control.
- Advanced video capabilities, including 8K recording.