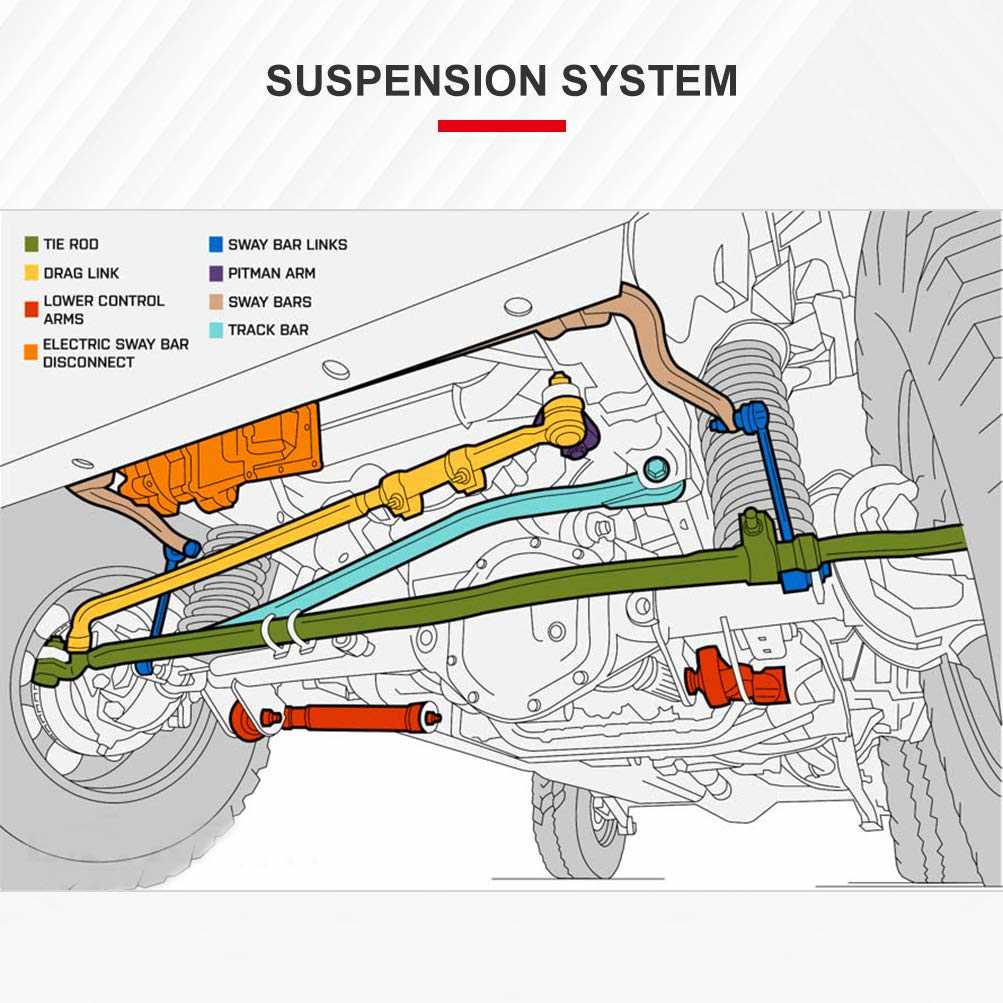
When it comes to maintaining a heavy-duty pickup, one crucial aspect is understanding the various elements involved in the steering and support system. Knowing how these components work together ensures a smooth and stable ride, especially when tackling challenging terrains or carrying heavy loads. An accurate comprehension of the key elements can greatly aid in identifying potential issues and performing necessary repairs.
The suspension and steering setup plays a vital role in the vehicle’s overall performance. Various interconnected elements work to absorb shocks, support the weight, and facilitate responsive steering. Each part has its unique function, contributing to the overall stability and handling. Recognizing these elements and their interactions is essential for effective upkeep.
Regular inspection of the steering and support system helps prevent wear and tear that can compromise safety. By familiarizing oneself with the layout and function of these key components, it becomes easier to detect any signs of deterioration and address them promptly, ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance on the road.
2001 Ford F350 Front End Parts Diagram
The structural components and essential mechanisms located at the vehicle’s leading section are vital for maintaining stability and steering precision. Understanding the arrangement and function of these elements can aid in troubleshooting issues, ensuring proper maintenance, and improving the driving experience. This guide outlines the key components, their roles, and typical signs of wear to look out for during inspections.
Key Components and Their Functions
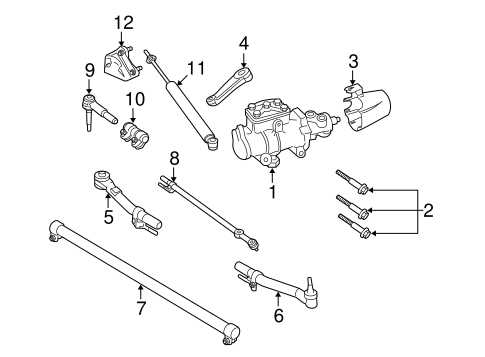
- Suspension Elements: These components are responsible for absorbing shocks from the road, ensuring a smoother ride and consistent tire contact with the surface.
- Steering Mechanisms: Essential for directional control, these parts include connections that transfer movement from the wheel to the vehicle’s road wheels.
- Structural Supports: Reinforce the stability of the vehicle, especially during turns or when driving on uneven surfaces.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check for signs of rust or corrosion that could compromise component integrity.
- Inspect for unusual noises during turns, which may indicate wear in the steering system.
- Ensure proper alignment to avoid uneven tire wear, which can signal underlying problems.
Keeping the leading section well-maintained ensures safety and extends the lifespan of the vehicle’s essential systems. Regular checks and timely repairs can help prevent major issues and enha
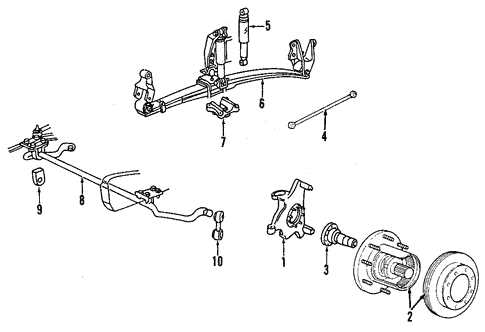
Identifying Front Suspension Components
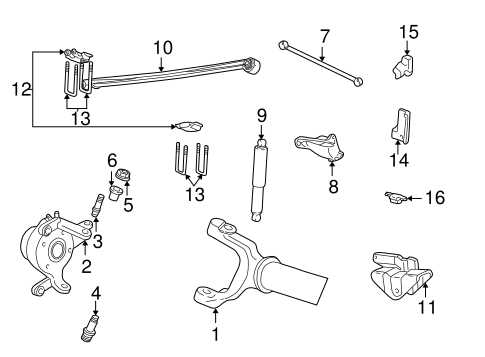
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride, absorbing shocks and maintaining wheel alignment. To understand the various elements that make up this system, it’s essential to recognize the key components that contribute to handling and safety. Each element has a unique function, working together to provide balance and control on the road.
Common Suspension Elements
Several parts work in unison to support the vehicle’s weight and manage movement. These components help absorb road irregularities and allow for proper steering. Below is a list of typical suspension elements and their functions.
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | Control the movement of the suspension and prevent excessive bouncing. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Control Arms | Connect the wheels to the frame and allow for up-and-down motion. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ball Joints | Enable pivoting between the steering knuckles and control arms, providing flexibility. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stabilizer Bar | Reduces body roll during cornering by linking opposite sides of the suspension. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coil Springs | Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb impacts from the road. |
| Component | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheel Bearings | Allow the wheel to rotate with minimal friction, supporting the vehicle’s weight. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hub Assembly | Connects the wheel to the suspension, serving as a mounting point for the wheel and brake components. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brake Rotor | Works with the brake pads to slow or stop the wheel’s rotation by creating friction. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stud Bolts | Provide secure attachment for the
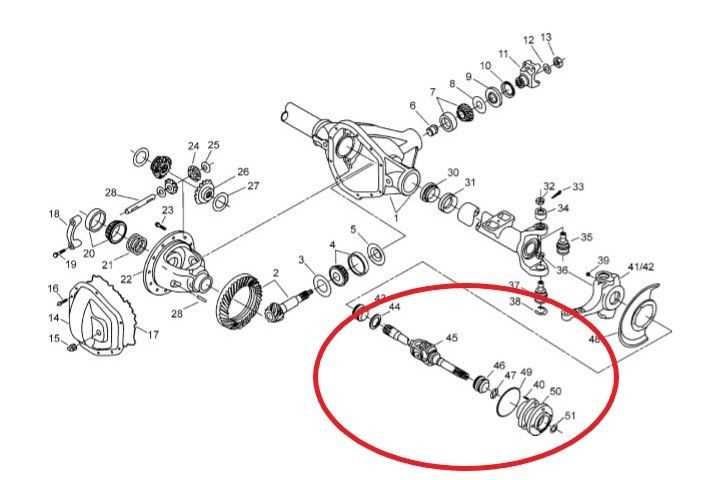
Front Axle Parts BreakdownThis section offers a comprehensive overview of the components associated with the front axle assembly of a heavy-duty vehicle. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal performance and safety on the road. Key Components Overview
The axle assembly is comprised of several crucial components that work in harmony to facilitate vehicle movement and stability. Key elements include the differential, which allows for varying wheel speeds during turns, and the wheel hubs, which support the weight of the vehicle while allowing wheels to rotate freely. Additional components such as bearings and seals play vital roles in reducing friction and preventing contaminants from entering sensitive areas. Assembly and Maintenance ConsiderationsProper assembly and maintenance of these components are critical for the longevity of the axle system. Regular inspection of seals and bearings helps to prevent leaks and wear, while ensuring that all connections are secure. When replacing or servicing these elements, it is advisable to follow manufacturer specifications to maintain vehicle integrity and performance. Bumper and Grille ConfigurationThe arrangement of the front protection and decorative elements plays a crucial role in the overall aesthetic and functionality of a vehicle. This section delves into the key components that define this section of the vehicle, focusing on their design, materials, and integration. Key Components
Material Considerations
When selecting materials for these components, factors such as weight, strength, and corrosion resistance come into play. Common materials include:
Understanding the configuration of the front protective and decorative elements is vital for ensuring proper maintenance and upgrades. This knowledge allows vehicle owners to make informed decisions when addressing aesthetic and functional needs. Headlight Assembly Components GuideThe headlight assembly plays a crucial role in vehicle safety and visibility, encompassing various elements that work together seamlessly. Understanding these components not only aids in maintenance but also enhances the ability to troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Each part contributes to the overall functionality, ensuring that drivers can see and be seen in different driving conditions. Key Elements of the Headlight AssemblyAt the core of the assembly is the housing, which provides structural support and protection for internal components. It encases the lens and secures the light source, often made of durable materials designed to withstand the rigors of road use. Complementing the housing are the reflectors, which are essential for directing light efficiently. These components amplify illumination, enhancing visibility during nighttime or adverse weather conditions. Lighting Sources and Additional ComponentsThe assembly also incorporates the light bulbs, which are available in various types, including halogen, LED, and xenon. Each type offers distinct advantages regarding brightness, energy efficiency, and longevity. Additionally, other critical parts include the wiring harness, responsible for delivering power, and the adjustment screws, which allow for precise alignment of the headlights. Properly functioning components ensure optimal performance and contribute to a safer driving experience. Radiator and Cooling System PartsThe cooling assembly plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient operation. This system comprises various components that work together to regulate coolant flow, dissipate heat, and maintain performance under varying conditions. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Tracking Down Frame ComponentsIdentifying and locating essential structural elements in a vehicle’s undercarriage is crucial for maintaining performance and safety. Understanding the layout and functionality of these components helps ensure proper repairs and replacements, enhancing the overall reliability of the vehicle. This process involves a thorough examination of various elements, allowing enthusiasts and mechanics to better appreciate the intricacies of automotive design. Understanding Structural IntegrityThe framework of any automobile serves as its backbone, providing stability and support. Familiarizing oneself with the different components, such as crossmembers, reinforcements, and mounts, is vital for diagnosing issues effectively. Each element plays a specific role in maintaining the vehicle’s structure, and recognizing their positions can aid in troubleshooting and repairs. Utilizing Resources for IdentificationConsulting reliable manuals, diagrams, or online forums can significantly assist in identifying and locating frame components. Engaging with experienced mechanics or automotive enthusiasts can also provide valuable insights. These resources not only enhance understanding but also facilitate informed decisions when it comes to purchasing replacements or upgrades. Shock Absorber Mounting LocationsUnderstanding the positioning of shock absorber attachments is crucial for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and stability. These components play a significant role in dampening road impacts, thus contributing to a smooth driving experience. Proper mounting is essential for maintaining alignment and enhancing the overall lifespan of the suspension system. Key Locations for Mounting
Considerations for Installation
Fender and Body Panel StructureThe outer shell of a vehicle plays a vital role in both aesthetics and protection. This section delves into the composition and function of fenders and body panels, highlighting their significance in the overall design and durability of the vehicle. Fender OverviewFenders serve as essential components that frame the wheel wells. Their primary responsibilities include:
Body Panel FunctionsThe body panels encompass various sections of the vehicle, each designed to fulfill specific roles:
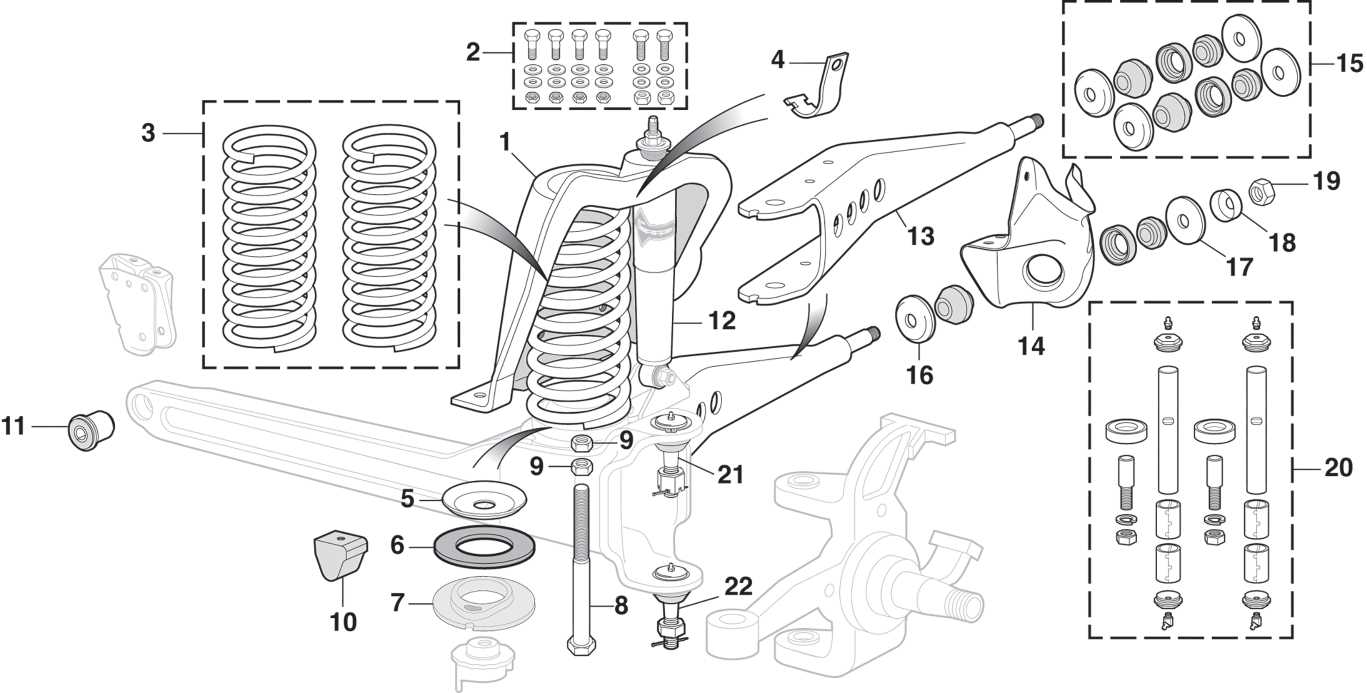
Understanding the structure and function of these elements is crucial for maintenance and modifications, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and functionality are preserved. Tie Rod and Ball Joint Details
The steering system plays a crucial role in vehicle control and stability. Essential components like the tie rod and ball joint contribute significantly to the overall performance of the steering mechanism. Understanding the functions and characteristics of these components is vital for effective maintenance and repair. The tie rod connects the steering rack to the steering knuckle, facilitating the transfer of motion. It is designed to withstand substantial forces while maintaining precise alignment. The ball joint, on the other hand, serves as a pivot point between the tie rod and the suspension system, allowing for smooth movement and flexibility in response to road conditions.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of these components are essential to ensure optimal steering performance. Worn or damaged tie rods and ball joints can lead to steering misalignment and compromised vehicle handling, highlighting the importance of routine maintenance. |