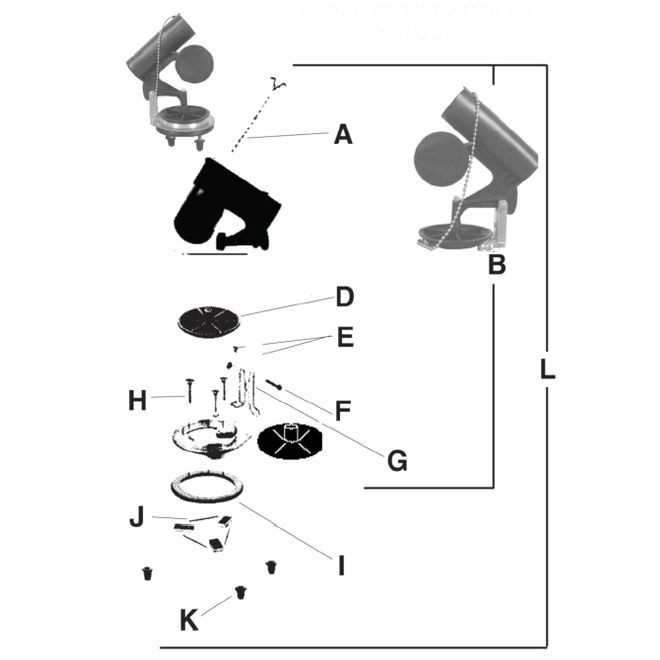
Understanding the internal workings of household fixtures helps ensure they function properly and last longer. This guide offers insights into key elements found in common water-operated devices used in washrooms. Familiarity with these components can aid in resolving performance issues efficiently.
Valves, seals, and connectors are integral to smooth operation, and knowing how they interrelate can prevent potential breakdowns. Identifying these individual elements makes it easier to maintain and repair them without professional assistance.
Exploring the layout of internal structures provides a clearer picture of how water flows and controls are managed. This breakdown helps you understand which pieces might need replacement over time and how to keep everything running smoothly.
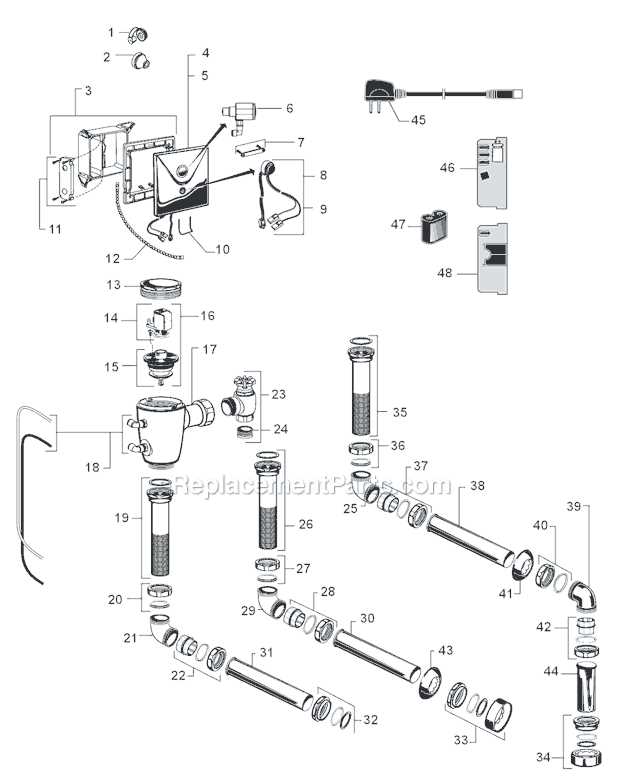
American Standard Toilet Parts Diagram
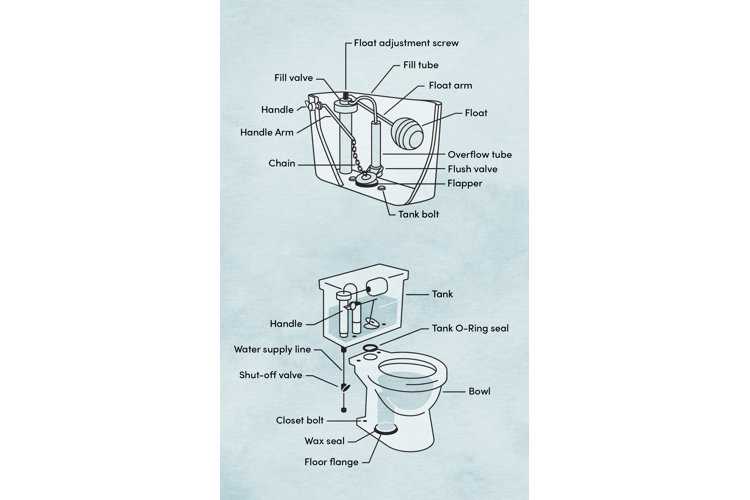
Plumbing fixtures consist of several essential components working together to ensure smooth operation and water flow. Understanding these elements can help with maintenance, repair, and replacements. Each piece, whether inside the tank or bowl, plays a role in water management and waste disposal.
Internal mechanisms inside the tank control water release and refill after each flush. These mechanisms are critical to maintaining the proper amount of water. If any part becomes faulty, it can result in water leakage or flushing issues.
Exterior components include elements like the bowl, seat, and handles. These ensure comfort and usability while facilitating easy interaction with the plumbing system. Knowing the names
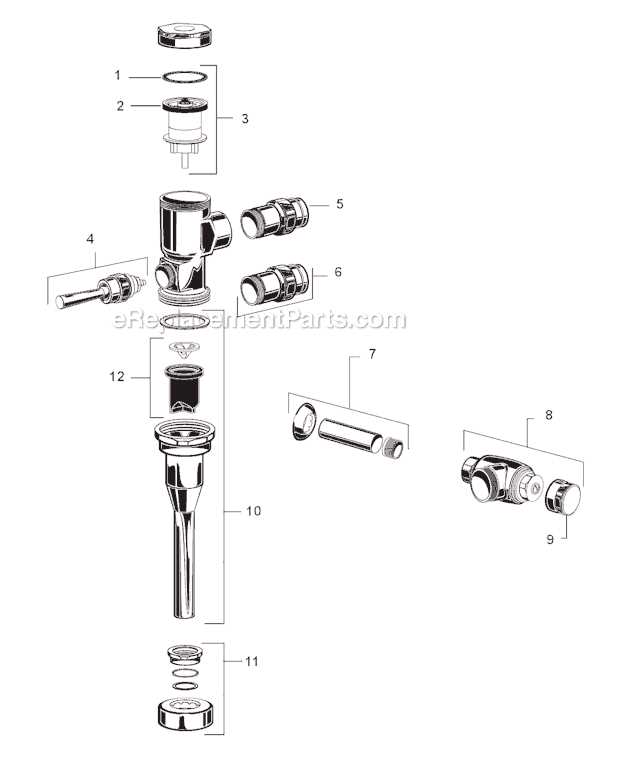
Main Components Inside the Tank
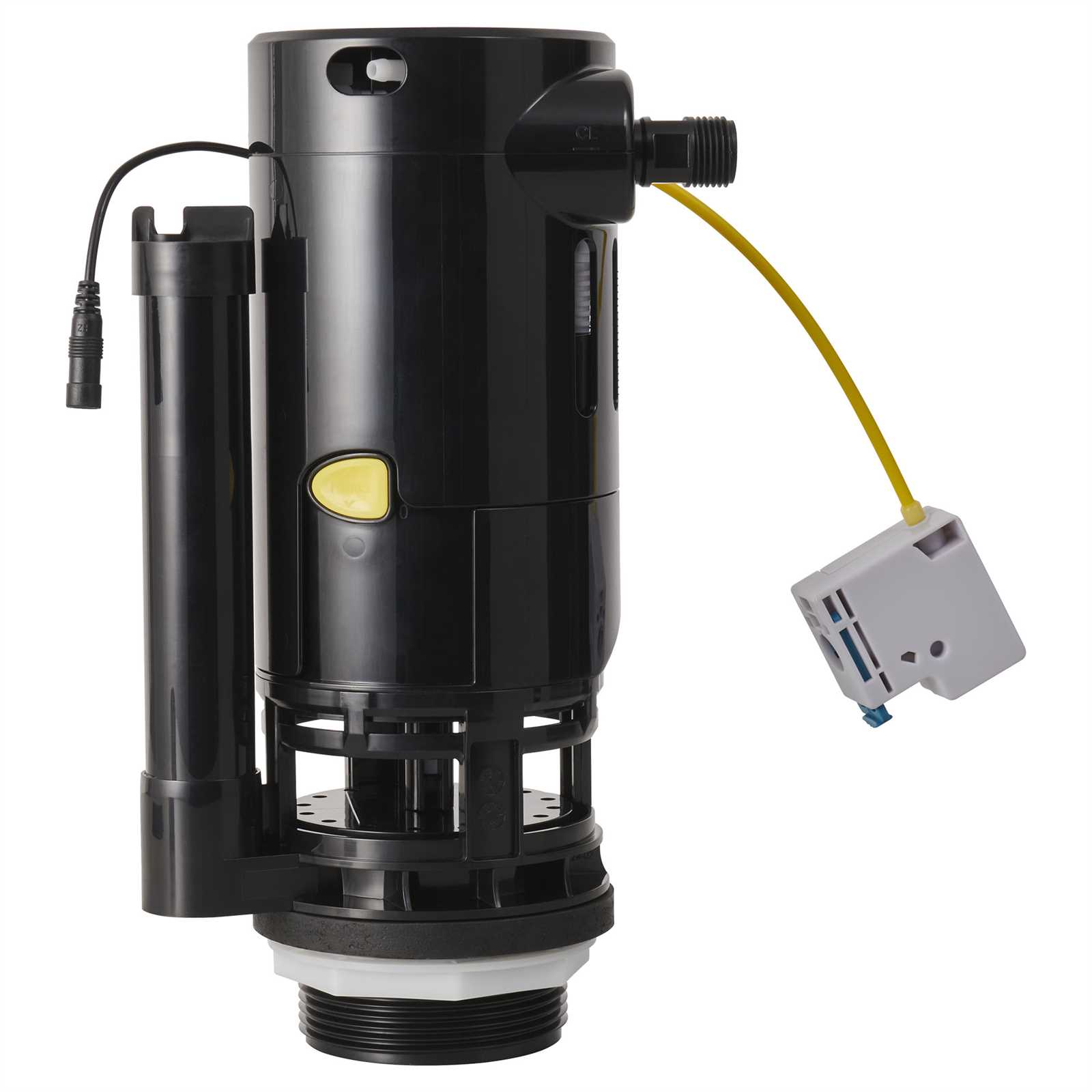

The inner structure of the tank contains several key elements working together to manage water flow. These components ensure proper refilling after each use and help regulate water levels efficiently, contributing to the smooth operation of the entire system.
Fill Mechanism
The fill mechanism controls how water enters the tank. It activates once the water level drops, allowing fresh water to flow in until the desired level is reached. This part ensures that the system is always ready for the next use by maintaining a consistent water supply.
Flush Mechanism
The flush mechanism is responsible for releasing stored water into the bowl when activated. It typically includes a handle or button connected to a valve,
Flushing Mechanism Overview
The flushing system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient water flow and waste removal. It relies on a series of interconnected components that work together to control the release of water and reset the system for the next use. Understanding these elements helps in troubleshooting and maintaining smooth operation.
Main Components and Functions
The mechanism typically includes a valve that regulates water discharge and a float system responsible for monitoring water levels. The float ensures that the tank fills to the correct point after each flush, while the valve opens briefly to release water, clearing the bowl effectively.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Differences Between Flush Valve Types
Flush valves play a critical role in managing water flow during flushing, with different designs offering unique performance characteristics. Each type is suited for specific situations, providing varied water efficiency and operational mechanisms. Understanding these variations can help users select the right option for their needs.
Piston vs. Diaphragm Valves
Piston-based systems rely on a sliding mechanism that delivers powerful flushes and ensures durability, even in high-pressure environments. In contrast, diaphragm valves utilize a flexible membrane, which responds faster but may require more frequent maintenance due to wear.
Single-Flush vs. Dual-Flush Mechanisms
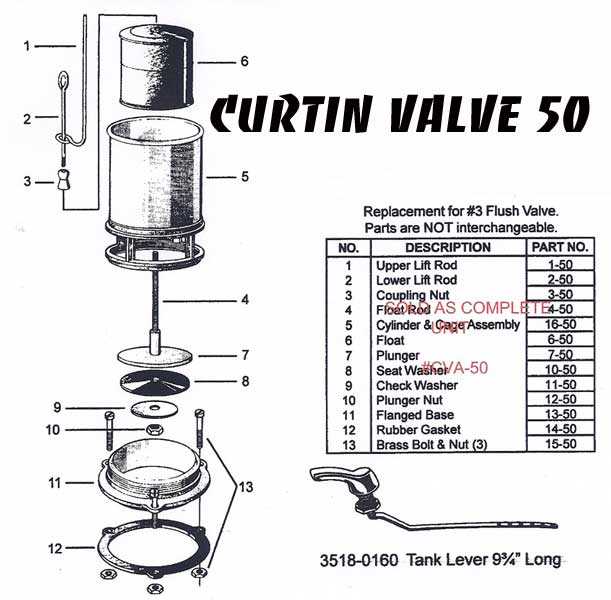
Single-flush valves
Fill Valve Functions and Adjustments

The fill valve plays a crucial role in maintaining the water level inside the system’s tank, ensuring smooth operation. This component controls the flow of water, refilling the reservoir after each cycle and preparing the system for the next use. Proper adjustment of the valve is essential to prevent issues such as overflow or inadequate water levels.
- Water Flow Regulation: The valve opens to allow water to enter and closes automatically when the correct level is reached.
- Float Mechanism: A float attached to the valve rises with the water level, helping to signal when to stop the flow.
Common Issues with Toilet Seals
Seals play a crucial role in maintaining the functionality of restroom fixtures by preventing leaks and ensuring efficient operation. Over time, these components can wear out or become damaged, leading to a variety of issues that can disrupt their performance. Understanding the common problems associated with these seals can help in addressing and preventing potential failures.
One frequent issue is leakage, which often occurs due to deterioration or improper installation. When a seal fails, it can allow water to escape, resulting in puddles and potential damage to the surrounding area. Another concern is foul odors that may arise when seals break down, allowing sewage gases to enter the restroom space. This not only affects the air quality but also indicates a need for immediate attention.
Additionally, improper alignment during installation can lead to premature wear. When seals are not fitted correctly, they may not create an adequate barrier, increasing the risk of leaks. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn seals can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of restroom fixtures, reducing the likelihood of unexpected issues.
Water Supply Line Setup
Establishing an efficient water supply system is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality of your fixture. This setup involves connecting a water source to the flushing mechanism, allowing for seamless operation. Proper installation not only enhances performance but also minimizes potential leaks and damages.
Connecting the Water Supply
Begin by locating the shut-off valve, typically positioned on the wall behind the fixture. Use a flexible hose or rigid pipe to connect this valve to the inlet on the unit. Ensure that all connections are secure, using appropriate tools to tighten any fittings. A well-sealed connection is essential to prevent leaks.
Testing for Leaks
Once the connections are complete, turn on the water supply and carefully inspect all joints for any signs of leakage. If any issues arise, tighten the fittings further or replace any damaged components. Regular maintenance of this system is important for long-term reliability. Always ensure that the shut-off valve is accessible for quick adjustments when necessary.
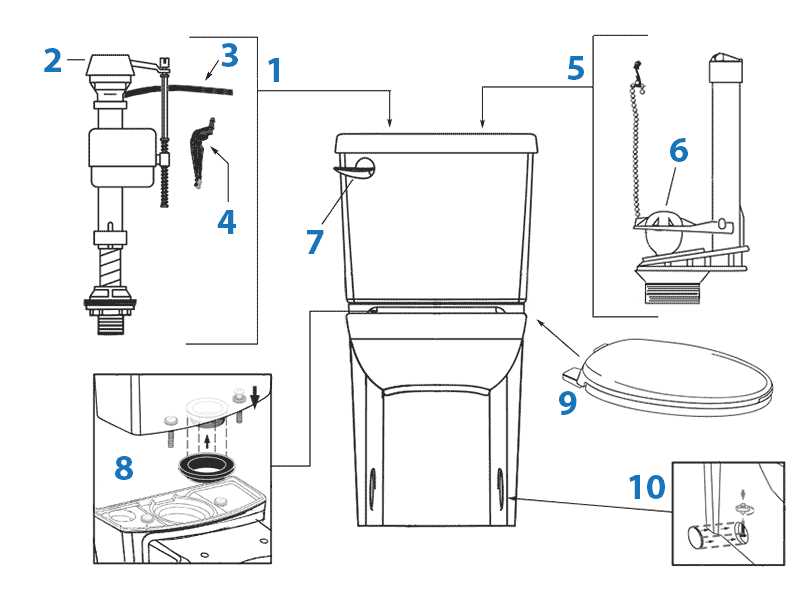
Tank-to-Bowl Connection Details

This section explores the essential aspects of the connection between the upper reservoir and the bowl of a water fixture. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. A secure and reliable connection ensures optimal performance and prevents leaks, contributing to the overall functionality of the unit.
Components Involved
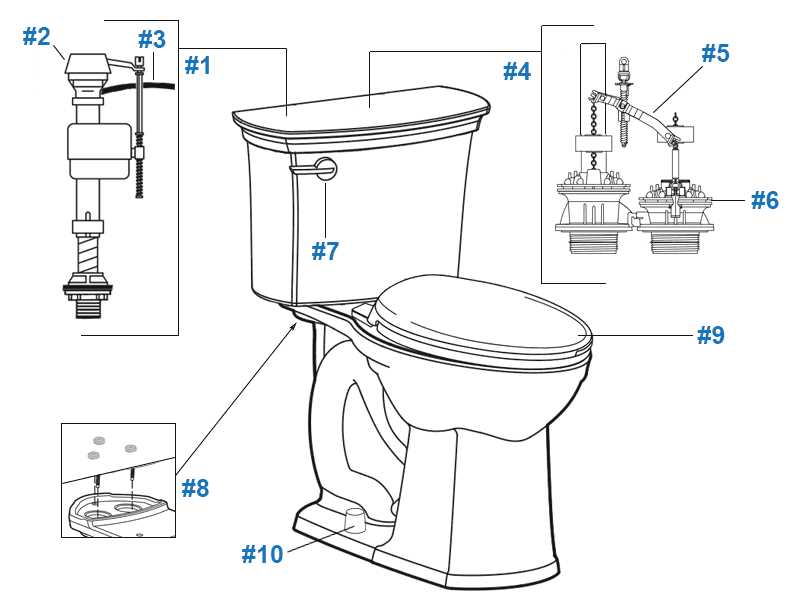
The connection typically includes various elements such as bolts, washers, and gaskets. Each of these components plays a vital role in creating a watertight seal. Bolts secure the tank to the bowl, while washers and gaskets help prevent any moisture from escaping during operation. Proper installation and regular inspection of these elements can enhance the longevity of the system.
Common Issues and Solutions
Several problems may arise at this junction, including leaks or instability. Leaks can often be traced back to worn-out gaskets or improperly tightened bolts. To resolve such issues, it is advisable to inspect these components regularly and replace them as necessary. Ensuring that the connection is snug and secure can greatly reduce the risk of water loss.
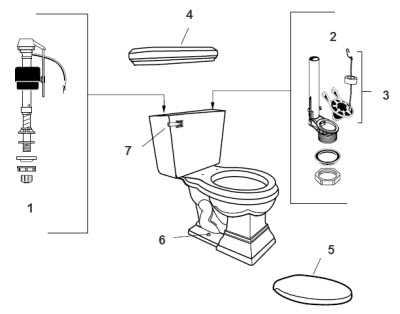
Toilet Bowl Parts and Structure

The design of a restroom fixture involves various essential components that contribute to its functionality and efficiency. Understanding these elements provides insight into how this commonly used item operates and ensures effective waste management.
Components of the Fixture
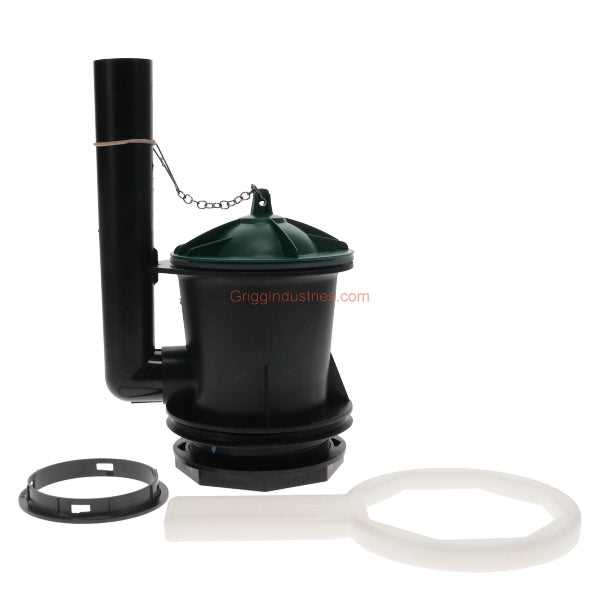

At the core of the fixture’s design lies the bowl, which is primarily responsible for holding waste. This part is typically shaped to facilitate efficient drainage and is constructed from durable materials to withstand constant use. Additionally, a water reservoir is often integrated, allowing for the necessary flushing mechanism that clears the contents.
Internal Mechanisms
Inside the bowl, several mechanisms work together to maintain functionality. A siphon jet plays a crucial role in expelling waste efficiently, while the flush valve regulates the flow of water during each cycle. The overflow tube serves to prevent flooding by redirecting excess water, showcasing the thoughtful engineering behind this essential household fixture.
Understanding these components is vital for anyone interested in maintenance or repair, as each plays a unique role in ensuring optimal performance. Proper knowledge of the structure enhances the ability to troubleshoot common issues that may arise over time.
How the Trip Lever Works
The trip lever is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the flushing mechanism of a restroom fixture. This lever allows users to initiate the flushing action, leading to the efficient disposal of waste. Understanding its functionality can help in troubleshooting and maintenance of the system.
Mechanism of Action

When the lever is pressed, it connects to a chain or rod that lifts a flapper valve. This action opens the pathway for water to flow from the reservoir into the basin. The pressure created by the rushing water helps push the contents down the drain. Once the flush is complete, the flapper returns to its original position, sealing the opening and allowing the tank to refill.
Importance in Maintenance
Regular inspection of the trip lever is essential for proper functioning. Wear and tear can lead to malfunction, resulting in incomplete flushing or leaks. Ensuring that the lever operates smoothly can enhance the overall performance and longevity of the fixture.
Flapper Valve Design and Operation
The flapper valve is a crucial component in the water-saving mechanism of a lavatory system. Its primary role is to control the release of liquid from the reservoir into the bowl. By efficiently regulating this flow, the device plays an essential part in ensuring optimal performance and water conservation.
Designed with flexibility in mind, the flapper typically consists of a rubber or silicone material that creates a watertight seal when closed. This design prevents any leakage while maintaining pressure within the tank. During a flushing event, the mechanism lifts, allowing water to flow swiftly into the bowl, ensuring a thorough cleanse.
Operationally, the flapper valve is activated by a chain or rod connected to the flush handle. When the handle is pressed, it lifts the flapper, initiating the flushing cycle. Once the tank empties to a certain level, the flapper returns to its original position, sealing the tank and allowing it to refill. This cycle is vital for maintaining the efficiency and functionality of the entire system.
Understanding Gaskets and Washers
Gaskets and washers are essential components in various plumbing fixtures, providing critical sealing capabilities to prevent leaks and ensure proper function. These small but significant elements play a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of water-related systems. By effectively bridging gaps between surfaces, they help create watertight seals that minimize the risk of moisture loss and potential damage.
Made from a variety of materials, including rubber, silicone, and cork, these sealing elements are designed to withstand varying levels of pressure and environmental conditions. Their flexibility allows them to conform to the surfaces they contact, ensuring a snug fit that enhances durability. Understanding the characteristics and functions of gaskets and washers is key to ensuring optimal performance in any plumbing application.
Regular inspection and replacement of these components can prevent costly repairs and water damage. Knowing when and how to replace gaskets and washers will contribute significantly to the overall efficiency of the plumbing system, promoting a seamless and effective operation.