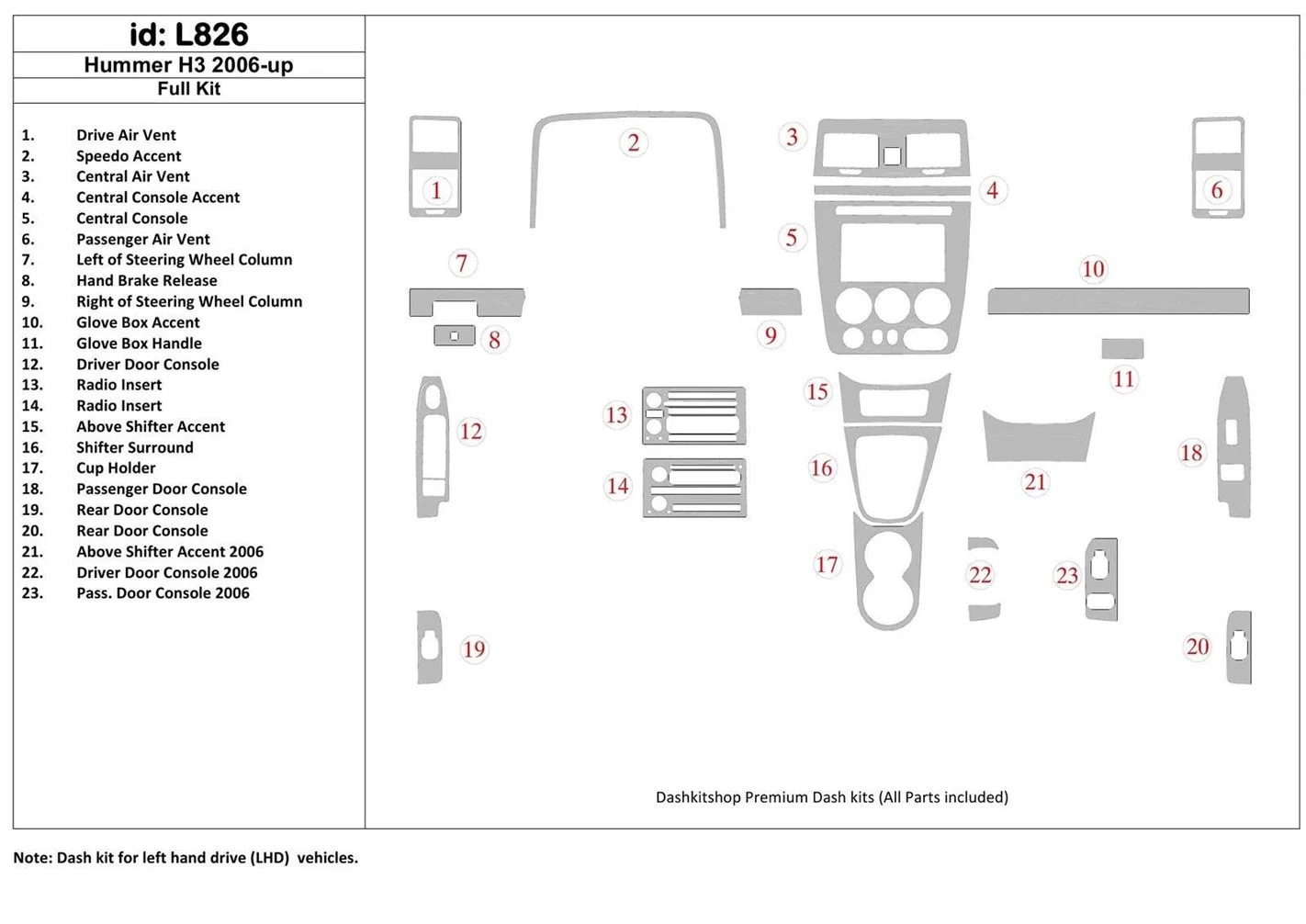
When it comes to understanding the internal structure of a vehicle, having access to detailed illustrations can make a significant difference. Whether you are performing maintenance or upgrades, these visual aids help ensure you work efficiently and with precision. The schematics not only highlight the arrangement of various elements but also clarify how different systems are interconnected, making it easier to navigate complex repairs.
Accurate technical drawings can provide clarity on the design and layout of key systems within a vehicle. These visual guides break down the intricate mechanisms, offering insight into the positioning and functionality of each component. By examining these designs, you can gain a better understanding of how the individual parts work together to keep the vehicle operating smoothly.
Overview of Key Components
Understanding the main elements of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring its optimal functionality and longevity. The core systems are interconnected, and each plays a vital role in the overall performance. This section provides a general look at these fundamental areas, offering insight into their functions and how they contribute to the efficient operation of the entire system.
Engine: The engine serves as the heart of the vehicle, transforming fuel into power. It drives the entire mechanism, ensuring that all other systems receive the energy they need to perform.
Transmission: This component controls how power from the engine is transferred to the wheels, ensuring smooth shifts between different speeds and efficient use of the engine’s output.
Suspension System: The suspension system is responsible for providing a balanced and stable ride. It absorbs shocks from uneven road surfaces and helps maintain control during various driving conditions.
Brake System: Safety is paramount, and the brake system ensures the vehicle can be brought to a stop when necessary. It uses hydraulic force to apply pressure on the wheels, slowing them down efficiently.
Electrical System: Powering everything from lights to the ignition
Engine Layout and Configuration
The layout and configuration of the engine are essential for understanding how power is generated and transmitted to the vehicle’s drivetrain. A well-designed engine not only delivers optimal performance but also ensures efficient fuel consumption and longevity. In this section, we will explore the basic structure of the engine, its main components, and how they interact to create the mechanical energy needed for propulsion.
Main Components and Structure
The engine is composed of several key parts, including the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, and valve train. These components work in unison to convert fuel into mechanical energy through the process of combustion. The cylinder block forms the foundation, housing the pistons that move within their chambers, while the crankshaft translates this motion into rotational force.
Engine Configuration Types
Engines come in various configurations, such as inline, V-shaped, or flat layouts. Each design has its own advantages in terms of balance, size, and power output. The choice of configuration affects how the engine performs under different conditions and influences factors such as weight distribution and fuel efficiency.
Transmission System Breakdown
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and functionality of any vehicle. Its main purpose is to ensure efficient power transfer from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth acceleration and control under various driving conditions. Understanding the components and structure of this system is essential for maintaining its reliability and performance over time.
The transmission assembly consists of several interconnected elements that work in harmony to adjust power delivery based on speed, terrain, and driver input. These include gears, clutches, and shafts, each responsible for specific functions within the system. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of worn components can prevent malfunctions and extend the life of the transmission, contributing to better vehicle operation.
In addition, modern transmission systems often incorporate advanced technologies designed to enhance efficiency, such as automated shifting mechanisms and electronic controls. These innovations have significantly improved fuel economy and driving experience, making it important for users to familiarize themselves with the operational details and potential issues associated with their specific setup.
Suspension System Structure
The suspension system plays a critical role in maintaining vehicle stability and comfort during driving. It ensures that the wheels remain in proper contact with the road, even when encountering uneven surfaces or rough terrain. This section provides a breakdown of the components involved and how they work together to support both the vehicle’s performance and ride quality.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | Control the movement of the springs and reduce impact from road irregularities. |
| Control Arms | Connect the wheel hub and steering knuckles to the frame, allowing up-and-down movement. |
| Springs | Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb shocks from the road. |
| Sway Bar | Minimizes body roll during turns and improves overall stability. |
| Bushings | Reduce friction between moving parts, ensuring smooth operation of the suspension. |
Brake Assembly and Components
The brake system is a vital part of any vehicle, ensuring safety by allowing the driver to control the speed and come to a stop when necessary. This section will delve into the main elements that make up this system, focusing on how they work together to provide efficient stopping power and maintain vehicle control.
Main Brake Components
The core elements of the brake assembly include the brake pads, rotors, and calipers. Brake pads apply pressure to the rotors, generating the friction needed to slow down or stop the vehicle. Rotors, attached to the wheels, work in tandem with the calipers, which house the pads and use hydraulic force to press them against the rotors.
Additional Components

Other important components include the brake lines, which carry hydraulic fluid, and the master cylinder, which generates the pressure needed for braking. The brake booster assists in amplifying the force applied by the driver, making the braking process smoother and more efficient.
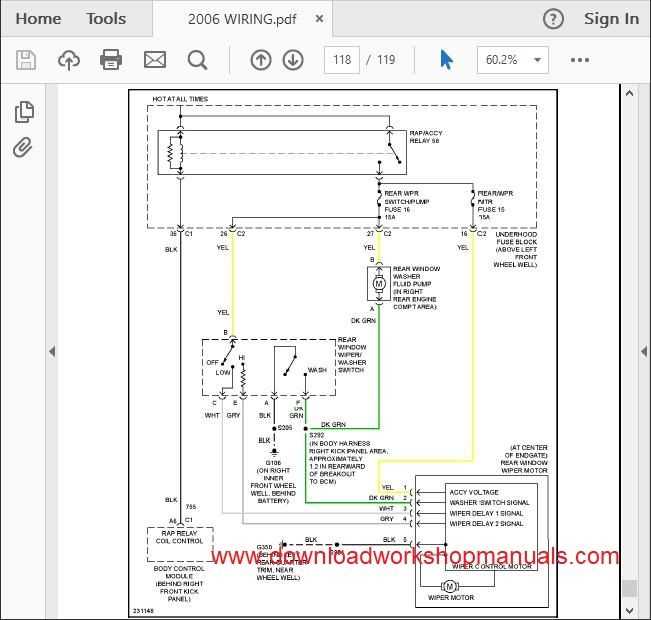
Electrical System Diagram
The electrical architecture of a vehicle is essential for its overall functionality, integrating various components to ensure optimal performance. Understanding this layout is crucial for troubleshooting issues and conducting maintenance. This section delves into the various elements that comprise the electrical framework, emphasizing their interconnections and roles within the system.
Key Components

The core elements of the electrical framework include the battery, alternator, and wiring harnesses. The battery serves as the power source, while the alternator recharges it during operation. Wiring harnesses facilitate the distribution of electrical current to different parts of the vehicle, ensuring seamless communication between components.
Functional Overview
This framework supports various functionalities, from lighting to ignition systems. Each component is designed to work harmoniously, contributing to the vehicle’s reliability. By familiarizing oneself with this intricate network, one can better address electrical concerns and enhance the overall performance of the vehicle.
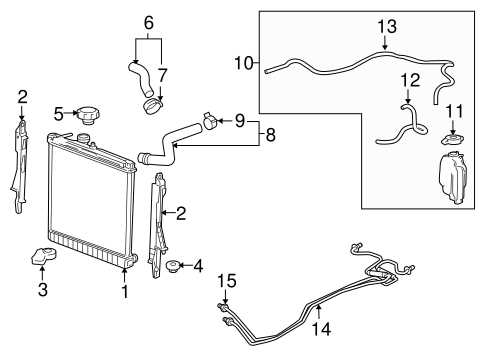
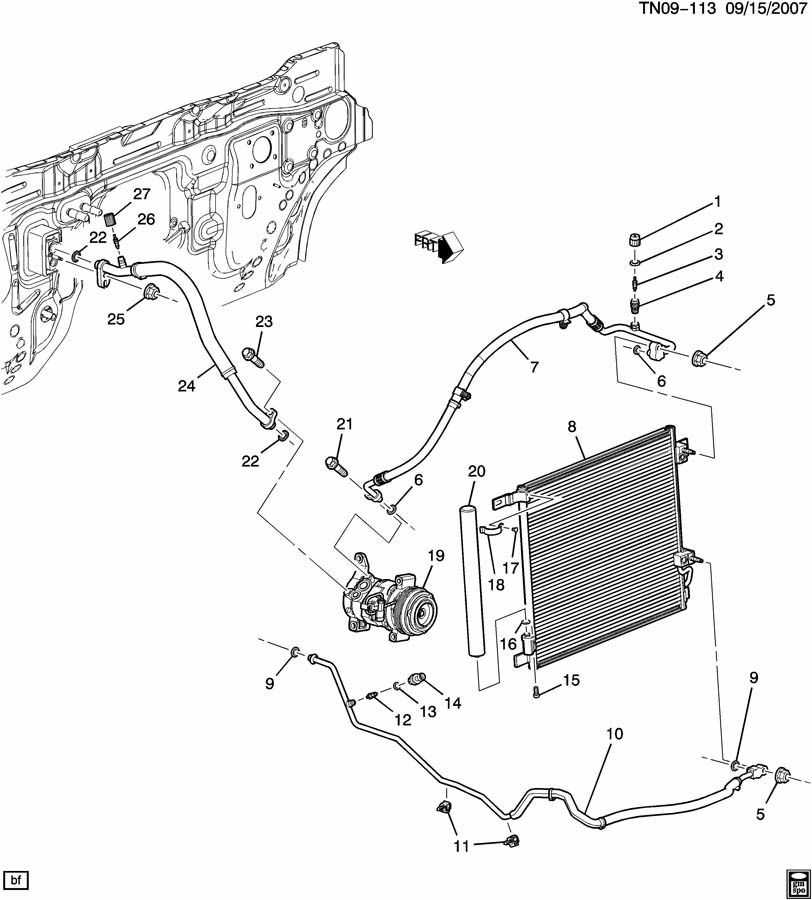
Cooling System Layout
The cooling system is a vital component in maintaining optimal engine temperature and performance. It is designed to regulate heat, preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of the engine. This section outlines the key elements and configuration of the cooling system.
- Radiator: The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool before returning to the engine.
- Water Pump: This component circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring efficient heat exchange.
- Thermostat: The thermostat regulates coolant flow, opening and closing to maintain the ideal operating temperature.
- Cooling Hoses: These flexible tubes connect various components, transporting coolant to and from the engine.
- Expansion Tank: This tank accommodates coolant expansion and helps maintain system pressure.
Understanding the arrangement and function of these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting of the cooling system.
Fuel System Overview
The fuel system in modern vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. This intricate network is designed to deliver the right amount of fuel to the engine while maintaining proper pressure and flow. Understanding the components and their functions can significantly enhance the vehicle’s reliability and longevity.
At the heart of the fuel system lies the fuel tank, which stores the fuel until it is needed. From the tank, fuel is pumped through a series of lines and filters that help remove contaminants and maintain the quality of the fuel. The fuel pump is essential for moving the fuel towards the engine, while the fuel injectors play a vital role in atomizing the fuel for optimal combustion.
Additionally, the fuel system incorporates various sensors and electronic control units to monitor fuel levels and manage the fuel delivery process. This sophisticated integration ensures that the engine operates smoothly, responds efficiently to the driver’s commands, and minimizes emissions.
Steering Mechanism Parts
The steering mechanism is a vital component that ensures the vehicle can navigate effectively and respond to driver input. It consists of various elements that work together to provide stability and control while driving.
Key components of this system include the steering column, which connects the steering wheel to the gearbox, and the steering rack, responsible for converting rotational motion into lateral movement of the wheels. Additionally, tie rods play a crucial role in linking the rack to the wheel assembly, facilitating precise steering actions.
Another essential part is the power steering pump, which assists in reducing the effort required to turn the wheel, particularly at lower speeds. Moreover, bushings and joints ensure smooth movement and minimize vibrations within the steering system, contributing to overall comfort and handling.
Understanding the individual roles of these elements is important for maintenance and repair, as each part must function correctly to ensure optimal performance of the steering mechanism.
Exhaust System Path
The exhaust system is a crucial component of any vehicle, serving the purpose of directing harmful gases away from the engine and passenger compartment. This system plays a significant role in optimizing performance while minimizing emissions. Understanding the route taken by exhaust gases helps in maintaining efficiency and functionality.
Components of the Exhaust Route
The exhaust system consists of several key elements that work together to ensure proper gas flow. These include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each part is designed to fulfill specific functions, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the system.
Flow Path Overview
The gases generated during combustion exit the engine through the exhaust manifold, which collects the emissions from the cylinders. From there, the gases flow into the catalytic converter, where harmful substances are reduced and converted into less harmful emissions. Following this, the exhaust passes through the muffler, which dampens noise before exiting through the tailpipe.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects emissions from the engine cylinders. |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful substances in exhaust gases. |
| Muffler | Dampens noise produced by the exhaust flow. |
| Tailpipe | Directs exhaust gases outside the vehicle. |
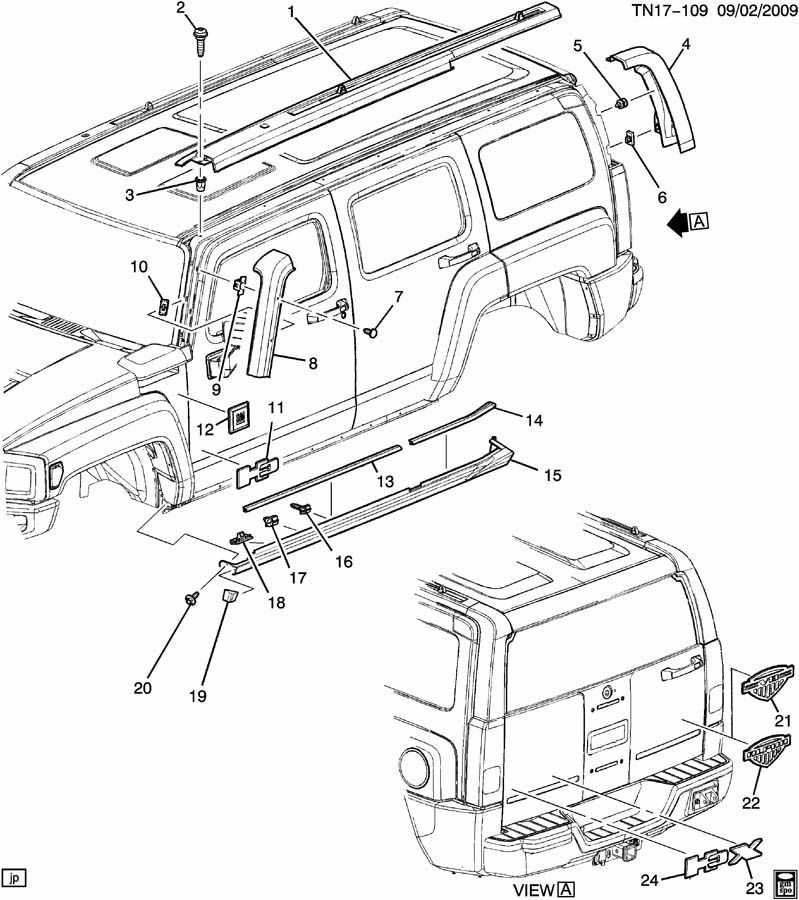
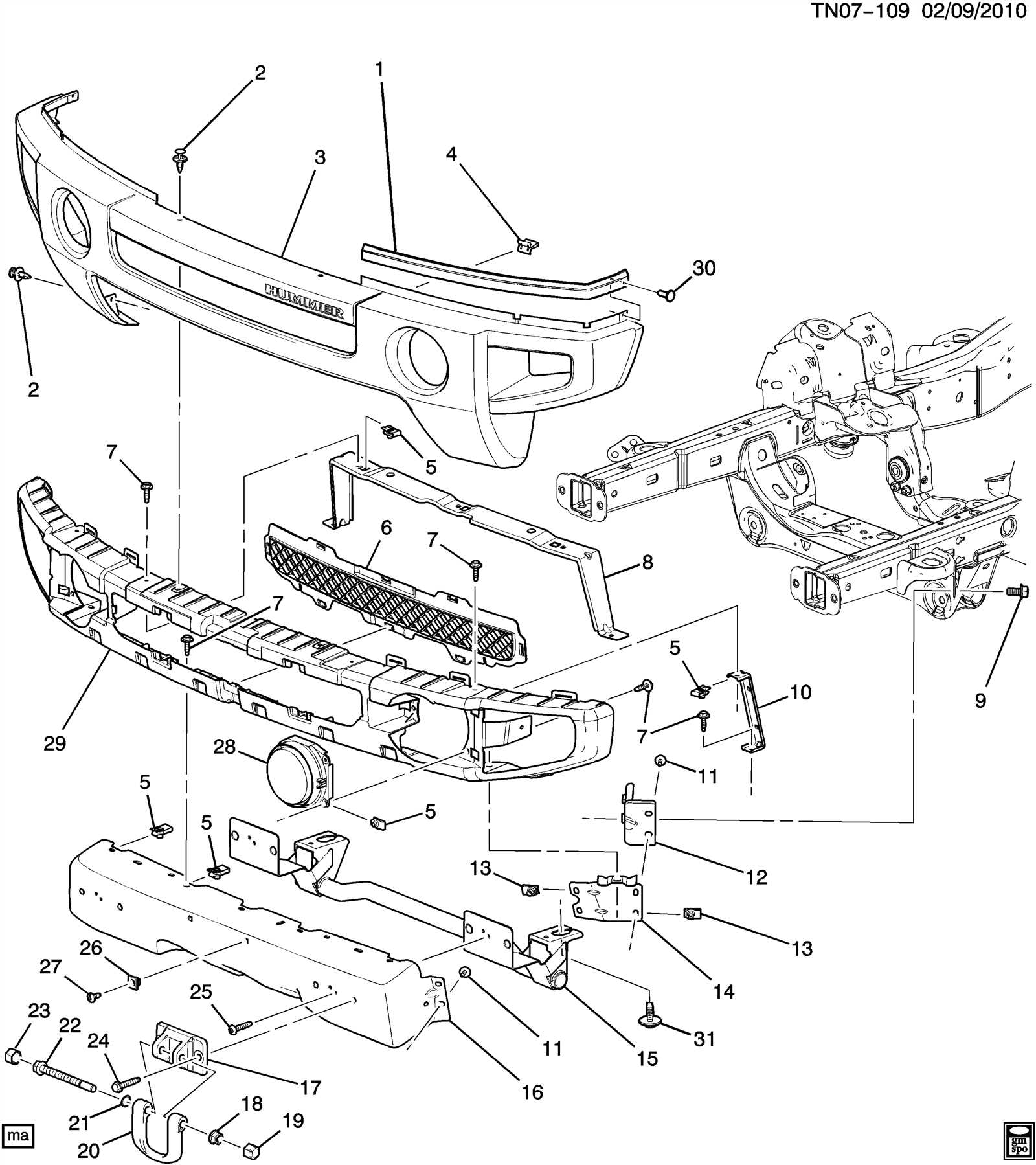
Body and Frame Construction
The structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall performance, safety, and aesthetic appeal. This section explores the various elements that contribute to the robust framework and exterior design, highlighting how they work together to create a cohesive unit. Understanding the materials and engineering involved can provide insights into the vehicle’s durability and functionality.
Structural Integrity
The frame of the vehicle serves as the backbone, providing support for various components and maintaining alignment. Typically constructed from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys, these materials offer a balance of weight and resilience. The design incorporates crumple zones that absorb impact, enhancing safety during collisions.
Exterior Body Panels
Body panels are crucial for both aesthetic and aerodynamic purposes. These panels are usually made from composite materials or metal, ensuring they withstand environmental stressors while contributing to the vehicle’s visual appeal. The integration of these panels is carefully engineered to ensure minimal gaps, enhancing both style and function.
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | High-strength steel | Support vehicle structure |
| Crumple Zones | Aluminum alloys | Absorb impact energy |
| Body Panels | Composite materials | Aesthetic and aerodynamic |
Interior Components and Dashboard
The interior of a vehicle plays a crucial role in providing comfort and functionality for both the driver and passengers. This section explores the various elements that contribute to the overall aesthetic and operational efficiency within the cabin. Each component is designed not only to enhance the driving experience but also to ensure ease of use and accessibility.
Dashboard Layout serves as the central hub for controls and information, presenting essential data in an organized manner. Typically, it houses instruments such as speedometers, fuel gauges, and warning lights, all of which are vital for monitoring the vehicle’s performance.
Another important feature is the infotainment system, which integrates entertainment and navigation functions. Modern setups often include touchscreen displays, Bluetooth connectivity, and smartphone integration, allowing users to access various applications and features seamlessly.
Seating and Storage arrangements also play a significant role in enhancing passenger comfort. Ergonomically designed seats provide support during journeys, while strategically placed storage compartments ensure that personal items are easily accessible yet securely stowed away.
Finally, the climate control system is essential for maintaining a comfortable environment within the vehicle. This system allows occupants to adjust temperature settings, ensuring a pleasant atmosphere regardless of external weather conditions.
Lighting System Configuration
The configuration of the lighting system in vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and visibility on the road. This system encompasses various components that work together to provide optimal illumination under different driving conditions. Understanding how these elements interact can enhance performance and reliability, making it essential for vehicle maintenance and upgrades.
Key components of a typical lighting arrangement include headlights, taillights, turn signals, and fog lights. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to overall driving safety and convenience. Proper installation and adjustment of these components are vital for achieving maximum effectiveness.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Headlights | Illuminate the road ahead during nighttime or low visibility conditions. |
| Taillights | Signal the presence of the vehicle to drivers behind it. |
| Turn Signals | Indicate the driver’s intent to change lanes or make a turn. |
| Fog Lights | Provide additional illumination during foggy or misty weather, enhancing visibility. |
Regular inspections and maintenance of the lighting system are recommended to ensure all components function effectively. Adjusting the alignment of headlights and replacing burnt-out bulbs promptly can significantly improve safety and driving experience.