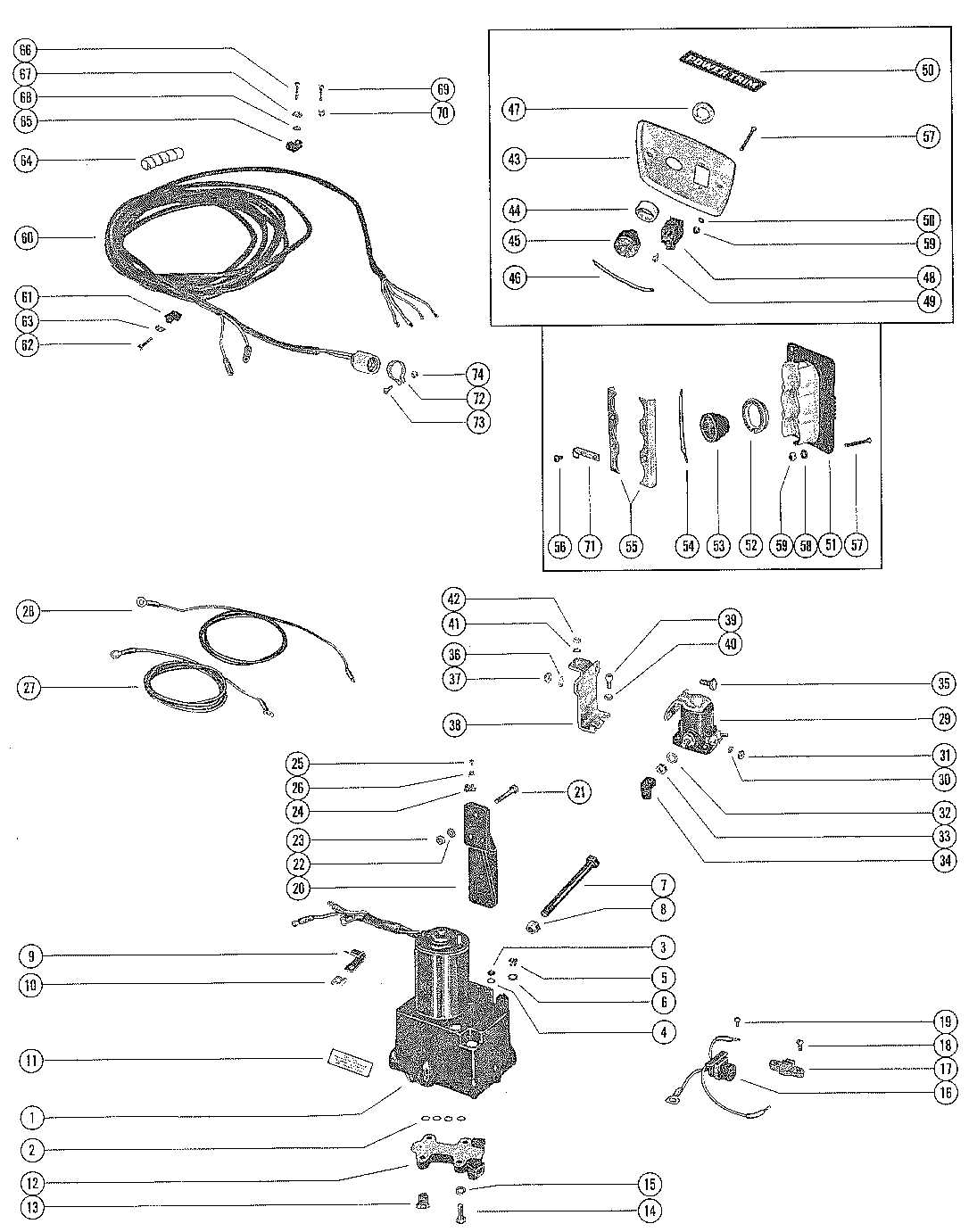
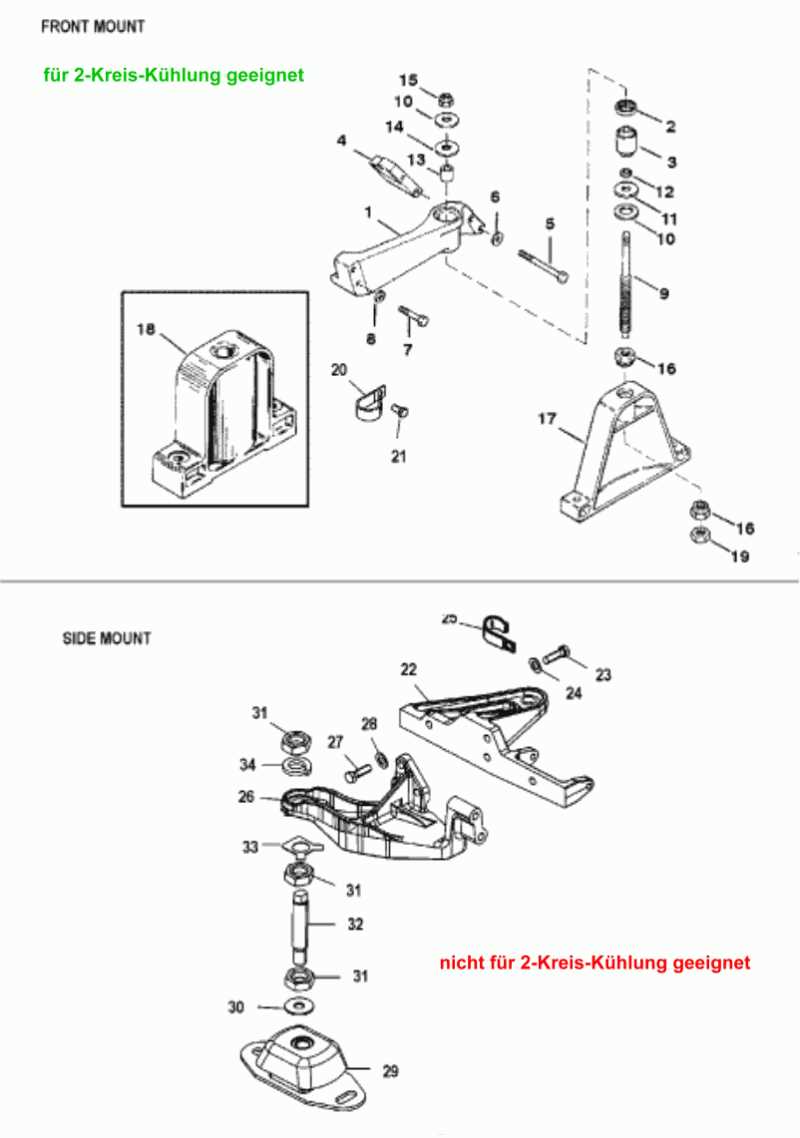
When maintaining or repairing an inboard marine engine, it’s crucial to have a clear grasp of how different elements come together to ensure smooth performance. Each mechanical structure in the engine is interconnected, with every detail playing a role in delivering power and efficiency on the water. This guide will help break down those key components and their interactions, offering a deeper insight into how the system functions as a whole.
By analyzing individual mechanisms, boat owners can develop a better understanding of the engine’s structure and operation. Whether it’s a matter of addressing common wear points or troubleshooting specific issues, knowledge of the inner workings is essential for anyone looking to maintain or improve their vessel’s performance. The following sections provide detailed insights into the most critical elements, enhancing both repair strategies and overall familiarity with marine engines.
For those looking
Mercruiser 120 Engine Components Overview
Understanding the various elements that make up a marine engine is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This guide offers a clear view of the critical components involved in powering a small watercraft. Each element plays a vital role in the overall performance and reliability of the motor, ensuring smooth operation during your time on the water.
Core Mechanical Structures
- Engine Block: The foundation of the system, housing the cylinders and internal mechanisms responsible for combustion and power generation.
- Cylinder Head: Seals the top of the block, containing the valves and camshaft that regulate airflow and fuel intake.
- Pistons and Crankshaft: Key moving parts that convert the energy from combustion into mechanical motion, driving the propeller.
Support Systems and Auxiliary Components
- Oil Pump: Responsible for circulating lubricant throughout the engine, maintaining pressure to ensure proper flow.
- Oil Filter: Removes contaminants from the lubricant, prolonging the life of the engine and its components.
- Oil Pan: Serves as the reservoir for the lubricant, allowing it to collect and be drawn into the pump as needed.
- Lubrication Lines: These passages carry lubricant to various engine parts, ensuring that every component receives adequate protection.
- Regularly check and replace the oil filter to ensure efficient operation.
- Monitor oil levels in the pan and top off as necessary to prevent starvation of components.
- Inspect lubrication lines for leaks or blockages that could impede flow.
- Engine: The heart of the system, responsible for generating power through combustion.
- Drive Unit: Connects the engine to the propeller, transmitting the engine’s power effectively.
- Propeller: Converts rotational energy into thrust, propelling the vessel forward.
- Steering Mechanism: Allows the operator to control the direction of the boat.
- Trim System: Adjusts the angle of the drive unit for optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
- Familiarize Yourself with Symbols: Different illustrations utilize specific symbols to represent various components. Start by identifying these symbols to better understand their meanings.
- Identify the Main Sections: Many visuals are divided into distinct sections. Focus on understanding each section’s purpose, as this will help you piece together the overall functionality.
- Use a Legend: A legend or key is often included to explain the symbols and lines used in the illustration. Always refer to it for clarification.
- Take Notes: As you analyze the visual, jot down notes or create a glossary of terms and symbols. This will reinforce your learning and provide a reference for future use.
- Practice with Real Components: Whenever possible, correlate the visual information with actual components. Hands-on experience will deepen your understanding and retention.
- Ask for Help: Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from experienced individuals. They can provide insights and explanations that may not be immediately obvious.
Key Mechanical Parts of Mercruiser 120
The internal configuration of this power unit is built around several critical components, each playing a vital role in ensuring efficient functionality and long-term durability. Understanding these elements helps in both routine maintenance and repairs, allowing for smooth operation under various conditions. Below is an overview of the primary mechanical elements and their interactions.
| Component | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Block | The core structure that houses the cylinders and other internal elements, providing the foundation for power generation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder Head | A critical part attached to the top of the engine block, controlling air and fuel flow into the cylinders and managing exhaust gases. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crankshaft | Responsible for converting the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy, driving the propeller. |
| Component | Description
Electrical Components BreakdownThe electrical system of marine engines involves several interconnected elements that ensure proper functioning and safety. Understanding how each of these components operates and interacts with one another is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting the system. Power DistributionThe power distribution network is responsible for delivering electricity to various subsystems. Key elements include the battery, wiring, and fuses, which regulate and protect against overloads. This setup ensures consistent and safe operation by managing voltage levels across all connected devices. Ignition and Charging SystemThe ignition mechanism initiates engine operation by generating the necessary spark, while the charging system replenishes battery power during operation. Essential components in this section include the alternator, starter motor, and ignition coil, all working together to keep the en Fuel System Parts and Their FunctionsThe fuel system is a critical component in ensuring the efficient operation of an engine. It is responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to the combustion chamber, allowing for optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Understanding the various elements of this system and their respective roles can help in maintaining and troubleshooting issues that may arise. Key Components of the Fuel System
Importance of Each Component
Each element within the fuel delivery mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring smooth engine operation. The pump initiates the process, drawing fuel from the tank, while the filter safeguards the system from debris. Proper mixing of fuel and air is achieved through injectors or carburetors, depending on the engine design. Lastly, the pressure regulator ensures that fuel is supplied consistently, preventing fluctuations that can lead to performance issues. Ignition System OverviewThe ignition system plays a crucial role in the operation of an engine by generating the necessary spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. A well-functioning ignition mechanism ensures optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and smooth operation, making it a vital component for any marine power unit. This system typically consists of several key elements that work together to create and distribute the spark. Understanding the components and their functions can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Maintaining the ignition assembly is essential for the longevity and reliability of the engine. Regular checks and timely replacements of worn components can prevent performance issues and costly repairs. Lubrication System ComponentsThe efficiency of any marine engine relies significantly on its lubrication system. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance by ensuring that all moving parts operate smoothly, reducing friction and wear. A well-designed lubrication setup contributes to the longevity of the engine and enhances overall functionality. Key Elements of the Lubrication SystemMaintenance ConsiderationsMaintaining the lubrication system is essential for the overall health of the engine. By understanding the key components and their functions, operators can better ensure the reliability and performance of their marine machinery. Propulsion System in Mercruiser 120The propulsion mechanism in this specific marine engine model is designed to deliver optimal performance and efficiency on the water. This system plays a crucial role in converting the engine’s power into thrust, enabling smooth navigation and control. Understanding the components and their functions is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. Key ComponentsFunctionality OverviewThis propulsion setup works by utilizing a combination of mechanical and hydraulic systems. When the engine operates, it produces rotational force that is transmitted through the drive unit to the propeller. The propeller then pushes against the water, creating thrust. The steering mechanism and trim system enhance maneuverability and stability, allowing for precise navigation under varying conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure reliable operation and longevity of the entire propulsion assembly. By understanding how each part contributes to the overall functionality, users can better manage their marine vessel’s performance. Maintenance Points and Critical PartsProper upkeep of marine engines is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspections and timely replacements of vital components play a significant role in ensuring reliability on the water. By focusing on key areas and crucial elements, boat owners can avoid costly repairs and enhance their vessel’s operational efficiency. Key Areas of AttentionOne of the most important aspects of engine maintenance involves monitoring fluid levels and quality. Regularly checking the oil, coolant, and fuel systems helps prevent overheating and contamination issues. Additionally, the electrical system should be examined for any signs of wear or corrosion, as these can lead to electrical failures. Essential Components to ReplaceComponents such as filters, belts, and impellers require routine attention. Filters should be changed frequently to ensure clean fluid flow and protect against debris. Belts should be inspected for signs of fraying or cracking, as these can lead to unexpected breakdowns. Impellers, responsible for cooling water circulation, should be replaced at recommended intervals to prevent engine damage. By maintaining vigilance on these critical areas and components, vessel operators can ensure a smoother and safer experience on the water. Diagram Interpretation Tips for BeginnersUnderstanding visual representations of mechanical components can be a daunting task for newcomers. This section provides practical advice to help you navigate these illustrations effectively, enhancing your comprehension and application in real-world scenarios. Here are some key tips to assist you in interpreting these visuals: By following these strategies, you can enhance your ability to interpret visual representations, making it easier to work with mechanical systems and components effectively. |
|---|