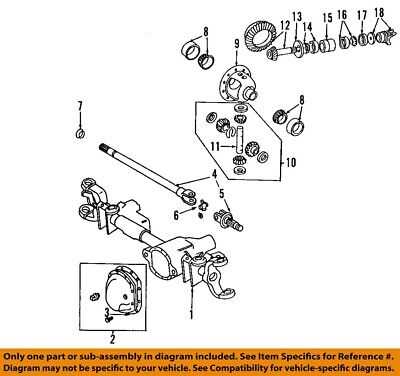
Understanding the inner workings of a vehicle is essential for ensuring smooth operation and long-term reliability. Each model has a unique arrangement of elements that work in harmony to deliver performance, safety, and comfort. This guide provides insights into the crucial elements that make up the structure and mechanics of a well-engineered automobile.
By exploring key sections of the vehicle’s design, we aim to shed light on the various functional areas, from the powertrain to the suspension system. Special attention is given to the components responsible for maintaining stability, efficiency, and durability. Whether you are a professional or a car enthusiast, this detailed breakdown will help you grasp the underlying technologies that support the entire framework of your automobile.
The goal of this article is to offer clear explanations and a detailed review of the core mechanisms found in this particular model. Every element, from the engine setup to the electrical connections, plays a vital role in the vehicle’s performance and overall function. Let’s dive into the specifics and explore how these parts come together to create a robust, reliable machine.
2004 Dodge Ram 2500 Components Overview
This section provides a detailed look at the key mechanical and structural elements of a popular heavy-duty truck. By breaking down the essential systems, it offers insight into the construction, performance capabilities, and the overall design. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the vehicle’s reliability and durability on the road.
- Engine System: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for power generation and efficiency. It includes multiple elements such as the fuel injector, intake manifold, and exhaust system, working together to deliver robust performance.
- Transmission and Drivetrain: This system ensures the smooth transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for optimal speed and torque control.
- Suspension: Designed for stability and comfort, this system includes shocks, struts, and springs, absorbing road impacts and enhancing the vehicle’s handling.
- Brake Assembly:
Engine Bay Layout and Key Elements
The engine compartment is a complex system of essential components that work together to ensure the smooth operation of the vehicle. Understanding the layout of this space and the critical elements housed within it is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting. In this section, we will explore the primary sections of the engine compartment and highlight the major elements that contribute to the vehicle’s overall performance.
- Power Unit Location: At the heart of the engine bay, the power unit serves as the central point for mechanical and electrical connections.
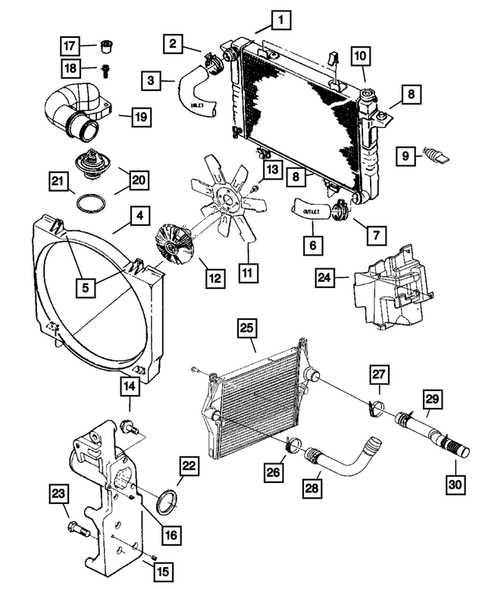
- Cooling System: This section contains the radiator, hoses, and fans that regulate engine temperature and prevent overheating.
- Fuel Delivery Components: This area is responsible for the precise flow of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal combustion.
- Electrical Systems: The battery and various wiring systems are positioned to provide energy to essential functions and accessories.
- Exhaust Management: This section handle
Suspension System Breakdown for Durability
The foundation of any vehicle’s endurance on various terrains is its suspension assembly, which ensures smooth handling, stability, and the ability to withstand prolonged use. A well-designed setup can significantly impact the overall performance and reliability, especially when subjected to demanding environments. Understanding how each component contributes to this resilience helps in maintaining and enhancing the vehicle’s operational life.
Shocks and Struts: These are critical for absorbing road impacts and providing a smoother ride. Their longevity depends on both material quality and regular maintenance.
Control Arms and Bushings: These elements allow for precise wheel movement, ensuring the wheels remain aligned with the surface. Proper lubrication and inspection of these parts prevent unnecessary wear and tear.
Springs: Acting as the backbone of the system, springs manage the vehicle’s weight and help maintain balance, even under load. Their design is key to both comfort and
Electrical System and Fuse Box Details
The electrical system in any vehicle is crucial for its functionality, powering a wide range of components from the engine management system to the lighting and safety features. One of the key elements within this system is the fuse box, which houses essential circuits and protects the wiring from potential damage caused by overloads or short circuits.
In this section, we will explore the various circuits and fuses, outlining their purposes and connections within the overall system. Understanding the placement and function of these elements is vital for troubleshooting and maintaining the electrical components.
Fuse Number Circuit Protected Amp Rating 1 Ignition System 20A 2 Headlights Cooling System Parts and Placement
The cooling system is essential for regulating engine temperature and ensuring optimal performance. A well-structured setup circulates coolant through various components, maintaining the necessary thermal balance. Below is an overview of the main elements involved in this process and where they are typically located within the engine bay.
- Radiator: Positioned at the front of the engine, it dissipates heat from the coolant before it returns to the engine block.
- Water Pump: Located near the engine block, it actively circulates the coolant through the system, maintaining a steady flow.
- Thermostat: This device is usually housed between the engine and the radiator, regulating coolant flow based on temperature conditions.
- Cooling Fan: Often mounted directly behind the radiator, the fan aids in heat dissipation by increasing airflow over the radiator fins.
- Coolant Reservoir: Positioned near the radiator, this tank stores excess coolant, ensuring there is alwa
Exhaust System Components for Emissions Control
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. It comprises various elements that work together to filter and treat exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. Understanding these components is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and meeting regulatory requirements.
Main Components
The primary elements of the exhaust system include catalytic converters, mufflers, and resonators. Each component serves a specific purpose in the overall emissions control strategy:
Component Function Catalytic Converter Transforms harmful gases into less harmful emissions through chemical reactions. Muffler Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the system. Resonator Tunes the exhaust sound and may help further reduce noise and emissions. Additional Components
In addition to the main parts, the exhaust system may include oxygen sensors, exhaust pipes, and heat shields. These components contribute to the efficiency and safety of the system:
Component Function Oxygen Sensor Monitors the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases to optimize fuel combustion. Exhaust Pipes Channel exhaust gases from the engine to the atmosphere while minimizing back pressure. Heat Shield Protects other components from excessive heat generated by the exhaust system. Brake System Parts for Safe Stopping
The effectiveness of a vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safety on the road. A well-functioning braking assembly ensures that drivers can halt their vehicles swiftly and reliably, thus preventing accidents and enhancing overall driving experience. This section delves into the essential components that constitute the braking system, highlighting their roles and importance.
- Brake Pads: These friction materials press against the rotors to create the necessary force for stopping the vehicle. Regular inspection is vital to ensure they are not worn out.
- Brake Rotors: These discs provide a surface for the brake pads to clamp down on, allowing for effective deceleration. Maintaining proper thickness is essential for optimal performance.
- Brake Calipers: These components house the brake pads and use hydraulic pressure to clamp them onto the rotors. Their functionality is crucial for translating pedal pressure into stopping power.
- Brake Lines: These tubes transport brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, ensuring that hydraulic pressure is efficiently delivered throughout the system.
- Master Cylinder: This unit converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, initiating the braking process. A malfunction can lead to complete brake failure.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of these components are necessary to ensure the braking system operates efficiently. Understanding each part’s function can aid in recognizing symptoms of wear or failure, ultimately promoting safer driving practices.
Transmission Assembly and Key Components
The transmission assembly serves as a crucial element in the vehicle’s drivetrain, facilitating power transfer from the engine to the wheels. This complex system consists of various essential components that work together to ensure smooth shifting and optimal performance. Understanding the assembly’s structure and its key components is vital for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Component Description Torque Converter A fluid coupling device that transfers power from the engine to the transmission while allowing for smooth acceleration. Transmission Control Module (TCM) An electronic control unit that manages gear shifting based on engine load and speed, optimizing performance and efficiency. Planetary Gear Set A gear system that provides various gear ratios, allowing for different speeds and torque outputs. Clutch Packs Assemblies that engage and disengage the gears within the transmission, facilitating smooth shifts between different drive modes. Oil Pump A component that circulates transmission fluid, ensuring proper lubrication and cooling of internal parts. Interior Dashboard Elements and Controls
The dashboard of a vehicle serves as the central hub for the driver, integrating various elements and controls essential for a seamless driving experience. Understanding these components is crucial for enhancing functionality and user comfort. This section delves into the various features found within the dashboard, highlighting their roles and significance in vehicle operation.
Key Components of the Dashboard
The interior layout comprises several critical instruments and controls that assist in monitoring the vehicle’s status and managing its functions. These elements not only provide information but also enhance the overall driving experience.
Component Description Speedometer Displays the current speed of the vehicle, allowing the driver to maintain safe driving speeds. Tachometer Indicates the engine’s RPM, helping the driver optimize gear changes and fuel efficiency. Fuel Gauge Shows the level of fuel in the tank, enabling timely refueling to avoid running out of gas. Temperature Gauge Monitors the engine’s temperature, alerting the driver to potential overheating issues. Warning Lights Various indicators that alert the driver to issues requiring attention, such as engine malfunctions or low oil pressure. Controls and Functionality
The dashboard is equipped with an array of controls that facilitate various functions within the vehicle. From climate control to infotainment systems, these features are designed to provide convenience and enhance the driving experience.
Fuel System Layout and Key Components

The fuel delivery mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance by supplying the necessary fuel for combustion. Understanding its layout and essential elements is crucial for maintaining efficiency and addressing potential issues that may arise during operation.
Core Elements of the Fuel Delivery System
This system comprises several key components that work in harmony to ensure a seamless fuel flow. At its foundation, the fuel tank stores the gasoline or diesel, while the fuel pump, usually located within or near the tank, facilitates the transfer of fuel to the engine. Once fuel is pumped, it travels through fuel lines, which are designed to withstand high pressure, towards the fuel injectors.
Injectors and Pressure Regulation
The fuel injectors are critical for atomizing the fuel, allowing for efficient combustion in the engine’s cylinders. In conjunction with the fuel pressure regulator, they maintain the appropriate pressure levels within the system, ensuring that the engine receives the correct fuel amount at all times. Proper function of these components is essential for performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
Exterior Body Panels and Trim Details
The external structure and decorative elements of a vehicle play a crucial role in both its aesthetic appeal and functionality. These components are designed to enhance the visual character while also providing essential protection against environmental factors. Understanding the various elements that constitute the exterior can help in maintenance, repair, or customization efforts.
Key Components Overview

Exterior panels and trim pieces serve multiple purposes, including aerodynamic efficiency, structural integrity, and visual enhancements. The following table summarizes the primary components typically found on the exterior of a heavy-duty vehicle.
Component Description Fenders Curved panels located over the wheel wells, protecting tires from debris. Hood The cover for the engine compartment, often featuring vents or scoops for airflow. Grille Front opening allowing airflow to the engine while providing a distinctive style. Bumpers Impact-absorbing structures at the front and rear, designed to minimize damage in collisions. Side Panels Flat sections along the sides of the vehicle, providing a smooth surface and additional style. Tailgate Rear panel that can be opened and closed, facilitating access to the cargo area. Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the exterior components are vital to preserve the vehicle’s appearance and functionality. Damaged or corroded panels not only detract from visual appeal but can also lead to more significant structural issues over time. Addressing minor wear and tear promptly can prolong the life of these exterior elements.