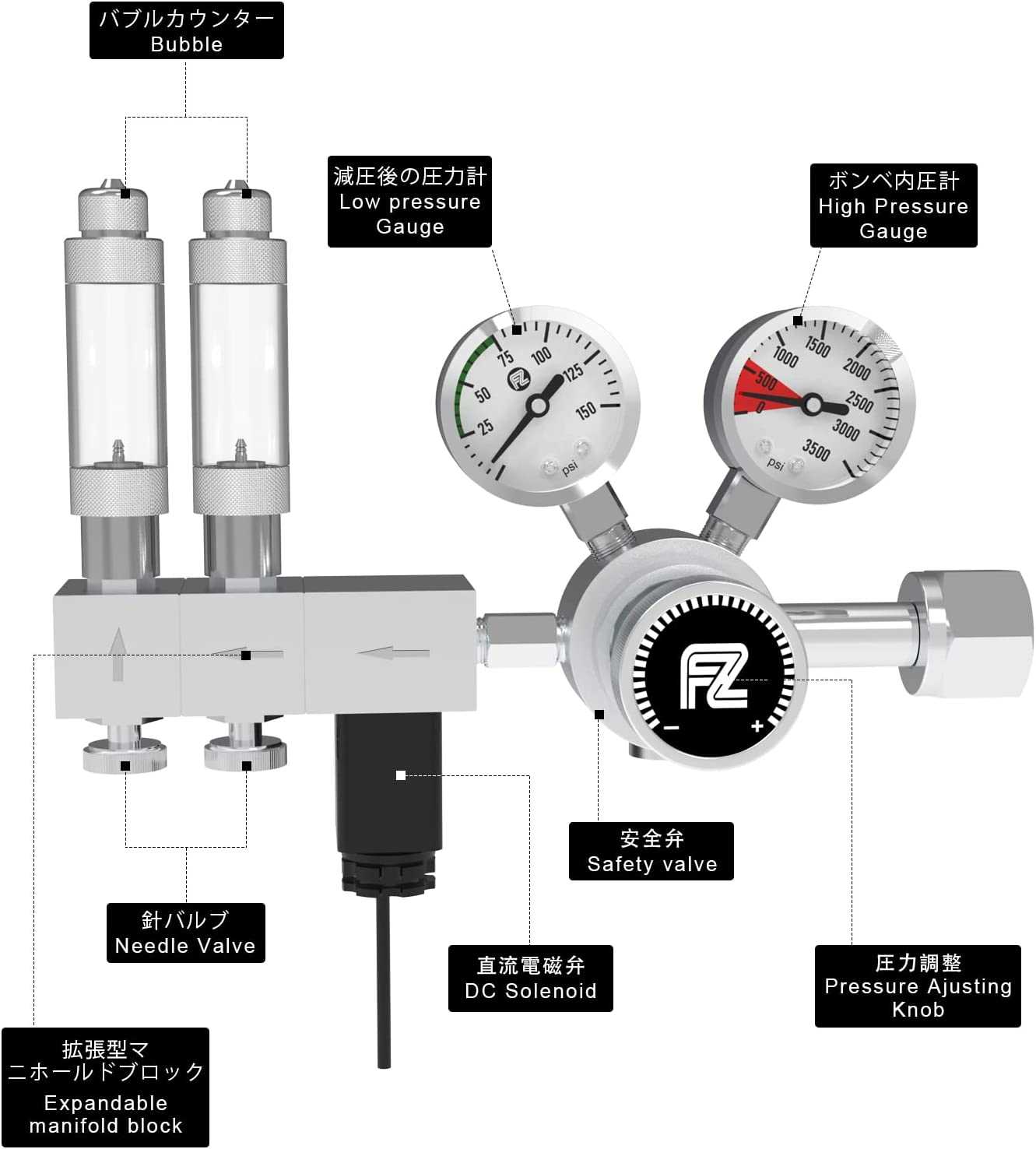
The management of compressed gases is crucial in many industries and applications. Ensuring smooth operation relies on a well-designed system that can control the pressure and flow of the gases involved. Each element within these control mechanisms plays a significant role in maintaining safety, efficiency, and precision.
To achieve optimal performance, the setup involves several interconnected elements that work together to adjust and measure various parameters. By breaking down these individual units, we can gain a deeper understanding of how each contributes to the overall functioning of the system.
In the following sections, we will explore the various components that make up this system, detailing their purpose and how they interact with one another to create a balanced and controlled environment for gas flow.
Understanding CO2 Regulator Functionality
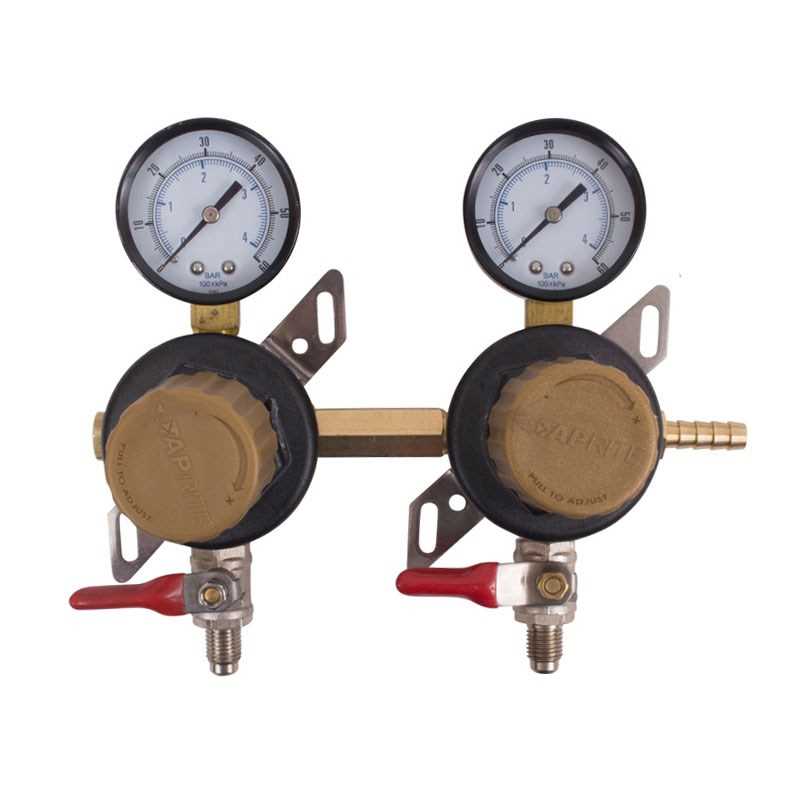

The main purpose of this device is to control and manage the flow of a specific gas to maintain a stable and safe operation in various applications. By adjusting the amount of pressure, it ensures that the gas supply is delivered in a controlled manner. This mechanism is commonly used in systems where maintaining consistent output is critical for effective performance.
Below are some key features of its operation:
- Control over the amount of gas being dispensed
- Ensuring pressure remains at safe levels
- Protection of equipment from potential over-pressurization
- Adjustability for different types of applications
The device plays a crucial role in various industries by offering precision and stability, which are essential for achieving desired results. It is often used in conjunction with other equipment to ensure smooth operation and safety.
Essential Components of a CO2 System
Understanding the key elements of a gas control setup is crucial for efficient operation. Each piece of equipment plays a specific role in managing the flow and pressure of gases, ensuring proper delivery and functionality within the system.
Control Valve: This component allows precise regulation of the flow rate, ensuring consistent output. Proper adjustment helps maintain the balance of the entire system.
Pressure Gauge: Monitoring pressure levels is vital for safe and effective operation. The gauge provides real-time feedback, helping to avoid potential issues.
Hose and Fittings: Durable tubing and secure connections are essential for transferring gas without leaks. They ensure that the system functions without interruptions.
Diffuser: This part disperses gas evenly, improving absorption and distribution across the system.
These primary components work together to maintain smooth and reliable performance in various applications, ensuring optimal results.
How CO2 Regulators Control Pressure
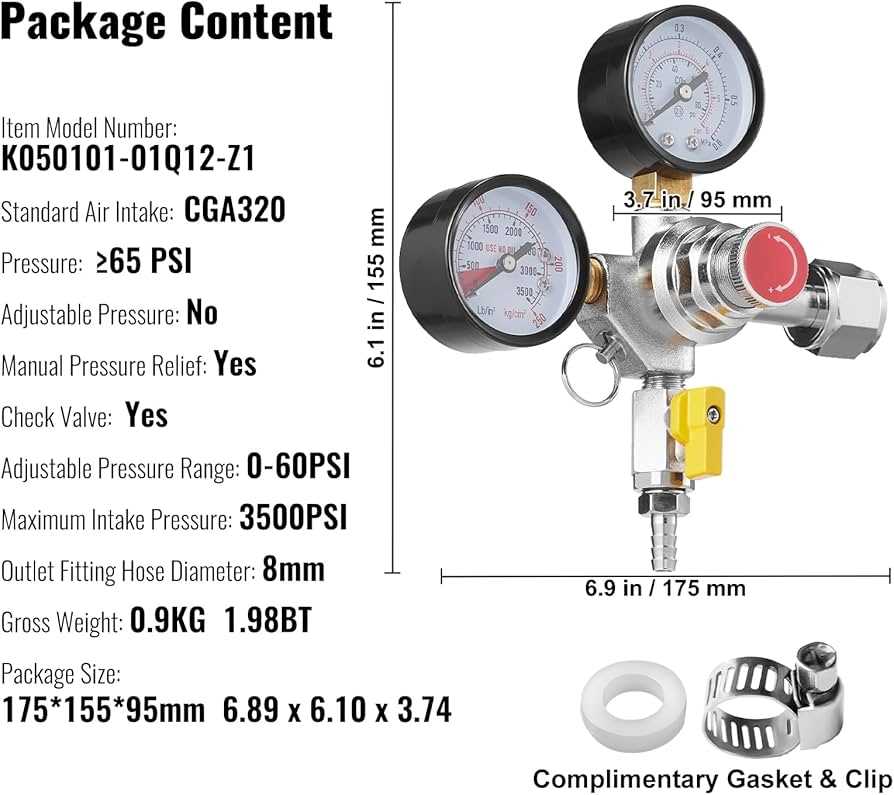
Pressure control devices play a crucial role in managing the flow and force of gas within various systems. These mechanisms ensure that the amount of force applied to a contained gas remains within safe limits, allowing for proper operation. Without this precise control, systems can become inefficient or even unsafe. The process involves a balance between internal components and external forces to maintain desired conditions.
Balancing Internal Forces
Inside the pressure management unit, several key components work together to adjust the flow and maintain steady levels. A valve is often used to release or restrict gas, depending on the pressure requirements. The spring-loaded mechanism responds dynamically, adjusting the amount of gas being allowed through, ensuring that the correct levels are achieved without manual intervention.
Maintaining Stability in Varying Conditions
External factors, such as temperature or volume changes, can influence gas behavior. These control units are designed to compensate for such variations, using internal feedback mechanisms. By constantly adjusting the release based on real-time conditions, they keep the pressure steady, ensuring the system operates safely and efficiently.
Types of CO2 Regulators Explained
Understanding the different mechanisms that control pressure in gas delivery systems is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Various models are designed to meet specific requirements depending on the application, and knowing the distinctions can help in choosing the right tool for the job.
Single-Stage Devices
Single-stage mechanisms adjust gas pressure in one step. They are commonly used for tasks that do not require high precision. However, these units may experience fluctuations in output as the input pressure decreases over time.
- Simple operation
- Affordable for general-purpose use
- Less precise over time
Dual-Stage Devices
Dual-stage systems offer a more consistent output as they regulate pressure in two stages. This makes them ideal for situations that demand a stable and precise flow over an extended period.
- Better pressure stability
- More suitable for sensitive applications
- Pressure Fluctuations: One common issue is inconsistent pressure, which can result in an unstable output. This can affect the overall performance and may require adjustments or replacements.
- Leaks: Unnoticed leaks in the system can lead to inefficient operation, increased costs, and potential safety hazards. Regular inspection and maintenance are key to preventing this problem.
- Clogs and Blockages: Debris or dirt can accumulate over time, leading to blockages in the piping or other components. This can restrict flow and reduce system efficiency.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, seals, valves, and other components may wear out, causing performance degradation. Monitoring and timely replacement of these parts is essential.
- Improper Calibration: Incorrect adjustments during setup can lead to inaccurate output levels, which might cause problems with downstream systems. Proper calibration ensures optimal performance.
- Check compatibility: Before starting, ensure that all components are compatible with your system. This will help prevent any mismatches that could lead to malfunctions.
- Prepare the workspace: Ensure that your working area is clean and free from any obstacles. It’s important to have easy access to the equipment during installation.
- Secure the connections: Attach the necessary fittings securely, avoiding over-tightening to prevent damage. Use the proper tools to ensure all joints are firmly connected.
- Inspect for leaks: After completing the connections, inspect the setup for any potential leaks. A leak test can be performed using a specific solution to detect any escaping gases.
- Adjust settings: Once the system is installed, make the necessary adjustments to control the flow as needed. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for setting the appropriate levels.
Key Features of CO2 Regulators
In systems that require precise control of pressure and flow, it is crucial to have components that can manage the delicate balance between input and output forces. These devices help ensure stability and accuracy, making them indispensable in various applications where maintaining a steady environment is vital for efficiency and safety.
Pressure Adjustment Mechanism
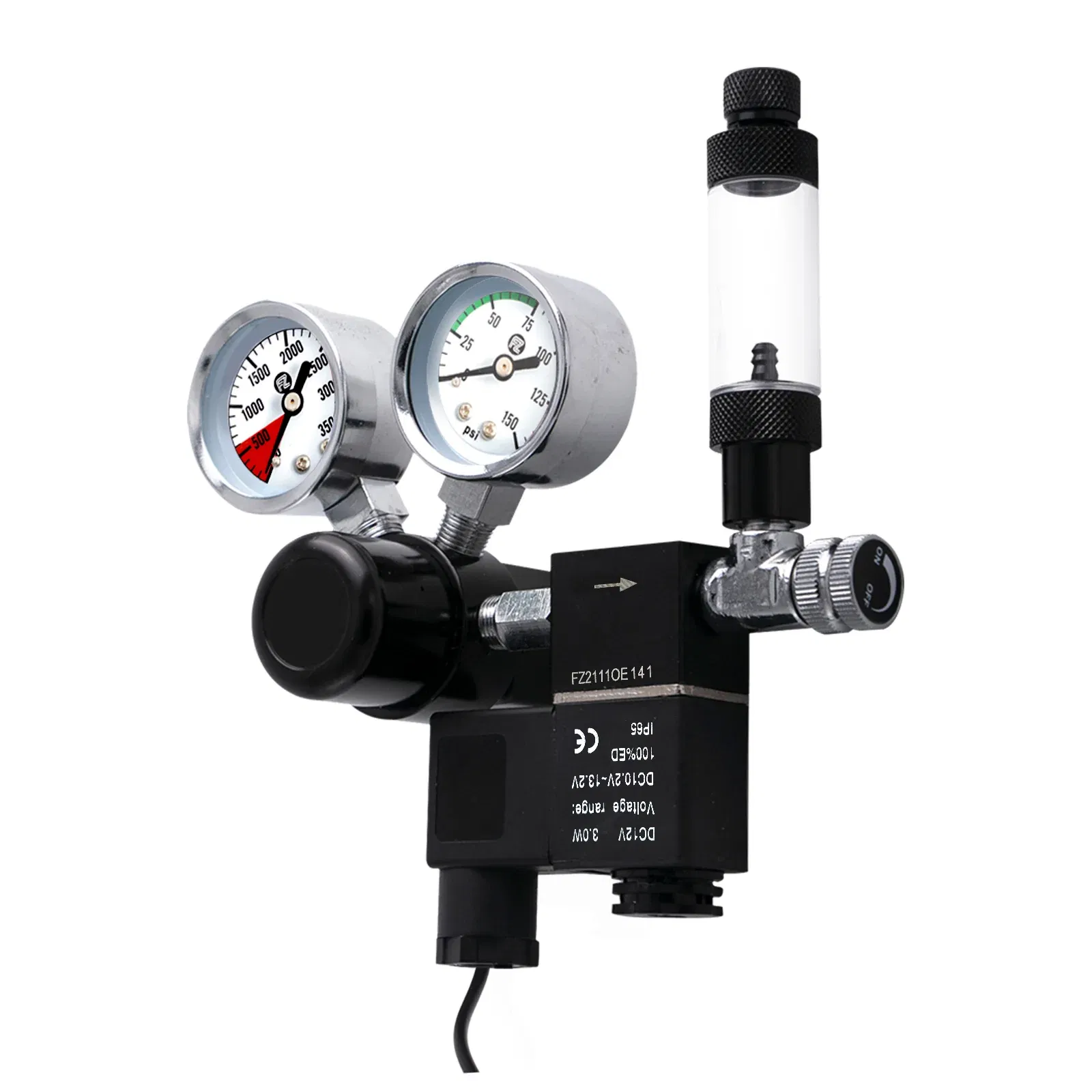

The pressure adjustment mechanism is one of the most critical elements. It allows users to fine-tune the output levels according to the specific needs of their setup. By controlling this, the device ensures that optimal performance is maintained without fluctuations that could affect the system.
Durability and Material Quality

The longevity and reliability of these components largely depend on the materials used in their construction. High-grade metals and corrosion-resistant coatings are commonly employed to extend the lifespan of the equipment, ensuring that it functions smoothly even in demanding conditions.
Common Issues in CO2 Systems
When working with gas-driven systems, certain challenges often arise due to the complexity of maintaining a steady flow. These challenges can impact both the efficiency and safety of the equipment, leading to potential malfunctions if not properly addressed.
Maintenance Tips for CO2 Equipment
Proper upkeep of gas handling devices is essential to ensure long-term performance and avoid unexpected malfunctions. Regular maintenance helps in maintaining accuracy and efficiency while extending the life of the equipment. By following simple practices, users can prevent wear and tear, ensuring reliable operation over time.
Regular Cleaning: It’s important to keep the equipment free from dust and residue. Routine cleaning of external components helps prevent blockages and ensures smooth operation.
Inspection of Seals and Connections: Periodic checks of seals, hoses, and connectors help to identify potential leaks or worn-out parts. Replacing damaged components promptly prevents performance issues.
Calibration Checks: Regular calibration ensures that the device operates at the correct settings. Schedule calibration checks according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to maintain accurate functionality.
Lubrication: Some components may require occasional lubrication to maintain smooth operation. Follow guidelines for the appropriate types of lubricants and application intervals.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, users can ensure consistent performance and safety, while also prolonging the equipment’s lifespan.
Choosing the Right CO2 Regulator

Selecting the appropriate device for managing the flow of gas is crucial for ensuring efficient operation in various applications. Different setups require specific tools to maintain stable pressure levels, and the right choice can make a significant difference in both performance and safety. Understanding the factors that influence this decision will help in selecting the best option for your needs.
Key Factors to Consider
When choosing a pressure management tool, consider several important factors. These include the type of system it will be integrated into, the required pressure range, and the durability of the device. Other elements like material quality and adjustment features can also play a role in long-term reliability.
Comparison of Options

| Feature | Option A | Option B |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Range | Low to Medium | High |
| Material | Stainless Steel | Brass |
| Adjustment Mechanism | Manual Knob | Automatic |
By carefully evaluating these features, you can ensure that the chosen device will meet the specific demands
Installation Guidelines for CO2 Regulators
Proper installation of equipment designed to control gas flow is crucial to ensure efficiency and safety. Following a step-by-step approach will help avoid potential issues and maintain optimal performance. Below is a detailed guide that covers the essential procedures for setting up your system correctly.
- Power
Safety Precautions for CO2 Use

Ensuring a secure environment when handling pressurized gases is essential for preventing accidents and injuries. Understanding the risks and implementing proper safety measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of incidents during operation.
Proper Ventilation: Adequate airflow is crucial when working with gases. Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated to avoid the accumulation of harmful concentrations, which can lead to asphyxiation.
Personal Protective Equipment: Always wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, goggles, and face shields, to protect against potential leaks and splashes. This equipment minimizes the risk of injuries during handling.
Storage Guidelines: Store containers in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ensure that cylinders are secured to prevent tipping or falling, which can cause leaks or explosions.
Leak Detection: Regularly check for leaks using soapy water or specific detection solutions. Any signs of leakage should be addressed immediately to prevent hazardous situations.
Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with emergency protocols in case of an accident. This includes knowing how to shut off the supply, evacuate the area, and contact emergency services if necessary.
Understanding CO2 Flow Rate Measurement
Measuring the flow of gas in a system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Accurate monitoring allows for precise adjustments, which can significantly impact overall operations. Understanding how to gauge the flow can help users maintain the desired levels and prevent potential issues.
The Importance of Accurate Measurement
Precision in gauging flow rates is essential for a variety of applications. It ensures that the correct volume of gas is supplied to the intended destination, facilitating the desired chemical reactions or processes. Inconsistent flow can lead to suboptimal results, affecting everything from product quality to system longevity.
Factors Influencing Flow Rate
Several elements can influence the flow rate in a system. Temperature, pressure, and the physical properties of the gas itself play significant roles. Additionally, the configuration of the pathways through which the gas travels can impact flow characteristics. Understanding these factors is vital for effective measurement and control.
Advancements in CO2 Regulator Technology
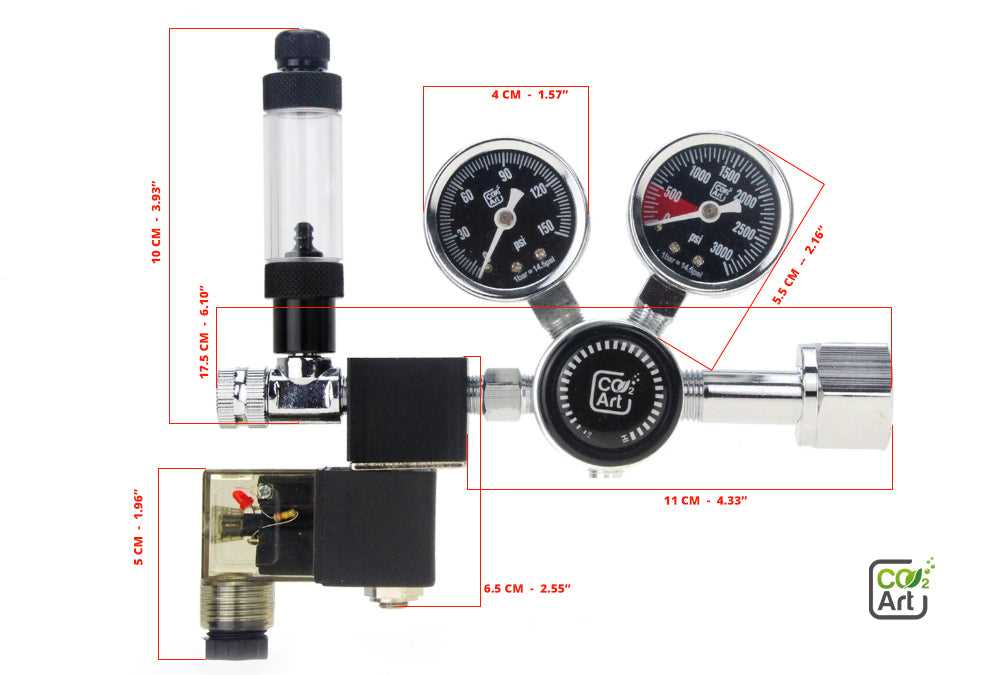

Recent innovations in the field of pressure control devices have significantly transformed their performance and efficiency. These advancements are aimed at enhancing the user experience and ensuring precise gas management across various applications, from industrial processes to home brewing systems.
Key developments include:
- Smart Technology Integration: Many modern systems now feature digital displays and smart connectivity, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments via mobile applications.
- Improved Materials: The use of advanced materials has led to enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring longer lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Enhanced Safety Features: New designs incorporate multiple safety mechanisms to prevent over-pressurization and leaks, thus minimizing risks associated with gas handling.
- Energy Efficiency: Recent innovations focus on optimizing energy consumption, making these devices more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of pressure control devices looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at further improving accuracy and reliability for diverse applications.