The human form is composed of various elements that work together in complex ways. These elements serve specific roles and are essential for the proper functioning of the entire organism. Each section is intricately designed to perform tasks that contribute to overall health and well-being.
When exploring the arrangement of these components, it is important to consider how they connect and interact with one another. Their organization reflects both the internal and external aspects, offering insight into the unique features that define the structure.
This overview aims to guide you through the various regions and features, highlighting their key functions and characteristics. By the end of this section, you will have a clearer understanding of how the various segments relate to the overall physical composition.
Anatomy Overview of Male Body
This section presents a detailed exploration of the structural composition and key elements of the human physique. It emphasizes the various systems and their interconnections, highlighting how each segment plays a crucial role in overall function and movement. The analysis encompasses the skeletal framework, muscular tissues, and internal networks, offering a comprehensive look at the harmonious organization of the human form.
| System | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Muscular | Facilitates movement and supports structure. |
| Skeletal | Provides a sturdy foundation and protects vital organs. |
| Cardiovascular | Circulates blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells. |
| Nervous | Coordinates actions and transmits signals across the body. |
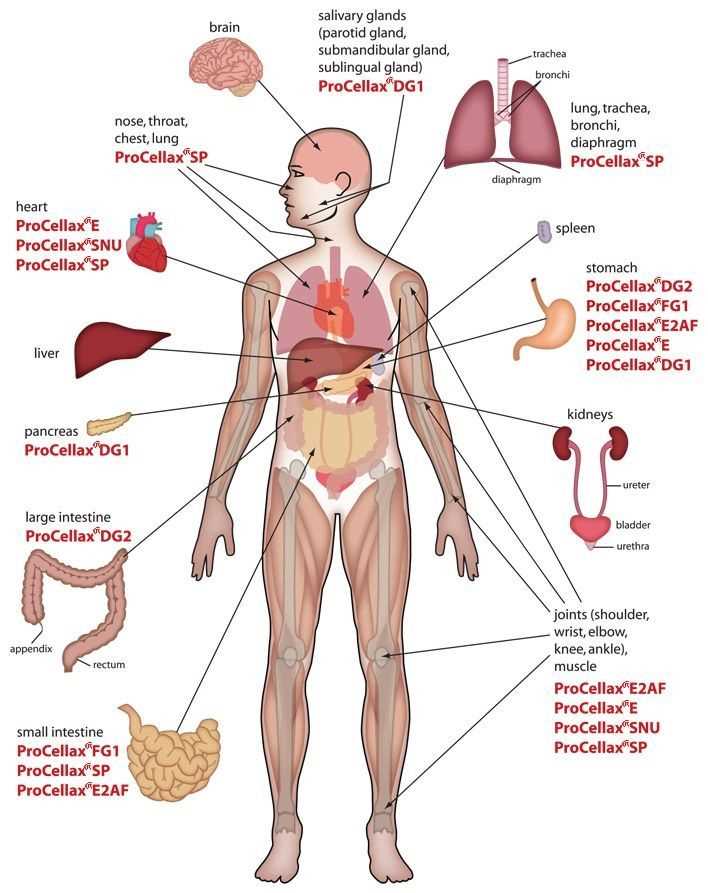
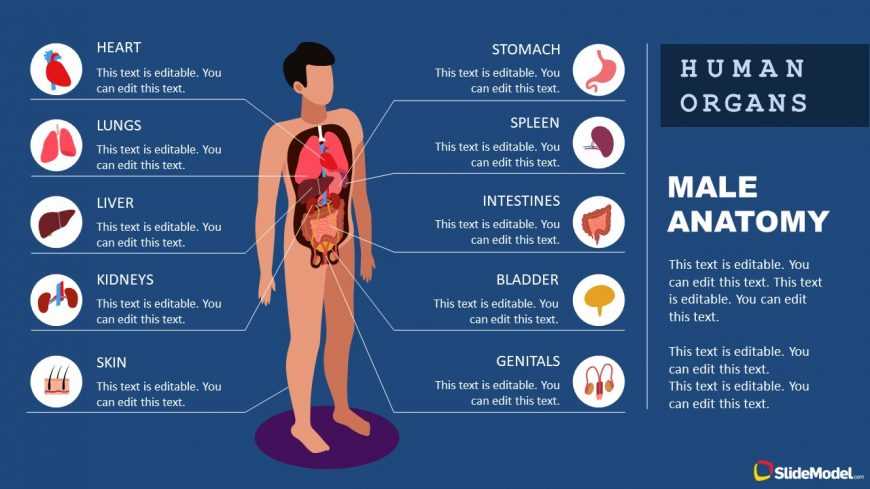
Main Functions of Male Organs
The human system is composed of complex structures, each contributing to the well-being and functionality of the entire organism. These structures play critical roles in various life-sustaining processes, impacting both physical and reproductive health.
Reproductive Function: Certain organs are primarily responsible for the continuation of life, facilitating the creation of new life. They ensure the production, storage, and delivery of vital elements necessary for reproduction.
Hormonal Balance: Another essential role is maintaining the balance of hormones, which regulate a wide range of bodily functions, from growth to emotional stability. These glands help in the release of substances that support overall well-being.
Excretory System: In addition to their reproductive and hormonal roles, some of these structures also contribute to the removal of waste materials, ensuring the purification and maintenance of the internal environment.
Bone Structure and Skeletal System
The skeletal framework is essential for providing support, protection, and movement. It serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the body’s systems rely, offering structural integrity and enabling a range of physical activities.
Functions of the Skeletal Framework
The primary role of the skeletal system is to maintain stability while allowing flexibility. It protects vital internal organs and works in conjunction with muscles to facilitate movement. Additionally, it serves as a reservoir for essential minerals and plays a crucial role in producing blood cells.
Main Components of the Skeleton
The framework is composed of various types of bones, each uniquely designed for specific purposes. These include long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones, all contributing to the overall function of the skeleton.
Muscles and Their Key RolesThe human musculature plays a crucial role in maintaining overall function and mobility. Different groups of muscles work together to ensure smooth and coordinated movement, supporting the body’s structural framework and facilitating a wide range of physical activities.
- Movement: Muscles are responsible for enabling movement by contracting and relaxing, working in pairs to control the motion of joints and limbs.
- Stability: Certain muscles provide stability to the skeleton, allowing for balanced posture and preventing unnecessary strain on bones and joints.
- Strength: Muscular strength is essential for tasks that require force, such as lifting, pushing, or pulling objects, contributing to overall physical power.
- Endurance: Muscles help sustain prolonged activity, ensuring that repetitive or continuous motions can be performed without fatigue.
- Heat production: Muscle contractions generate heat, helping to maintain optimal internal temperature and support metabolic processes.
These key functions highlight the critical role muscles play inCirculatory System in Male Body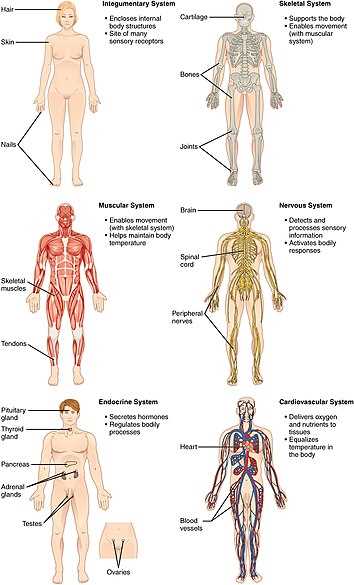 The circulatory network plays a critical role in maintaining overall health by transporting essential nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. It ensures the proper functioning of various organs, supporting the body’s physiological needs through a complex series of vessels and pumping mechanisms.At the center of this system is a powerful pump, which circulates life-sustaining fluids through arteries, veins, and capillaries. These pathways deliver vital resources to every part of the organism, while also removing waste products, ensuring balance and efficient functioning.This system operates in unison with other networks, helping to regulate temperature, support immune responses, and ensure consistent performance during physical and mental activities. Its structure and efficiency are key to maintaining the overall vitality and endurance of the individual.Nervous System and Brain AnatomyThe nervous system serves as the intricate communication network of the organism, facilitating the coordination of various functions and responses. It comprises a vast array of structures that work harmoniously to process sensory information, regulate bodily activities, and enable cognitive functions. Understanding the organization and functionality of this system is essential for comprehending how it influences overall well-being and behavior.The central component of this network is the brain, which acts as the control center for numerous processes. Its anatomy reveals a complex arrangement of regions, each responsible for specific tasks, from movement coordination to emotional regulation. Additionally, the peripheral nervous system extends beyond the brain and spinal cord, connecting various organs and tissues, thus allowing for a seamless flow of information.Respiratory System Components
The circulatory network plays a critical role in maintaining overall health by transporting essential nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. It ensures the proper functioning of various organs, supporting the body’s physiological needs through a complex series of vessels and pumping mechanisms.At the center of this system is a powerful pump, which circulates life-sustaining fluids through arteries, veins, and capillaries. These pathways deliver vital resources to every part of the organism, while also removing waste products, ensuring balance and efficient functioning.This system operates in unison with other networks, helping to regulate temperature, support immune responses, and ensure consistent performance during physical and mental activities. Its structure and efficiency are key to maintaining the overall vitality and endurance of the individual.Nervous System and Brain AnatomyThe nervous system serves as the intricate communication network of the organism, facilitating the coordination of various functions and responses. It comprises a vast array of structures that work harmoniously to process sensory information, regulate bodily activities, and enable cognitive functions. Understanding the organization and functionality of this system is essential for comprehending how it influences overall well-being and behavior.The central component of this network is the brain, which acts as the control center for numerous processes. Its anatomy reveals a complex arrangement of regions, each responsible for specific tasks, from movement coordination to emotional regulation. Additionally, the peripheral nervous system extends beyond the brain and spinal cord, connecting various organs and tissues, thus allowing for a seamless flow of information.Respiratory System Components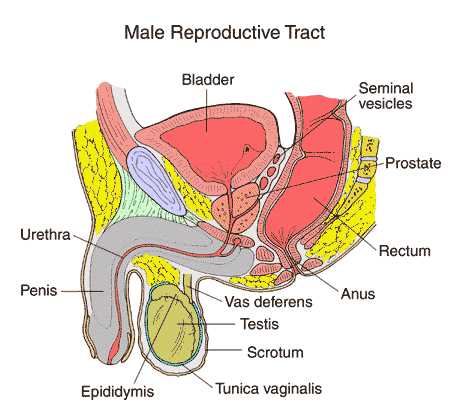 The respiratory system plays a crucial role in sustaining life by facilitating gas exchange and ensuring that oxygen reaches vital organs while removing carbon dioxide. This complex system comprises several key structures, each contributing to its overall functionality and efficiency. Understanding these components is essential for comprehending how breathing supports bodily functions.Major Structures of the Respiratory SystemThe main components include both upper and lower structures, which work together to perform essential tasks related to respiration. Each segment has distinct roles that enhance the overall process of breathing and gas exchange.Supporting Elements
The respiratory system plays a crucial role in sustaining life by facilitating gas exchange and ensuring that oxygen reaches vital organs while removing carbon dioxide. This complex system comprises several key structures, each contributing to its overall functionality and efficiency. Understanding these components is essential for comprehending how breathing supports bodily functions.Major Structures of the Respiratory SystemThe main components include both upper and lower structures, which work together to perform essential tasks related to respiration. Each segment has distinct roles that enhance the overall process of breathing and gas exchange.Supporting Elements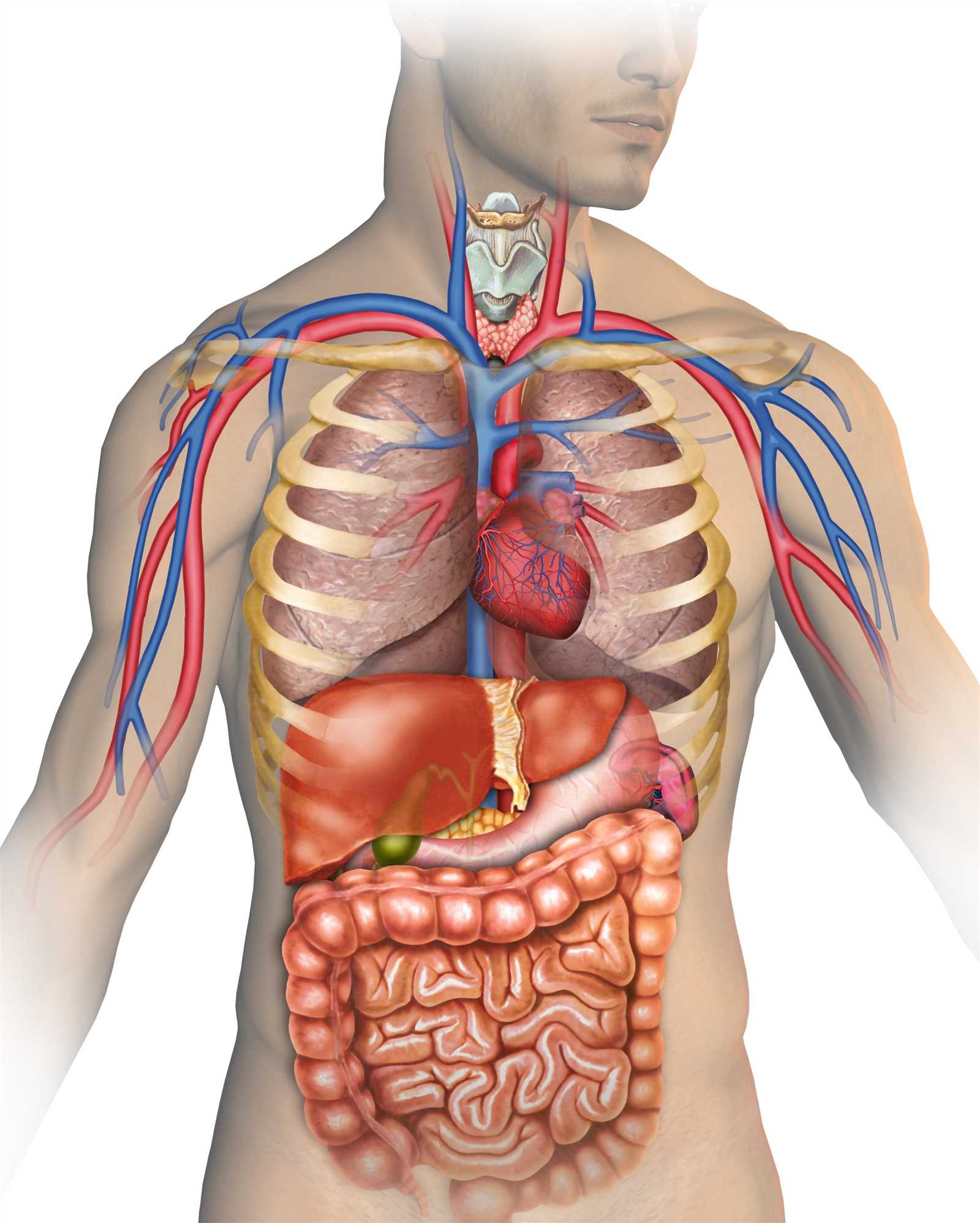 In addition to the main structures, there are various supporting elements that contribute to the efficiency of the respiratory process. These include muscles and tissues that assist in the mechanics of breathing, enabling proper expansion and contraction of the lungs.Digestive Organs and Their FunctionThe intricate network responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients is essential for maintaining overall health. This system involves various components that work together to process ingested substances, converting them into forms that the body can utilize effectively. Understanding how these organs operate provides insight into the complex mechanisms of nourishment and energy production.Salivary Glands: These glands initiate the digestive process by producing saliva, which contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of carbohydrates. They also help in moistening food, making it easier to swallow.Stomach: The stomach plays a crucial role in digestion by mixing food with gastric juices. These secretions contain strong acids and enzymes that further break down food into a semi-liquid form known as chyme.Small Intestine: This organ is vital for nutrient absorption. It is lined with tiny projections called villi, which increase the surface area for efficient uptake of essential nutrients into the bloodstream.Large Intestine: The primary function of the large intestine is to absorb water and electrolytes from indigestible food residues. It also plays a role in forming and excreting waste products from the body.Liver: The liver is a powerhouse of metabolic activity. It produces bile, which aids in the digestion of fats, and processes nutrients absorbed from the small intestine, regulating their distribution throughout the body.Pancreas: This organ produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are released into the small intestine. These substances help neutralize stomach acids and further aid in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.Each component of this system is integral to the overall functionality, ensuring that the body receives the necessary sustenance for vitality and health.Endocrine System and Hormonal ControlThe endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating various physiological functions through the secretion of hormones. These biochemical messengers travel through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues, influencing processes such as growth, metabolism, and mood. Understanding the interplay between different glands and the hormones they produce is crucial for grasping how the body maintains homeostasis and responds to internal and external stimuli.Key Glands and Their FunctionsSeveral key glands constitute the endocrine system, including the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and pancreas. Each gland has distinct functions and contributes to overall health. For instance, the pituitary gland, often termed the “master gland,” regulates the activity of other glands and releases hormones that control growth and reproductive functions. The thyroid gland plays a significant role in metabolic regulation, influencing energy levels and weight management.Hormonal Feedback MechanismsThe control of hormonal release is primarily managed through feedback loops. In a negative feedback system, elevated hormone levels signal the glands to reduce production, thus maintaining balance. Conversely, positive feedback mechanisms amplify responses in specific situations, such as during childbirth. This dynamic regulation ensures that hormone levels remain within optimal ranges, safeguarding overall well-being.Male Reproductive Anatomy ExplainedThis section delves into the intricate structure responsible for the continuation of species. Understanding this system is vital for grasping its role in reproduction and overall health. Each component plays a unique role in various processes, contributing to the biological functions necessary for procreation.Skin Layers and Their Importance
In addition to the main structures, there are various supporting elements that contribute to the efficiency of the respiratory process. These include muscles and tissues that assist in the mechanics of breathing, enabling proper expansion and contraction of the lungs.Digestive Organs and Their FunctionThe intricate network responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients is essential for maintaining overall health. This system involves various components that work together to process ingested substances, converting them into forms that the body can utilize effectively. Understanding how these organs operate provides insight into the complex mechanisms of nourishment and energy production.Salivary Glands: These glands initiate the digestive process by producing saliva, which contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of carbohydrates. They also help in moistening food, making it easier to swallow.Stomach: The stomach plays a crucial role in digestion by mixing food with gastric juices. These secretions contain strong acids and enzymes that further break down food into a semi-liquid form known as chyme.Small Intestine: This organ is vital for nutrient absorption. It is lined with tiny projections called villi, which increase the surface area for efficient uptake of essential nutrients into the bloodstream.Large Intestine: The primary function of the large intestine is to absorb water and electrolytes from indigestible food residues. It also plays a role in forming and excreting waste products from the body.Liver: The liver is a powerhouse of metabolic activity. It produces bile, which aids in the digestion of fats, and processes nutrients absorbed from the small intestine, regulating their distribution throughout the body.Pancreas: This organ produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are released into the small intestine. These substances help neutralize stomach acids and further aid in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.Each component of this system is integral to the overall functionality, ensuring that the body receives the necessary sustenance for vitality and health.Endocrine System and Hormonal ControlThe endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating various physiological functions through the secretion of hormones. These biochemical messengers travel through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues, influencing processes such as growth, metabolism, and mood. Understanding the interplay between different glands and the hormones they produce is crucial for grasping how the body maintains homeostasis and responds to internal and external stimuli.Key Glands and Their FunctionsSeveral key glands constitute the endocrine system, including the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and pancreas. Each gland has distinct functions and contributes to overall health. For instance, the pituitary gland, often termed the “master gland,” regulates the activity of other glands and releases hormones that control growth and reproductive functions. The thyroid gland plays a significant role in metabolic regulation, influencing energy levels and weight management.Hormonal Feedback MechanismsThe control of hormonal release is primarily managed through feedback loops. In a negative feedback system, elevated hormone levels signal the glands to reduce production, thus maintaining balance. Conversely, positive feedback mechanisms amplify responses in specific situations, such as during childbirth. This dynamic regulation ensures that hormone levels remain within optimal ranges, safeguarding overall well-being.Male Reproductive Anatomy ExplainedThis section delves into the intricate structure responsible for the continuation of species. Understanding this system is vital for grasping its role in reproduction and overall health. Each component plays a unique role in various processes, contributing to the biological functions necessary for procreation.Skin Layers and Their Importance The integumentary system serves as a protective barrier, playing a crucial role in overall health and well-being. Comprising multiple layers, each with distinct functions, it safeguards against environmental hazards while regulating various physiological processes. Understanding the significance of these layers can enhance awareness of their vital contributions to bodily functions.Structure of Skin Layers
The integumentary system serves as a protective barrier, playing a crucial role in overall health and well-being. Comprising multiple layers, each with distinct functions, it safeguards against environmental hazards while regulating various physiological processes. Understanding the significance of these layers can enhance awareness of their vital contributions to bodily functions.Structure of Skin Layers The outermost layer, which serves as the primary defense, is essential for preventing external elements from penetrating deeper tissues. Beneath this, additional layers provide further protection, support, and facilitate sensory perception, making the integumentary system a complex yet cohesive unit.Functions and BenefitsEach layer contributes uniquely to maintaining homeostasis and protecting against pathogens, UV radiation, and dehydration. This interplay ensures optimal functioning and resilience against various stressors, highlighting the importance of maintaining skin health.Immune System and Defense Mechanisms
The outermost layer, which serves as the primary defense, is essential for preventing external elements from penetrating deeper tissues. Beneath this, additional layers provide further protection, support, and facilitate sensory perception, making the integumentary system a complex yet cohesive unit.Functions and BenefitsEach layer contributes uniquely to maintaining homeostasis and protecting against pathogens, UV radiation, and dehydration. This interplay ensures optimal functioning and resilience against various stressors, highlighting the importance of maintaining skin health.Immune System and Defense Mechanisms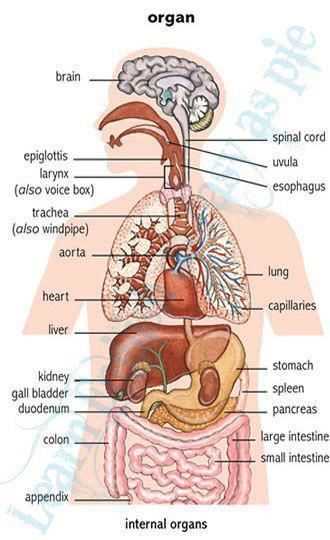 The human body is equipped with a sophisticated network designed to protect against harmful agents and maintain overall health. This intricate system operates through various components that work collaboratively to identify and neutralize potential threats, ensuring the organism’s survival.At the core of this protective framework are specialized cells and substances that respond to infections, injuries, and other challenges. White blood cells, for instance, play a crucial role in detecting and attacking invaders, while antibodies help to neutralize pathogens by binding to them and marking them for destruction. The body also employs barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, to prevent entry of harmful substances.Moreover, the immune response can be divided into two main categories: innate immunity, which provides immediate but non-specific defense, and adaptive immunity, which develops more slowly but offers a tailored response to specific pathogens. This dual approach ensures that the body can effectively adapt to and remember past encounters with threats, enhancing its ability to fend off future infections.
The human body is equipped with a sophisticated network designed to protect against harmful agents and maintain overall health. This intricate system operates through various components that work collaboratively to identify and neutralize potential threats, ensuring the organism’s survival.At the core of this protective framework are specialized cells and substances that respond to infections, injuries, and other challenges. White blood cells, for instance, play a crucial role in detecting and attacking invaders, while antibodies help to neutralize pathogens by binding to them and marking them for destruction. The body also employs barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, to prevent entry of harmful substances.Moreover, the immune response can be divided into two main categories: innate immunity, which provides immediate but non-specific defense, and adaptive immunity, which develops more slowly but offers a tailored response to specific pathogens. This dual approach ensures that the body can effectively adapt to and remember past encounters with threats, enhancing its ability to fend off future infections.
| Bone Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Long Bones | Provide strength and mobility, crucial for movement. | Femur |
| Structure | Function | |
| Cerebrum | Responsible for higher cognitive functions, including thought, memory, and voluntary movement. | |
| Cerebellum | Coordinates balance and fine motor skills, ensuring smooth movements. | |
| Brainstem | Regulates vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and sleep cycles. | |
| Spinal Cord | Transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, facilitating reflex actions. | |
| Nerves | Carry information to and from various body regions, connecting them to the central system. | |
| Component | Function | |
| Nasal Cavity | Filters, warms, and humidifies incoming air | |
| Pharynx | Passageway for air and food; assists in swallowing | |
| Larynx | Produces sound; protects the trachea against food aspiration | |
| Trachea | Conducts air to and from the lungs | |
| Bronchi | Branches into each lung; distributes air within the lungs | |
| Alveoli | Sites of gas exchange; facilitate oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer | |
| Component | Function | |
| Testes | Production of sperm and hormones, primarily testosterone. | |
| Epididymis | Storage and maturation of sperm. | |
| Vas deferens | Transport of sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct. | |
| Seminal vesicles | Secretion of fluid that nourishes sperm and forms a significant part of semen. | |
| Prostate gland | Production of fluid that protects and energizes sperm in semen. | |
| Penis | Delivery of sperm into the female reproductive system. | |
| Layer | Function | |
| epidermis | Protection against environmental damage | |
| dermis | Support and elasticity | |
| hypodermis | Insulation and cushioning |