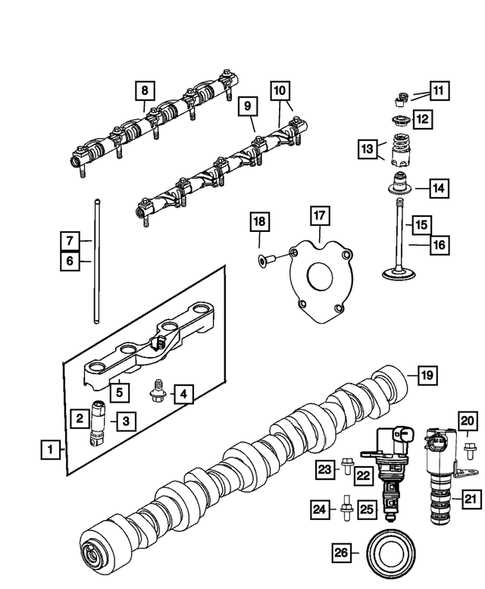
In the realm of automotive engineering, comprehending the intricate layout of various elements is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This section delves into the essential components that make up a vehicle’s structure, providing insights into their functions and interconnections. A well-organized overview can greatly enhance your understanding, allowing for more informed decisions when it comes to upkeep.
By examining the intricate arrangement of these components, enthusiasts and professionals alike can gain valuable knowledge. Each segment plays a pivotal role in the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle. Whether you are looking to upgrade, replace, or simply familiarize yourself with these crucial elements, a detailed exploration can lead to greater proficiency in automotive care.
Additionally, having a clear reference of the various assemblies and their specifications can streamline any repair or enhancement process. Understanding the unique characteristics and relationships between different sections can empower individuals to tackle projects with confidence and precision. This knowledge not only supports better functionality but also contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience.
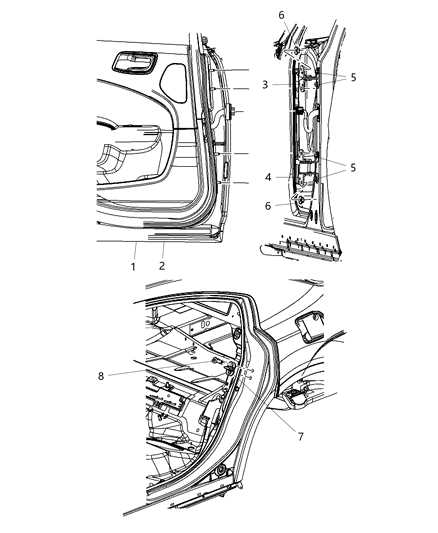
Understanding the intricacies of electrical wiring and connections is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety in modern vehicles. This section explores the various components involved in the electrical system, providing insights into their roles and interconnections.
Properly functioning electrical systems rely on a series of connections that facilitate communication between components. The following elements are crucial:
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires that transmit electrical signals between various parts.
- Connectors: Devices that join different segments of the wiring harness, ensuring secure connections.
- Ground Points: Locations where electrical components connect to the vehicle’s chassis, completing circuits.
- Fuses: Safety devices that protect the electrical system from overload by breaking the circuit when necessary.
- Relays: Electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using low-current signals.
To maintain the integrity of the electrical system, regular inspection and testing are recommended. Following a systematic approach can prevent potential issues:
- Check for loose or corroded connections.
- Inspect the wiring harness for signs of wear or damage.
- Test electrical components for proper functionality.
- Replace any faulty connectors or fuses as needed.
By understanding these aspects of electrical wiring and connections, vehicle owners can enhance reliability and extend the lifespan of their automotive electrical systems.
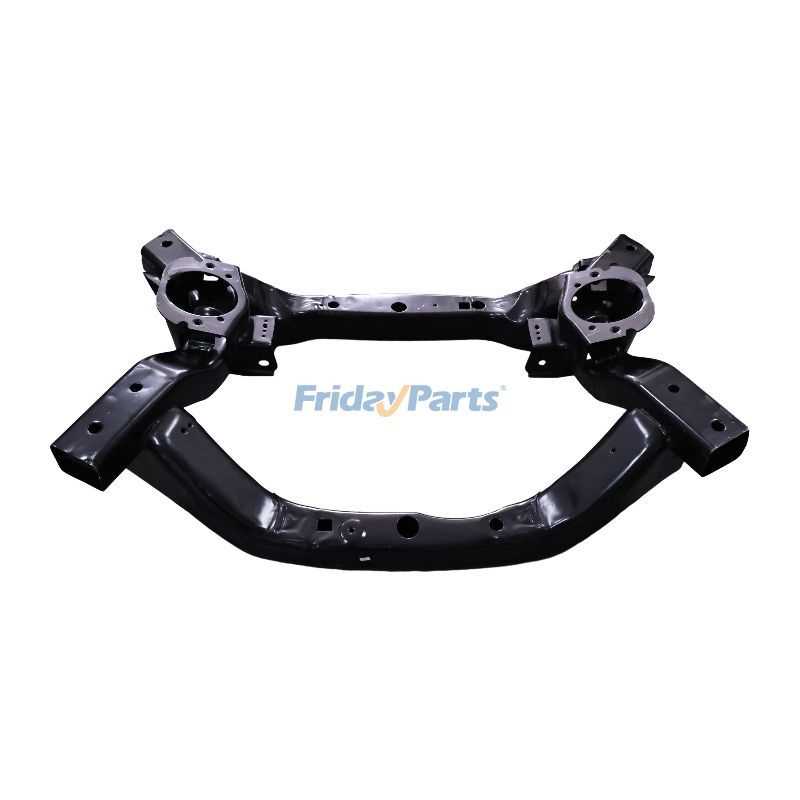
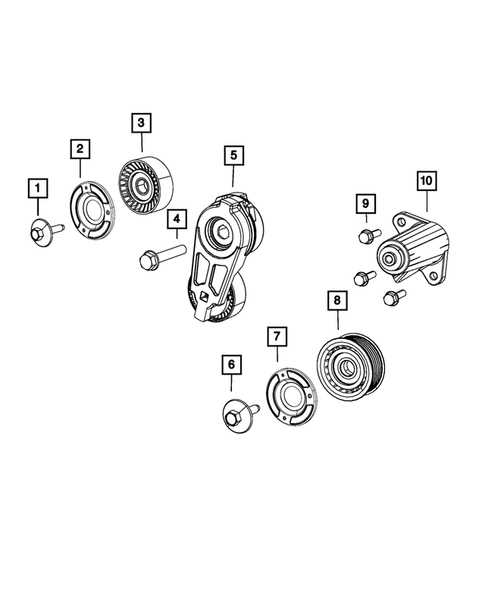
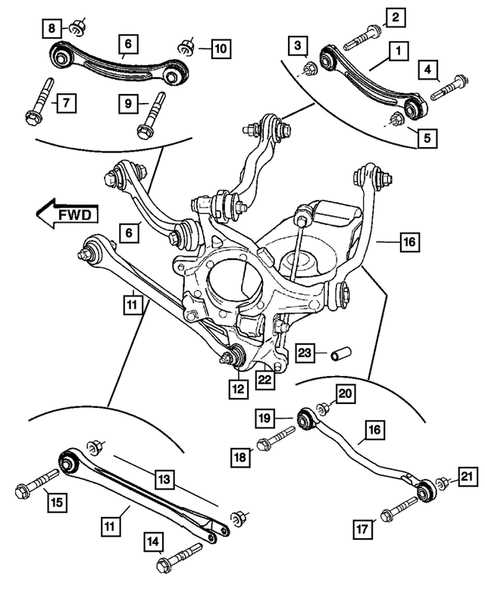
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension framework plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth ride and optimal handling of a vehicle. It serves to absorb shocks from the road, providing stability and comfort while navigating various terrains. Understanding the components and their functions is essential for effective maintenance and performance enhancement.
This system comprises several key elements:
- Struts and Shocks: These parts absorb impact and help maintain vehicle stability during movement.
- Springs: Springs support the weight of the vehicle and facilitate a smooth transition over bumps and uneven surfaces.
- Control Arms: These components connect the suspension to the chassis, allowing for controlled wheel movement.
- Sway Bars: These bars minimize body roll during sharp turns, enhancing handling and stability.
- Bushings: Bushings reduce friction and provide cushioning between moving parts, promoting longevity and comfort.
Proper inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance. Regular checks can help identify wear and tear, ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly and safely.
Braking Components and Layout

The braking system plays a crucial role in vehicle safety and performance, ensuring effective deceleration and control during various driving conditions. Understanding the arrangement and function of these components is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section will explore the key elements involved in the braking mechanism and their respective configurations.
Key Components
- Brake Pads: These are friction materials that press against the rotors to slow down the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors: Also known as discs, these components provide a surface for the brake pads to grip during braking.
- Calipers: These house the brake pads and contain the hydraulic mechanism that applies pressure.
- Brake Lines: These conduits carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
- Master Cylinder: This device generates hydraulic pressure to activate the braking system.
Layout Overview
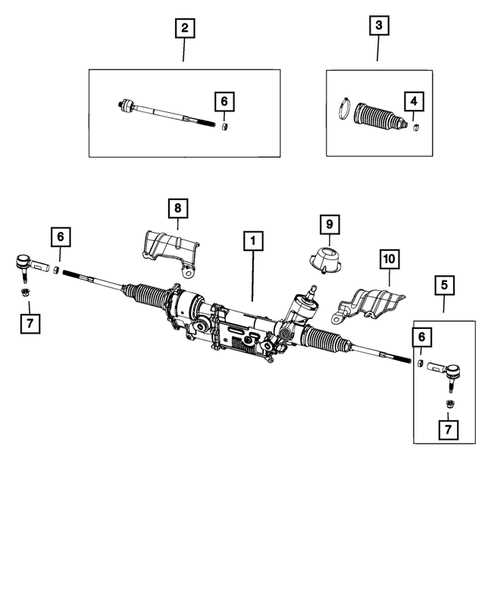
The configuration of braking components is typically standardized across various models, allowing for efficient replacement and repair. The main elements are strategically positioned to maximize effectiveness and ensure even distribution of braking forces. Below is a general outline of their layout:
- Master cylinder located near the driver’s seat for easy access to controls.
- Brake lines running from the master cylinder to each wheel.
- Calipers mounted on each wheel assembly, securing the brake pads against the rotors.
- Brake pads fitted within the calipers, ensuring contact with the rotors during application.
- Rotors securely attached to the wheel hub, providing a sturdy surface for braking.
Regular inspection and understanding of these components are vital for ensuring optimal performance and safety during operation.
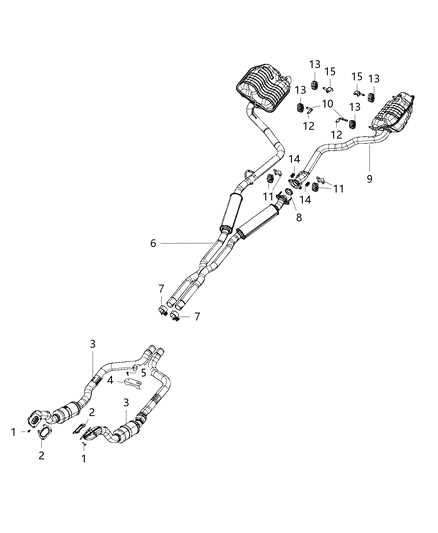
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a vital role in the performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Its design influences how exhaust gases are expelled from the engine, which can affect overall power and fuel consumption. Understanding the layout and components of this system is essential for both maintenance and performance enhancement.
Key components of an exhaust assembly include:
- Exhaust Manifold
- Catalytic Converter
- Resonator
- Muffler
- Exhaust Pipes
Each element serves a distinct function:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects gases from the engine’s cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions through chemical reactions.
- Resonator: Modifies sound and can enhance performance by optimizing airflow.
- Muffler: Controls noise produced by the exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Pipes: Directs gases away from the vehicle.
Proper configuration of these components ensures optimal engine performance and complies with environmental regulations. Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system can prevent costly repairs and enhance vehicle longevity.
Fuel System and Components

The fuel delivery system is crucial for the optimal performance of any vehicle. It encompasses a variety of elements that work in unison to ensure that the engine receives the right amount of fuel at the appropriate pressure. Understanding these components is essential for diagnosing issues and maintaining the efficiency of the engine.
Key Elements of the Fuel System
This system primarily consists of the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel lines. Each part plays a vital role in transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, where it is mixed with air and ignited for combustion. Regular maintenance of these components can help prevent common issues such as fuel leaks and pressure drops.
Importance of Proper Functioning
Ensuring that the fuel system operates correctly is vital for achieving optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Any malfunction in the system can lead to decreased power output, increased emissions, and poor fuel economy. Therefore, it is important to conduct regular inspections and address any irregularities promptly.
Cooling System Arrangement
The arrangement of the cooling mechanism is vital for maintaining optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating. This system comprises various components that work in unison to ensure efficient heat dissipation and fluid circulation.
Key Components
- Radiator: Responsible for transferring heat away from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow based on temperature.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and provides a buffer during expansion.
Cooling Process Overview
- The water pump initiates the circulation of coolant from the reservoir.
- Coolant absorbs heat from the engine components.
- The heated coolant flows into the radiator, where it is cooled by airflow.
- Once cooled, the coolant returns to the engine, completing the cycle.
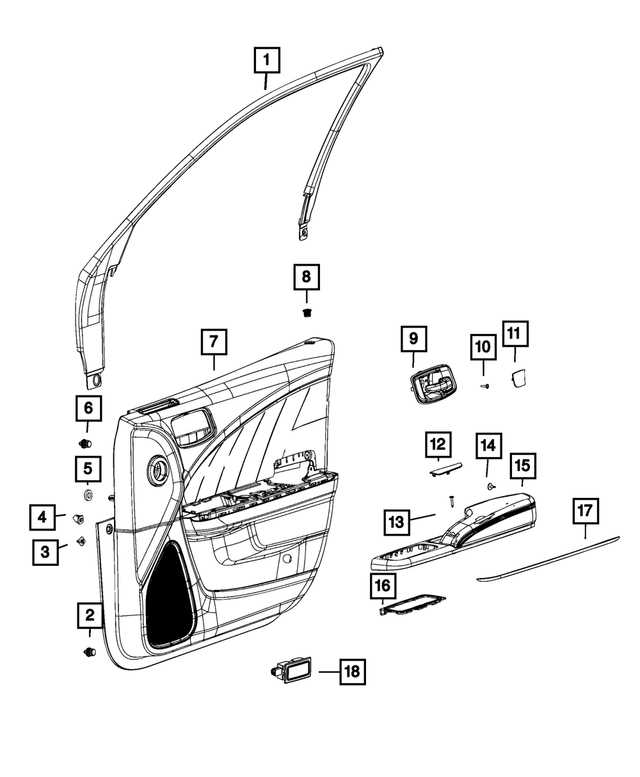
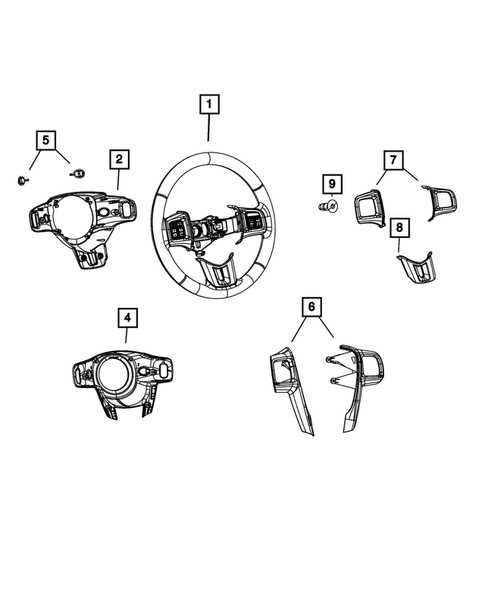
Interior and Dashboard Components

This section delves into the various elements that make up the inner space and control interface of a modern vehicle. Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and upgrades, ensuring optimal functionality and comfort.
The interior area includes numerous critical sections, each serving a unique purpose:
- Control Panel: This area houses essential buttons and displays that regulate vehicle functions.
- Dashboard: This panel provides important information such as speed, fuel levels, and navigation data.
- Center Console: Positioned between the front seats, it offers storage, connectivity options, and controls for multimedia systems.
- Door Panels: These components include controls for windows and locks, as well as storage pockets.
- Seats: Designed for comfort and support, seats can be manually adjusted or electronically controlled.
Additionally, there are several smaller yet significant features that enhance the user experience:
- Air Vents: Allow for climate control and air circulation within the cabin.
- Interior Lighting: Provides visibility and ambiance during nighttime driving.
- Infotainment System: Integrates entertainment and communication functions, often featuring touchscreens.
- Trim and Upholstery: Materials and finishes that enhance the aesthetic appeal and comfort of the interior.
Understanding these components can aid in troubleshooting issues and selecting suitable upgrades to enhance the overall driving experience.
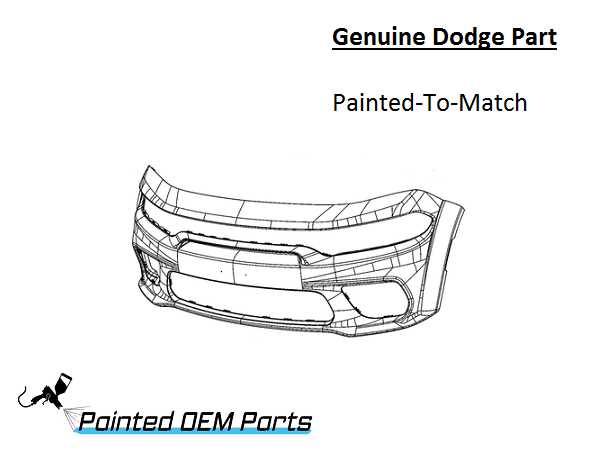
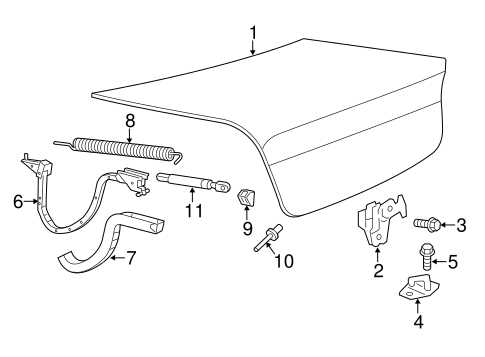
Body Structure and Panels
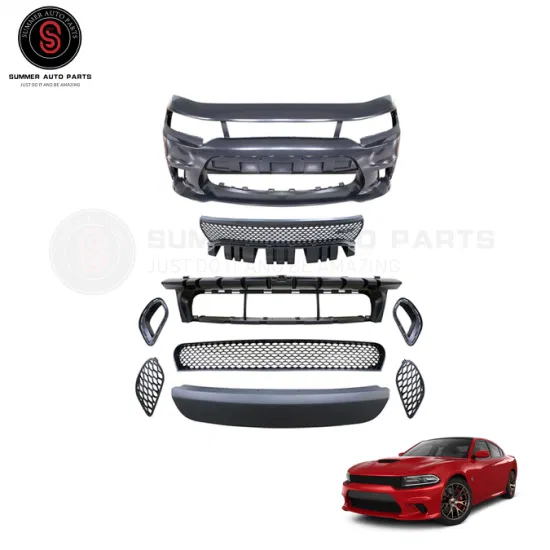

The integrity and design of a vehicle’s outer framework are crucial for both safety and aesthetics. This section delves into the components that constitute the exterior shell and how they contribute to the overall durability and visual appeal.
The body structure is primarily composed of various panels, each serving distinct purposes. Understanding these elements helps in appreciating their roles in performance, maintenance, and repair.
- Front Fascia: This panel often houses the grille and headlights, playing a vital role in aerodynamics and style.
- Rear Panel: It supports the taillights and provides a clean finish at the back, contributing to the vehicle’s overall silhouette.
- Doors: Essential for access to the interior, they are designed with safety features such as side impact beams.
- Roof Structure: A critical element for passenger safety, it is engineered to withstand various stressors.
- Fenders: These panels protect the wheels and provide a smooth transition from the body to the tires, enhancing the vehicle’s profile.
Each of these components is manufactured using high-quality materials to ensure resilience and longevity. Regular inspections and understanding their configurations can aid in timely maintenance and repair, thus preserving the vehicle’s functionality and appearance.
Safety Features and Equipment
Ensuring occupant protection and enhancing vehicle security are paramount considerations in automotive design. Various technologies and components work together to create a secure environment for all passengers. This section delves into the essential safety measures integrated into modern vehicles, focusing on innovative systems and equipment that contribute to accident prevention and injury reduction.
Active Safety Systems
Active safety systems play a critical role in accident avoidance. These features actively monitor driving conditions and assist the operator in maintaining control. Key elements include:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during hard braking, ensuring steering control.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): Helps maintain vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the car ahead.
- Lane Departure Warning: Alerts the driver if the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane without signaling.
Passive Safety Features
Passive safety features are designed to protect occupants in the event of a collision. These components absorb and dissipate energy, minimizing injury risks. Important features include:
- Airbags: Deploy during a collision to cushion and protect passengers.
- Reinforced Structure: Strong materials and design elements enhance the vehicle’s crashworthiness.
- Seatbelts: Essential for restraining occupants and preventing ejection during accidents.
- Child Safety Locks: Prevent rear doors from being opened by children, enhancing passenger security.